leetcode 0211
✅ 1217. 玩筹码
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/play-with-chips
描述
数轴上放置了一些筹码,每个筹码的位置存在数组 chips 当中。
你可以对 任何筹码 执行下面两种操作之一(不限操作次数,0 次也可以):
将第 i 个筹码向左或者右移动 2 个单位,代价为 0。
将第 i 个筹码向左或者右移动 1 个单位,代价为 1。
最开始的时候,同一位置上也可能放着两个或者更多的筹码。
返回将所有筹码移动到同一位置(任意位置)上所需要的最小代价。
示例 1:
输入:chips = [1,2,3]
输出:1
解释:第二个筹码移动到位置三的代价是 1,第一个筹码移动到位置三的代价是 0,总代价为 1。
示例 2:
输入:chips = [2,2,2,3,3]
输出:2
解释:第四和第五个筹码移动到位置二的代价都是 1,所以最小总代价为 2。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/play-with-chips
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
解答
因为移动2个位置不需要代价,那么奇数位置移到奇数位置不用代价,偶数位置移到偶数位置不用代价,那就分别统计奇数位置和偶数位置的个数,相当于把所有奇数放一起,所有偶数的放一起,然后比较奇数的少还是偶数的少,将少的个数移到多的个数位置上去就可以了
c
int minCostToMoveChips(int* chips, int chipsSize){
int odd = 0, even = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < chipsSize; i++) {
if(chips[i] % 2 == 0){
even++;
} else {
odd++;
}
}
return even > odd ? odd : even;
}
/*执行用时 :
0 ms
, 在所有 C 提交中击败了
100.00%
的用户
内存消耗 :
6.7 MB
, 在所有 C 提交中击败了
99.28%
的用户*/
java
class Solution {
public int minCostToMoveChips(int[] chips) {
int odd = 0;
int even = 0;
for(int i: chips){
if(i % 2 == 0) {
even++;
} else {
odd++;
}
}
return Math.min(even, odd);
}
}
/*执行用时 :
0 ms
, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了
100.00%
的用户
内存消耗 :
41.2 MB
, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了
5.64%
的用户*/
py
class Solution:
def minCostToMoveChips(self, chips: List[int]) -> int:
even = 0
for i in chips:
if i&1 == 0:
even+=1
return min(even, len(chips) - even)
'''执行用时 :
32 ms
, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了
87.26%
的用户
内存消耗 :
13 MB
, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了
54.84%
的用户'''
✅ 206. 反转链表
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list
描述
反转一个单链表。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
进阶:
你可以迭代或递归地反转链表。你能否用两种方法解决这道题?
解答
c
他人:
//递归
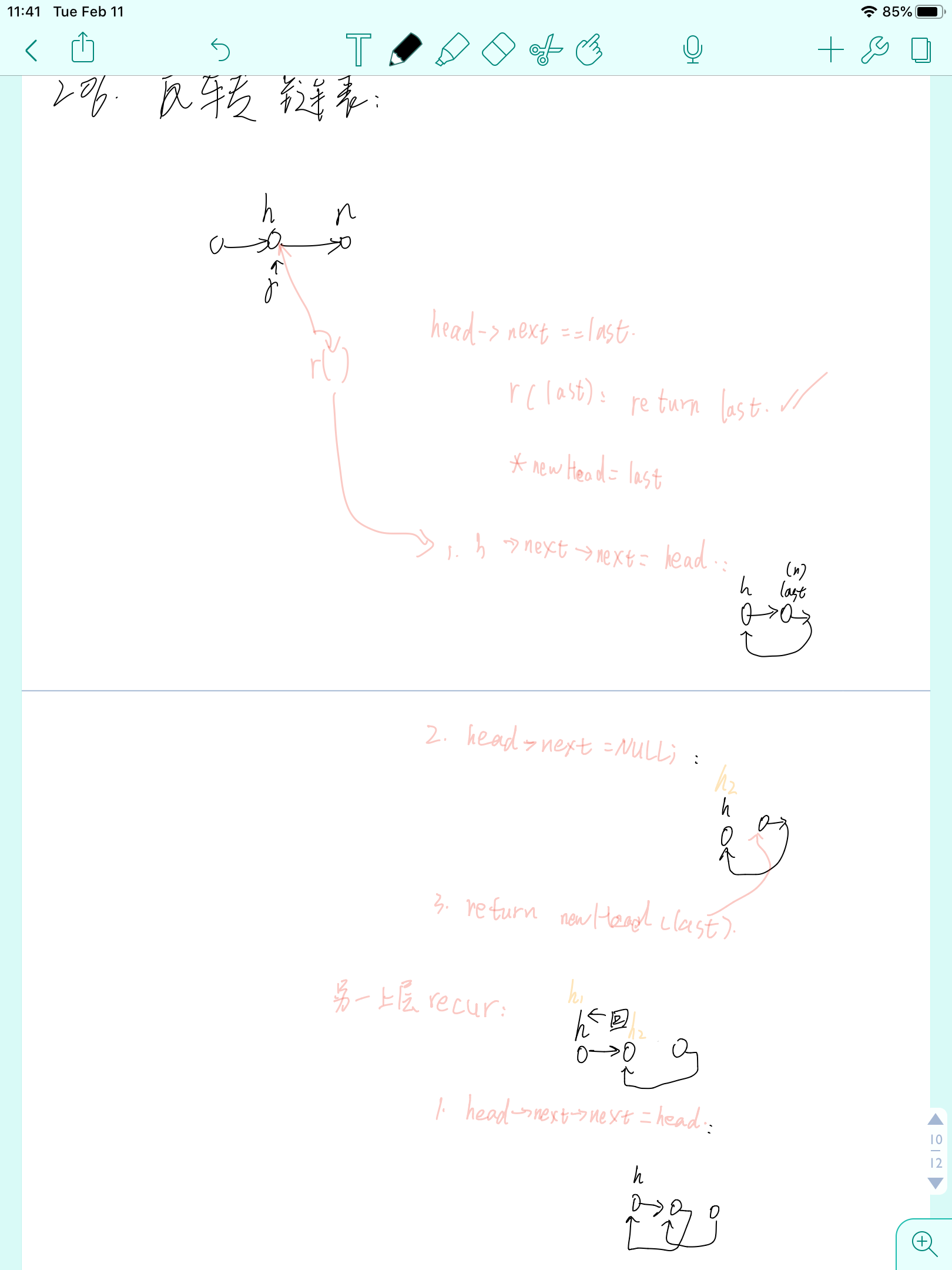
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
if(!head || !head->next)
return head;
struct ListNode *newhead = reverseList(head->next);//newhead指针记录链表末尾节点。
head->next->next = head;
head->next = NULL;
return newhead;
}
图片解释
java
迭代的,while loop 其实就是soldier 方式了:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
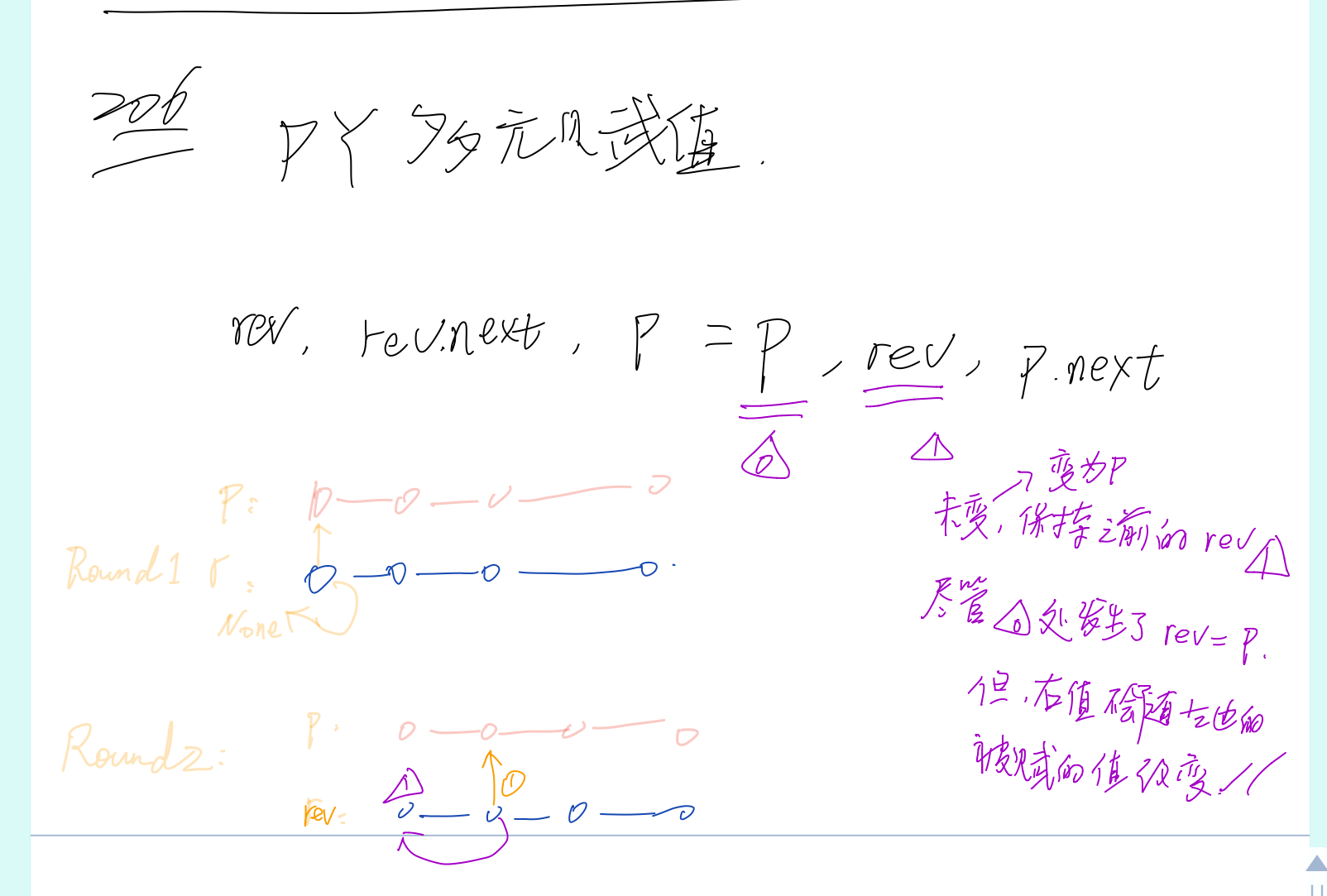
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode curr = head;
while(curr != null) {
ListNode tmp = curr.next;
curr.next = pre;
pre = curr;
