统计计算——Bootstrap总结整理
Bootstrapping
Boostrap 有放回的重抽样。
符号定义: 重复抽样的bootstrap \(F^*\) 观测到的样本\(\hat F\),是一个经验分布
真实分布\(F\)
Eg.
有一个要做估计的参数\(\alpha\)
用原始样本做估计的估计值\(\hat \alpha\)
用重抽样样本做估计的估计值\(\hat \alpha^*\)
重复抽样的bootstrap \(\bar \alpha^* = E(\hat \alpha^*)\)
Bootstrapping generates an empirical distribution of a test statistic or
set of test statistics. 有放回的重抽样。 Advantages:It allows you to
generate confidence intervals and test statistical hypotheses without
having to assume a specific underlying theoretical distribution.
- Randomly select 10 observations from the sample, with replacement
after each selection. Some observations may be selected more than
once, and some may not be selected at all. - Calculate and record the sample mean.
- Repeat steps 1 and 2 a thousand times.
- Order the 1,000 sample means from smallest to largest.
- Find the sample means representing the 2.5th and 97.5th percentiles.
In this case, it's the 25th number from the bottom and top. These
are your 95 percent confidence limits
What if you wanted confidence intervals for the sample median, or
the difference between two sample medians?
When to use ? - the underlying distributions are unknown - outliers
problems - sample sizes are small - parametric approach don't exist.
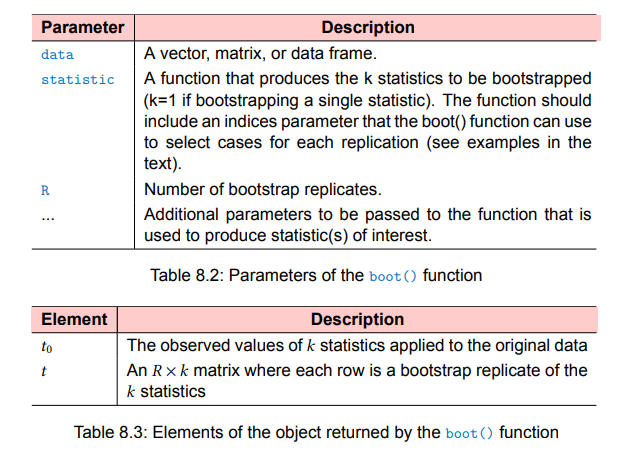
Bootstrapping with R
- Write a function that returns the statistic or statistics of
interest. If there is a single statistic (for example, a median),
the function should return a number. If there is a set of statistics
(for example, a set of regression coefficients), the function should
return a vector. - Process this function through the
boot()function in order to
generate R bootstrap replications of the statistic(s). - Use the
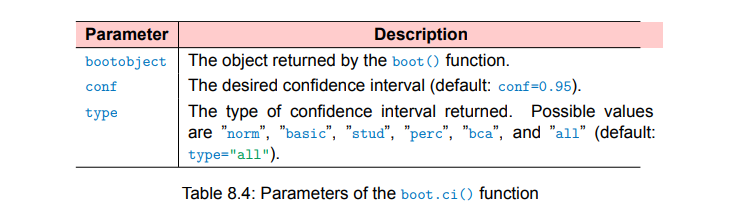
boot.ci()function to obtain confidence intervals for the
statistic(s) generated in step 2.
library(boot)
#bootobject <- boot(data=, statistic =, R=, ...)
#boot.ci(bootobject , conf= ..., type = ...)
The
bcaprovides an interval that makes simple adjustments for bias.
I findbcapreferable in most circumstances.
#indices <- c[3,1,4,1]
# data[c(3,1,4,1)]
my_mean <- function(x,indices){#这个函数的返回值:要估计的统计量。
mean(x[indices])
}
x <- iris$Petal.Length
library(boot)
boot(x, statistic = my_mean, R = 1000)
- std. error: std of
\(\hat{\mu_1^*}, \hat{\mu_2^*}...\hat\mu_{R=1000}^*\) - bias: 重抽样样本均值估计值和原始抽样值的差异。\(E(\hat\mu^*) - \hat \mu = \bar \mu^* - \hat \mu\)
- original:\(\hat \mu\),原始抽样估计值
Bootstrapping for an arbitrary parameter
Eg. Financial assets
Bootstrap for an arbitrary parameter
Example (Financial assets)
- Suppose that we wish to invest a fixed sum of money in two financial assets that yield returns of \(X\) and \(Y\), respectively, where \(X\) and \(Y\) are random quantities.
