c++11之std::bind简单使用
note
- 更多用法,请参考: cppreference
- 用的少,容易忘。
我的理解
- 类似延迟计算。 比如,回调函数,将回调函数传入后,回调函数不一定马上被调用。
- 它是一个模板类,调用后将生成一个新的调用对象A。调用该对象A与调用原函数是等价的。
声明
截至目前,它的声明如下

需要包含头文件
#include <functional>
一个例子
代码
下面的print函数负责输出参数的值, 通过使用std::bind, 生成一个新的对象 func, 此时, func(a, b, c);与print(a, b, c);**的调用结果是等价的。
#include <functional>
void print(int a, int b, int c)
{
std::cout << "a = " << a << ", b=" << b << ", c=" << c << "\n\n";
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[], char* env[])
{
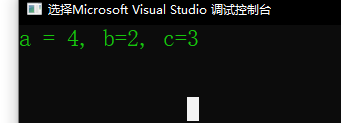
auto func = std::bind(print, std::placeholders::_2, 2, std::placeholders::_1);
func(3, 4);
return 0;
}
std::placeholders 说明
std::placeholders::_2和std::placeholders::_1表示参数的顺序,比如, 上面的代码示例中, 3是func的第一个参数,但是,func在声明时,指定了第一个参数的位置,放在了最后。 所以,上面的代码输出结果: a=4, b=2, c=3。
注意
- std::bind的函数参数默认使用的是拷贝, 如果需要使用引用,则需要配合std::ref。
- 下面一个例子,帮助理解。
print2函数负责输出参数的值,且参数都是引用, print2函数内完成对参数的自增
#include <functional>
void print2(int &a, int &b)
{
std::cout << "函数调用:a=" << a << ", b=" << b << "\n";
++a;
++b;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[], char* env[])
{
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
auto func2 = std::bind(print2, a, std::ref(b));
std::cout << "调用前,a=" << a << ", b=" << b << "\n";
func2();
std::cout << "调用后,a=" << a << ", b=" << b << "\n";
return 0;
}
调用时,尽管都采用了传入引用的方式,但略有不同。参数a使用的是传统的方式,参数b采用的是 std::ref的方式。 观察输出结果
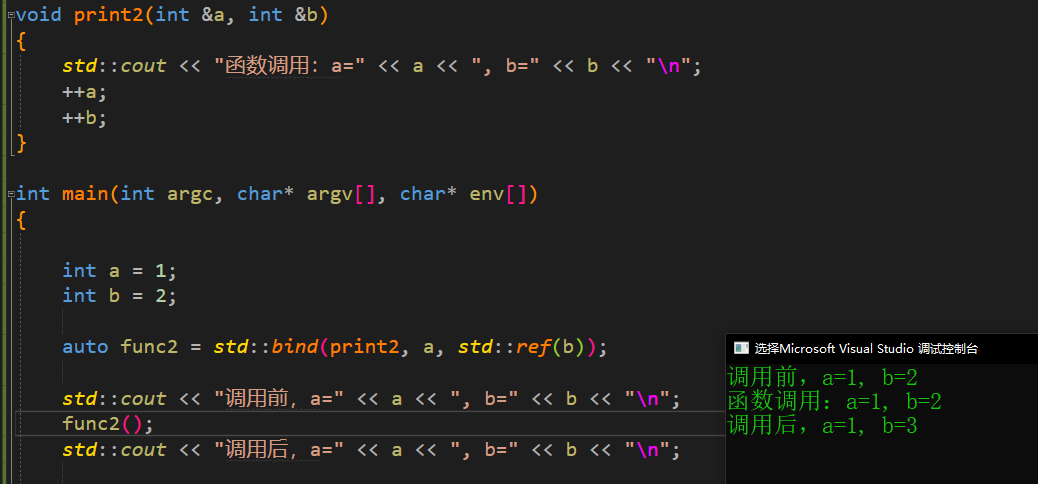
可以看到,std::bind的参数是以 拷贝的方式,使用 std::ref 的方式可以实现参数在std::bind的引用。
官方的例子
#include <random>
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <functional>
void f(int n1, int n2, int n3, const int& n4, int n5)
{
std::cout << n1 << ' ' << n2 << ' ' << n3 << ' ' << n4 << ' ' << n5 << '\n';
}
int g(int n1)
{
return n1;
}
struct Foo {
void print_sum(int n1, int n2)
{
std::cout << n1+n2 << '\n';
}
int data = 10;
};
int main()
{
using namespace std::placeholders; // for _1, _2, _3...
// demonstrates argument reordering and pass-by-reference
int n = 7;
// (_1 and _2 are from std::placeholders, and represent future
// arguments that will be passed to f1)
auto f1 = std::bind(f, _2, 42, _1, std::cref(n), n);
n = 10;
f1(1, 2, 1001); // 1 is bound by _1, 2 is bound by _2, 1001 is unused
// makes a call to f(2, 42, 1, n, 7)
// nested bind subexpressions share the placeholders
auto f2 = std::bind(f, _3, std::bind(g, _3), _3, 4, 5);
f2(10, 11, 12); // makes a call to f(12, g(12), 12, 4, 5);
// common use case: binding a RNG with a distribution
std::default_random_engine e;
std::uniform_int_distribution<> d(0, 10);
auto rnd = std::bind(d, e); // a copy of e is stored in rnd
for(int n=0; n<10; ++n)
std::cout << rnd() << ' ';
std::cout << '\n';
// bind to a pointer to member function
Foo foo;
auto f3 = std::bind(&Foo::print_sum, &foo, 95, _1);
f3(5);
// bind to a pointer to data member
auto f4 = std::bind(&Foo::data, _1);
std::cout << f4(foo) << '\n';
// smart pointers can be used to call members of the referenced objects, too
std::cout << f4(std::make_shared<Foo>(foo)) << '\n'
<< f4(std::make_unique<Foo>(foo)) << '\n';
}
官方例子输出
2 42 1 10 7
12 12 12 4 5
1 5 0 2 0 8 2 2 10 8
100
10
10
10
c++11之std::bind简单使用的更多相关文章
- C++11中std::bind的使用
std::bind: Each argument may either be bound to a value or be a placeholder: (1).If bound to a value ...