curr = tmp;
}
return pre;
}
}
/*执行用时 :
0 ms
, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了
100.00%
的用户
内存消耗 :
42.3 MB
, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了
5.26%
的用户*/
py
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
cur, pre = head, None
while cur:
pre, pre.next, cur = cur, pre, cur.next
return pre
'''执行用时 :
52 ms
, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了
21.50%
的用户
内存消耗 :
14.2 MB
, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了
62.26%
的用户'''
图片解释:
✅ 922. 按奇偶排序数组 II
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sort-array-by-parity-ii
描述
给定一个非负整数数组 A, A 中一半整数是奇数,一半整数是偶数。
对数组进行排序,以便当 A[i] 为奇数时,i 也是奇数;当 A[i] 为偶数时, i 也是偶数。
你可以返回任何满足上述条件的数组作为答案。
示例:
输入:[4,2,5,7]
输出:[4,5,2,7]
解释:[4,7,2,5],[2,5,4,7],[2,7,4,5] 也会被接受。
提示:
2 <= A.length <= 20000
A.length % 2 == 0
0 <= A[i] <= 1000
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sort-array-by-parity-ii
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
解答
c 双指针soldier
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> sortArrayByParityII(vector<int>& A) {
int i ,l=A.size(),j,temp;
for(i=0,j=1;i<l&&j<l;)
{
while(i<l&&A[i]%2==0)
{
i+=2;
}
while(j<l&&A[j]%2==1)
{
