Django SimpleCMDB 项目
创建 SimpleCMDB 项目:
[root@localhost ~]$ django-admin.py startproject SimpleCMDB
创建应用,收集主机信息:
[root@localhost ~]$ cd SimpleCMDB/
[root@localhost SimpleCMDB]$ python manage.py startapp hostinfo
修改配置:
[root@localhost SimpleCMDB]$ cat SimpleCMDB/settings.py INSTALLED_APPS = ( # 添加应用
......
'hostinfo',
) MIDDLEWARE_CLASSES = ( # 禁用CSRF,使得可以使用POST传递数据
......
#'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware',
) LANGUAGE_CODE = 'zh-cn' # 修改语言 TIME_ZONE = 'Asia/Shanghai' # 修改时区
启动开发服务器:
[root@localhost SimpleCMDB]$ python manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8000
定义数据模型:
[root@localhost SimpleCMDB]$ cat hostinfo/models.py
from django.db import models # Create your models here. class Host(models.Model):
hostname = models.CharField(max_length=50)
ip = models.IPAddressField()
vendor = models.CharField(max_length=50)
product = models.CharField(max_length=50)
sn = models.CharField(max_length=50)
cpu_model = models.CharField(max_length=50)
cpu_num = models.IntegerField()
memory = models.CharField(max_length=50)
osver = models.CharField(max_length=50)
同步到数据库:
[root@localhost SimpleCMDB]$ python manage.py validate
[root@localhost SimpleCMDB]$ python manage.py syncdb
将数据模型注册到管理后台:
[root@localhost SimpleCMDB]$ cat hostinfo/admin.py
from django.contrib import admin
from hostinfo.models import Host # Register your models here. class HostAdmin(admin.ModelAdmin):
list_display = [
'hostname',
'ip',
'cpu_model',
'cpu_num',
'memory',
'vendor',
'product',
'osver',
'sn',
] admin.site.register(Host, HostAdmin)
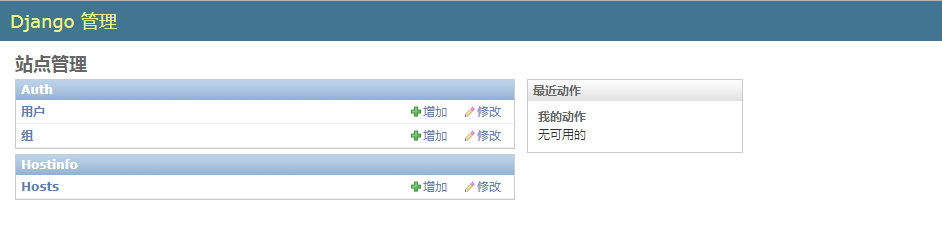
通过 POST 方法收集主机信息到 SimpleCMDB:
[root@localhost SimpleCMDB]$ cat SimpleCMDB/urls.py
....
urlpatterns = patterns('',
....
url(r'^hostinfo/collect/$', 'hostinfo.views.collect'),
)
[root@localhost SimpleCMDB]$ cat hostinfo/views.py
from django.shortcuts import render
from django.http import HttpResponse
from hostinfo.models import Host # Create your views here. def collect(request):
if request.POST:
hostname = request.POST.get('hostname')
ip = request.POST.get('ip')
osver = request.POST.get('osver')
vendor = request.POST.get('vendor')
product = request.POST.get('product')
cpu_model = request.POST.get('cpu_model')
cpu_num = request.POST.get('cpu_num')
memory = request.POST.get('memory')
sn = request.POST.get('sn') host = Host()
host.hostname = hostname
host.ip = ip
host.osver = osver
host.vendor = vendor
host.product = product
host.cpu_model = cpu_model
host.cpu_num = cpu_num
host.memory = memory
host.sn = sn
host.save() return HttpResponse('OK') else:
return HttpResponse('No Data!')