- 第11课 std::bind和std::function(2)_std::bind绑定器
1. 温故知新:std::bind1st和std::bind2nd (1)bind1st.bind2nd首先它们都是函数模板,用于将参数绑定到可调用对象(如函数.仿函数等)的第1个或第2个参数上. ( ...
- std::bind技术内幕
引子 最近群里比较热闹,大家都在山寨c++11的std::bind,三位童孩分别实现了自己的bind,代码分别在这里: 木头云的实现 mr.li的实现 null的实现,null的另一个版本的实现 这些 ...
- std::bind与std::ref, why and how
首先解释下为什么有时候需要bind. 我们可以用bind从函数T add(T a, T b)造出个inc()来,即把b写死为1.这个例子本身比较傻,但有不傻的应用. template<typen ...
- C++11多线程std::thread的简单使用
在cocos2dx 2.0时代,我们使用的是pthread库,是一套用户级线程库,被广泛地使用在跨平台应用上.但在cocos2dx 3.0中并未发现有pthread的支持文件,原来c++11中已经拥有 ...
- C++11中提供了std::bind
再来看看std::bind C++11中提供了std::bind.bind()函数的意义就像它的函数名一样,是用来绑定函数调用的某些参数的. bind的思想实际上是一种延迟计算的思想,将可调用对象保存 ...
- c++11 符号修饰与函数签名、函数指针、匿名函数、仿函数、std::function与std::bind
一.符号修饰与函数签名 1.符号修饰 编译器将c++源代码编译成目标文件时,用函数签名的信息对函数名进行改编,形成修饰名.GCC的C++符号修饰方法如下: 1)所有符号都以_z开头 2)名字空间的名字 ...
- C++11之std::function和std::bind
std::function是可调用对象的包装器,它最重要的功能是实现延时调用: #include "stdafx.h" #include<iostream>// std ...
- [C/C++11]_[初级]_[std::bind介绍和使用]
场景 1.C++11 引入了std::function 对象, 这个对象可以通过std::bind封装所有的函数, 并通过代理调用这个std::function的方式调用这个函数. 比如通过统一的方式 ...
随机推荐
- 洛谷 P1224 - [NOI2013] 向量内积(随机化)
洛谷题面传送门 一道很神的随机化. 首先由于我们要求向量点乘 \(\bmod k\) 的值,因此我们可以将所有 \(x_{i,j}\) 都模上 \(k\),显然该操作不影响结果正确性. 注意到这里的 ...
- Codeforces 1158F - Density of subarrays(dp,神仙题)
Codeforces 题目传送门 & 洛谷题目传送门 人生中第一道 *3500(显然不是自己独立 AC 的),不过还是祭一下罢 神仙 D1F 首先考虑对于给定的序列 \(a_1,a_2,\do ...
- time 查看命令执行时间
在命令执行完成之后就会打印出CPU的使用情况: real 0m5.064s <== 实际使用时间(real time) user 0m0.020s <== 用 ...
- Identity Server 4 从入门到落地(七)—— 控制台客户端
前面的部分: Identity Server 4 从入门到落地(一)-- 从IdentityServer4.Admin开始 Identity Server 4 从入门到落地(二)-- 理解授权码模式 ...
- A Child's History of England.33
To strengthen his power, the King with great ceremony betrothed his eldest daughter Matilda, then a ...
- Scala(五)【集合的高级使用】
目录 一.集合属性 size length contains mkString 二.集合方法 drop.dropRight distinct:去重 head.last:获取第一个.最后一个元素 tai ...
- css通配样式初始化(多款,供君自选)
腾讯官网 body,ol,ul,h1,h2,h3,h4,h5,h6,p,th,td,dl,dd,form,fieldset,legend,input,textarea,select{margin:0; ...
- IDEA 超实用使用技巧分享
前言 工欲善其事 必先利其器 最近受部门的邀请,给入职新人统一培训IDEA,发现有很多新人虽然日常开发使用的是IDEA,但是还是很多好用的技巧没有用到,只是用到一些基本的功能,蛮浪费IDEA这个优 ...
- 使用NSURLSessionDownloadTask实现大文件下载-监听下载进度
- 5.1 涉及知识点(1)创建NSURLSession并设置代理,通过NSURLSessionDownloadTask并以代理的方式来完成大文件的下载 //1.创建NSURLSession,设置代理 ...
- 微服务中心Eureka
一.简介 Eureka是Netflix开发的服务发现框架,本身是一个基于REST的服务,主要用于定位运行在AWS(AWS 是业务流程管理开发平台AWS Enterprise BPM Platform ...
