SpringBoot中使用SpringDataJPA
SpringDataJPA的使用
JPA是什么?
JPA(Java Persistence API)是Sun官方提出的Java持久化规范. 为Java开发人员提供了一种对象/关联映射工具来管理Java应用中的关系数据. 它的出现是为了简化现有的持久化开发工作和整合ORM技术. 结束各个ORM框架各自为营的局面.
JPA仅仅是一套规范,不是一套产品, 也就是说Hibernate, TopLink等是实现了JPA规范的一套产品.
Spring Data JPA
Spring Data JPA是Spring基于ORM框架、JPA规范的基础上封装的一套JPA应用框架,是基于Hibernate之上构建的JPA使用解决方案,用极简的代码实现了对数据库的访问和操作,包括了增、删、改、查等在内的常用功能.
实践
- 引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
- 添加配置文件
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://39.105.167.131:3306/smile_boot?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=true
username: root
password: Nrblwbb7$
jpa:
properties:
hibernate:
hbm2ddl:
auto: create
dialect: org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect
format_sql: true
show-sql: true
hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto 参数的作用主要用于:自动创建、更新、验证数据库表结构,有四个值。
- create:每次加载 Hibernate 时都会删除上一次生成的表,然后根据 model 类再重新来生成新表,哪怕两次没有任何改变也要这样执行,这就是导致数据库表数据丢失的一个重要原因。
- create-drop:每次加载 Hibernate 时根据 model 类生成表,但是 sessionFactory 一关闭,表就自动删除。
- update:最常用的属性,第一次加载 Hibernate 时根据 model 类会自动建立起表的结构(前提是先建立好数据库),以后加载 Hibernate 时根据 model 类自动更新表结构,即使表结构改变了,但表中的行仍然存在,不会删除以前的行。要注意的是当部署到服务器后,表结构是不会被马上建立起来的,是要等应用第一次运行起来后才会。
- validate :每次加载 Hibernate 时,验证创建数据库表结构,只会和数据库中的表进行比较,不会创建新表,但是会插入新值。
配置文件中:
- dialect 主要是指定生成表名的存储引擎为 InnoDB
- show-sql 是否在日志中打印出自动生成的 SQL,方便调试的时候查看
- 编写代码
实体类:
@Entity
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
@Column(nullable = false, unique = true)
private String userName;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String passWord;
@Column(nullable = false, unique = true)
private String email;
@Column(nullable = true, unique = true)
private String nickName;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String regTime;
public User(String userName, String passWord, String email, String nickName, String regTime) {
this.userName = userName;
this.passWord = passWord;
this.email = email;
this.nickName = nickName;
this.regTime = regTime;
}
public User() {
}
// getter and setter
}
注解:
- @Entity(name="EntityName") 必须,用来标注一个数据库对应的实体,数据库中创建的表名默认和类名一致。其中,name 为可选,对应数据库中一个表,使用此注解标记 Pojo 是一个 JPA 实体。
- @Table(name="",catalog="",schema="") 可选,用来标注一个数据库对应的实体,数据库中创建的表名默认和类名一致。通常和 @Entity 配合使用,只能标注在实体的 class 定义处,表示实体对应的数据库表的信息。
- @Id 必须,@Id 定义了映射到数据库表的主键的属性,一个实体只能有一个属性被映射为主键。
- @GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType,generator="") 可选,strategy: 表示主键生成策略,有 AUTO、INDENTITY、SEQUENCE 和 TABLE 4 种,分别表示让 ORM 框架自动选择,generator: 表示主键生成器的名称。
- @Column(name = "user_code", nullable = false, length=32) 可选,@Column 描述了数据库表中该字段的详细定义,这对于根据 JPA 注解生成数据库表结构的工具。name: 表示数据库表中该字段的名称,默认情形属性名称一致;nullable: 表示该字段是否允许为 null,默认为 true;unique: 表示该字段是否是唯一标识,默认为 false;length: 表示该字段的大小,仅对 String 类型的字段有效。
- @Transient可选,@Transient 表示该属性并非一个到数据库表的字段的映射,ORM 框架将忽略该属性。
- @Enumerated 可选,使用枚举的时候,我们希望数据库中存储的是枚举对应的 String 类型,而不是枚举的索引值,需要在属性上面添加 @Enumerated(EnumType.STRING) 注解。
基本都是hibernate的注解
4. Repository构建
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User,Long> {
User findByUserNameOrEmail(String userName, String email);
User findByUserName(String userName);
}
因为是继承,所以父类有的方法全部继承,可以查看父类的源码来看看有哪些方法.
