Python(六)之文件对象
Python文件对象
明确文件系统:



- 获取文件对象:
var_name = open(file_name[mode,[bufsize]])
缓冲:
0:禁用
1:使用缓冲,只缓冲一行数据
2+:指定缓存空间大小
负数:使用系统默认缓冲区
- 文件对象的内置方法、函数、属相
next:
In [10]: f1 = open('/etc/passwd','r')
In [11]: type(f1)
Out[11]: file
In [12]: f1.next()
Out[12]: 'root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash\n'
In [13]: f1.next()
Out[13]: 'bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin\n'
In [14]: f1.next()
Out[14]: 'daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin\n'
close:
In [35]: f1.close()
fileno 返回文件描述符
In [38]: f1 = open('/etc/passwd','r')
In [39]: f1.fileno()
Out[39]: 8
readline,readlines
返回字符串对象
In [40]: f1.readline()
Out[40]: 'root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash\n'
返回文件所有行为列表对象:
In [41]: f1.readlines()
Out[41]:
['bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin\n',
'daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin\n',
'mail:x:8:12:mail:/var/spool/mail:/sbin/nologin\n',
'nobody:x:99:99:Nobody:/:/sbin/nologin\n']
tell:游标在文件中的位置,字节
In [47]: f1.tell()
Out[47]: 951
file.seek(offset[whence])
whence:起点
0:从文件头偏移,默认
1:从当前位置偏移
2:从文件尾部偏移
In [48]: f1.tell()
Out[48]: 951
In [49]: f1.seek(0)
In [50]: f1.tell()
Out[50]: 0
file.read([size])
file.read([size]) 读取多少个字节
In [51]: f1.read(10)
Out[51]: 'root:x:0:0'
此时在readline,或next读取的是位置到行尾
In [52]: f1.readline()
Out[52]: ':root:/root:/bin/bash\n'
file.write打开文件保存数据
In [61]: cp /etc/passwd .
In [62]: ls
passwd
In [64]: f1 = open('passwd','r+')
In [65]: f1.next()
Out[65]: 'root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash\n'
I [66]: f1.seek(0,2)
In [67]: f1.tell()
Out[67]: 951
In [68]: f1.write('new line.\n')
In [69]: f1.tell()
Out[69]: 961
In [70]: cat passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
mysql:x:306:306::/home/mysql:/bin/bash
new line.
In [71]: f1.close()
In [72]: f2 = open('new_file','w+')
In [73]: f2.write('Python')
In [74]: f2.close()
In [75]: cat new_file
Python
读模式打开不存在文件,报IOError
In [76]: f3 = open('new_file2','r+')
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
IOError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-76-1d0d8a99b4f2> in <module>()
----> 1 f3 = open('new_file2','r+')
IOError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: 'new_file2'
In [77]: f3 = open('new_file2','a')
In [78]: ls
new_file new_file2 passwd
writelines(...)
writelines(sequence_of_strings) -> None. Write the strings to the file.
Note that newlines are not added. The sequence can be any iterable object
producing strings. This is equivalent to calling write() for each string
In [13]: f4 = open('new_file4','w+')
In [14]: import os
In [15]: l4 = os.listdir(‘/etc’)
返回列表对象:

In [19]: f4.writelines(l4)
In [20]: f4.flush()
可以看到,writelines把列表中多有对象当成一个字符串写入文件,没有换行
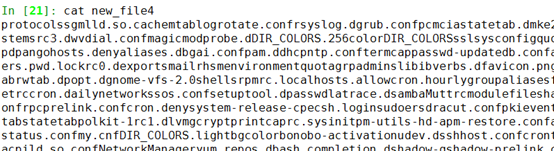
下面进行手动换行:
重新生成列表,添加换行符:
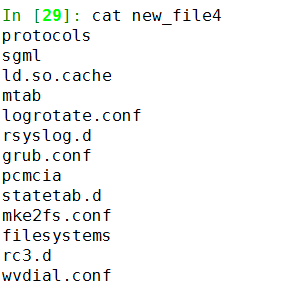
In [23]: l4 = [i+'\n' for i in os.listdir('/etc')]