j+=2;
}
if(i<l&&j<l)
{
temp=A[i];
A[i]=A[j];
A[j]=temp;
}
}
return A;
}
};
tddo fix: my c (0214 fixed)
非常奇怪,看着和上面的一样啊。
/**
* Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
int* sortArrayByParityII(int* A, int ASize, int* returnSize){
int i, j, tmp;
for(i = 0, j = 1; i < ASize && j < ASize;){
while(i < ASize && (A[i] % 2 == 0)){
//even, ok for i soldier, move foward
i+=2;
}
while(j < ASize && (A[j] % 2 == 1)){
//odd, ok for j soldier, move foward
j+=2;
}
if(i < ASize && j < ASize) {
tmp = A[i];
A[i] = A[j];
A[j] = A[i];
}
}
*returnSize = ASize;
return A;
}
/*输入:
[4,2,5,7]
输出
[4,2,2,7]
预期结果
[4,5,2,7]*/
fixed: by change: A[j] = A[i] to A[j] = tmp
/**
* Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
int* sortArrayByParityII(int* A, int ASize, int* returnSize){
int i, j, tmp;
for(i = 0, j = 1; (i < ASize) && (j < ASize);){
while(i < ASize && (A[i] % 2 == 0)){
//even, ok for i soldier, move foward
i+=2;
}
while(j < ASize && (A[j] % 2 == 1)){
//odd, ok for j soldier, move foward
j+=2;
}
if(i < ASize && j < ASize) {
tmp = A[i];
A[i] = A[j];
A[j] = tmp;//tt i was fucked here, plz don't use: A[j] = A[i]; fuxkkk
}
}
*returnSize = ASize;
return A;
}
/*执行用时 :
80 ms
, 在所有 C 提交中击败了
