Apache Spark 2.3.0 重要特性介绍
文章标题
Introducing Apache Spark 2.3
Apache Spark 2.3 介绍
Now Available on Databricks Runtime 4.0
现在可以在Databrcks Runtime 4.0上使用。
作者介绍
Sameer Agarwal, Xiao Li, Reynold Xin and Jules Damji
文章正文:
Today we are happy to announce the availability of Apache Spark 2.3.0 on Databricks as part of its Databricks Runtime 4.0. We want to thank the Apache Spark community for all their valuable contributions to Spark 2.3 release.
今天,我们很高兴地

Continuing with the objectives to make Spark faster, easier, and smarter, Spark 2.3 marks a major milestone for Structured Streaming by introducing low-latency continuous processing and stream-to-stream joins; boosts PySpark by improving performance with pandas UDFs; and runs on Kubernetes clusters by providing native support for Apache Spark applications.
In addition to extending new functionality to SparkR, Python, MLlib, and GraphX, the release focuses on usability, stability, and refinement, resolving over 1400 tickets. Other salient features from Spark contributors include:
- DataSource v2 APIs [SPARK-15689, SPARK-20928]
- Vectorized ORC reader [SPARK-16060]
- Spark History Server v2 with K-V store [SPARK-18085]
- Machine Learning Pipeline API model scoring with Structured Streaming [SPARK-13030, SPARK-22346, SPARK-23037]
- MLlib Enhancements Highlights [SPARK-21866, SPARK-3181, SPARK-21087, SPARK-20199]
- Spark SQL Enhancements [SPARK-21485, SPARK-21975, SPARK-20331, SPARK-22510, SPARK-20236]
In this blog post, we briefly summarize some of the high-level features and improvements, and in the coming days, we will publish in-depth blogs for these features. For a comprehensive list of major features across all Spark components and JIRAs resolved, read the Apache Spark 2.3.0 release notes.
1、Continuous Stream Processing at Millisecond Latencies
Structured Streaming in Apache Spark 2.0 decoupled micro-batch processing from its high-level APIs for a couple of reasons. First, it made developer’s experience with the APIs simpler: the APIs did not have to account for micro-batches. Second, it allowed developers to treat a stream as an infinite table to which they could issue queries as they would a static table.
However, to provide developers with different modes of stream processing, we introduce a new millisecond low-latency mode of streaming: continuous mode.