In [25]: f4 = open('new_file4','w+')
In [26]: f4.writelines(l4)
In [27]: f4.flush()
In [28]: f4.close()
isatty()判断是不是终端
In [52]: f3 = open('new_file3','r+')
In [53]: f3.isatty()
Out[53]: False
truncate(N)截取保留N个字节:
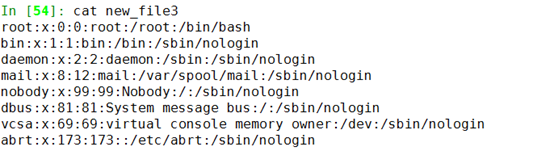
In [55]: f3.readline()
Out[55]: 'root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash\n'
In [56]: f3.readline()
Out[56]: 'bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin\n'
In [57]: f3.readline()
Out[57]: 'daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin\n'
截取保留当前游标位置及之前字节数
In [58]: f3.truncate(f3.tell())
In [59]: f3.flush()
In [60]: f3.seek(0)
In [61]: f3.readlines()
Out[61]:
['root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash\n',
'bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin\n',
'daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin\n']
closed 属性,判断文件打开状态
In [62]: f4.closed Out[62]: False
file.name属性
In [53]: f1.name Out[53]: '/etc/passwd'
mode文件打开模式,另外还有encoding、softspace等。
file.close file.flush file.next file.seek file.writelines
file.closed file.isatty file.read file.softspace file.xreadlines
file.encoding file.mode file.readinto file.tell
file.errors file.name file.readline file.truncate
file.fileno file.newlines file.readlines file.write
- 练习
1、1-10的平方写进文件new_file3,一次写一个对象
2、上面writelines方法,写入/etc下所有文件名到文件。
In [7]: f3 = open('new_file3','w+')
In [8]: for line in (i**2 for i in range(1,11)):
...: f3.write(str(line)+'\n')
...:
In [9]: f3.flush()
In [10]: f3.close()
In [11]: cat new_file3
1
4
9
16
25
36
49
64
81
100
Python(六)之文件对象的更多相关文章
- 【Python】写入文件
1.1写入空文件 若将文本写入文件,在调用open()时候需要提供另外一个实参,告诉Python你要写入打开的文件 file_path = 'txt\MyFavoriteFruit.txt' with ...
- 十:python 对象类型详解六:文件
一:文件 1.简介:内置open 函数会创建一个python 文件对象,可以作为计算机上的一个文件链接.在调用open 之后,可以通过调用返回文件对象的方法来读写相关外部文件.文件对象只是常见文件处理 ...
- python学习笔记(六)文件夹遍历,异常处理
python学习笔记(六) 文件夹遍历 1.递归遍历 import os allfile = [] def dirList(path): filelist = os.listdir(path) for ...
- Python自动化运维之4、格式化输出、文件对象
Python格式化输出: Python的字符串格式化有两种方式: 百分号方式.format方式 百分号的方式相对来说比较老,而format方式则是比较先进的方式,企图替换古老的方式,目前两者并存.[P ...
- Python 文件对象
Python 文件对象 1) 内置函数 open() 用于打开和创建文件对象 open(name,[,mode[,bufsize]]) 文件名.模式.缓冲区参数 mode: r 只读 w 写入 a 附 ...
- Python StringIO与BytesIO、类文件对象
StringIO与BytesIO StringIO与BytesIO.类文件对象的用途,应用场景,优.缺点. StringIO StringIO 是io 模块中的类,在内存中开辟的一个文本模式的buff ...
- Python Cookbook(第3版)中文版:15.19 从C语言中读取类文件对象
15.19 从C语言中读取类文件对象¶ 问题¶ 你要写C扩展来读取来自任何Python类文件对象中的数据(比如普通文件.StringIO对象等). 解决方案¶ 要读取一个类文件对象的数据,你需要重复调 ...
- Python学习笔记 -- 第六章 文件操作
I/O编程 在磁盘上读写文件的功能都是由操作系统提供的,现代操作系统不允许普通的程序直接操作磁盘,所以,读写文件就是请求操作系统打开一个文件对象(通常称为文件描述符),然后,通过操作系统提供的接口从这 ...
- python 将文件描述符包装成文件对象
有一个对应于操作系统上一个已打开的I/O 通道(比如文件.管道.套接字等)的整型文件描述符,你想将它包装成一个更高层的Python 文件对象. 一个文件描述符和一个打开的普通文件是不一样的.文件描述符 ...
随机推荐
- 在 iOS 中实现方法链调用
编译:伯乐在线 - 林欣达 如有好文章投稿,请点击 → 这里了解详情 如需转载,发送「转载」二字查看说明 前言 链式调用(chained calls)是指在函数调用返回了一个对象的时候,使得这个调用链 ...
- 【DeepLearning】Exercise:Self-Taught Learning
Exercise:Self-Taught Learning 习题链接:Exercise:Self-Taught Learning feedForwardAutoencoder.m function [ ...
- 重写Checkbox 改写选择框的大小
/* 作者:Starts_2000 * 日期:2009-07-30 * 网站:http://www.csharpwin.com CS 程序员之窗. * 你可以免费使用或修改以下代码,但请保留版权信息. ...
- MySQL 分区表原理及数据备份转移实战
MySQL 分区表原理及数据备份转移实战 1.分区表含义 分区表定义指根据可以设置为任意大小的规则,跨文件系统分配单个表的多个部分.实际上,表的不同部分在不同的位置被存储为单独的表.用户所选择的.实现 ...
- /proc/net/sockstat 里的信息是什么意思?
cat /proc/net/sockstat sockets: used 294 TCP: inuse 35 orphan 0 tw 0 alloc 45 mem 1 UDP: inuse 13 me ...
- 【Java】解析Java对XML的操作
目录结构: contents structure [+] 什么是XML 解析XML 使用DOM解析 使用SAX解析 使用PULL解析 使用dom4j解析xml dom4j的部分API 打印一个XML文 ...
- Html中 <tr> 标签的隐藏与显示
TR标签的隐藏与显示:block(显示)和none(隐藏) <tr style="display:none"> <tr id="sample" ...
- C 语言整型谜题
如题,此篇文章是描述C语言中的整数谜题. 假定机器字长是32位的,用2的补码表示整数.对以下C表达式,请问它们在所有情况下都正确吗?如果不是,请给出反例. 初始化: 1 2 3 4 int x = f ...
- Python 文件 next() 方法
描述 Python 3 中的 文件 对象不支持 next() 方法. Python 3 的内置函数 next() 通过迭代器调用 __next__() 方法返回下一项. 在循环中,next()方法会在 ...
- 公网用户接入NAT后面的freeswitch配置
大致网络示意和终端号码: 客户端侧: 终端号码(1019)终端IP(192.168.1.15)+ 网关(192.168.1.1) + 路由器公网IP(动态地址) 服务器侧: 防火墙(181.92.2. ...