81.63%
的用户
内存消耗 :
14.1 MB
, 在所有 C 提交中击败了
96.14%
的用户*/
java 内部实际上是选择排序
class Solution {
public int[] sortArrayByParityII(int[] A) {
int j = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < A.length - 1; i = i + 2) {
if ((A[i] & 1) != 0) {
//实际上是选择排序
while ((A[j] & 1) != 0) {
j = j + 2;
}
int tmp = A[i];
A[i] = A[j];
A[j] = tmp;
}
}
return A;
}
}
py
todo 深刻理解zip
class Solution:
def sortArrayByParityII(self, A):
"""
:type A: List[int]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
ou = [i for i in A if i % 2]
ji = [i for i in A if not i % 2]
return [i for n in zip(ji, ou) for i in n]
✅ 867. 转置矩阵
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/transpose-matrix
描述
给定一个矩阵 A, 返回 A 的转置矩阵。
矩阵的转置是指将矩阵的主对角线翻转,交换矩阵的行索引与列索引。
示例 1:
输入:[[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
输出:[[1,4,7],[2,5,8],[3,6,9]]
示例 2:
输入:[[1,2,3],[4,5,6]]
输出:[[1,4],[2,5],[3,6]]
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/transpose-matrix
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
解答
c
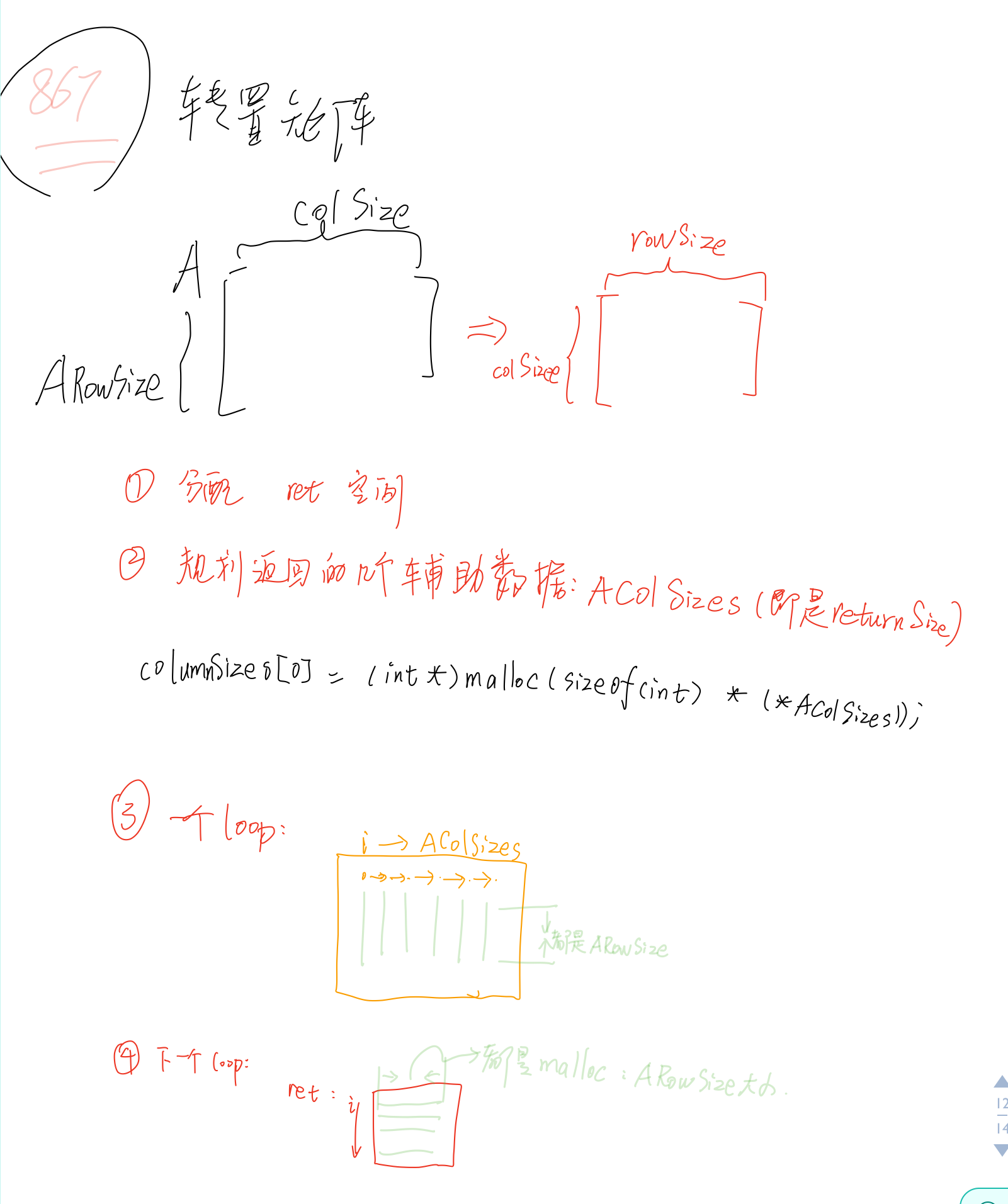
int** transpose(int** A, int ARowSize, int *AColSizes, int** columnSizes, int* returnSize)
{
int i, j;
int** ret = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int*) * (*AColSizes));
