Java Buffer
1.1 NIO Buffers - Class java.nio.Buffer
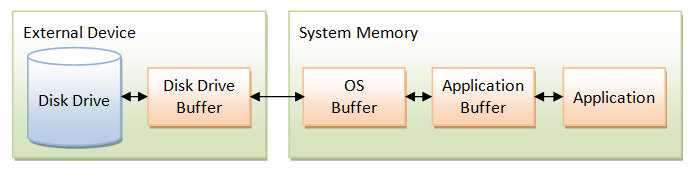
NIO data transfer is through the so-called buffers implemented in java.nio.Buffer class. A Buffer is similar to an array, except that it's implemented much more efficiently by closely coupled with the underlying OS.A Buffer is a contiguous, linear storage. Similar to an array, a Buffer has a fixed capacity.
The Buffer class for each of the primitibe types(except boolean), as shown in the above diagram. The abstarct superclass java.nio.Buffer provides the common properties and some common operatons of all buffers.
A Buffer has a capacity, position, limit, and an optional mark:
- The capacity must be specified when the
Bufferis constructed and cannot be changed (similar to an array). You can retrieve it via methodcapacity(). - The limit specifies the current occupancy. In other word, the buffer contains valid data in the range 0 to limit-1. You can retrieve the current limit via method
limit()or set thelimitvia methodlimit(int newLimit). Limit shall not be greater than capacity. - Unlike array, there is a so-called position (or cursor) in a
Bufferthat indicates where the next piece of data is to be read or written. You can retrieve the current position via methodposition()or change the current position via methodposition(int newPosition). Position shall not be greater than the limit. - A mark provide a positional marker. You can mark the current position via the method
mark().
Data Transfer (Get/Put):
Each of the primitive buffers provides a set of get() and put() methods to read/write an element or a array of elements from/to the buffer. The position increases by the number of elements transferred. For example, the IntBuffer provides:
ByteBuffer is special. It provides additional getXxx()/putXxx() methods to parse raw bytes into other primitive types. It also can be used as the sources and targets of I/O operations, which will be explained later in channel I/O.
Mark and Reset:
You can use mark() method to mark the current position. Invoking reset() sets the position to the previously-marked position. The mark may or may not be set. If the mark is not set, invoking reset() triggers an InvalidMarkException. If the mark is set, it should never be greater than the position (because the mark() marks the current position and position advances). The mark will be discarded when the position or the limit is adjusted to a value smaller than the mark. Hence, 0 ≤ mark ≤ position ≤ limit ≤ capacity.
Clear, Flip and Rewind:
clear(): sets thepositionto 0,limitto thecapacity, and discardsmark. It prepares the buffer for input.flip(): sets thelimitto the currentposition,positionto 0, and discardmark. Buffer populated and ready for output.rewind(): set the position to 0, and discard mark. It prepares the buffer for re-read.
Creating a Buffer: There are 3 ways to create a buffer:
- via method
allocate(int capacity), which allocates a new buffer, sets position to 0 and limit to capacity, and clear the mark. - wrap an existing array into buffer via
wrap(type[] array, int offset, int length)orwrap(type[] array)method. - by creating a view of an existing
ByteBuffer(to be discussed later).
Slicing and data sharing:
The slice() method creates sub-buffer from an existing buffer. That is it creates a new buffer sharing a portion of the original buffer.
We can see a example:
Then we alter elements in the buffer(two buffers and the sub-buffers share the same underlying data array).
Here is the ouput:
before alter sub-buffer:0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
alter elements in sub buffer.
After altering sub buffer0 1 2 33 44 55 66 7 8 9
Read-only buffers
Read-only buffers means only read operation allowed. We can turn any regular buffer into a read-only buffer by calling its asReadOnlyBuffer() method, which returns a new buffer that is identical to the first (and shares data with it), but is read-only. But we can not turn an read-only buffer to writable buffer.
Direct and in Direct buffer
To see the difference between these two buffer, please see Analysis about different methods for reading and writing file in Java language.
Memory-mapped file I/O
Memory-mapped file I/O can read and write file more fast than regular stream or channel based I/O.