- 测试
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class UserRepositoryTest {
@Resource
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Test
public void test(){
Date data = new Date();
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String formattedDate = dateFormat.format(data);
userRepository.save(new User("aa","aa123456","aa@126.com","aa",formattedDate));
userRepository.save(new User("bb","bb123456","bb@126.com","bb",formattedDate));
userRepository.save(new User("cc","cc123456","cc@126.com","cc",formattedDate));
Assert.assertEquals(3,userRepository.findAll().size());
Assert.assertEquals("bb",userRepository.findByUserNameOrEmail("bb","bb@126.com").getNickName());
userRepository.delete(userRepository.findByUserName("aa"));
}
}
查询语句
在jpa中查询分为两类,一类是继承了父类的方法的基本查询,另一类是自定义查询.
基本查询
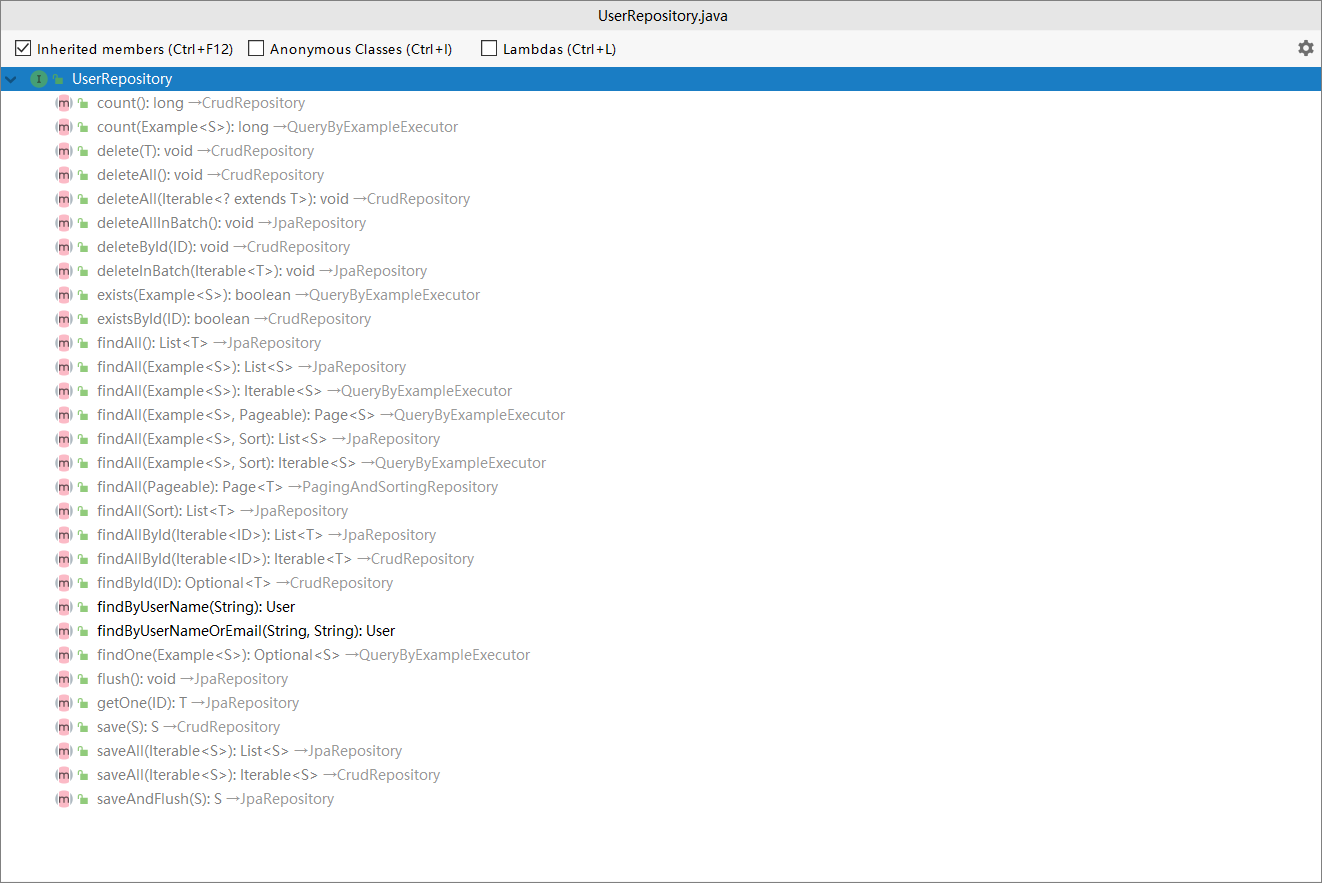
图中黑色就是自定义的,灰色的就是从父类继承的.
自定义查询
Spring Data JPA 可以根据接口方法名来实现数据库操作,主要的语法是 findXXBy、readAXXBy、queryXXBy、countXXBy、getXXBy 后面跟属性名称,利用这个功能仅需要在定义的 Repository 中添加对应的方法名即可,使用时 Spring Boot 会自动帮我们实现.
根据用户名查询用户:
User findByUserName(String userName);
也可以加一些关键字 And、or:
User findByUserNameOrEmail(String username,String email);
修改、删除、统计也是类似语法:
Long deleteById(Long id);
Long countByUserName(String userName)
基本上 SQL 体系中的关键词都可以使用,如 LIKE 、IgnoreCase、OrderBy:
List<User> findByEmailLike(String email);
User findByUserNameIgnoreCase(String userName);
List<User> findByUserNameOrderByEmailDesc(String email);
关键字的使用和生产SQL:
| Keyword | Sample | JPQL snippet |
|---|---|---|
| And | findByLastnameAndFirstname | … where x.lastname = ?1 and x.firstname = ?2 |
| Or | findByLastnameOrFirstname | … where x.lastname = ?1 or x.firstname = ?2 |
| Is,Equals | findByFirstnameIs,findByFirstnameEquals | … where x.firstname = ?1 |
| Between | findByStartDateBetween | … where x.startDate between ?1 and ?2 |
