FROM USE CASES TO TEST CASES
FROM USE CASES TO TEST CASES
-Test note of “Essential Software Test Design”
2015-08-31
Content:
12.1 What are Use Cases?
12.2 Use cases
12.2.1 Example: Use Case – Withdraw Money
12.3 The Model – Compiling the Flow Graph
12.4 Creating Base Test Cases
12.4.1 List All Scenarios
TO DESCRIBE THE requirements on a system, a technique is often used which is called use cases.
12.1 What are Use Cases?
Use cases are a step-by-step description of a flow, where an actor interact with a system. An actor may be one of a number of different user types, the system itself, or other external systems.
The commonest flow – normal use – is called the main flow (also called the normal flow or Happy Path) and variations of this are termed alternative flows.
The overarching work procedure is this:
- Compile an activity diagram. If this is already in place, the first step is to review it.
- List all scenarios
- Analyze and prioritize the scenarios according to risk – which are most important, commonest
- Identify the operational variables which can affect the expected result
- Write one or more test cases for each scenario
12.2 Use cases
Let us go back to the example of an ATM machine. A simple use case may look like this:
12.2.1 Example: Use Case – Withdraw Money
Assumptions:
- The customer’s bank is one which is connected to the ATM system.
- The customer has a correct and functioning magnetic strip card.
- The ATM is switched on and is in ready mode.
- The ATM is situated in Sweden so all withdrawals will be in swedish crowns,
- SEK, and bills that can be withdrawn are 100 or 500 only.
Actors
- Customer
- ATM (network)
Main Flow:
H-1. The use case begins when the customer inserts the card.
H-2. The ATM verifies the card and requests the PIN number.
H-3. The customer types in the correct PIN (4 digits).
H-4. The ATM verifies the PIN and asks the customer to type in an amount.
H-5. The customer types in the amount (100-2000 SEK manually or by using the multiple choice keys).
H-6. The ATM verifies that the amount is available in the customer’s account and ejects the card, the money and the receipt, and registers the transaction in the customer’s account.
H-7. The customer takes the card, the money and the receipt.
H-8. The ATM returns to standby mode.
H-9. End of use case.
Results
The customer has carried out a successful withdrawal of money.
The customer’s account is updated with the transaction.
Alternative Flows
Alternative flow – A1 Invalid card
A1-1. At step H-1, the customer inserts an invalid card.
A1-2. The ATM aborts the transaction and the card is ejected.
Alternative flow – A2 Wrong PIN
A2-1. At step H-3, the customer types in the wrong PIN.
A2-2. The ATM registers an incorrect PIN and asks the user to try again.
A2-3. The use case continues with step H-3.
Alternative flow – A3 Wrong PIN, 3 times
A3-1. At step H-3, the customer types in the wrong PIN three times in a row.
A3-2. The ATM swallows the card and the transaction is aborted.
A3-3. End of use case.
Alternative flow – A4 Incorrect input of amount
A4-1. At step H-5, the customer makes an incorrect entry (not divisible by a hundred, funds are not in the account, exceeds permitted maximum withdrawal…)
A4-2. The ATM disallows the entered amount and asks the user to try again.
A4-3. The use case continues with step H-5.
Alternative flow – A5 Customer does not take the money
A5-1. At step H-7, the customer takes the card, but not the money or the receipt within 20 seconds.
A5-2. The ATM leaves the receipt hanging out of the machine and retracts the money, places it in a separate container and writes the amount, account number and cause of defect into a defect log.
A5-3. The use case continues with step H-8.
Alternative flow – A6 The customer’s bank is not on-line (other than Handelsbanken)
A6-1. At step H-6, the ATM cannot verify whether the amount is available in the customer’s account. A message shows that contact with the customer’s bank is being established and the card is ejected.
A6-2. The use case continues with step H-8.
Alternative flow – A7 Customer aborts the withdrawal
A7-1. At all times in the Main flow, apart from steps H-6 and H-7, the customer can choose to abort the transaction
A7-2. The ATM aborts the transaction and ejects the card, and no withdrawal is recorded on the customer’s account.
A7-3. The use case continues with step H-8.
12.3 The Model – Compiling the Flow Graph
If there is not one already, you compile a flow diagram based on the use case.
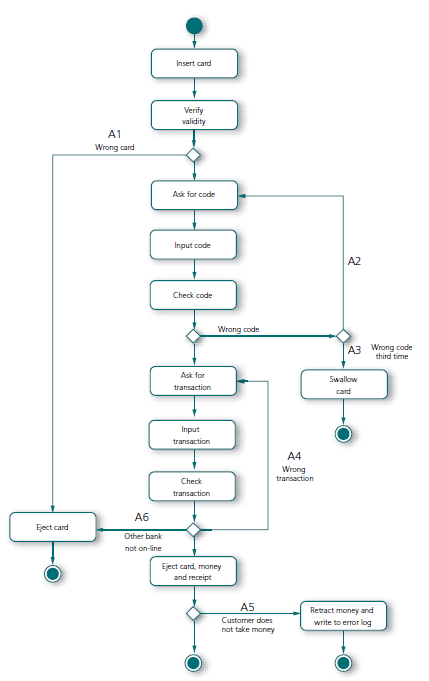
Figure 12.1: Activity diagram of the flow in the use case «Withdraw Money». We have a starting point but several different end points, with different results.
