使用Magisk+riru实现全局改机
前言
提到全局改机,我们想到修改的不是修改Android源码就是利用Xposed改机,前者成本太高,后者只能修改Java层的数据不够彻底。magisk是Android平台上功能强大的工具,利用它可以随心所欲的修改系统。它或许帮我们在不修改系统源码的情况实现相对完美的改机。那么,riru是什么?它和magisk有什么关系?它又和我们的模块有什么关系?简而言之,riru是magisk的模块,本文写的模块也是magisk模块,但是它又依赖于riru。那riru模块提供了什么功能呢?riru模块能够感知App的启动,并且能够给App注入一些代码,依赖riru模块的模块也能拥有这个能力。我们实现改机,其实就是需要尽早的感知App启动的,这样我们才能尽早hook一些函数,使App启动的时候获取到的数据是我们修改后的数据。了解了相关知识,我们就可以开始编写模块了。
准备
riru模块的作者写了riru模块的模板,我们在这个项目的基础上改就行,首先将模块克隆下来并使用Android Studio打开:
git clone https://github.com/RikkaApps/Riru-ModuleTemplate
因为改机不仅要改Java层的数据,还要改Native层的数据,所以我们要用Native层的Hook框架,这里用的Hook框架是Dobby。作者编译了静态链接文件,我们去下载下来用即可:https://github.com/jmpews/Dobby/releases/tag/latest
下载好后解压,将android目录里的子目录全部放入Riru-ModuleTemplate项目的module模块下的libs目录下(没有则创建),然后将文件夹重命名:
- arm64 -> arm64-v8a
- armv7 -> armeabi-v7a
修改后的目录结构应如下:
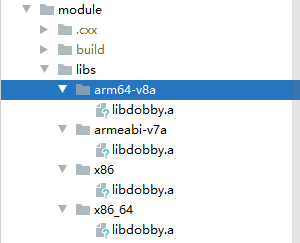
同时在module/src/main/cpp目录下创建一个dobby目录,然后去下载dobby.h文件,来放入该目录下。下载地址:https://github.com/jmpews/Dobby/blob/master/include/dobby.h
修改cmake文件,使编译的时候,把dobby的静态链接库也链接上。修改module/src/main/cpp/CMakeLists.txt
include_directories(
dobby
)
add_library(local_dobby STATIC IMPORTED)
set_target_properties(local_dobby PROPERTIES IMPORTED_LOCATION ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/../../../libs/${ANDROID_ABI}/libdobby.a)
add_library(${MODULE_NAME} SHARED main.cpp ${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/config.cpp)
target_link_libraries(${MODULE_NAME} local_dobby log riru::riru)
准备工作完成,就可以开始编写代码了
编写代码
转到module/src/main/cpp/main.cpp文件,这是模块的核心代码文件,里面定义一些不太丰满的函数,等着我们去填补。
static void forkAndSpecializePost(JNIEnv *env, jclass clazz, jint res) {
// Called "after" com_android_internal_os_Zygote_nativeForkAndSpecialize in frameworks/base/core/jni/com_android_internal_os_Zygote.cpp
// "res" is the return value of com_android_internal_os_Zygote_nativeForkAndSpecialize
if (res == 0) {
// In app process
// When unload allowed is true, the module will be unloaded (dlclose) by Riru
// If this modules has hooks installed, DONOT set it to true, or there will be SIGSEGV
// This value will be automatically reset to false before the "pre" function is called
riru_set_unload_allowed(true);
} else {
// In zygote process
}
}
static void specializeAppProcessPre(
JNIEnv *env, jclass clazz, jint *uid, jint *gid, jintArray *gids, jint *runtimeFlags,
jobjectArray *rlimits, jint *mountExternal, jstring *seInfo, jstring *niceName,
jboolean *startChildZygote, jstring *instructionSet, jstring *appDataDir,
jboolean *isTopApp, jobjectArray *pkgDataInfoList, jobjectArray *whitelistedDataInfoList,
jboolean *bindMountAppDataDirs, jboolean *bindMountAppStorageDirs) {
// Called "before" com_android_internal_os_Zygote_nativeSpecializeAppProcess in frameworks/base/core/jni/com_android_internal_os_Zygote.cpp
// Parameters are pointers, you can change the value of them if you want
// Some parameters are not exist is older Android versions, in this case, they are null or 0
}
static void specializeAppProcessPost(