[root@localhost ~]$ cat /data/script/getHostInfo.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*- import urllib, urllib2
from subprocess import Popen, PIPE # 获取IP地址
def getIP():
p = Popen('ifconfig', stdout=PIPE, shell=True)
data = p.stdout.read().split('\n\n')
for lines in data:
if lines.startswith('lo'):
continue
if lines:
ip = lines.split('\n')[1].split()[1].split(':')[1]
break return ip # 获取主机名
def getHostname():
p = Popen('hostname', stdout=PIPE, shell=True)
hostname = p.stdout.read().strip()
return hostname # 获取操作系统版本
def getOSVersion():
with open('/etc/issue') as fd:
data = fd.read().split('\n')[0]
osVer = data.split()[0] + ' ' + data.split()[2] return osVer # 获取服务器硬件信息
def getHardwareInfo(name):
cmd = ''' dmidecode --type system | grep "%s" ''' % name
p = Popen(cmd, stdout=PIPE, shell=True)
hardwareInfo = p.stdout.read().split(':')[1].strip()
return hardwareInfo # 获取CPU型号
def getCPUModel():
with open('/proc/cpuinfo') as fd:
for line in fd.readlines():
if line.startswith('model name'):
cpuModel = line.split()[3].split('(')[0]
break return cpuModel # 获取CPU核数
def getCPUNum():
with open('/proc/cpuinfo') as fd:
for line in fd.readlines():
if line.startswith('cpu cores'):
cpuNum = line.split()[3]
break return cpuNum # 获取物理内存大小
def getMemorySize():
with open('/proc/meminfo') as fd:
memTotal = fd.readline().split()[1] memSize = str(int(memTotal)/1024) + 'M'
return memSize if __name__ == '__main__':
hostInfo = {}
hostInfo['ip'] = getIP()
hostInfo['hostname'] = getHostname()
hostInfo['osver'] = getOSVersion()
hostInfo['vendor'] = getHardwareInfo('Manufacturer')
hostInfo['product'] = getHardwareInfo('Product Name')
hostInfo['sn'] = getHardwareInfo('Serial Number')
hostInfo['cpu_model'] = getCPUModel()
hostInfo['cpu_num'] = getCPUNum()
hostInfo['memory'] = getMemorySize() data = urllib.urlencode(hostInfo) # 通过POST方法传递数据
request = urllib2.urlopen('http://192.168.216.128:8000/hostinfo/collect/', data)
print(request.read())
[root@localhost ~]$ python /data/script/getHostInfo.py # 如果想收集其他主机信息,直接在其他主机跑这个脚本即可
OK
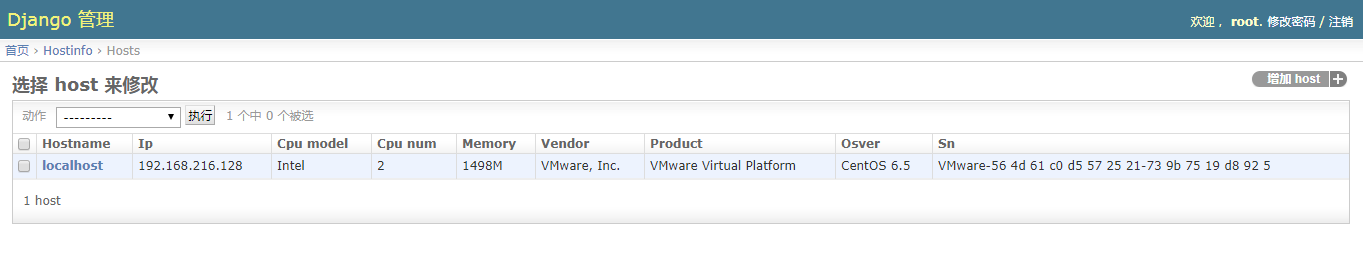
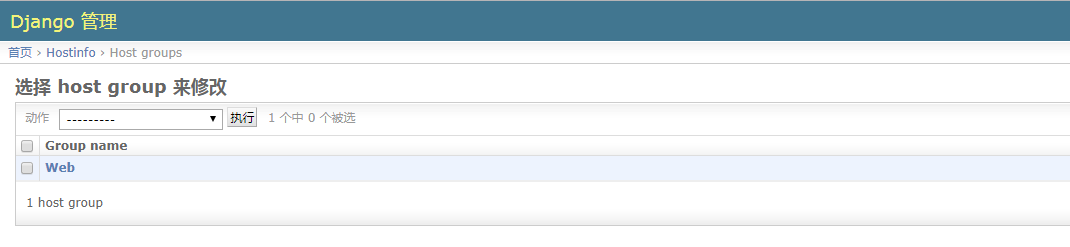
主机分组管理:
[root@localhost SimpleCMDB]$ cat hostinfo/models.py # 创建模型,添加一张主机组的表
from django.db import models .... class HostGroup(models.Model):
group_name = models.CharField(max_length=50) # 组名,使用的字段类型是CharField