Under the hood, the structured streaming engine incrementally executed query computations in micro-batches, dictated by a trigger interval, with tolerable latencies suitable for most real-world streaming applications.
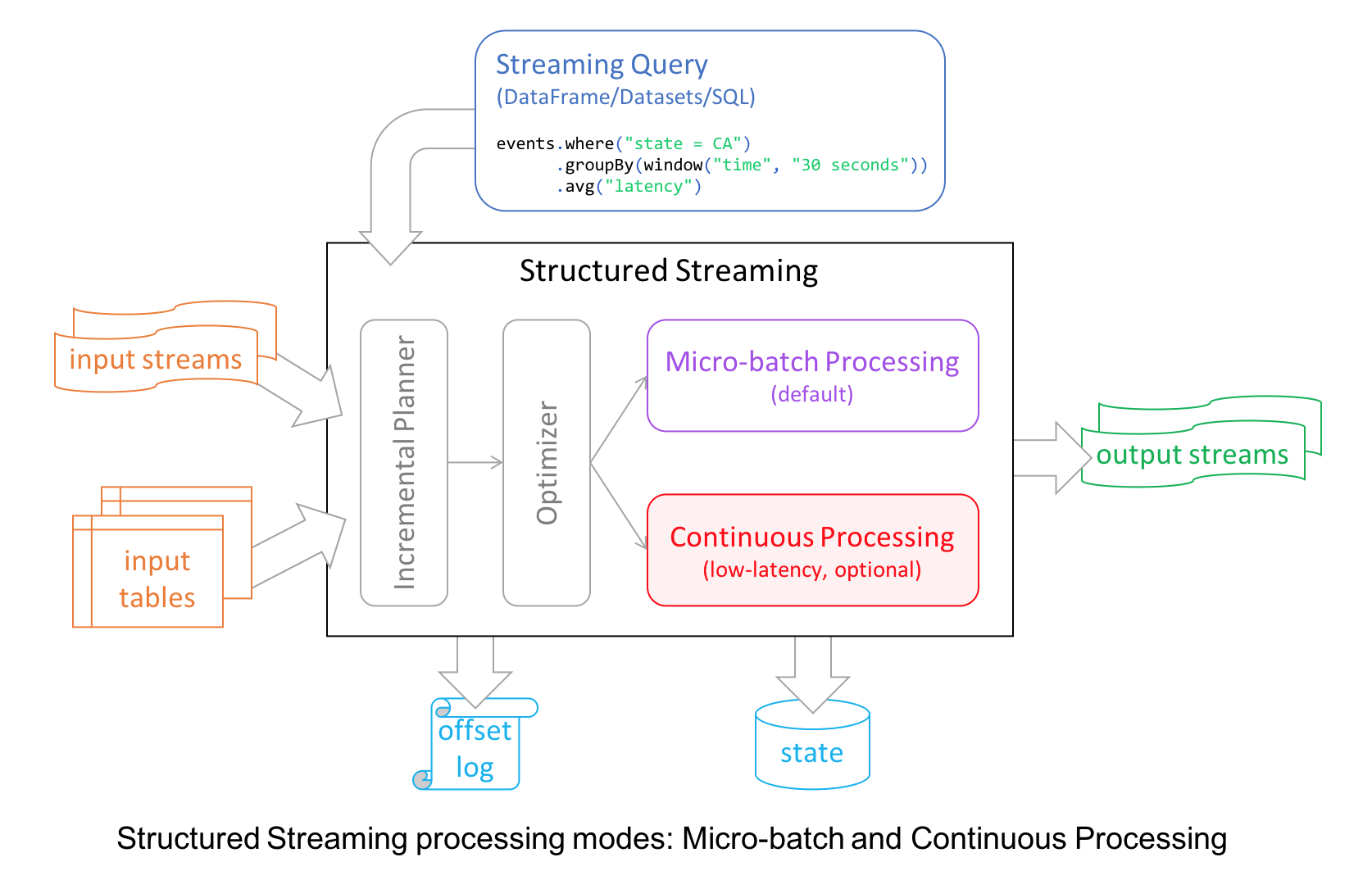
For continuous mode, instead of micro-batch execution, the streaming readers continuously poll source and process data rather than read a batch of data at a specified trigger interval. By continuously polling the sources and processing data, new records are processed immediately upon arrival, as shown in the timeline figure below, reducing latencies to milliseconds and satisfying low-level latency requirements.

As for operations, it currently supports map-like Dataset operations such as projections or selections and SQL functions, with the exception of current_timestamp(), current_date() and aggregate functions. As well as supporting Apache Kafka as a source and sink, continuous mode currently supports console and memory as sinks, too.
Now developers can elect either mode—continuous or micro-batching—depending on their latency requirements to build real-time streaming applications at scale while benefiting from the fault-tolerance and reliability guarantees that Structured Streaming engine affords.
In short, the continuous mode in Spark 2.3 is experimental and it offers the following:
- end-to-end millisecond low latencies
- provides at-least-once guarantees.
- supports map-like Dataset operations
In this technical blog on Continuous Processing mode, we illustrate how to use it, its merits, and
how developers can write continuous streaming applications with millisecond low-latency requirements.
2、Stream-to-Stream Joins
While Structured Streaming in Spark 2.0 has supported joins between a streaming DataFrame/Dataset and a static one, this release introduces the much awaited stream-to-stream joins, both inner and outer joins for numerous real-time use cases.
The canonical use case of joining two streams is that of ad-monetization. For instance, an impression stream and an ad-click stream share a common key (say, adId) and relevant data on which you wish to conduct streaming analytics, such as, which adId led to a click.
