Python基础第二天
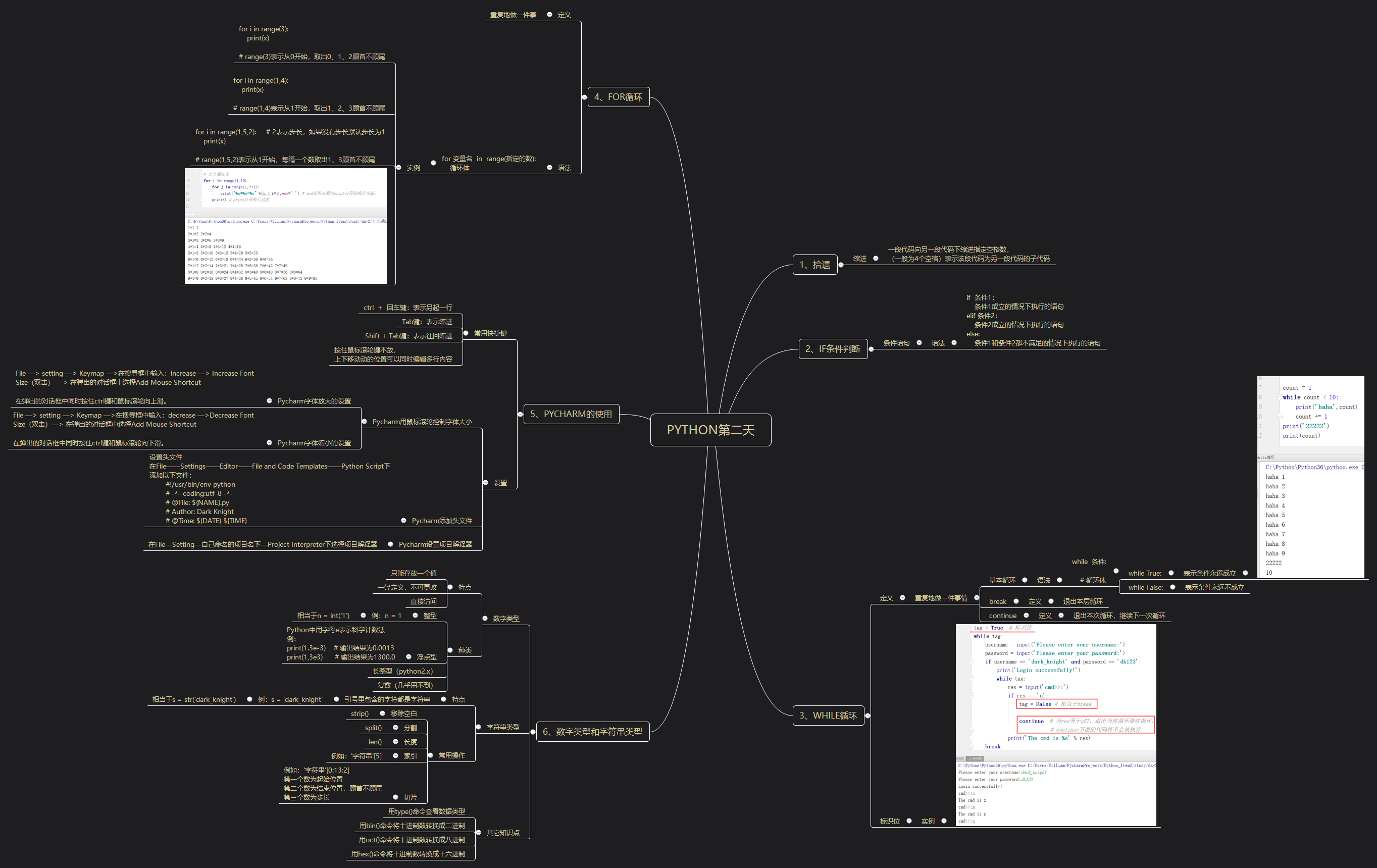
一、内容
二、练习
练习1
题目:已知msg='hello knight 666'编写for循环,利用索引遍历出每一个字符
图示:
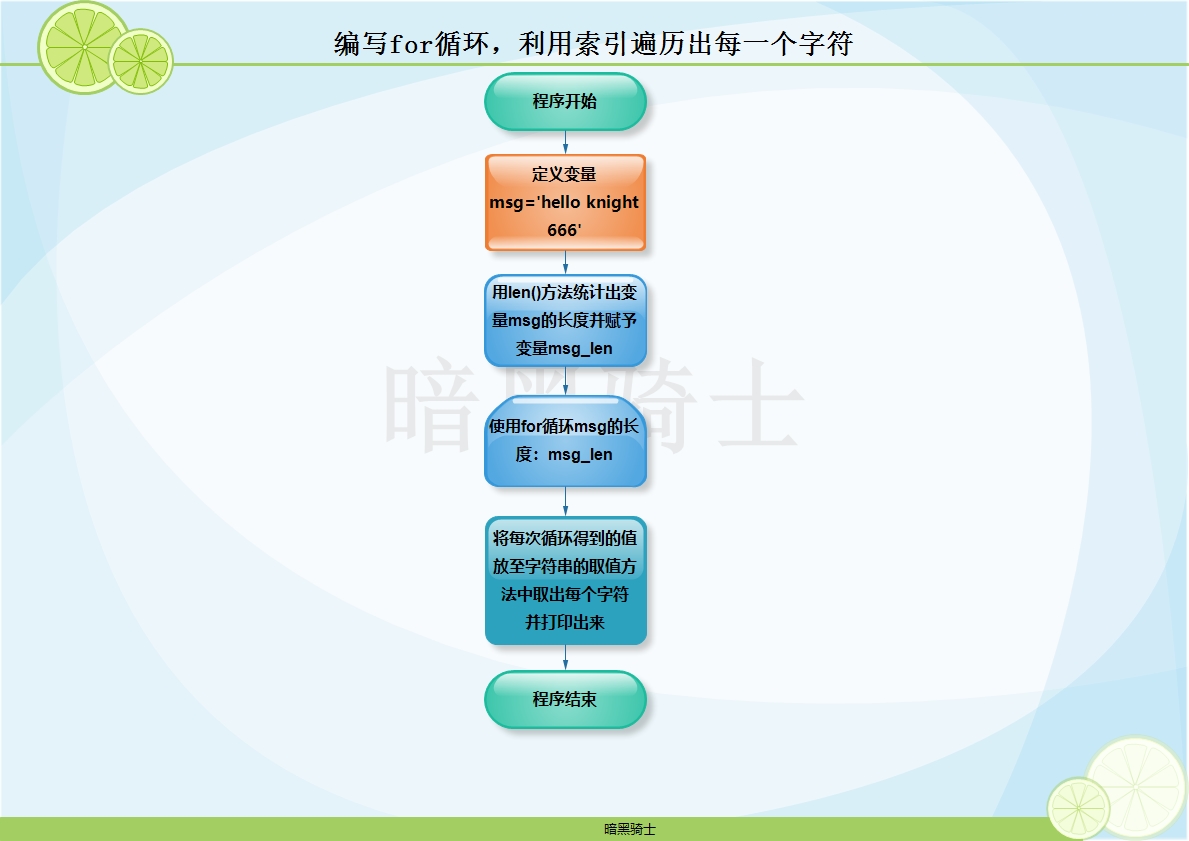
代码:
msg = 'hello knight 666'
msg_len = len(msg)
for i in range(msg_len):
print(msg[i])
输出结果:
h
e
l
l
o k
n
i
g
h
t 6
6
6
练习2
题目:已知msg='hello knight 666'编写for循环,利用索引遍历出每一个字符
图示:
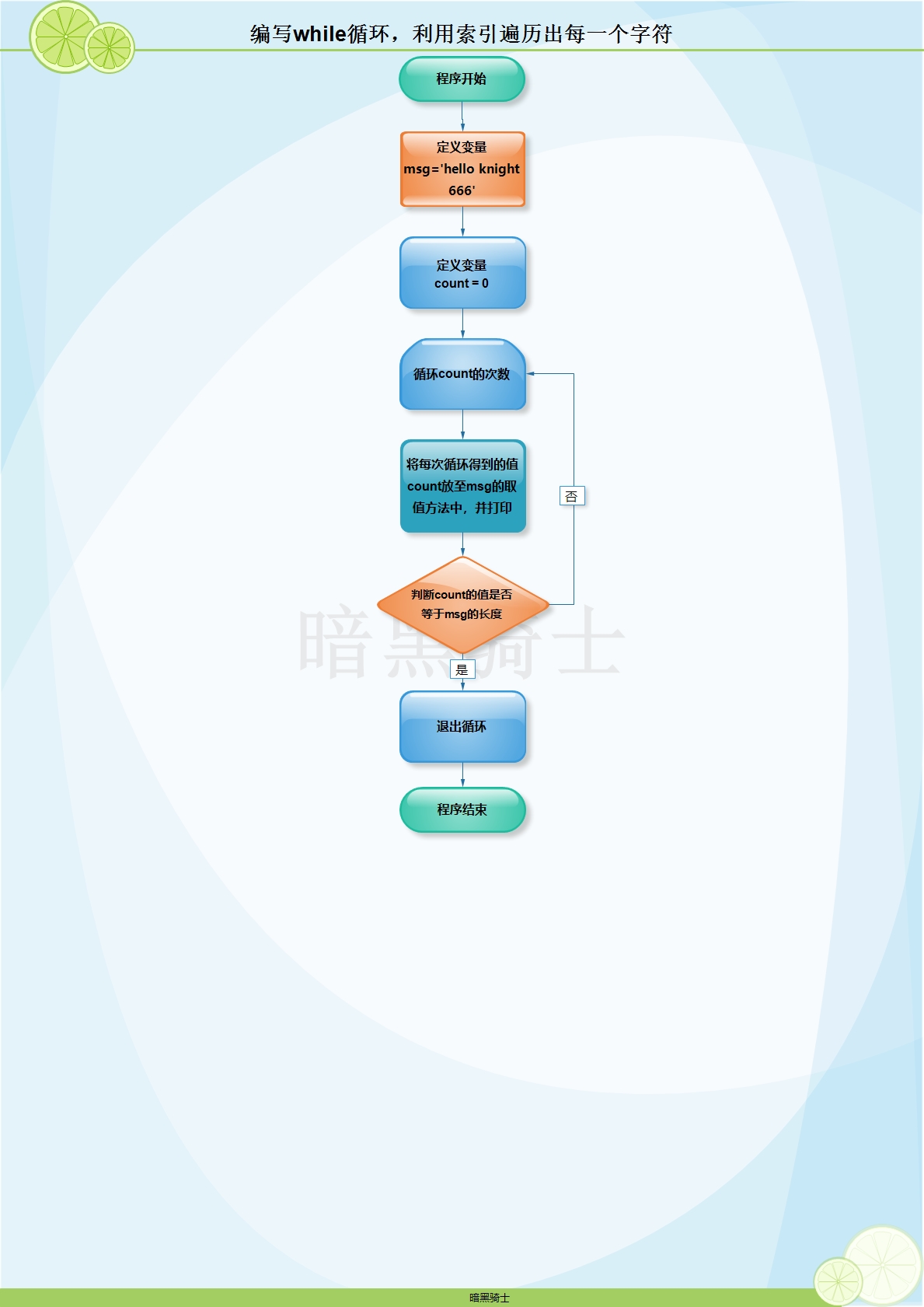
代码:
msg = 'hello knight 666'
count = 0
while True:
print(msg[count])
count += 1
if count == len(msg):
break
输出结果:
h
e
l
l
o k
n
i
g
h
t 6
6
6
练习3
题目:已知变量msg='hello qishi',将msg中的qishi替换成knight