columnSizes[0] = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * (*AColSizes));
*returnSize = *AColSizes;
for(i = 0; i < *AColSizes; i++) columnSizes[0][i] = ARowSize;
for(i = 0; i < *AColSizes; i++) ret[i] = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * ARowSize);
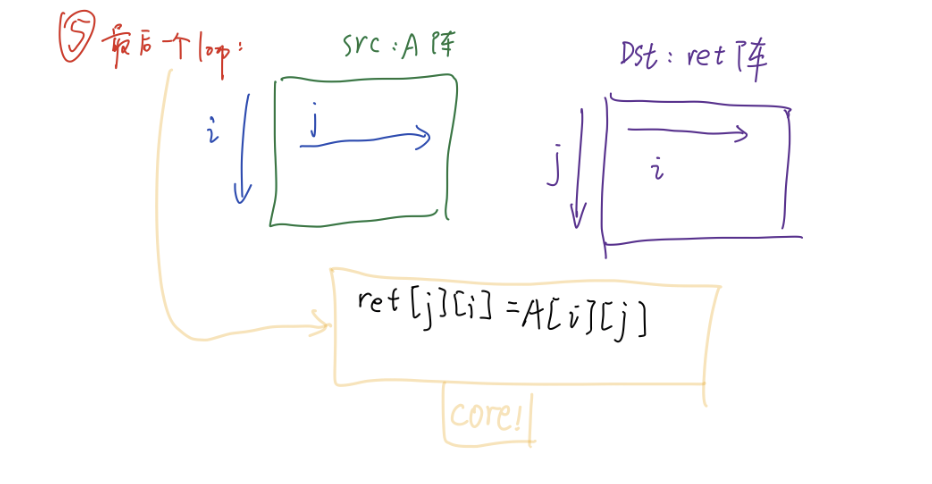
for(i = 0; i < ARowSize; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < *AColSizes; j++)
{
ret[j][i] = A[i][j];
}
}
return ret;
}
图片解释 上述:
二维数组需要两次dereference, there is why:
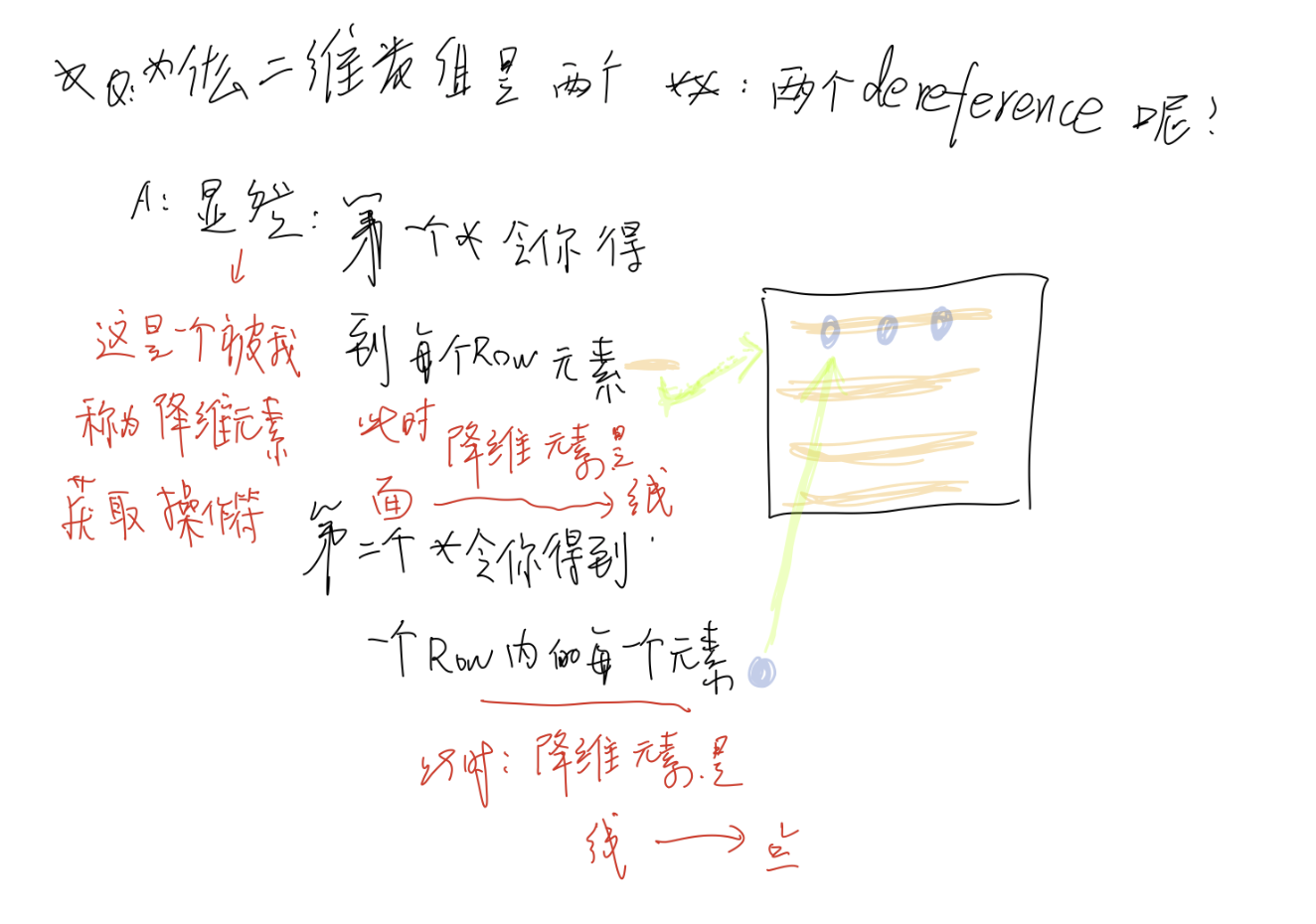
java
class Solution {
public int[][] transpose(int[][] A) {
int d1 = A.length;
int d2 = A[0].length;
int[][] ans = new int[d2][d1];
for(int i = 0; i < d1; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < d2; j++){
ans[j][i] = A[i][j];
}
}
return ans;
}
}
/*执行用时 :
0 ms
, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了
100.00%
的用户
内存消耗 :
48.1 MB
, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了
5.15%
的用户*/
py
class Solution:
def transpose(self, A: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
return zip(*A)
'''1 小时前 通过 88 ms 13.9 MB Python3
'''
leetcode 0211的更多相关文章
- 我为什么要写LeetCode的博客?