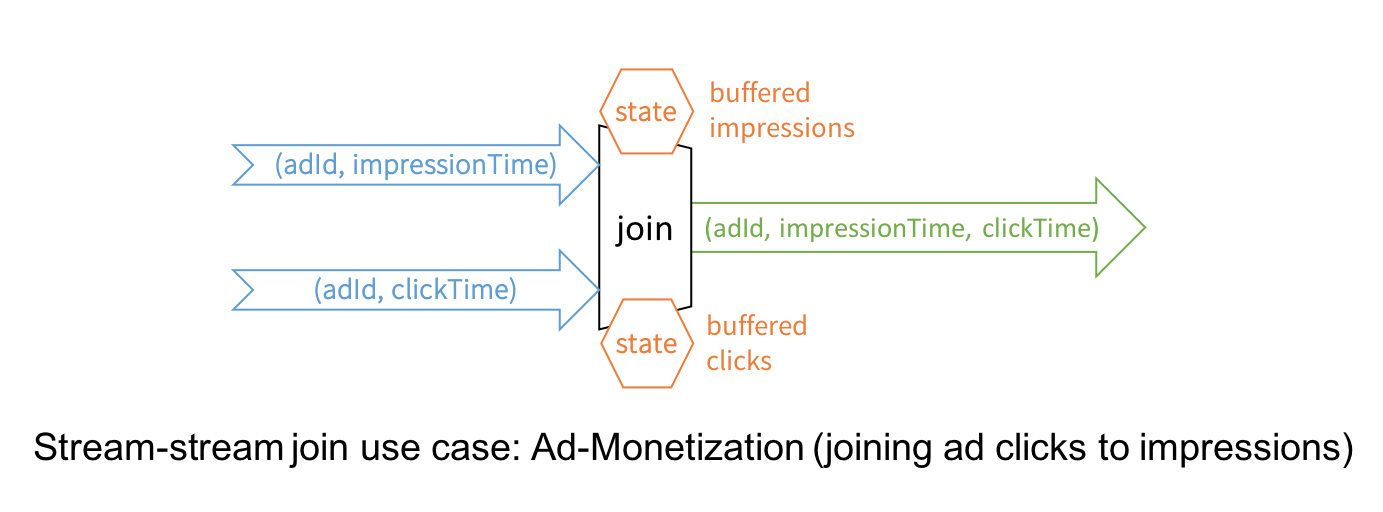
While conceptually the idea is simple, stream-to-stream joins resolve a few technical challenges. For example, they:
- handle delayed data by buffering late events as streaming “state” until matching event is found from the other stream
- limit the buffer from growing and consuming memory with watermarking, which allows tracking of event-time and accordingly clearing of old state
- allow a user to control the tradeoff between the resources consumed by state and the maximum delay handled by the query
- maintain consistent SQL join semantics between static joins and streaming joins
In this technical blog, we dive deeper into streams-to-stream joins.
3、Apache Spark and Kubernetes
No surprise that two popular open source projects Apache Spark and Kubernetes combine their functionality and utility to provide distributed data processing and orchestration at scale. In Spark 2.3, users can launch Spark workloads natively on a Kubernetes cluster leveraging the new Kubernetes scheduler backend. This helps achieve better resource utilization and multi-tenancy by enabling Spark workloads to share Kubernetes clusters with other types of workloads.
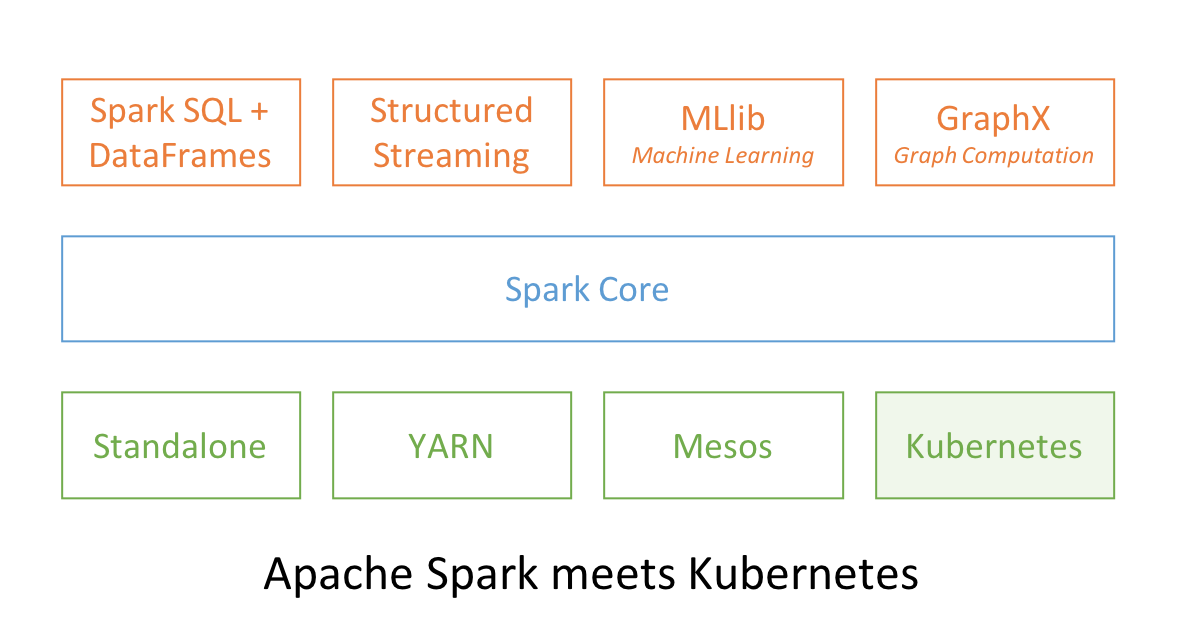
Also, Spark can employ all the administrative features such as Resource Quotas, Pluggable Authorization, and Logging. What’s more, it’s as simple as creating a docker image and setting up the RBAC to start employing your existing Kubernetes cluster for your Spark workloads.