12.4 Creating Base Test Cases
12.4.1 List All Scenarios
To cover the graph, we generate base test cases for the different flows at hand
- Start with the Main flow, which you use for the Happy Day test.
- Continue with the alternative flows – one at a time.
- There are different combinations of alternative flows. It is not always possible to draw up all the combinations: there may be infinite loops.
FROM USE CASES TO TEST CASES的更多相关文章
- USER STORIES AND USE CASES - DON’T USE BOTH
We’re in Orlando for a working session as part of the Core Team building BABOK V3 and over dinner th ...
- 深入理解openstack网络架构(2)----Basic Use Cases
原文地址: https://blogs.oracle.com/ronen/entry/diving_into_openstack_network_architecture1 译文转自: http:// ...
- Security Test Cases
https://www.owasp.org/index.php/OWASP_Testing_Guide_v4_Table_of_Contents Username Enumeration Vulner ...
- SSAS CUBE TEST CASES
经过周末两天和今天的努力,基本上完成并修复了一些bug并且集成到我的MSBIHelper项目中去,可以进行数据测试了.效果图如下: 可以帮助开发人员快速生成等值的Tsql和mdx查询,辅助测试人员快速 ...
- 算法最坏,平均和最佳情况(Worst, Average and Best Cases)-------geeksforgeeks 翻译
最坏,平均和最佳运行时间(Worst, Average and Best Cases) 在上一篇文章中,我们讨论到了渐进分析可以解决分析算法的问题,那么在这一篇中,我们用线性搜索来举例说明一下如何用渐 ...
- As of ADT 14, resource fields cannot be used as switch cases
在导入Android Sample的ApiDemos的时候,发现R.id.xx的文件不能够在 switch cases 中使用 在google查询了下,找到以下答案: As of ADT 14 ...
- Unsupervised Learning: Use Cases
Unsupervised Learning: Use Cases Contents Visualization K-Means Clustering Transfer Learning K-Neare ...
- MapReduce 模式、算法和用例(MapReduce Patterns, Algorithms, and Use Cases)
在新文章“MapReduce模式.算法和用例”中,Ilya Katsov提供了一个系统化的综述,阐述了能够应用MapReduce框架解决的问题. 文章开始描述了一个非常简单的.作为通用的并行计算框架的 ...
- Cannot declare class app\home\controller\Cases because the name is already in use
Cannot declare class app\home\controller\Cases because the name is already in use 命名空间冲突了 use 模型类的时候 ...
随机推荐
- Python库资源大全
转载地址:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/27350980 本文是一个精心设计的Python框架.库.软件和资源列表,是一个Awesome XXX系列的资源整理,由BigQu ...
- 事物注解方式: @Transactional
当标于类前时, 标示类中所有方法都进行事物处理 , 例子: 1 @Transactional public class TestServiceBean implements TestService { ...
- bzoj4709: [Jsoi2011]柠檬 斜率优化
题目链接 bzoj4709: [Jsoi2011]柠檬 题解 斜率优化 设 \(f[i]\) 表示前 \(i\)个数分成若干段的最大总价值. 对于分成的每一段,左端点的数.右端点的数.选择的数一定是相 ...
- C++ 多继承与虚基类
转载来自:CSDN insistGoGo (http://blog.csdn.net/insistgogo) 多继承的定义:派生类的基类大于一个 语法: class 派生类名:继承方式1 基类名1 ...
- MySql数据库事务正常提交,回滚失败
问题:在初次练习Mysql数据库事务时,事务正常提交,但是在遇到异常应当回滚时,回滚失败. 代码如下: //2.更新操作. public void update(Connection conn, St ...
- 使用 IntraWeb (28) - 基本控件之 TIWTemplateProcessorHTML、TIWLayoutMgrHTML、TIWLayoutMgrForm
TIWTemplateProcessorHTML //使用外部的 html 文件做模板 TIWLayoutMgrHTML //直接输入 Html 文本做模板 TIWLayoutMgrForm //这应 ...
- Nodejs后台管理员登录实例
思路: 直接访问后台页面时如果无session则跳转到404 当在登录页的表单提交时对数据库进行匹配,匹配成功生成session,否则提示用户名或密码错误 准备页面 :后台首页.登录页.404页, 步 ...
- Kubernetes基础:编排调度的那些Controllers
0. 概述 Kubernetes提供了很多Controller资源来管理.调度Pod,包括Replication Controller.ReplicaSet.Deployments.StatefulS ...
- 461.汉明距离(c++实现)
问题描述: 两个整数之间的汉明距离指的是这两个数字对应二进制位不同的位置的数目. 给出两个整数 x 和 y,计算它们之间的汉明距离. 注意:0 ≤ x, y < 231. 示例: 输入: x = ...
- hyper-v的p2v工具
1.Disk2vhd v1.64 可以在线p2v http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/ee656415.aspx 2.物理机转换到HYPER ...