# 增强学习成果 有一个研究成果,在学习中传授他人知识和讨论是最高效的做法,而看书则是最低效的做法(具体研究成果没找到地址).我写LeetCode博客主要目的是增强学习成果.当然,我也想出名,然而不知 ...
- LeetCode All in One 题目讲解汇总(持续更新中...)
终于将LeetCode的免费题刷完了,真是漫长的第一遍啊,估计很多题都忘的差不多了,这次开个题目汇总贴,并附上每道题目的解题连接,方便之后查阅吧~ 477 Total Hamming Distance ...
- [LeetCode] Longest Substring with At Least K Repeating Characters 至少有K个重复字符的最长子字符串
Find the length of the longest substring T of a given string (consists of lowercase letters only) su ...
- Leetcode 笔记 113 - Path Sum II
题目链接:Path Sum II | LeetCode OJ Given a binary tree and a sum, find all root-to-leaf paths where each ...
- Leetcode 笔记 112 - Path Sum
题目链接:Path Sum | LeetCode OJ Given a binary tree and a sum, determine if the tree has a root-to-leaf ...
- Leetcode 笔记 110 - Balanced Binary Tree
题目链接:Balanced Binary Tree | LeetCode OJ Given a binary tree, determine if it is height-balanced. For ...
- Leetcode 笔记 100 - Same Tree
题目链接:Same Tree | LeetCode OJ Given two binary trees, write a function to check if they are equal or ...
- Leetcode 笔记 99 - Recover Binary Search Tree
题目链接:Recover Binary Search Tree | LeetCode OJ Two elements of a binary search tree (BST) are swapped ...
- Leetcode 笔记 98 - Validate Binary Search Tree
题目链接:Validate Binary Search Tree | LeetCode OJ Given a binary tree, determine if it is a valid binar ...
随机推荐
- AWD - IDE For Web dev汉化版
一款安卓上的HTML网页编辑软件,不错哦 下载链接 http://t.cn/AiRIvtoL
- NIO-BufferAPI
一 核心要素 capacity (容量):不能为负,不可更改:就是buffer的长度(buffer.length) limit (限制):指第一个不可被读入缓冲区元素的位置:不可为负,若positio ...
- Vue学习 Day01
介绍 这个系列记录自己学习Vue的过程. Vue官方不推荐新手直接使用 vue-cli,所以前面这几天都是根据官方文档学习. 步骤 新建一个html文件. 在html中导入vue.js依赖. < ...
- Linux Centos7文件系统
上期教大家创建分区,刚分区完成后没有文件系统,分区不能使用.本期教大家创建文件系统,(文件系统:操作系统通过文件系统管理文件及数据,创建文件系统的过程俗称格式化.)没有文件系统的设备称之为裸(raw) ...
- HPS—虚拟地址映射
HPS 如何对FPGA外设进行操作?hardware:在Qsys中将外设连接到AXI bridge上software:映射外设物理地址到到应用程序可以操作的虚拟地址,应用程序通过得到的虚拟地址入口控制 ...
- 解决tomcat控制台乱码问题
问题原因:编码不一致,tomcat启动后默认编码UTF-8,而windows的默认编码是GBK.所以只需配置启动tomcat后为GBK编码即可. 做法:找到路径 $xxx$\apache-tomcat ...
- bugku 矛盾 30
首先打开网址链接会发现一串代码 然后进行分析代码的意思首先是一个函数查一下这个函数 然后会发现现代码第一句写的是输入数字,然后会发现第二行有一个感叹号意思是输入的如果不是数字则回复数字 如果输入数字则 ...
- 数据库程序接口——JDBC——功能第四篇——事务之Spring事务
综述 事务的实现方式有三种,JTA,Spring事务,Web Container方式.本篇讲述Spring事务. Spring事务分为两个部分核心对象,Spring事务的实现方式. Spring事务实 ...
- jquery 相同ID 绑定事件
本文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/lan_13217/article/details/84079441 http://hi.baidu.com/meneye/blog/item/1 ...
- 多表连接面试题:ERROR:Not unique table/alias
class_info id class_name 2 s204 5 s205 1 s207 7 s203 match_info id host_id guest_id match_time mat ...