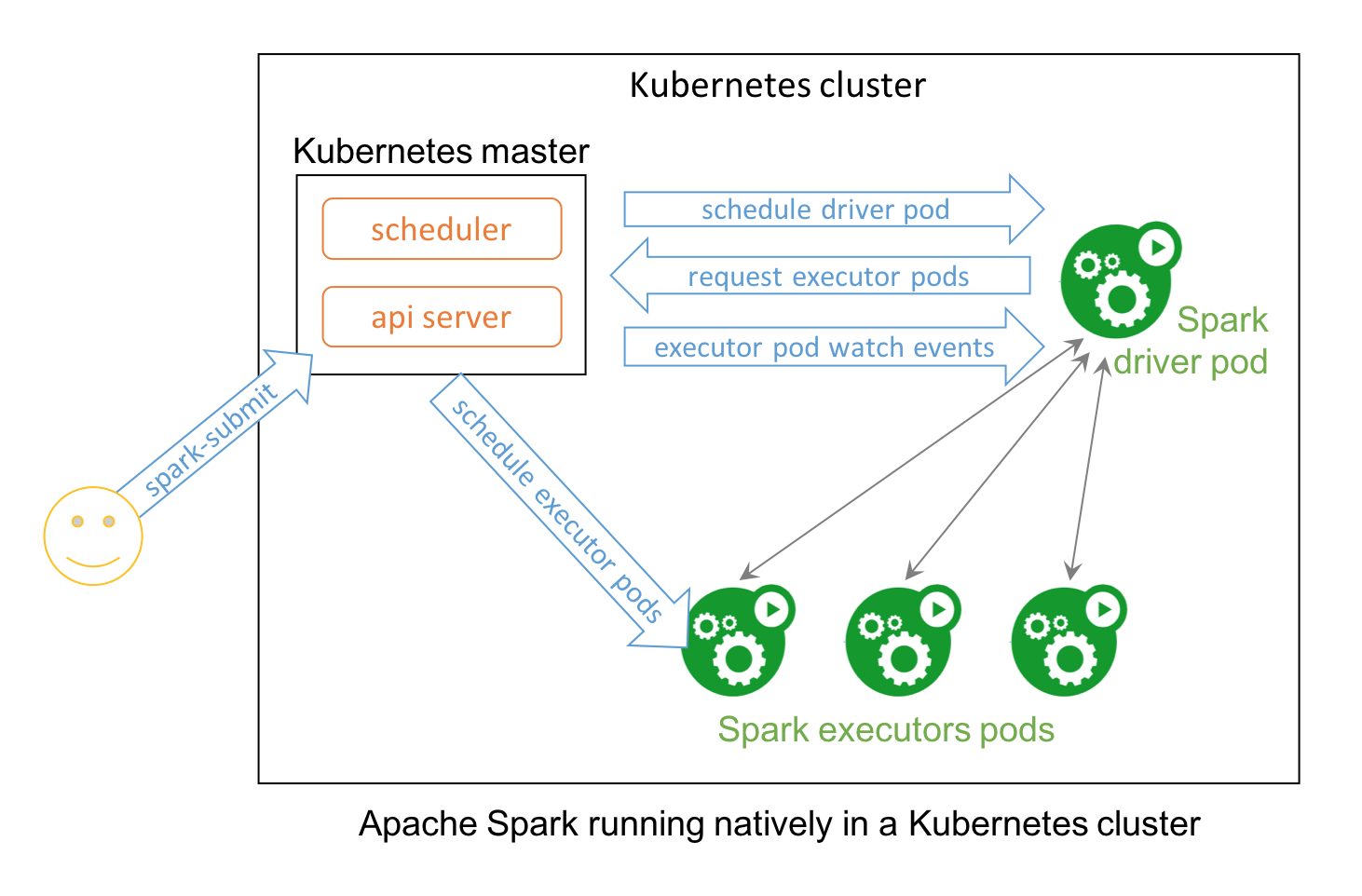
This technical blog explains how you can use Spark natively with Kubernetes and how to get involved in this community endeavor.