JNIEnv *env, jclass clazz) {
// Called "after" com_android_internal_os_Zygote_nativeSpecializeAppProcess in frameworks/base/core/jni/com_android_internal_os_Zygote.cpp
// When unload allowed is true, the module will be unloaded (dlclose) by Riru
// If this modules has hooks installed, DONOT set it to true, or there will be SIGSEGV
// This value will be automatically reset to false before the "pre" function is called
riru_set_unload_allowed(true);
}
static void forkSystemServerPre(
JNIEnv *env, jclass clazz, uid_t *uid, gid_t *gid, jintArray *gids, jint *runtimeFlags,
jobjectArray *rlimits, jlong *permittedCapabilities, jlong *effectiveCapabilities) {
// Called "before" com_android_internal_os_Zygote_forkSystemServer in frameworks/base/core/jni/com_android_internal_os_Zygote.cpp
// Parameters are pointers, you can change the value of them if you want
// Some parameters are not exist is older Android versions, in this case, they are null or 0
}
static void forkSystemServerPost(JNIEnv *env, jclass clazz, jint res) {
// Called "after" com_android_internal_os_Zygote_forkSystemServer in frameworks/base/core/jni/com_android_internal_os_Zygote.cpp
if (res == 0) {
// In system server process
} else {
// In zygote process
}
}
static void onModuleLoaded() {
// Called when this library is loaded and "hidden" by Riru (see Riru's hide.cpp)
// If you want to use threads, start them here rather than the constructors
// __attribute__((constructor)) or constructors of static variables,
// or the "hide" will cause SIGSEGV
}
函数名和注释都非常清晰,虽然函数很多,但是我们只需要在forkAndSpecializePost函数中编写hook代码就可以。因为我们要hook代码运行在App进程中
if (res == 0) {
// In app process
// When unload allowed is true, the module will be unloaded (dlclose) by Riru
// If this modules has hooks installed, DONOT set it to true, or there will be SIGSEGV
// This value will be automatically reset to false before the "pre" function is called
riru_set_unload_allowed(true);
}
当我们编写Native层代码的时候,想要获取当前手机的机型信息,最好的方式是通过调用__system_property_get来获取,那么我们可以hook这个函数。但在这之前,我们需要知道要修改哪个字段,这些字段又分别赋予什么值。那这些信息通过读取文件来得到好了,由模块使用者来定义,编写一个读取配置的函数:
void readPropFile(const char* filename,std::map<std::string,std::string> &map){
FILE *fp = fopen(filename,"r");
if(fp == NULL){
return;
}
char buf[256];
while(fgets(buf,256,fp) != NULL){
char *sep = strchr(buf,'=');
*sep = '\0';
std::string key(buf);
std::string value(sep + 1);
map[key] = value;
}
fclose(fp);
}
readPropFile函数读取一个文件,然后将每一行等号前面的内容作为key,等号后面的内容作为value放入传进来的map,假设一个文件内容如下:
MODEL=Mi5
那么它读到的key是MODEL,value是Mi5
知道要修改成什么,就可以hook __system_property_get函数,下面是hook代码
static int my__system_property_get(const char* name, char* value){
if(NULL == name || NULL == value){
return origin__system_property_get(name,value);
}
auto ret = propMap.find(name);
if(ret != propMap.end()){
const char* valueChs = ret->second.c_str();
strcpy(value,valueChs);
return strlen(valueChs);
}
return origin__system_property_get(name,value);
}
void initDobby(){