- Invest a fraction \(\alpha\) of our money in \(X\), and invest the remaining \(1-\alpha\) in \(Y\).
- Minimize
\]
and we have
\]
where \(\sigma_X^2=\operatorname{Var}(X), \sigma_Y^2=\operatorname{Var}(Y)\) and \(\sigma_{X Y}=\operatorname{Cov}(X, Y)\)
Question:
How to estimate \(\alpha\), and what is the standard error this estimator?
Solution:
Solution
- In reality, \(\sigma_X^2, \sigma_Y^2\) and \(\sigma_{X Y}\) are unknown.
- Compute estimates for these quantities: \(\hat{\sigma}_X^2, \hat{\sigma}_Y^2\) and \(\hat{\sigma}_{X Y}\).
- Estimate \(\alpha\) by
\]
Estimate the accuracy of \(\hat{\alpha}\).
If we know the distribution of \((X, Y)\)
- Resample \((X, Y) 1000\) times, and calculate \(\hat{\alpha}\) using the same precedure.
- Then, the estimtor for \(E(\hat{\alpha})\) is
\]
- The estimator for the standard deviation of \(\hat{\alpha}\) is
\]
If we do not know the distribution of \((X, Y)\)
- Usually, we don't know the distribution of \((X, Y)\). Resample \(\left(X^*, Y^*\right) 1000\) times from the original sample, and calculate \(\hat{\alpha}^*\) using the same precedure.
- Then, the estimtor for \(E(\hat{\alpha})\) is
\]
- The estimator for the standard deviation of \(\hat{\alpha}\) is
\]
总体的\(\sigma_{X}, \sigma_{Y}, \sigma_{XY}\)都可以用样本的来估计。
\]
问题在于,这个估计是有偏的,因为除了一些东西在下面,就不是线性的了。
注意在抽样时X,Y两者是一一对应的。
偏差的计算:\(E(\hat \alpha) - \alpha\) -> \(\bar{\alpha*} - \hat{\alpha}\)
两页ppt上的公式s里面都少了个平方。这里补上了。
alpha.fn = function(data, index) {
X = data$X[index]
Y = data$Y[index]
alpha.hat = (var(Y) - cov(X, Y)) / (var(X) + var(Y) - 2 * cov(X, Y))
return(alpha.hat)
}
library(ISLR2)
alpha.fn(Portfolio, 1:100) # alpha.hat
set.seed(1)
alpha.fn(Portfolio, sample(100, 100, replace = TRUE)) # alpha.hat* # run R=1000 times, we will have E(alpha.hat)
library(boot)
boot.model = boot(Portfolio, alpha.fn, R = 1000)
boot.model
Estimating the accuracy of a linear regression model
summary(lm(mpg ~ horsepower, data = Auto))$coef
coef.fn = function(data, index) {
coef(lm(mpg ~ horsepower, data = data, subset = index))
}
想知道std是否正确,因为\(\sigma\)不一定是正态的,独立的。
coef.fn = function(data, index) {
coef(lm(mpg ~ horsepower, data = data, subset = index))
}
coef.fn(Auto, 1:392)
set.seed(2)
coef.fn(Auto, sample(392, 392, replace = TRUE))
boot.lm = boot(Auto, coef.fn, 1000)
boot.lm
Question: lm的结果和boot的结果应该相信哪一个?
相信boot的结果,因为lm是参数方法,需要满足一些假设,但是boot是非参方法,不需要数据符合什么假设。
但是如果所有正态(参数)的假设都满足,肯定还是参数的好,但是只要(参数)检验的假设不能满足,那肯定是非参的更好。
t-based bootstrap confidence interval
t-based bootstrap confidence interval
- Let \(\theta\) be a parameter.
- Let \(\hat{\theta}\) be the estimator based on the original data. (使用参数估计方法,例如矩估计等)
- Under most circumstances, as the sample size \(n\) increases, the sampling distribution of \(\hat{\theta}\) becomes more normally distributed.
