Python笔记 #02# Inner workings of lists
源:DataCamp
datacamp 的 DAILY PRACTICE + 日常收集。
List of lists
As a data scientist, you'll often be dealing with a lot of data, and it will make sense to group some of this data.
Instead of creating a flat list containing strings and floats, representing the names and areas of the rooms in your house, you can create a list of lists. The script on the right can already give you an idea.
Don't get confused here: "hallway" is a string, while hall is a variable that represents the float 11.25 you specified earlier.
# area variables (in square meters)
hall = 11.25
kit = 18.0
liv = 20.0
bed = 10.75
bath = 9.50 # house information as list of lists
house = [["hallway", hall],
["kitchen", kit],
["living room", liv],
["bedroom", bed],
["bathroom", bath]] # Print out house
print(house) # Print out the type of house
print(type(house))
Subset and conquer
一个元素毫无疑问也是一个子集,因此不论是取一段或者随机访问一个元素都叫做 subsetting
# Create the areas list
areas = ["hallway", 11.25, "kitchen", 18.0, "living room", 20.0, "bedroom", 10.75, "bathroom", 9.50] # Print out second element from areas
print(areas[1]) # Print out last element from areas
print(areas[-1]) # Print out the area of the living room
print(areas[5])
#Subset and calculate
# Create the areas list
areas = ["hallway", 11.25, "kitchen", 18.0, "living room", 20.0, "bedroom", 10.75, "bathroom", 9.50] # Sum of kitchen and bedroom area: eat_sleep_area
eat_sleep_area = areas[3] + areas[-3] # Print the variable eat_sleep_area
print(eat_sleep_area)
Slicing and dicing
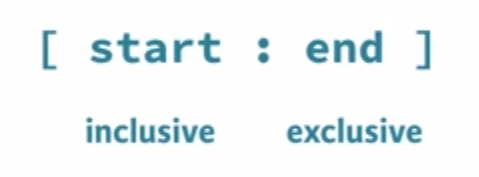
Selecting single values from a list is just one part of the story. It's also possible to slice your list, which means selecting multiple elements from your list. Use the following syntax:
my_list[start:end]
The start index will be included, while the end index is not.
# Create the areas list
areas = ["hallway", 11.25, "kitchen", 18.0, "living room", 20.0, "bedroom", 10.75, "bathroom", 9.50] # Use slicing to create downstairs
downstairs = areas[0:6] # Use slicing to create upstairs
upstairs = areas[6:10] # Print out downstairs and upstairs
print(downstairs)
print(upstairs)
However, it's also possible not to specify these indexes. If you don't specify the begin index, Python figures out that you want to start your slice at the beginning of your list. If you don't specify the end index, the slice will go all the way to the last element of your list.
# Create the areas list
areas = ["hallway", 11.25, "kitchen", 18.0, "living room", 20.0, "bedroom", 10.75, "bathroom", 9.50] # Alternative slicing to create downstairs
downstairs = areas[:6] # Alternative slicing to create upstairs
upstairs = areas[6:]
List Manipulation
1、反向选就不用考虑 0 了,数到几就是几
2、如下操作也可以增加元素
In [3]: x
Out[3]: ['a', 'b', 's', 't']
In [4]: x[2:] = ["s", "t", "hi"]
In [5]: x
Out[5]: ['a', 'b', 's', 't', 'hi']
Extend a list
# Create the areas list and make some changes
areas = ["hallway", 11.25, "kitchen", 18.0, "chill zone", 20.0,
"bedroom", 10.75, "bathroom", 10.50] # Add poolhouse data to areas, new list is areas_1
areas_1 = areas + ["poolhouse", 24.5] # Add garage data to areas_1, new list is areas_2
areas_2 = areas_1 + ["garage", 15.45]
Delete list elements
del(areas[-4:-2])
Inner workings of lists
Change the second command, that creates the variable areas_copy, such that areas_copy is an explicit copy of areas
# Create list areas
areas = [11.25, 18.0, 20.0, 10.75, 9.50] # Create areas_copy
# areas_copy = areas
areas_copy = list(areas) # Change areas_copy
areas_copy[0] = 5.0 # Print areas
print(areas)
areas_copy = areas[:] 也是可以的!
Python笔记 #02# Inner workings of lists的更多相关文章
- 我的Python笔记02
声明:本文整理借鉴金角大王的Python之路,Day2 - Python基础2,仅供本人学习使用!!! 本节内容 列表.元组操作 字符串操作 字典操作 集合操作 文件操作 字符编码与转码 1. 列表. ...