void* sym = DobbySymbolResolver(NULL,"__system_property_get");
if(NULL != sym) {
DobbyHook(sym, (void *) my__system_property_get, (void **) &origin__system_property_get);
}
}
其中:
- DobbySymbolResolver 是寻找函数符号地址
- DobbyHook 是启用hook的函数
- my__system_property_get 是跳板函数,就是原函数被调用时会调用的函数
- origin__system_property_get 是原函数的地址
Hook代码编写完成后,在forkAndSpecializePost函数中调用initDobby函数开始我们的hook
static void forkAndSpecializePost(JNIEnv *env, jclass clazz, jint res) {
// Called "after" com_android_internal_os_Zygote_nativeForkAndSpecialize in frameworks/base/core/jni/com_android_internal_os_Zygote.cpp
// "res" is the return value of com_android_internal_os_Zygote_nativeForkAndSpecialize
LOGE("forkAndSpecializePost");
if (res == 0) {
// In app process
readPropFile(PROP_CONF_PATH,propMap);
initDobby();
// When unload allowed is true, the module will be unloaded (dlclose) by Riru
// If this modules has hooks installed, DONOT set it to true, or there will be SIGSEGV
// This value will be automatically reset to false before the "pre" function is called
riru_set_unload_allowed(false);
} else {
// In zygote process
}
}
注意:riru_set_unload_allowed(false);这一行,注释明确写道如果要进行hook必须设为false,不然会崩溃,事实也确实如此。
hook了native层的函数,实现修改层的机型数据,还需要修改Java层的数据,Java层的机型信息我们只要修改android.os.Build类的字段。而这些字段不用Hook,直接设置即可。
static void setBuild(JNIEnv* env){
jclass BuildClass = env->FindClass("android/os/Build");
std::map<std::string,std::string>::iterator it;
for(it = buildMap.begin();it != buildMap.end();it++){
jstring key = env->NewStringUTF(it->first.c_str());
jstring value = env->NewStringUTF(it->second.c_str());
jfieldID buildField = env->GetStaticFieldID(BuildClass,it->first.c_str(),"Ljava/lang/String;");
if(env->ExceptionCheck()){
env->ExceptionClear();
continue;
}
env->SetStaticObjectField(BuildClass,buildField,value);
if(env->ExceptionCheck()){
env->ExceptionClear();
}
}
}
注意:在编写代码时要十分注意,如果代码崩溃,会导致手机无法开机。
这样我们的代码基本写完了
配置模块信息
上文我们提到过,我们编写的模块虽然是依赖riru模块,但是它本质也是Magisk模块。那么它也会有它的名字,版本,说明,作者信息等,然而这些是由我们开发者去配置的
这些配置信息可以在Riru-ModuleTemplate项目的module.gradle中配置,这个文件的模板在module.example.gradle,可以将module.example.gradle重命名为module.gradle然后进一步修改
ext {
/*
This name will be used in the name of the so file ("lib${moduleLibraryName}.so").
*/
moduleLibraryName = "template"
/* Minimal supported Riru API version, used in the version check of riru.sh */
moduleMinRiruApiVersion = 24
/* The version name of minimal supported Riru, used in the version check of riru.sh */
moduleMinRiruVersionName = "v24.0.0"
/* Maximum supported Riru API version, used in the version check of riru.sh */
moduleRiruApiVersion = 26
/*
Magisk module ID
Since Magisk use it to distinguish different modules, you should never change it.
Note, the older version of the template uses '-' instead of '_', if your are upgrading from
the older version, please pay attention.
*/
magiskModuleId = "riru_template"
moduleName = "Template"
moduleAuthor = "Template"
moduleDescription = "Riru module template. Requires Riru $moduleMinRiruVersionName or above."