group_members = models.ManyToManyField(Host) # 组成员,注意使用的字段及字段参数
[root@localhost SimpleCMDB]$ python manage.py validate
[root@localhost SimpleCMDB]$ python manage.py syncdb
[root@localhost SimpleCMDB]$ cat hostinfo/models.py # 注册模型
from django.db import models # Create your models here. class Host(models.Model):
hostname = models.CharField(max_length=50)
ip = models.IPAddressField()
vendor = models.CharField(max_length=50)
product = models.CharField(max_length=50)
sn = models.CharField(max_length=50)
cpu_model = models.CharField(max_length=50)
cpu_num = models.IntegerField()
memory = models.CharField(max_length=50)
osver = models.CharField(max_length=50) def __str__(self):
return self.ip class HostGroup(models.Model):
group_name = models.CharField(max_length=50)
group_members = models.ManyToManyField(Host)
如下,当我们多次使用指定脚本收集主机信息时,如果数据库里有记录了,它还是会添加一条相同的记录:
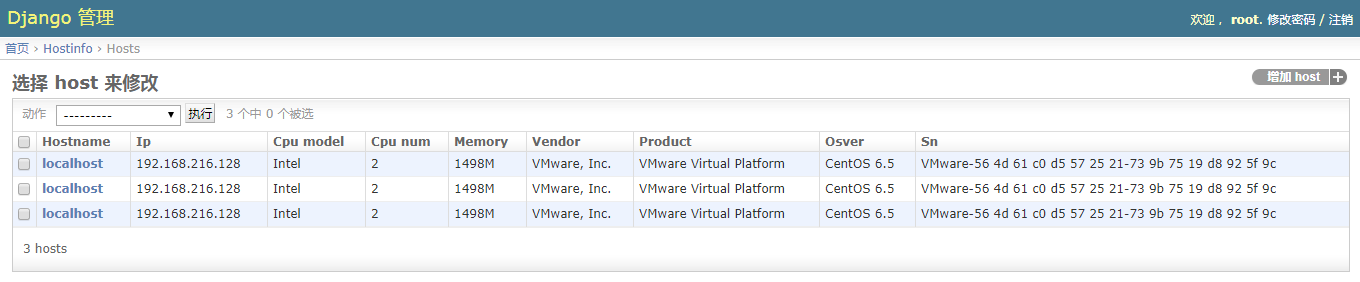
因此我们需要修改一下视图函数,加个判断:
[root@localhost SimpleCMDB]$ cat hostinfo/views.py
from django.shortcuts import render
from django.http import HttpResponse
from hostinfo.models import Host # Create your views here. def collect(request):
if request.POST:
hostname = request.POST.get('hostname')
ip = request.POST.get('ip')
osver = request.POST.get('osver')
vendor = request.POST.get('vendor')
product = request.POST.get('product')
cpu_model = request.POST.get('cpu_model')
cpu_num = request.POST.get('cpu_num')
memory = request.POST.get('memory')
sn = request.POST.get('sn') try:
host = Host.objects.get(sn=sn) # 查询数据库,查看是否有记录,如果有就重写记录,没有就添加记录
except:
host = Host() host.hostname = hostname
host.ip = ip
host.osver = osver
host.vendor = vendor
host.product = product
host.cpu_model = cpu_model
host.cpu_num = cpu_num
host.memory = memory
host.sn = sn
host.save() return HttpResponse('OK') else:
return HttpResponse('No Data!')
Django SimpleCMDB 项目的更多相关文章
- Python第十三天 django 1.6 导入模板 定义数据模型 访问数据库 GET和POST方法 SimpleCMDB项目 urllib模块 urllib2模块 httplib模块 django和web服务器整合 wsgi模块 gunicorn模块
Python第十三天 django 1.6 导入模板 定义数据模型 访问数据库 GET和POST方法 SimpleCMDB项目 urllib模块 urllib2模块 ...
- Django SimpleCMDB WSGI
一.WSGI 介绍 (1) 在前面的学习中,我们是通过 python manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8000 来启动并访问开发服务器的:(2) 但在实际中我们是通过直接访问 ...
- django创建项目
django创建项目 安装django pip install django==1.9 Note: C:\Python34\Scripts\pip.exe 创建项目 django-admin star ...
