uva-699 Not so Mobile (杠杆,巧妙递归)
| Not so Mobile |
Before being an ubiquous communications gadget, a mobile was just a structure made of strings and wires suspending colourfull things. This kind of mobile is usually found hanging over cradles of small babies.
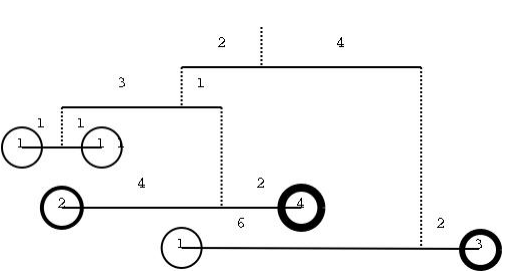
The figure illustrates a simple mobile. It is just a wire, suspended by a string, with an object on each side. It can also be seen as a kind of lever with the fulcrum on the point where the string ties the wire. From the lever principle we know that to balance a simple mobile the product of the weight of the objects by their distance to the fulcrum must be equal. That isWl×Dl = Wr×Dr where Dl is the left distance, Dr is the right distance, Wl is the left weight and Wr is the right weight.
In a more complex mobile the object may be replaced by a sub-mobile, as shown in the next figure. In this case it is not so straightforward to check if the mobile is balanced so we need you to write a program that, given a description of a mobile as input, checks whether the mobile is in equilibrium or not.

Input
The input begins with a single positive integer on a line by itself indicating the number of the cases following, each of them as described below. This line is followed by a blank line, and there is also a blank line between two consecutive inputs.
The input is composed of several lines, each containing 4 integers separated by a single space. The 4 integers represent the distances of each object to the fulcrum and their weights, in the format: Wl Dl Wr Dr
If Wl or Wr is zero then there is a sub-mobile hanging from that end and the following lines define the the sub-mobile. In this case we compute the weight of the sub-mobile as the sum of weights of all its objects, disregarding the weight of the wires and strings. If both Wl and Wr are zero then the following lines define two sub-mobiles: first the left then the right one.
Output
For each test case, the output must follow the description below. The outputs of two consecutive cases will be separated by a blank line.
Write `YES' if the mobile is in equilibrium, write `NO' otherwise.
Sample Input
1 0 2 0 4
0 3 0 1
1 1 1 1
2 4 4 2
1 6 3 2
Sample Output
YES
题解:题意是让求这个杠杆是不是平衡;看了大神的代码,处理的很巧妙,如果当前质量是0,递归输入子天平,每个子天平判断是否平衡,就可以了;
代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
#define SI(x) scanf("%d",&x)
#define mem(x,y) memset(x,y,sizeof(x))
#define PI(x) printf("%d",x)
#define P_ printf(" ")
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
typedef long long LL;
bool solve(int &w){
int w1,d1,w2,d2;
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&w1,&d1,&w2,&d2);
int temp1=true,temp2=true;
if(!w1)temp1=solve(w1);
if(!w2)temp2=solve(w2);
w=w1+w2;
if(w1*d1==w2*d2&&temp1&&temp2)return true;
else return false;
}
int main(){
int T;
SI(T);
while(T--){
int w;
if(solve(w))puts("YES");
else puts("NO");
if(T)puts("");
}
return 0;
}
uva-699 Not so Mobile (杠杆,巧妙递归)的更多相关文章
- UVa 839 -- Not so Mobile(树的递归输入)
UVa 839 Not so Mobile(树的递归输入) 判断一个树状天平是否平衡,每个测试样例每行4个数 wl,dl,wr,dr,当wl*dl=wr*dr时,视为这个天平平衡,当wl或wr等于0是 ...
- UVa 699 The Falling Leaves(递归建树)
UVa 699 The Falling Leaves(递归建树) 假设一棵二叉树也会落叶 而且叶子只会垂直下落 每个节点保存的值为那个节点上的叶子数 求所有叶子全部下落后 地面从左到右每 ...
- UVA.839 Not so Mobile ( 二叉树 DFS)
UVA.839 Not so Mobile ( 二叉树 DFS) 题意分析 给出一份天平,判断天平是否平衡. 一开始使用的是保存每个节点,节点存储着两边的质量和距离,但是一直是Runtime erro ...
