PAT 1053 Path of Equal Weight[比较]
1053 Path of Equal Weight(30 分)
Given a non-empty tree with root R, and with weight Wi assigned to each tree node Ti. The weight of a path from R to L is defined to be the sum of the weights of all the nodes along the path from R to any leaf node L.
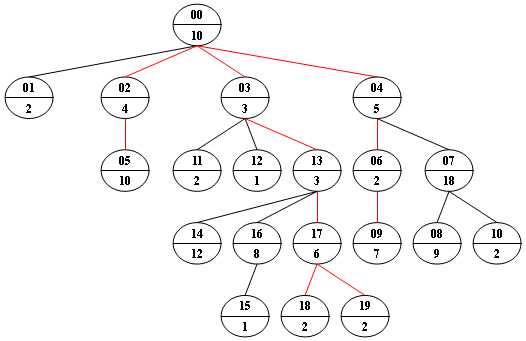
Now given any weighted tree, you are supposed to find all the paths with their weights equal to a given number. For example, let's consider the tree showed in the following figure: for each node, the upper number is the node ID which is a two-digit number, and the lower number is the weight of that node. Suppose that the given number is 24, then there exists 4 different paths which have the same given weight: {10 5 2 7}, {10 4 10}, {10 3 3 6 2} and {10 3 3 6 2}, which correspond to the red edges in the figure.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. Each case starts with a line containing 0<N≤100, the number of nodes in a tree, M (<N), the number of non-leaf nodes, and 0<S<230, the given weight number. The next line contains N positive numbers where Wi (<1000) corresponds to the tree node Ti. Then M lines follow, each in the format:
ID K ID[1] ID[2] ... ID[K]
where ID is a two-digit number representing a given non-leaf node, K is the number of its children, followed by a sequence of two-digit ID's of its children. For the sake of simplicity, let us fix the root ID to be 00.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print all the paths with weight S in non-increasing order. Each path occupies a line with printed weights from the root to the leaf in order. All the numbers must be separated by a space with no extra space at the end of the line.
Note: sequence {A1,A2,⋯,An} is said to be greater than sequence {B1,B2,⋯,Bm} if there exists 1≤k<min{n,m} such that Ai=Bi for i=1,⋯,k, and Ak+1>Bk+1.
Sample Input:
20 9 24
10 2 4 3 5 10 2 18 9 7 2 2 1 3 12 1 8 6 2 2
00 4 01 02 03 04
02 1 05
04 2 06 07
03 3 11 12 13
06 1 09
07 2 08 10
16 1 15
13 3 14 16 17
17 2 18 19
Sample Output:
10 5 2 7
10 4 10
10 3 3 6 2
10 3 3 6 2题目大意:给出一棵树,每个节点有一个编号和一个权重,输入给定了一个总权重K,求根节点R到任一叶子节点的路径代价=总权重K,找出所有这样的路径,并按字典序从大到小输出。
//我的代码:写不下去的:
#include <cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include <vector>
#include<set>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
vector<int> vt[];
map<int,int> mp;
vector<int> path;//用什么去存这个路径呢?
set<vector<int>> st;
void dfs(int r){//你这sum都没有作为参数传进去欸。。。
if(vt[r].size()==){//这里你还判断错了。。
for(int i=;i<path.size();i++){
st.insert(path);
}
return ;
}
path.push_back(r);
//最后怎么将其按照字典序排序呢?
for(int i=vt[r][];i<vt[r].size();i++){
path.push_back(vt[r][i]);
dfs(i);//.没有这个函数啊.
path.erase(vt[r][i]);
} }
int main(){
int n,leaf,k;
cin>>n>>leaf>>k;
int weight;
for(int i=;i<n;i++){
cin>>weight;
mp[i]=weight;
}
int nei=n-leaf;
int u,ct,temp;
for(int i=;i<nei;i++){
cin>>u>>ct;
for(int j=;j<ct;j++){
cin>>temp;
vt[u].push_back(temp);
}
}
//path.push_back(0);
dfs();
return ;
}
//dfs很多东西都没考虑好。
代码来自:https://www.liuchuo.net/archives/2285
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int target;
struct NODE {
int w;
vector<int> child;//将孩子节点作为一个向量进行存储。便于排序
};
vector<NODE> v;
vector<int> path;
void dfs(int index, int nodeNum, int sum) {
if(sum > target) return ;
if(sum == target) {
if(v[index].child.size() != ) return;//如果不是叶节点那么也返回。
for(int i = ; i < nodeNum; i++)
printf("%d%c", v[path[i]].w, i != nodeNum - ? ' ' : '\n');//直接在输出判断,十分简洁。
return ;
}
for(int i = ; i < v[index].child.size(); i++) {
int node = v[index].child[i];
path[nodeNum] = node;//不是push_back,向量没有erase函数,所以传了个参数表示节点数量。
dfs(node, nodeNum + , sum + v[node].w);
} }
int cmp1(int a, int b) {
return v[a].w > v[b].w;
}
int main() {
int n, m, node, k;
scanf("%d %d %d", &n, &m, &target);
v.resize(n), path.resize(n);
for(int i = ; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d", &v[i].w);
for(int i = ; i < m; i++) {
scanf("%d %d", &node, &k);
v[node].child.resize(k);
for(int j = ; j < k; j++)
scanf("%d", &v[node].child[j]);
sort(v[node].child.begin(), v[node].child.end(), cmp1);
//对子节点从大到小排序,这样就能保证是按字典序最大来找到并输出的。
}
dfs(, , v[].w);
return ;
}
1.如何保证输出的路径是按字典序从大到小呢?将每个节点的子节点按权重从大到小排列即可。学习了
2.path如果用Vector表示,但是又不能弹出,该怎么办呢?在dfs中传入参数nodeNum,而不是在跳出递归进行计算时,使用path.size();下一次的就被覆盖了。
3.要注意dfs传入的参数,当前下标、解中节点数、总和。
//值得学习!