代码:
msg='hello qishi'
msg_new = msg.replace('qishi','knight')
print(msg_new)
输出结果:
hello knight
练习4
题目:已知 msg='/etc/a.txt|365|get' 将该字符的文件名,文件大小,操作方法切割出来。
代码:
msg ='/etc/a.txt|365|get'
msg_new = msg.split('|')
print('文件名:',msg_new[0])
print('文件大小:',msg_new[1])
print('操作方法:',msg_new[2])
输出结果:
文件名: /etc/a.txt
文件大小: 365
操作方法: get
练习5
题目:编写while循环,要求用户输入命令,如果命令为空,则继续输入
图示:
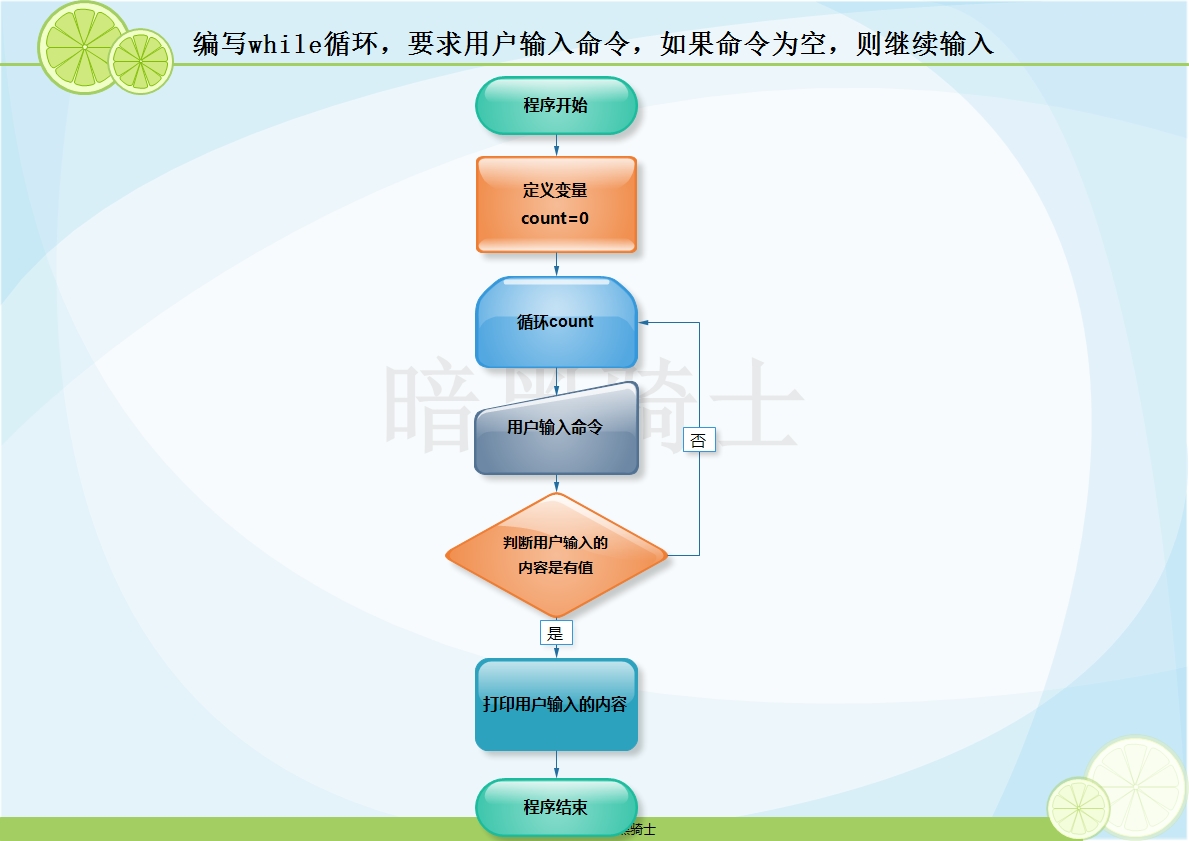
代码:
count = 0
while True:
user_input = input('Please enter command:').strip()
if not user_input:
continue
print('The cmd is %s'%user_input)