- python笔记02:列表与元素
本章将引入一个新的概念:数据结构.数据结构是通过某种方式(例如对元素进行编号)组织在一起的数据元素的集合.这些数据元素可以是数字或者字符,甚至可以是其他数据结构.在python中,最基本的数据结构是序 ...
- python笔记02
day02笔记记录 一.今日摘要 循环.字符串格式化.运算符.编码.博客. 二.内容回顾 (一)计算机基础 计算机由硬件和软件组成.传统计算机的硬件一般有输入单元.输出单元,算数逻辑单元.控制单元及记 ...
- python笔记-02
Python基础知识 —————————————— A,B,先把A乘以3,然后加上B,最后在加上列表A A = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] 赋值 B = [1, 2, 3] 变量 定义一个变 ...
- Python学习02 列表 List
Python学习02 列表 List Python列表 List Python中的列表(List)用逗号分隔,方括号包围(comma-separated values (items) between ...
- python笔记 - day6
python笔记 - day6 参考: http://www.cnblogs.com/wupeiqi/articles/5501365.html 大纲: 利用递归,实现阶乘: Python反射 pyt ...
- guxh的python笔记一:数据类型
1,基本概念 1.1,数据类型 基本数据类型:字符串,数字,布尔等 引用数据类型:相对不可变(元组),可变(列表,字典,集合等) 基本数据类型存放实际值,引用数据类型存放对象的地址(即引用) ==:判 ...
- python笔记-1(import导入、time/datetime/random/os/sys模块)
python笔记-6(import导入.time/datetime/random/os/sys模块) 一.了解模块导入的基本知识 此部分此处不展开细说import导入,仅写几个点目前的认知即可.其 ...
- 机器学习实战(Machine Learning in Action)学习笔记————02.k-邻近算法(KNN)
机器学习实战(Machine Learning in Action)学习笔记————02.k-邻近算法(KNN) 关键字:邻近算法(kNN: k Nearest Neighbors).python.源 ...
随机推荐
- 报错:org.springframework.http.converter.json.MappingJacksonHttpMessageConverter
org.springframework.http.converter.json.MappingJacksonHttpMessageConverter 1.错误描述 严重: Servlet /hux ...
- 创建4个线程,两个对j加一,两个对j减一(j两同两内)
package multithread; public class MyThread { //j变量私有 private int j; //同步的+1方法 private synchronized v ...
- Java中关于枚举的7种用法
1.定义常量: public enum Color { RED,ORANGE,YELLOW,GREEN,INDIGO,BLUE,PURPLE } 2.用于switch: enum Color { RE ...
- 逐一取Map值
String[] mKeys = starDetil.getRows().keySet().toArray(new String[starDetil.getRows().size()]); starD ...
- 修改记事本默认编码为UTF-8
1. 新建一个txt文档,不输入任何内容.然后“另存为”,将编码由默认的 ANSI 修改为 Unicode 或 UTF-8,并将新文档命名为 temp.txt 2.将 temp.txt 移动至系统目录 ...
- 20165330 2017-2018-2 《Java程序设计》第8周学习总结
课本知识总结 第十二章 Java多线程机制 Java中的线程 进程:是程序的一次动态执行过程,它对应了从代码加载.执行至执行完毕的一个完整过程 线程:一个进程在其执行过程中,可以产生多个线程,形成多条 ...
- 20165330 2017-2018-2 《Java程序设计》第4周学习总结
课本知识总结 第五章 子类与继承 子类:在类的声明中,通过使用关键字extends来定义一个类的子类. class 子类名 extends 父类名 { ... } 继承:子类继承父类的成员变量作为自己 ...
- ORACLE内存结构:PGA And UGA,ORACLE用户进程、服务器进程
执行一个SQL语句 执行查询语句的过程: 用户进程执行一个查询语句如select * from emp where empno=7839 用户进程和服务器进程建立连接,把改用户进程的信息存储到PGA的 ...
- C#中字符数组,字节数组和string之间的转化
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/wangxiaoqin00007/article/details/17675419 NDC(NetworkDiskClient)的界面和后台程序之间用S ...
- Allocation-Free Collections(在堆栈上使用内存)
假设你有一个方法,通过创建临时的List来收集某些数据,并根据这些数据来统计信息,然后销毁这个临时列表.这个方法被经常调用,导致大量内存分配和释放以及增加的内存碎片.此外,所有这些内存管理都需要时间, ...