| LessThan | findByAgeLessThan | … where x.age < ?1 |
| LessThanEqual | findByAgeLessThanEqual | … where x.age ⇐ ?1 |
| GreaterThan | findByAgeGreaterThan | … where x.age > ?1 |
| GreaterThanEqual | findByAgeGreaterThanEqual | … where x.age >= ?1 |
| After | findByStartDateAfter | … where x.startDate > ?1 |
| Before | findByStartDateBefore | … where x.startDate < ?1 |
| IsNull | findByAgeIsNull | … where x.age is null |
| IsNotNull,NotNull | findByAge(Is)NotNull | … where x.age not null |
| Like | findByFirstnameLike | … where x.firstname like ?1 |
| NotLike | findByFirstnameNotLike | … where x.firstname not like ?1 |
| StartingWith | findByFirstnameStartingWith | … where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound with appended %) |
| EndingWith | findByFirstnameEndingWith | … where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound with prepended %) |
| Containing | findByFirstnameContaining | … where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound wrapped in %) |
| OrderBy | findByAgeOrderByLastnameDesc | … where x.age = ?1 order by x.lastname desc |
| Not | findByLastnameNot | … where x.lastname <> ?1 |
| In | findByAgeIn(Collection ages) | … where x.age in ?1 |
| NotIn | findByAgeNotIn(Collection age) | … where x.age not in ?1 |
| TRUE | findByActiveTrue() | … where x.active = true |
| FALSE | findByActiveFalse() | … where x.active = false |
| IgnoreCase | findByFirstnameIgnoreCase | … where UPPER(x.firstame) = UPPER(?1) |
自定义SQL查询
- 在UserRepository中增加方法:
/**
* @Author Smith
* @Description 自定义Sql查询.(这个本来是HQL的写法,我的运行不了,改成了本地的SQL)
* @Date 10:18 2019/1/24
* @Param
* @return org.springframework.data.domain.Page<com.jpa.springdatajpa.model.User>
**/
@Query(value = "select * from user",nativeQuery = true)
Page<User> findALL(Pageable pageable);