练习6
题目:编写while循环,让用户输入用户名和密码,如果用户为空或者数字,则重新输入
图示:
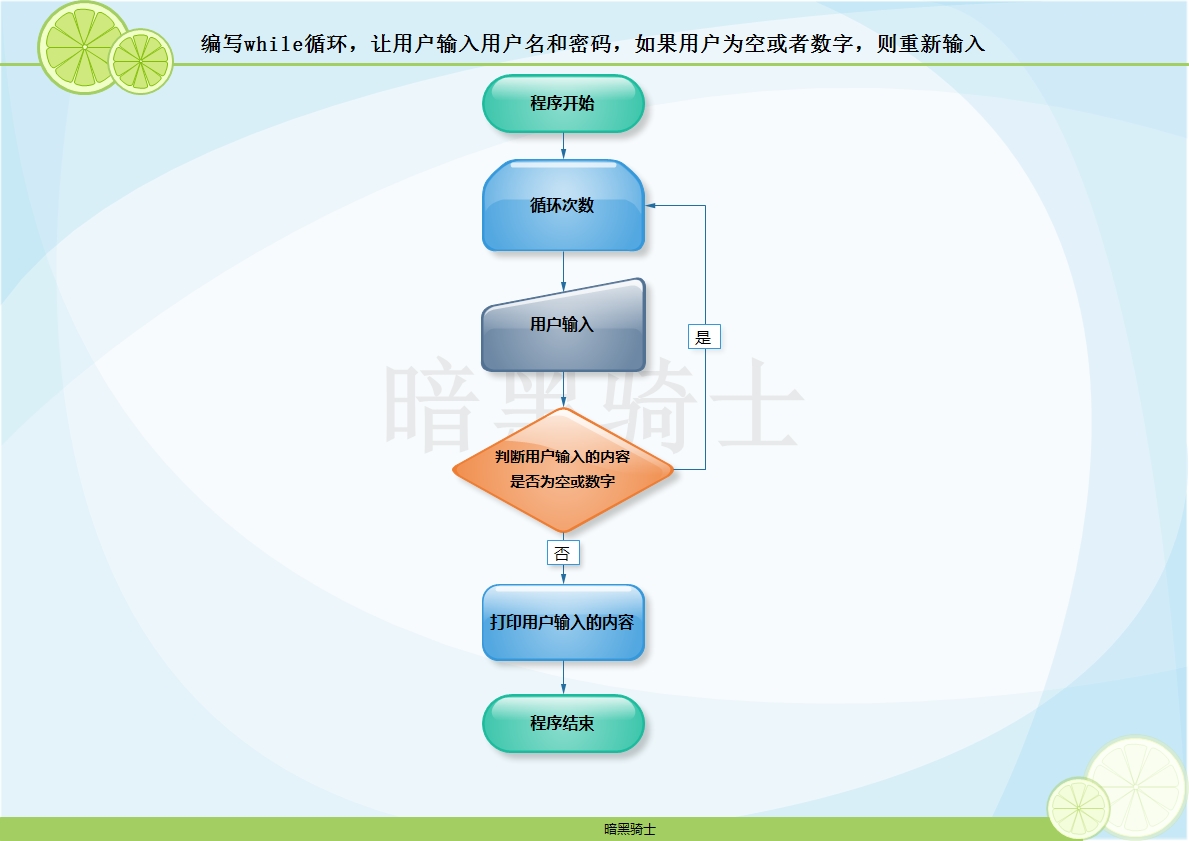
代码:
while True:
user = input('Please enter username:').strip()
password = input('Please enter password:')
if not user or user.isdigit():
print('The username you entered is blank, please re-enter')
continue
print('Welcome %s'%user)
break
练习7
题目:编写while循环,让用户输入内容,判断输入的内容以knight开头的,则将该字符串加上_successful结尾
图示:
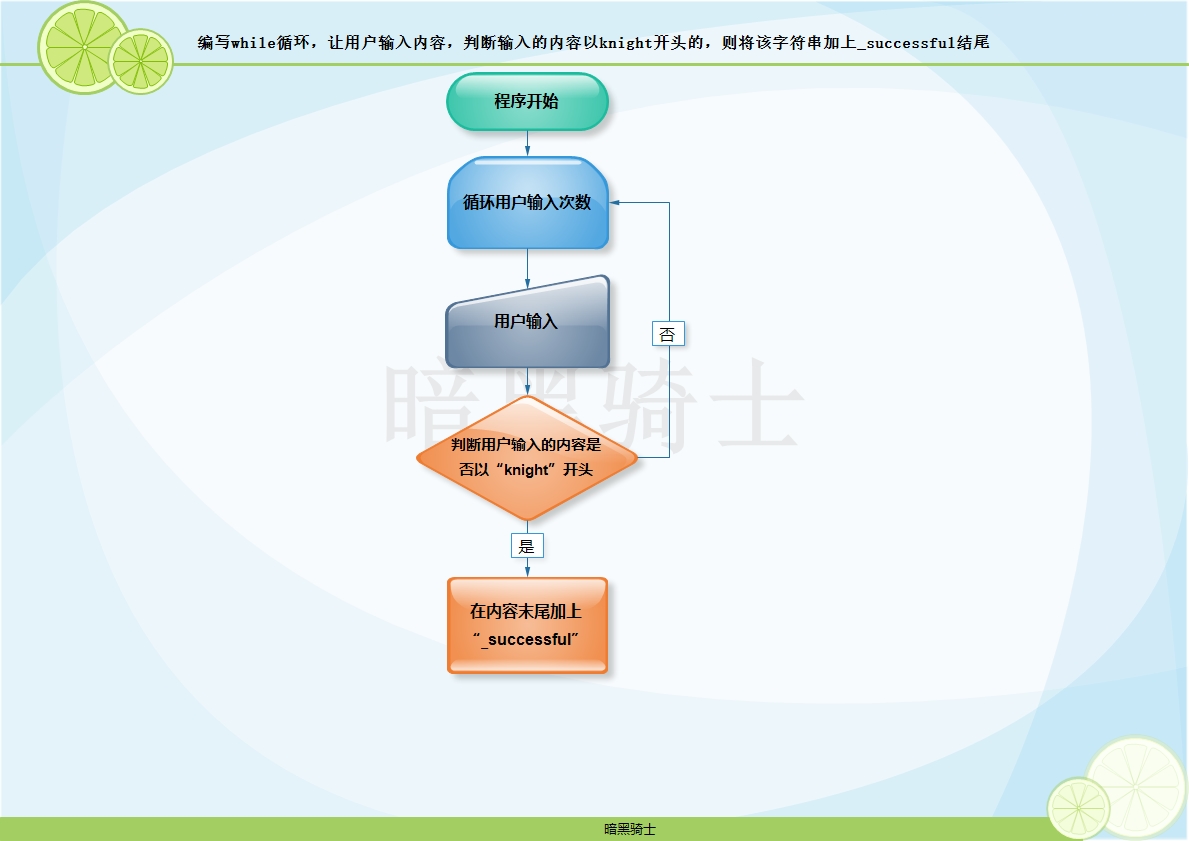
代码1:
while True:
user = input('Please enter:').strip()
if user.startswith('knight'):
print(user+'_successful')
代码2:
while True:
user = input('Please enter:').strip()
if user.startswith('knight'):
print('%s%s'%(user,'_successful'))
练习8
题目:
(1)两层while循环,外层的while循环,让用户输入用户名、密码、工作了几个月、每月的工资(整数),用户名或密码为空,或者工作的月数不为整数,或者月工资不为整数,则重新输入
(2)认证成功,进入下一层while循环,打印命令提示,有查询总工资,查询用户身份(如果用户名为knight则打印super user,如果用户名为tangbao或者zhuozi则打印normal user,其余情况均打印unknown user),退出功能
(3)要求用户输入退出,则退出所有循环(使用tag的方式)
图示:
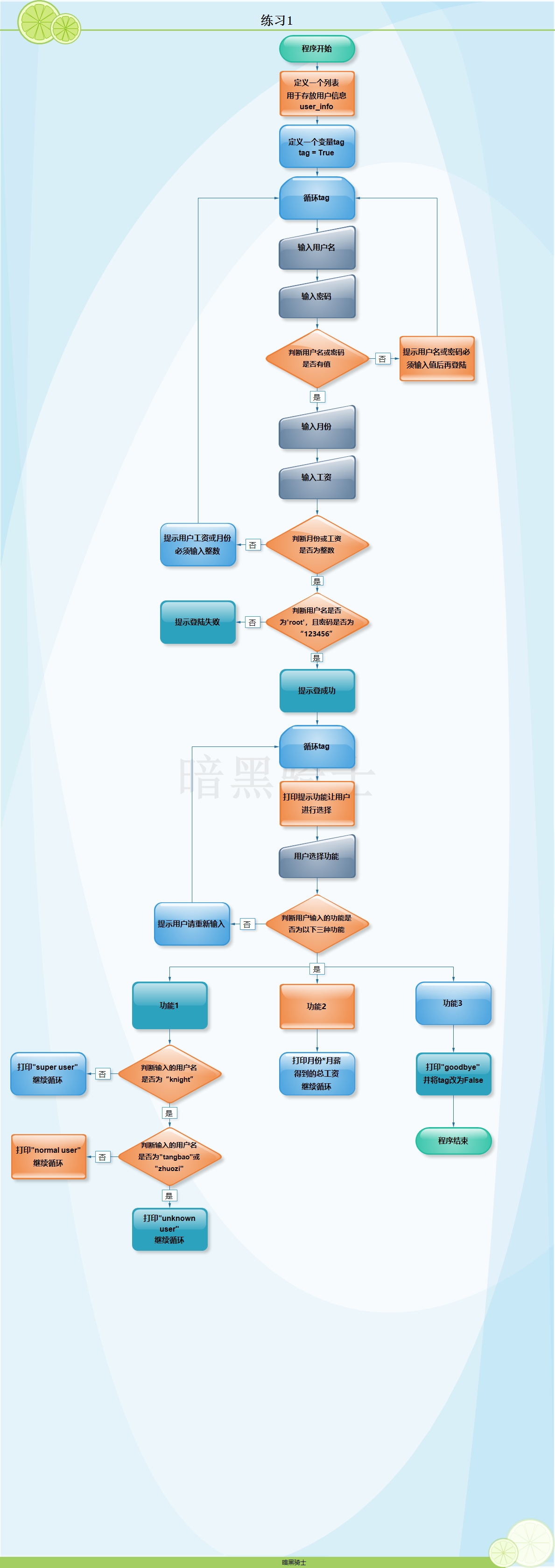
代码:
user_info = ['knight','zhuozi','tangbao']
tag = True
while tag:
username = input('Please enter username:').strip()
password = input('Please enter password:')