- UVA.699 The Falling Leaves (二叉树 思维题)
UVA.699 The Falling Leaves (二叉树 思维题) 题意分析 理解题意花了好半天,其实就是求建完树后再一条竖线上的所有节点的权值之和,如果按照普通的建树然后在计算的方法,是不方便 ...
- UVA 839 Not so Mobile (递归建立二叉树)
题目连接:http://acm.hust.edu.cn/vjudge/problem/19486 给你一个杠杆两端的物体的质量和力臂,如果质量为零,则下面是一个杠杆,判断是否所有杠杆平衡. 分析:递归 ...
- UVa 839 Not so Mobile (递归思想处理树)
Before being an ubiquous communications gadget, a mobilewas just a structure made of strings and wir ...
- 二叉树的递归遍历 The Falling Leaves UVa 699
题意:对于每一棵树,每一个结点都有它的水平位置,左子结点在根节点的水平位置-1,右子节点在根节点的位置+1,从左至右输出每个水平位置的节点之和 解题思路:由于上题所示的遍历方式如同二叉树的前序遍历,与 ...
- 【紫书】 The Falling Leaves UVA - 699 递归得简单
题意:给你一颗二叉树的前序遍历,空子树以-1表示,将左右子树的权值投影到一维数轴上,左儿子位置为根位置-1,右儿子+1求个个整点上的和: 题解:递归,整个过程只需维护一个sum数组. 更新根,更新le ...
- UVA 699 The Falling Leaves (递归先序建立二叉树)
题目链接:http://acm.hust.edu.cn/vjudge/problem/19244 #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> # ...
随机推荐
- 重拾php---以及zend-studio 的使用快捷方式
感觉好久没有碰php了,今天心血来潮,重新入门.先整理一下刚刚学习的笔记. 一个字符串是用双引号括起来的一个词或一个句字,比如:“Hi,imooc!”.你可以用PHP语言输出把这个字符串输出,像这样: ...
- 搞了一个独立博客,请各位光临pingworld.cn
嘿嘿,每次在一个大网站上建立自己的博客后总是没有动力持续更新下去,回想其原因很大是因为没有一个自己的地盘,懒得维护!还有一个原因就是自己也没有什么干货值得跟大家分享. 随着工作的时日见长,有了各种各样 ...
- MVC 4 结合jquery.uploadify 上传实例
前言:由于今天公司源代码服务瘫痪,没法编写代码,利用这个有限的时间,做了一个小小的 基于MVC的图片上传demo,貌似近些年来MVC十分火爆,相关的demo也数不胜数,小弟就在这里打着MVC的旗子,狐 ...
- 开发框架CIIP
github开源:企业级应用快速开发框架CIIP WEB+WIN+移动端 简介 CIIP是基于XAF开发的开源信息系统框架.CIIP最常见的应用场景是基于数据库的企业级应用程序,例如供应链系统,E ...
- 关于ODI agent的配置部署
分类: Linux 最近,做了几个ODI项目的部署,发现ODI agent所在的位置对整个E-LT工作的影响还是比较大的,根据Oracle的官方说法,agent一般需要部署在目标端的数据库服务器上,或 ...
- Windows Azure 社区新闻综述(#70 版)
欢迎查看最新版本的每周综述,其中包含有关云计算和 Windows Azure 的社区推动新闻.内容和对话. 以下是过去一周基于您的反馈汇集在一起的内容: 文章.视频和博客文章 · 如何选择 No ...
- date tod = boost::gregorian::day_clock::local_day(); //当前日期
boost 时间和日期 - 苦逼码农 - 博客频道 - CSDN.NET date tod = boost::gregorian::day_clock::local_day(); //当前日期
- php curl模拟post请求提交数据样例总结
在php中要模拟post请求数据提交我们会使用到curl函数,以下我来给大家举几个curl模拟post请求提交数据样例有须要的朋友可參考參考.注意:curl函数在php中默认是不被支持的,假设须要使用 ...
- 2.Visual Studio 2013中的默认快捷键
这篇大致是IDE的使用技巧,常用的也就那么几个. 我自己用的最多的是注释.取消注释.格式调整.运行测试.开始调试.断开调试.重新开始调试.删除行ctrl+L.保存.全部保存.打开资源管理器.搜索等几个 ...
- sql server 2005 表master..spt_values
IF OBJECT_ID('tempdb..#t') IS NOT NULL DROP TABLE #tGOcreate table #t(id int identity,Dt varchar(10) ...