Consistency:
\(\hat \theta_n \rightarrow \theta\) as \(n \rightarrow \infty\)
Normality??:\(\sqrt{n}(\hat \theta_n - \theta) \rightarrow N(0, \sigma^2)\)
- Under this assumption, an approximate \(t\)-based bootstrap confidence interval can be generated using \(\mathrm{SE}(\hat{\theta})\) and a t-distribution:
\]
If \(\alpha=0.05\), then \(t^*\) can be chosen as the \(100(\alpha / 2)\) th quantile of a t-distribution with \(n-1\) degrees of freedom.
很多时候\(t=2\), 即\(\hat{\theta} \pm 2 * SE(\hat\theta)\) 因为正态里是3 sigma是1.96.
Complete Bootstrap Estimation
在上述参数估计难以给出时,可以完全用非参的方法。从所有重采样的样本中去找一个下分位点处的样本,和一个上分位点处的样本。
The Bootstrap Estimate of Bias
The Bootstrap Estimate of Bias
- Bootstrapping can also be used to estimate the bias of \(\hat{\theta}\).
- Let \(\theta\) be a parameter, and \(\hat{\theta}=S\left(X_1, \ldots, X_n\right)\) is an estimator of \(\theta\).
- The Bias of \(\hat{\theta}\) is defined as
\]
- Let \(F\) be the distribution of the population, let \(\hat{F}\) be the empirical distribution of \(X_1, \ldots, X_n\), the original sample data.
- Let \(F^*\) be the bootstrapping distribution from \(\hat{F}\).
- Based on the Bootstrap method, we can generated \(B\) replications of the estimator: \(\hat{\theta}_1^*, \ldots, \hat{\theta}_B^*\). Then,
\]
where
\]
- The bias-corrected estimate of \(\theta\) is given by
\]
Eg.
\(bias(\hat \theta) = E(\hat \theta) - \theta\)
unbiased:\(\hat \theta = \frac{1}{n-1}\sum_{i = 1}^n(X_i - \bar X)^2\)
biased:\(\theta = \frac{1}{n}\sum_{i = 1}^n(X_i - \bar X)^2\)
\(Bias = E(\hat \theta) - \theta = - \frac{1}{n} \theta^2\)
n = 20
set.seed(2022)
data = rnorm(n, 0, 1)
variance = sum((data - mean(data))^2)/n
variance
boots = rep(0,1000)
for(b in 1:1000){
data_b <- sample(data, n, replace=T)
boots[b] = sum((data_b - mean(data_b))^2)/n
}
mean(boots) - variance # estimated bias
((n-1)/n)*1 -1 #true
修偏 = \(\bar \theta - \hat \theta\) = 1.0005638
方差的真实值1,naive variance = 0.95.
not working well on
但是真实值是1.
x = runif(100)
boots = rep(0,1000)
for(b in 1:1000){
boots[b] = max(sample(x,replace=TRUE))
}
quantile(boots,c(0.025,0.975))
Bootstrapping a single statistic
rsq <- function(formula , data , indices) {
d <- data[indices, ]
fit <- lm(formula, data = d)
return (summary(fit)$r.square)
}
library(boot)
set.seed(1234)
attach(mtcars)
results <- boot(data = mtcars, statistic = rsq, R = 1000, formula = mpg ~ wt + disp)
print(results)
plot(results)
boot.ci(results, type = c("perc", "bca"))
Bootstrapping several statistics
when adding or removing a few data points changes the estimator too much, the bootstrapping does not work well.
bs <- function(formula, data, indices){
d <- data[indices, ]
fit <- lm(formula, data = d)
return(coef(fit))
}
library(boot)
set.seed(1234)
results <- boot(data = mtcars, statistic = bs, R = 1000, formula = mpg ~ wt + disp)
print(results)
plot(results, index = 2)
print(boot.ci(results, type = "bca", index = 2))
print(boot.ci(results, type = "bca", index = 3))
Q:How large does the original sample need to be?
A:An original sample size of 20--30 is sufficient for good results, as long as the sample is representative of the population.
Q: How many replications are needed? A: I find that 1000 replications are more than adequate in most cases.
Permutation tests
统计计算——Bootstrap总结整理的更多相关文章
- 统计计算与R语言的资料汇总(截止2016年12月)
本文在Creative Commons许可证下发布. 在fedora Linux上断断续续使用R语言过了9年后,发现R语言在国内用的人逐渐多了起来.由于工作原因,直到今年暑假一个赴京工作的机会与一位统 ...