/**
* @Author Smith
* @Description 原生SQL的写法,?1表示方法参数中的顺序
* @Date 10:20 2019/1/24
* @Param
* @return org.springframework.data.domain.Page<com.jpa.springdatajpa.model.User>
**/
@Query(value = "select * from user where nick_name = ?1",nativeQuery = true)
Page<User> findByNickName(String nickName, Pageable pageable);
/**
* @Author Smith
* @Description 修改,添加事务的支持
* @Date 10:21 2019/1/24
* @Param
* @return int
**/
@Transactional(timeout = 10)
@Modifying
@Query("update User set userName = ?1 where id = ?2")
int modifyById(String userName, Long id);
/**
* @Author Smith
* @Description 删除
* @Date 10:22 2019/1/24
* @Param
* @return void
**/
@Transactional
@Modifying
@Query("delete from User where id = ?1")
@Override
void deleteById(Long id);
测试
@Test
public void testFindALL(){
int page = 1;
int size = 1;
Sort sort = new Sort(Sort.Direction.DESC,"id");
Pageable pageable = PageRequest.of(page,size,sort);
Page<User> all = userRepository.findALL(pageable);
Assert.assertEquals(1,all.getContent().size());
Assert.assertEquals(2,all.getTotalPages());
}
@Test
public void testFindByNickName(){
int page = 0;
int size = 1;
Sort sort = new Sort(Sort.Direction.DESC,"id");
Pageable pageable = PageRequest.of(page,size,sort);
Page<User> all = userRepository.findByNickName("bb",pageable);
Assert.assertEquals(1,all.getContent().size());
Assert.assertEquals(1,all.getTotalPages());
}
需要注意的是Pageable分页的使用,其余的基本没什么需要注意的.
限制查询
只需要查询前 N 个元素,或者只取前一个实体。
User findFirstByOrderByNickNameAsc();
User findTopByOrderByIdDesc();
Page<User> queryFirst10ByNickName(String nickName, Pageable pageable);
List<User> findFirst10ByNickName(String nickName, Sort sort);
List<User> findTop10ByNickName(String nickName, Pageable pageable);
这没有做测试
复杂查询
在某些情况下查询条件很多,需要不断拼接属性,方法名会显得很长,这个时候就要使用JpaSpecificationExecutor 接口了.