moduleVersion = "v26.0.0"
moduleVersionCode = 26
}
编译
Riru-ModuleTemplate项目编译需要Jdk11以上,装好后在项目的根目录执行:
gradlew :module:assembleRelease
如果没有错误,就会在项目的out目录生成一个zip文件,这个就是我们编译好的magisk模块
刷入模块
在手机上,安装Magisk和riru模块,安装后,将编译好的模块zip文件推入手机,在MagiskManager中安装我们的模块:
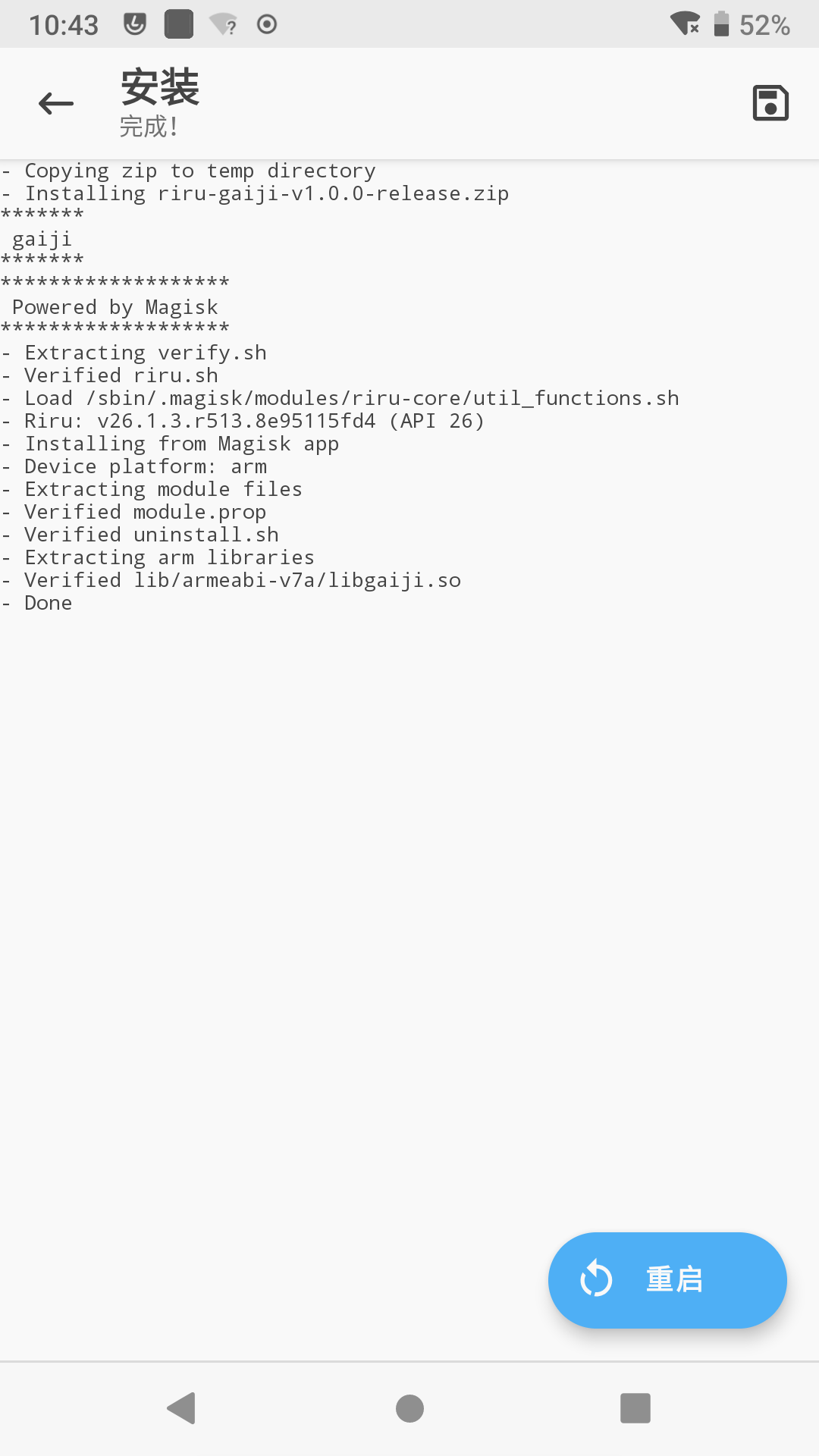
效果
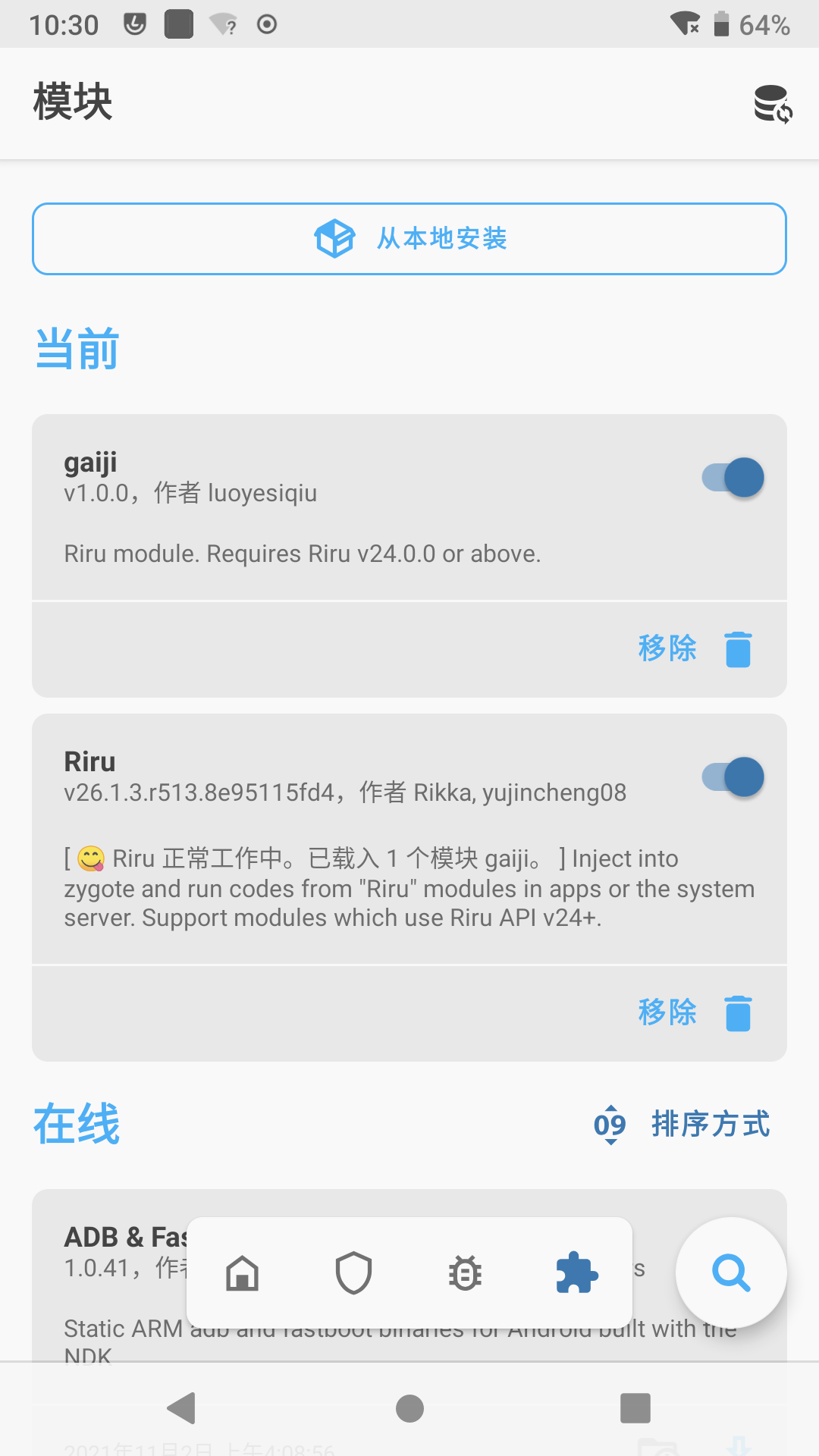
安装后,重启手机。打开MagiskManager看到我们的模块已正常启用:
去AIDA看看效果:

机型已经被我们修改,说明改机生效了。最后附上我写的改机模块:https://github.com/luoyesiqiu/Riru-gaiji
使用Magisk+riru实现全局改机的更多相关文章
- 爱伪装(AWZ)/爱立思(ALS)改机改串一键新机原理分析
简介 爱伪装(AWZ)/爱立思(ALS)是一款iOS越狱系统上的改机工具,可以修改多种系统参数达到伪装设备型号及各种软硬件属性的目的,同时提供了防越狱检测机制,常用于iOS上的推广刷量,配合代理/VP ...
- 玩机之HUAWEI_Nova
Nova是一款挺早的机型了.最开始使用华为就觉得这一款最好挺好用,屏幕小巧功能强大.当然也离不开手机,最早的TWRP就是在此机型上初步尝试成功,也算学习,那时候还没有玩过.这部手机算是改机最完美的一部 ...