- Pandas的函数应用、层级索引、统计计算
1.Pandas的函数应用 1.apply 和 applymap 1. 可直接使用NumPy的函数 示例代码: # Numpy ufunc 函数 df = pd.DataFrame(np.random ...
- sql: T-SQL 统计计算(父子關係,樹形,分級分類的統計)
---sql: T-SQL 统计计算(父子關係,樹形,分級分類的統計) ---2014-08-26 塗聚文(Geovin Du) CREATE PROCEDURE proc_Select_BookKi ...
- Pandas统计计算和描述
Pandas统计计算和描述 示例代码: import numpy as np import pandas as pd df_obj = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(5,4 ...
- Python基础-使用range创建数字列表以及简单的统计计算和列表解析
1.使用函数 range() numbers = list(range[1,6]) print (numbers) 结果: [1,2,3,4,5] 使用range函数,还可以指定步长,例如,打印1~1 ...
- CyclicBarrier开启多个线程进行计算,最后统计计算结果
有一个大小为50000的数组,要求开启5个线程分别计算10000个元素的和,然后累加得到总和 /** * 开启5个线程进行计算,最后所有的线程都计算完了再统计计算结果 */ public class ...
- 使用if else if else 统计计算
package review20140419;/* * 统计一个班级的成绩,并统计优良中差和不及格同学个数以及求平均分 */public class Test2 { //程序的入口 pub ...
- 智能ERP收银统计-优惠统计计算规则
1.报表统计->收银统计->优惠统计规则 第三方平台优惠:(堂食订单:支付宝口碑券优惠)+(外卖订单:商家承担优惠) 自平台优惠:(堂食订单:商家后台优 ...
- MongoDB 中聚合统计计算--$SUM表达式
我们一般通过表达式$sum来计算总和.因为MongoDB的文档有数组字段,所以可以简单的将计算总和分成两种:1,统计符合条件的所有文档的某个字段的总和:2,统计每个文档的数组字段里面的各个数据值的和. ...
- 简单常用的sql,统计语句,陆续整理添加吧
1. 分段统计分数 if object_id('[score]') is not null drop table [score] go create table [score]([学号] i ...
随机推荐
- power shell 删除应用
public static UwpAppInfo SearchUwpAppByName(string appName) { UwpAppInfo app = null; try { string re ...
- 解决git仓库项目 添加到github非空仓库冲突问题 error: failed to push some refs to 'https://github.com/Qtoken/......'
error: failed to push some refs to 'https://github.com/Qtoken/......' 1. 问题描述:执行命令:git push origin m ...
- java获取当前类的绝对路径
转自: http://blog.csdn.net/elina_1992/article/details/47419097 1.如何获得当前文件路径 常用: (1).Test.class.getRe ...
- c# datagridview列宽自适应设置
- LeedCode 85. 最大矩形(/)
原题解 题目 约束 题解 解法一 class Solution { public: int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& ...
- 2020.11.24 typeScript命名空间
命名空间:定义了标识符的可见范围,一个标识符可以在多个命名空间中定义,它在不同命名空间的含义是互不相干的.在一个新的命名空间可以定义任何新的标识符,它不会与已有的任何标识符发生冲突. 使用: 这个时候 ...
- appium 遇到连接设备状态是offline
1.查看连接手机设备 adb derivces 时,手机状态是offline状态(无法正常连接). 解决法: 1.adb kill-server 终止adb调试服务 2.adb start-serve ...
- 第二章启动引导器GRUB2
第二章启动引导器GRUB2grub的配置文件路径:vim /boot/grub2/grub.cfg (不建议直接编辑)vim /etc/default/grub (可编辑的文件)将编辑的操作刷新到/b ...
- 痞子衡嵌入式:RISC-V指令集架构MCU开发那些事 - 索引
大家好,我是痞子衡,是正经搞技术的痞子.本系列痞子衡给大家介绍的是RISC-V指令集架构微控制器相关知识. RISC-V指令集最早要追溯到2010年,是加州大学伯克利分校的一个研究团队的项目,目标是设 ...
- gRPC之.Net6中的初步使用说明
1.介绍 GRPC是一个高性能.通用的开源远程过程调用(RPC)框架,基于底层HTTP/2协议标准和协议层Protobuf序列化协议开发,支持众多的开发语言,由Google开源. gRPC也是基于以下 ...