概念:
- Root root,代表了可以查询和操作的实体对象的根,开一个通过 get("属性名") 来获取对应的值。
- CriteriaQuery query,代表一个 specific 的顶层查询对象,它包含着查询的各个部分,比如 select 、from、where、group by、order by 等。
- CriteriaBuilder cb,来构建 CritiaQuery 的构建器对象,其实就相当于条件或者是条件组合,并以 Predicate 的形式返回。
实体:
@Entity
public class UserDetail {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
@Column(nullable = false, unique = true)
private Long userId;
private Integer age;
private String realName;
private String status;
private String hobby;
private String introduction;
private String lastLoginIp;
// getter/setter
repository:
public interface UserDetailRepository extends JpaSpecificationExecutor<UserDetail>,
JpaRepository<UserDetail, Long> {
}
service和serviceImpl
public interface UserDetailService {
public Page<UserDetail> findByCondition(UserDetailParam detailParam, Pageable pageable);
}
@Service
public class UserDetailServiceImpl implements UserDetailService {
@Resource
private UserDetailRepository userDetailRepository;
@Override
public Page<UserDetail> findByCondition(UserDetailParam detailParam, Pageable pageable){
return userDetailRepository.findAll((root, query, cb) -> {
List<Predicate> predicates = new ArrayList<>();
//equal 示例
if (!StringUtils.isNullOrEmpty(detailParam.getIntroduction())){
predicates.add(cb.equal(root.get("introduction"),detailParam.getIntroduction()));
}
//like 示例
if (!StringUtils.isNullOrEmpty(detailParam.getRealName())){
predicates.add(cb.like(root.get("realName"),"%"+detailParam.getRealName()+"%"));
}
//between 示例
if (detailParam.getMinAge()!=null && detailParam.getMaxAge()!=null) {
Predicate agePredicate = cb.between(root.get("age"), detailParam.getMinAge(), detailParam.getMaxAge());
predicates.add(agePredicate);
}
//greaterThan 大于等于示例
/*if (detailParam.getMinAge()!=null){
predicates.add(cb.greaterThan(root.get("age"),detailParam.getMinAge()));
}*/
return query.where(predicates.toArray(new Predicate[predicates.size()])).getRestriction();
}, pageable);
}
}
测试:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class UserDetailTest {
@Resource
private UserDetailService userDetailService;
@Test
public void testFindByCondition() {
int page=0,size=10;
Sort sort = new Sort(Sort.Direction.DESC, "id");
Pageable pageable = PageRequest.of(page, size, sort);
UserDetailParam param=new UserDetailParam();
param.setIntroduction("程序员");
param.setMinAge(10);
param.setMaxAge(30);
Page<UserDetail> page1=userDetailService.findByCondition(param,pageable);
for (UserDetail userDetail:page1){
System.out.println("userDetail: "+userDetail.toString());
}
}
}
在我本地测试失败了,报了个mysql的混合字符集的错,找了会发现使用的方言的问题,可以从数据库看到生成表的排序规则是latin1_swedish_ci,所以报错.解决方案是:新建一个配置类:
public class MysqlConfig extends MySQL5Dialect {
@Override
public String getTableTypeString() {
return " ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8";
}
}
在配置文件中进行修改
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://39.105.167.131:3306/smile_boot?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=true
username: root
password: Nrblwbb7$
jpa:
properties:
hibernate:
hbm2ddl:
auto: create
# 注意这行,为自己的配置文件的路径
dialect: com.jpa.springdatajpa.config.MysqlConfig
format_sql: true
show-sql: true
这样生成的表就是utf8_general_ci了,问题就解决了.
多表查询
新建实体类:
public interface UserInfo {
String getUserName();
String getEmail();
String getHobby();
String getIntroduction();
}
repository方法:
@Query("select u.userName as userName, u.email as email, d.introduction as introduction , d.hobby as hobby from User u , UserDetail d " +
"where u.id=d.userId and d.hobby = ?1 ")
List<UserInfo> findUserInfo(String hobby);
测试:
@Test
public void testUserInfo() {
List<UserInfo> userInfos=userDetailRepository.findUserInfo("钓鱼");
for (UserInfo userInfo:userInfos){
System.out.println("userInfo: "+userInfo.getUserName()+"-"+userInfo.getEmail()+"-"+userInfo.getHobby()+"-"+userInfo.getIntroduction());
}
}
上面就是关于springdatajpa在springboot中的使用了.
源码链接: https://github.com/MissWangLove/SpringBoot
SpringBoot中使用SpringDataJPA的更多相关文章
- SpringBoot中使用spring-data-jpa 数据库操作(上)
Java客户端使用Spring-Data-Jpa这个组件. Spring-Data-Jpa就是Spring对Hibernate的一个整合. 选择create在运行的时候它会自动帮我们创建一个表. sp ...
- SpringBoot中使用spring-data-jpa 数据库操作(下)
- SpringBoot中yaml配置对象
转载请在页首注明作者与出处 一:前言 YAML可以代替传统的xx.properties文件,但是它支持声明map,数组,list,字符串,boolean值,数值,NULL,日期,基本满足开发过程中的所 ...