if not username or not password:
print('Your account or password is blank, please re-enter')
continue
month = input('Please enter the month:').strip()
salary = input('Please enter the salary:').strip()
if not month.isdigit() or not salary.isdigit():
print('The month or salary you enter must be an integer.')
if username == 'root' and password == '123456':
print('Login successfully!')
while tag:
print('请选择以下功能\n1、查询用户功能\n2、查询总工资功能\n3、退出')
cmd = input('Please select function:').strip()
if cmd == '1':
user = input('Please enter username:').strip()
if user == 'knight':
print('super user')
elif user == 'tangbao' or user == 'zhuozi':
print('normal user')
else:
print('known user')
elif cmd =='2':
print('Your total salary is %s'%(int(month)*int(salary)))
elif cmd =='3':
print('Goodbye!')
tag = False
else:
print('Invalid command,please try again!')
else:
print('Sorry,your account or password is incorrect,please try again!')
三、英语
1、invalid
[ˈɪnvəlɪd;ɪnˈvælɪd] adj.无效的
2、item
['aɪtəm] n.项目
3、incorrect
[,ɪnkə'rɛkt] adj. 错误的,不正确的
4、range
[rendʒ] n. 范围
5、parameter
[pə'ræmɪtɚ] n. 参数
6、error
['ɛrɚ] n.错误
7、step
[stɛp] n.步
8、setting
['sɛtɪŋ] v.设定
9、key
[kiː] n.键
10、value
['vælju] n.值
11、increase
['ɪnkris] v.增加
12、decrease
[dɪ'kris] v.减少
13、script
[skrɪpt] n.脚本
14、font
[fɑnt] n. 字体
15、type
[taɪp] n.类型
16、strip
[strɪp] vt.剥离;脱去
17、split
[splɪt] vt.分割
18、count
[kaʊnt] vt.计数
19、continue
[kən'tɪnju] vi. 继续
20、break
[brek] vi.打断
Python基础第二天的更多相关文章
- python基础-第二篇-基本数据类型
一.运算符 1.算数运算: 算数运算符相信大家都不陌生吧,尤其是加减乘除,好!那我就带着大家看看最后三个,这三个到底是干什么玩意的? %,取两数相除的余数,看图: **,x的多少次幂,看图: //,取 ...
- Python基础第二篇
一.三元运算 if True: name='a' else: name='b' #上面的代码用三元运算表示: name="a" if True else "b" ...