PAT 1053 Path of Equal Weight[比较]的更多相关文章
- PAT 1053 Path of Equal Weight
#include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> ...
- 【PAT】1053 Path of Equal Weight(30 分)
1053 Path of Equal Weight(30 分) Given a non-empty tree with root R, and with weight Wi assigned t ...
- pat 甲级 1053. Path of Equal Weight (30)
1053. Path of Equal Weight (30) 时间限制 100 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 16000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yue ...
- PAT 甲级 1053 Path of Equal Weight (30 分)(dfs,vector内元素排序,有一小坑点)
1053 Path of Equal Weight (30 分) Given a non-empty tree with root R, and with weight Wi assigne ...
- 1053 Path of Equal Weight——PAT甲级真题
1053 Path of Equal Weight 给定一个非空的树,树根为 RR. 树中每个节点 TiTi 的权重为 WiWi. 从 RR 到 LL 的路径权重定义为从根节点 RR 到任何叶节点 L ...
- PAT Advanced 1053 Path of Equal Weight (30) [树的遍历]
题目 Given a non-empty tree with root R, and with weight Wi assigned to each tree node Ti. The weight ...
- PAT (Advanced Level) 1053. Path of Equal Weight (30)
简单DFS #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<cmath> #include<vector> #i ...
- PAT甲题题解-1053. Path of Equal Weight (30)-dfs
由于最后输出的路径排序是降序输出,相当于dfs的时候应该先遍历w最大的子节点. 链式前向星的遍历是从最后add的子节点开始,最后添加的应该是w最大的子节点, 因此建树的时候先对child按w从小到大排 ...
- 【PAT甲级】1053 Path of Equal Weight (30 分)(DFS)
题意: 输入三个正整数N,M,S(N<=100,M<N,S<=2^30)分别代表数的结点个数,非叶子结点个数和需要查询的值,接下来输入N个正整数(<1000)代表每个结点的权重 ...
随机推荐
- win7 64位下android开发环境的搭建
本文转自:http://www.cfanz.cn/index.php?c=article&a=read&id=65289 最近换了新电脑,装了win7 64位系统,安装了各种开发环境, ...
- opencv-从图像旋转学习Mat数据訪问
先看一个简单的样例 代码: // ConsoleApplication3_6_23.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application. ...
- ftplib模块【python】
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/kaituorensheng/p/4480512.html 函数释义 Python中默认安装的ftplib模块定义了FTP类,其中函数有限,可用来实 ...
- dos命令临时和永久设置环境变量方法
方法一:批处理中,修改环境变量,一次性有效(也就是在当前的脚本中有效) CMD中运行:set path==%path%;d:/mypath 用 set path可以查看,当前的环境变量 方 ...
- oracle 与mysql 的当前时间比较
select p.id,p.order_Num,p.image_url,p.url,p.image_topic, p.is_download, p.big_image_url, p.begin_tim ...
- CentOS6.4配置163的yum源
CentOS系统自带的更新源的速度实在是慢,为了让CentOS6使用速度更快的YUM更新源,可以选择163(网易)的更新源. 1.下载repo文件 wget http://mirrors.163.co ...
- 【LNMP】基于阿里云的https免费证书配置
1 登录阿里云账户,左侧菜单选择 -> 2 右上角选择购买证书,选择免费型 3 按照流程购买,回到订单列表.填写认证信息,选择DNS解析, 在列表 选择下载证书 4 我的服务器是ng ...
- LNMP一键安装包phpMyAdmin无法正常登录,提示:您的Session已过期,请再次登录。
找到文件: /usr/local/php/etc/php.ini 搜索: session.auto_start = 0 修改为 session.auto_start = 1 保存即可!
- TCP关闭连接(为什么会能Time_wait,Close_wait?)
版权声明:本文由胡文斌原创文章,转载请注明出处: 文章原文链接:https://www.qcloud.com/community/article/102 来源:腾云阁 https://www.qclo ...
- SRC常见WEB漏洞系列之HTTP-HOST头攻击
一.背景: web程序需要知道网站的域名比较麻烦,需要使用HTTP的 host头字段: <?php _SERVER["HTTP_HOST"] ?> @app.route ...