- 如何在SpringBoot中使用JSP ?但强烈不推荐,果断改Themeleaf吧
做WEB项目,一定都用过JSP这个大牌.Spring MVC里面也可以很方便的将JSP与一个View关联起来,使用还是非常方便的.当你从一个传统的Spring MVC项目转入一个Spring Boot ...
- springboot中swaggerUI的使用
demo地址:demo-swagger-springboot springboot中swaggerUI的使用 1.pom文件中添加swagger依赖 2.从github项目中下载swaggerUI 然 ...
- spring-boot+mybatis开发实战:如何在spring-boot中使用myabtis持久层框架
前言: 本项目基于maven构建,使用mybatis-spring-boot作为spring-boot项目的持久层框架 spring-boot中使用mybatis持久层框架与原spring项目使用方式 ...
- 由浅入深学习springboot中使用redis
很多时候,我们会在springboot中配置redis,但是就那么几个配置就配好了,没办法知道为什么,这里就详细的讲解一下 这里假设已经成功创建了一个springboot项目. redis连接工厂类 ...
- Springboot中使用AOP统一处理Web请求日志
title: Springboot中使用AOP统一处理Web请求日志 date: 2017-04-26 16:30:48 tags: ['Spring Boot','AOP'] categories: ...
- SpringBoot 中常用注解
本篇博文将介绍几种SpringBoot 中常用注解 其中,各注解的作用为: @PathVaribale 获取url中的数据 @RequestParam 获取请求参数的值 @GetMapping 组合注 ...
随机推荐
- 动画:view从点逐渐变大(放大效果)
-(void) animationAlert:(UIView *)view { CAKeyframeAnimation *popAnimation = [CAKeyframeAnimation ani ...
- jsp页面中日期的格式化
在一次开发中,由于数据库中生日采用的是datetime的数据类型,因此数据库中数据格式为:2017-07-11 00:00:00. 但是,编辑页面中回显生日肯定是不可以显示出时分秒的, ...
- 升级webpack2
更新:webpack3已经出来了,官方说从2到升级到3不用改一行配置,98%的人没有错误. 项目中用的是webpack1.webpack2已经出来一段时间了.决定升级.其实改动不是很大.修改加测试共花 ...
- [CF1007B]Pave the Parallelepiped[组合计数+状态压缩]
题意 \(t\) 组询问,给你 \(A, B, C\) ,问有多少组三元组 \((a, b, c)\) 满足他们任意排列后有: \(a|A,\ b|B,\ c|C\) . \(A,B,C,t\leq ...
- Java 多线程之 Thread 类 和 Runnable 接口初步使用
目录 Thread 类 Thread之定义线程类 Thread之开启线程 Runnable 接口 Runnable 之定义线程类 Runnable 之开启线程 @ Thread 类 Thread 类是 ...
- Java关键字 Finally执行与break, continue, return等关键字的关系
长文短总结: 在程序没有在执行到finally之前异常退出的情况下,finally是一定执行的,即在finally之前的return语句将在finally执行之后执行. finally总是在控制转移语 ...
- Sqlserver_分组
create table orders ( id int, orderName varchar() ) go create table cars ( id ,) , ordersid int, pna ...
- OPPO A7X 刷机小结
OPPO A7X 刷机小结: 概述:根据网上找到的教程(MTK模式刷机教程),没有成功.在QQ上询问一位提供刷机服务的大神,说是只有老版本才能刷. 操作步骤: 刷机工具: MediaTek SP Fl ...
- Accer 4752G添加固态硬盘 双系统
(此文一直在草稿箱里躺了一年,略作修改后发布~) 背景:电脑是2011年年末买的,用到现在也已经5年多了,好在没坏过什么硬件,有过2年疯狂打LOL的经历,之后电脑就打不动了,FPS始终上不去,启动游戏 ...
- selenium+ python自动化--断言assertpy
前言: 在对登录验证时,不知道为何原因用unittest的断言不成功,就在网上发现这个assertpy,因此做个笔记 准备: pip install assertypy 例子: from assert ...