4、Pandas UDFs for PySpark
Pandas UDFs, also called Vectorized UDFs, is a major boost to PySpark performance. Built on top of Apache Arrow, they afford you the best of both worlds—the ability to define low-overhead, high-performance UDFs and write entirely in Python.
In Spark 2.3, there are two types of Pandas UDFs: scalar and grouped map. Both are now available in Spark 2.3. Li Jin of Two Sigma had penned an earlier blog, explaining their usage through four examples: Plus One, Cumulative Probability, Subtract Mean, Ordinary Least Squares Linear Regression.
Running some micro benchmarks, Pandas UDFs demonstrate orders of magnitude better performance than row-at-time UDFs.
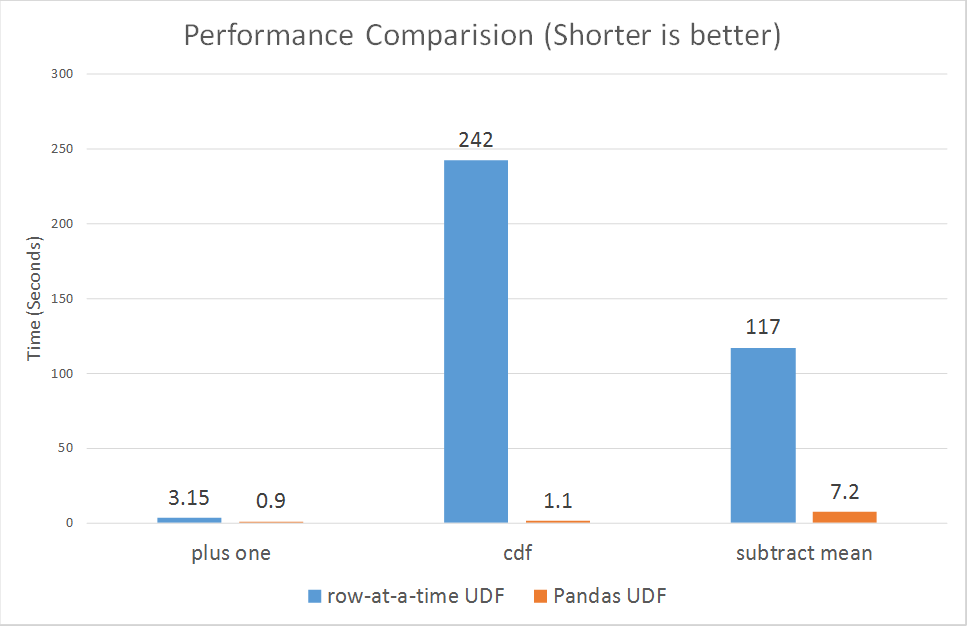
According to Li Jin and other contributors, they plan to introduce support for Pandas UDFs in aggregations and window functions, and its related work can be tracked in SPARK-22216.
5、MLlib Improvements
Spark 2.3 includes many MLlib improvements for algorithms and features, performance and scalability, and usability. We mention three highlights.
First, for moving MLlib models and Pipelines to production, fitted models and Pipelines now work within Structured Streaming jobs. Some existing Pipelines will require modifications to make predictions in streaming jobs, so look for upcoming blog posts on migration tips.
Second, to enable many Deep Learning image analysis use cases, Spark 2.3 introduces an ImageSchema [SPARK-21866] for representing images in Spark DataFrames, plus utilities for loading images from common formats.
And finally, for developers, Spark 2.3 introduces improved APIs in Python for writing custom algorithms, including a UnaryTransformer for writing simple custom feature transformers and utilities for automating ML persistence for saving and loading algorithms. See this blog post for details.
参考文献:
Apache Spark 2.3.0 重要特性介绍的更多相关文章
- Apache Spark 2.2.0新特性介绍(转载)
这个版本是 Structured Streaming 的一个重要里程碑,因为其终于可以正式在生产环境中使用,实验标签(experimental tag)已经被移除.在流系统中支持对任意状态进行操作:A ...