- Python基础 第二天
1.http://www.cnblogs.com/beer/p/5672678.html requests和beautifulsoup
- Python基础第二课
字符串(引号):四种表达方式 n1 = "我是" n1 = '我是' n1 = """我是""" n1 = '" ...
- python基础(二)----数据类型
Python基础第二章 二进制 字符编码 基本数据类型-数字 基本数据类型-字符串 基本数据类型-列表 基本数据类型-元组 可变.不可变数据类型和hash 基本数据类型-字典 基本数据类型-集合 二进 ...
- Python之路【第二篇】:Python基础
参考链接:老师 BLOG : http://www.cnblogs.com/wupeiqi/articles/4906230.html 入门拾遗 一.作用域 只要变量在内存中就能被调用!但是(函数的栈 ...
- Python之路【第二篇】:Python基础(一)
一.作用域 对于变量的作用域,执行声明并在内存中存在,该变量就可以在下面的代码中使用. 1 2 3 if 1==1: name = 'wupeiqi' print name 下面的结论对吗? ...
- 第二章:python基础,数据类型
"""第二章:python基础,数据类型2.1 变量及身份运算补充2.2 二进制数2.3 字符编码每8位所占的空间位一个比特,这是计算机中最小的表示单位.每8个比特组成一 ...
- 《python基础教程(第二版)》学习笔记 文件和素材(第11章)
<python基础教程(第二版)>学习笔记 文件和素材(第11章) 打开文件:open(filename[,mode[,buffering]]) mode是读写文件的模式f=open(r' ...
随机推荐
- N分之一 竖式除法模拟
N分之一 Description Alice越来越痴迷于数学问题了.一天,爸爸出了个数学题想难倒她,让她求1 / n. 可怜的Alice只有一岁零九个月,回答不上来 ~~~~(>_<)~~ ...
- git clone问题
中秋节回来上班 竟然忘记带电脑了  ̄□ ̄||还好同事有备用电脑,这要是回去拿估计上午都不用干什么了,用同事电脑当然需要安装环境,下面说一下git上遇到的问题吧 (1)首先我尝试用https方式克隆代码 ...
- Linux学习总结(22)——CentOS7.2安装Nginx
一.使用Yum安装(推荐) 使用Yum安装是推荐的方式,整体的流程非常的简单,也不容易出错,如果不需要什么特殊配置,建议使用Yum尽进行安装. 1.安装epel-release源并进行安装 1 2 3 ...
- ZOJ1004 && HDU1515 dfs回溯
题目大意: 就是通过一个栈进行字母入栈出栈得到想要的字符,把所有可能的方式全部输出 自己写的方法一开始一直不能过,后来参考了别人的方法,写出来的比较简单的代码 这段代码更有回溯的感觉,自己后来又把自己 ...
- 【bzoj2152】聪聪可可 点分治
[bzoj2152]聪聪可可 2014年9月7日3,5472 Description 聪聪和可可是兄弟俩,他们俩经常为了一些琐事打起来,例如家中只剩下最后一根冰棍而两人都想吃.两个人都想玩儿电脑(可是 ...
- 解方程(codevs 3732)
题目描述 已知多项式方程: a0+a1x+a2x^2+..+anx^n=0 求这个方程在[1, m ] 内的整数解(n 和m 均为正整数) 输入输出格式 输入格式: 输入文件名为equation .i ...
- memcache 原理 & 监测 & 查看状态 & stats & 结构
Mencache内存存储方式:slab/LRU,采用预先申请固定大小的内存页(slab/page),然后再把内存分成多个块(chunk) 先放一张从网上找到的memcache内存结构图,觉得非常的赞:
- 删除右键open foler as pycharm project(WIN10)
1.打开注册表(WIN+R 输入regedit) 2.找到 HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\Background 路径 下找到Parcharm文件夹,删除,右键的open fo ...
- jquery判断单选按钮radio是否选中的方法
JQuery控制radio选中和不选中方法总结 一.设置选中方法 复制代码代码如下: $("input[name='名字']").get(0).checked=true; $(&q ...
- [bzoj3527][Zjoi2014]力_FFT
力 bzoj-3527 Zjoi-2014 题目大意:给定长度为$n$的$q$序列,定义$F_i=\sum\limits_{i<j}\frac{q_iq_j}{(i-j)^2}-\sum\lim ...