- Magisk了解以及简单的模块制作
Magisk,就是刷机经常会需要使用的,也是就是我们说的面具或者脸谱.因为它的logo就是面具或者说脸谱.我们先简单了解一下: XDA上论坛的说明:Magisk - The Universal Sys ...
- SSH面试题(struts2+Spring+hibernate)
struts2 + Spring +hibernate Hibernate工作原理及为什么要用? 原理: 1.读取并解析配置文件 2.读取并解析映射信息,创建SessionFactory ...
- java SSH框架详解(面试和学习都是最好的收藏资料)
Java—SSH(MVC)1. 谈谈你mvc的理解MVC是Model—View—Controler的简称.即模型—视图—控制器.MVC是一种设计模式,它强制性的把应用程序的输入.处理和输出分开.MVC ...
- $.ajax()引发的对Deferred的总结 (转)
传统的ajax写法: $.ajax({ url:"1.json", type:"get", success:function(data){}, error:fu ...
- Openwrt flash 空间不足的临时解决方法
最近有网友在安装软件的时候发现flash空间不够用了: 一个临时的解决方案是在RAM里面使用这个程序.因为 1.路由器改机后的RAM有64MB,flash一般有16MB,RAM空间比较大./tmp是挂 ...
- $.ajax()引发的对Deferred的总结
传统的ajax写法: $.ajax({ url:"1.json", type:"get", success:function(data){}, error:fu ...
- Django-Views模块详解
http请求中产生的两个核心对象 http请求: HttpRequest http响应: HttpResponse 所在位置 django.http httpRequest属性: HttpReques ...
随机推荐
- Mongodb的基本使用及对接多数据源
mongodb介绍 MongoDB(来自于英文单词"Humongous",中文含义为"庞大")是可以应用于各种规模的企业.各个行业以及各类应用程序的开源数据库. ...
- gitlab与git命令
gitlab安装目录 /etc/gitlab#配置文件目录 /run/gitlab#运行pid目录 /opt/gitlab#安装目录 /var/opt/gitlab#数据目录 /var/log/git ...
- jmeter旅程第一站:Jmeter抓包浏览器或者抓取手机app的包
学习jmeter?从实际出发,我也是一个初学者,会优先考虑先用来做一些简单的抓包.接口测试,在实践的过程中学习jmeter用途.那么接下来,这篇文章我会以jmeter抓包开启我的jmeter旅程. 这 ...
- 『Python』matplotlib初识
1. 核心原理 使用matplotlib绘图的原理,主要就是理解figure(画布).axes(坐标系).axis(坐标轴)三者之间的关系. 下面这幅图更详细: 以"美院学生张三写生画画&q ...
- Nginx禁止ip方式访问80、443端口
在nginx.conf配置文件中 include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf; 之前加入以下内容 server { listen 80 default; listen 443 d ...
- centos7 .net core 使用supervisor守护进程后台运行
安装supervisor yum install supervisor 配置supervisor vi /etc/supervisord.conf 拉到最后,这里的意思是 /etc/superviso ...
- CF183D-T-shirtx【dp,贪心】
正题 题目链接:https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/CF183D 题目大意 \(n\)个人,\(m\)种衣服,给出每个人喜欢某件衣服的概率,你可以选择\(n\)件衣服带过 ...
- P5445-[APIO2019]路灯【set,树状数组套线段树】
正题 题目链接:https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P5445 题目大意 \(n+1\)个点,\(i\)和\(i+1\)个点之间有一条边,\(q\)个操作 断开/连接第\ ...
- 🚴♂️全套MySQL数据库教程_Mysql基础入门教程,零基础小白自学MySQL数据库必备教程☔ #002 # 第二单元 MySQL数据类型、操作表#
二.本单元知识点概述 (Ⅰ)知识点概述 二.本单元教学目标 (Ⅰ)重点知识目标 1.Mysql的数据类型2.如何选择数据类型3.创建表4.修改表5.删除表 (Ⅱ)能力目标 1.熟练创建数据库及删除数据 ...
- Java秘诀!零基础怎样快速学习Java?
对于零基础想学Java的朋友,其实一开始最应该做的就是定好学习目标和端正学习态度,切记不要三天打鱼两天晒网! 首先你是零基础,现在急需把Java学好,在保证学习质量的同时,用最短的时间学好Java应该 ...