- Apache Spark 2.2.0 新特性详细介绍
本章内容: 待整理 参考文献: Apache Spark 2.2.0新特性详细介绍 Introducing Apache Spark 2.2
- Apache Spark 1.6公布(新特性介绍)
Apache Spark 1.6公布 CSDN大数据 | 2016-01-06 17:34 今天我们很高兴可以公布Apache Spark 1.6,通过该版本号,Spark在社区开发中达到一个重要的里 ...
- Hadoop3.0新特性介绍,比Spark快10倍的Hadoop3.0新特性
Hadoop3.0新特性介绍,比Spark快10倍的Hadoop3.0新特性 Apache hadoop 项目组最新消息,hadoop3.x以后将会调整方案架构,将Mapreduce 基于内存+io+ ...
- Apache Spark 2.2.0 中文文档
Apache Spark 2.2.0 中文文档 - 快速入门 | ApacheCN Geekhoo 关注 2017.09.20 13:55* 字数 2062 阅读 13评论 0喜欢 1 快速入门 使用 ...
- webpack 4.0.0-beta.0 新特性介绍
webpack 可以看做是模块打包机.它做的事情是:分析你的项目结构,找到JavaScript模块以及其它的一些浏览器不能直接运行的拓展语言(Scss,TypeScript等),并将其打包为合适的格式 ...
- Apache Spark 2.2.0 正式发布
本章内容: 待整理 参考文献: Apache Spark 2.2.0正式发布 Spark Release 2.2.0
- Pivotal Greenplum 6.0 新特性介绍
Pivotal Greenplum 6.0 新特性介绍 在1月12日举办的Greenplum开源有道智数未来技术研讨会上,Pivotal中国研发中心Greenplum 产品经理李阳向大家介绍了Pi ...
- [转帖]Pivotal Greenplum 6.0 新特性介绍
Pivotal Greenplum 6.0 新特性介绍 https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/news/391063 原来 greenplum 也是基于pg研发的. ...
随机推荐
- Codeforces 1102F Elongated Matrix 状压dp
Elongated Matrix 预处理一下两两之间的最小值, 然后直接dp. #include<bits/stdc++.h> #define LL long long #define f ...
- 【noip模拟赛9】123法典
描述 很久很久以前,有个叫123的国家,这个国家的国王很喜欢颁布各种法令,并把这些法令记录在一部<123法典>中.最近这部法典终于被发掘了出来,专家们经过研究发现法典中的法令是按颁布的时间 ...
- 020 Spark中分组后的TopN,以及Spark的优化(重点)
一:准备 1.源数据 2.上传数据 二:TopN程序编码 1.程序 package com.ibeifeng.bigdata.spark.core import java.util.concurren ...
- C#资源管理器
窗体搭建:ContextMenuStrip右键菜单,Treeview树形菜单,Listview控件 新建"我的文件"类: public class MyFile { public ...
- 高级Bash脚本编程指南《Advanced Bash-Scripting Guide》 in Chinese
<Advanced Bash-Scripting Guide> in Chinese <高级Bash脚本编程指南>Revision 10中文版 在线阅读链接:http://ww ...
- QT学习之windows下安装配置PyQt5
windows下安装配置PyQt5 目录 为什么要学习QT 命令行安装PyQt5以及PyQt5-tools 配置QtDesigner.PyUIC及PyRcc 为什么要学习QT python下与界面开发 ...
- 在webpack中使用postcss之插件cssnext
学习了precss插件包在webpack中的用法后,下面介绍postcss的另一个重要插件cssnext,步骤没有precss用法详细,主要介绍css4的语法,cssnext目前支持了部分新特性,你可 ...
- Codeforces.392E.Deleting Substrings(区间DP)
题目链接 \(Description\) \(Solution\) 合法的子序列只有三种情况:递增,递减,前半部分递增然后一直递减(下去了就不会再上去了)(当然还要都满足\(|a_{i+1}-a_i| ...
- COGS.264.数列操作(分块 单点加 区间求和)
题目链接 #include<cmath> #include<cstdio> #include<cctype> #include<algorithm> u ...
- 关于WEB前端开发的工具
俗话说:"工谷善其事,先必利其器."一个用得顺手的工具,确实能为我们的开发带来方 便,更重要的是会让我们更加享受工具开发过程中所带来的乐趣. 1.编码工具: 记事本之类的编辑器都可 ...