- Django练习项目之搭建博客
背景:自从今年回家过年后,来到公司给我转了试用,我的学习效率感觉不如从前,而且刚步入社会我总是想要怎么想明白想清楚一些事,这通常会花掉,消耗我大量的精力,因为我想把我的生活管理规划好了,而在it技术学 ...
- Python Django CMDB项目实战之-3创建form表单,并在前端页面上展示
基于之前的项目代码 Python Django CMDB项目实战之-1如何开启一个Django-并设置base页.index页.文章页面 Python Django CMDB项目实战之-2创建APP. ...
- Python Django CMDB项目实战之-2创建APP、建模(models.py)、数据库同步、高级URL、前端页面展示数据库中数据
基于之前的项目代码来编写 Python Django CMDB项目实战之-1如何开启一个Django-并设置base页index页文章页面 现在我们修改一个文章列表是从数据库中获取数据, 下面我们就需 ...
- Python Django CMDB项目实战之-1如何开启一个Django-并设置base页、index页、文章页面
1.环境 win10 python 2.7.14 django 1.8.2 需要用到的依赖包:MySQLdb(数据库的接口包).PIL/pillow(处理图片的包) 安装命令: pip install ...
- nginx + uwsgi 部署 Django+Vue项目
nginx + uwsgi 部署 Django+Vue项目 windows 本地 DNS 解析 文件路径 C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc 单机本地测试运行方式,调用dj ...
- Django商城项目笔记No.12用户部分-QQ登录2获取QQ用户openid
Django商城项目笔记No.12用户部分-QQ登录2获取QQ用户openid 上一步获取QQ登录网址之后,测试登录之后本该跳转到这个界面 但是报错了: 新建oauth_callback.html & ...
随机推荐
- 100 行代码实现的 JavaScript MVC 样式框架
介绍 使用过 JavaScript框架(如 AngularJS, Backbone 或者Ember)的人都很熟悉在UI(用户界面,前端)中mvc的工作机理.这些框架实现了MVC,使得在一个单页面中实现 ...
- paoding分词
Paoding 详细介绍 庖丁中文分词库是一个使用Java开发的,可结合到Lucene应用中的,为互联网.企业内部网使用的中文搜索引擎分词组件.Paoding填补了国内中文分词方面开源组件的空白,致力 ...
- svn解决不能clean的方法
http://blog.csdn.net/victory08/article/details/42100325 svn执行clean up后出现提示:svn cleanup failed–previo ...
- oracle 中execute immediate
简单来说 就是你一个存储过程当中 创建了一个表 table_a 然后要用insert into将其他的数据插入到这个table_a当中,但是因为你在创建过程的时候 table_a还不存在,过程就会显示 ...
- 第三百七十九节,Django+Xadmin打造上线标准的在线教育平台—xadmin的安装
第三百七十九节,Django+Xadmin打造上线标准的在线教育平台—xadmin的安装 xadmin介绍 xadmin是基于Django的admin开发的更完善的后台管理系统,页面基于Bootstr ...
- (转)关于yuv 格式:planar和semi-planar格式
关于yuv 格式 YUV 格式通常有两大类:打包(packed)格式和平面(planar)格式.前者将 YUV 分量存放在同一个数组中,通常是几个相邻的像素组成一个宏像素(macro-pixel);而 ...
- Androidpn 简单实现及分析
(文中部分内容来自网络) XMPP协议: XMPP : The Extensible Messaging andPresence Protocol. 中文全称:可扩展通讯和表示协议. 简介:可扩展通讯 ...
- TargetScan 数据库简介
TargetScan 是一个miRNA 靶基因预测的网站, 包括了 人, 小鼠,果蝇 , 线虫, 斑马鱼 共5个物种的miRNA 靶基因结果, 人 : TargetScanHuman 小鼠 :Targ ...
- linux中find命令
1.使用name选项: 文件名选项是find命令最常用的选项,要么单独使用该选项,要么和其他选项一起使用. 可以使用某种文件名模式来匹配文件,记住要用引号将文件名模式引起来. 不管当前路径是什么,如果 ...
- Service 保活法之二
正确应对系统内存不足,OnLowMemory和OnTrimMemory回调 理论上,一个具备良好行为的应用应该考虑Android系统内存紧张的问题,这样有助于维持一个良好的生态.在前人的基础上,本文对 ...