Memory-mapped file I/O is accomplished by causing the data in a file to magically appear as the contents of a memory array. For it provide access to the facility that OS implement FS by mapping portions of a file into portions of memory, doing so on demand.
Mapping a file into memory example:
static void MappingFileMem() throws IOException{
String inFileStr = "/users/wsy/Documents/job/kimchi_v2.pdf";
String outFileStr = "./kimchi_v2.pdf";
long startTime, elapsedTime; // for speed benchmarking
int bufferSizeKB = 4;
int bufferSize = bufferSizeKB * 1024;
FileInputStream input = new FileInputStream(inFileStr);
FileChannel channel = input.getChannel();
MappedByteBuffer mbb = channel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, 1024);
}
Scattering and gathering
Scatter/gather I/O is a method of reading and writing that uses multiple buffers, rather than a single buffer. A scatter read reads data into a array of buffers rather than a single buffer. A gathering write writes data from a array of buffers rather than a single buffer.
Applications of scatter/gather:
Scatter/gather I/O is useful for dividing a piece of data into sections. For example, we can write a networking app that uses message objects, and each messages divided into a fixed-length header and body We can create 2 buffers, one for the header, and other for the body.When we put these 2 in an array and read data into them by scattering read, then the header and body will be neatly divided into 2 buffers. The scatter read will automatically find the first with room in it. After the previous filled, it movs to the next one.
long read( ByteBuffer[] dsts );long read( ByteBuffer[] dsts, int offset, int length );
Gathering writes is like the Scattering reads.
Java Buffer的更多相关文章
- Java学习笔记20(String类应用、StringBuffer类、StringBuilder类)
1.获取指定字符串中大小写和数字的个数: package demo; public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) ...
- Java IO、NIO、AIO知识总结
本文主要讲述下自己对IO的理解,对IO的用法和细则可能没有顾虑到. 本文的理解基于以下几篇文章,他们对各自部分都讲的很细,对我理解IO提供了很大帮助. https://www.cnblogs.com/ ...
- 【JAVA语法】01Java-变量与数据类型
数据类型初阶 基本数据类型的包装类 整数类型&浮点类型&字符类型 大小类型转换 通过Scanner从控制台获取数据 变量相关基础算法 Java的错误类型 字符串String 补充-Pa ...
- java#tostring
通常使用apache-commons 来生成tostring方法,但是对于类型为java.util.Date的字段打印效果并不是我们想要的. @Override public String toStr ...
- Android OpenGL ES(三)OpenGL ES API 命名习惯 .
OpenGL ES是个跨平台的3D图形开发包规范,最常见的实现是采用C语言实现的,Android OpenGL ES 实现上是使用Java 语言对底层的C接口进行了封装,因此在android.open ...
- 代码生成器实现的Entity,Dao,Service,Controller,JSP神器(含代码附件)
package com.flong.codegenerator; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DatabaseMetaData; impor ...
- 11jsp
1.JSP 1. 指令 作用:用于配置JSP页面,导入资源文件 格式: <%@ 指令名称 属性名1=属性值1 属性名2=属性值2 ... %> 分类: ...
- SprinfJdbcTemplate+SpringMVC 代码生成器实现的Entity,Dao,Service,Controller,JSP神器(含代码附件)
代码生成器实现的Entity,Dao,Service,Controller,JSP神器(含代码附件) 原文地址: http://jilongliang.iteye.com/blog/2262070 p ...
- Spark案例分析
一.需求:计算网页访问量前三名 import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext} /* ...
随机推荐
- 创建ORACLE 查询用户
[apptest@vis appl]$ su -oravis [oravis@vis 11.1.0]$ sqlplus / as sysdba SQL> create user erpquery ...
- 引用jquery框架后出错
问题描述:当引用了jquery框架后,页面的js不能正常工作. 后面我的解决办法:是因为在引用 jquery的框架时的代码为 <script type="text/javascript ...
- getchar()用法
getchar() .从缓冲区读走一个字符,相当于清除缓冲区 .前面的scanf()在读取输入时会在缓冲区中留下一个字符'\n'(输入完s[i]的值后按回车键所致),所以如果不在此加一个getchar ...
- 关于webapp中的文字单位的一些捣腾
前言 文字是网页内容的一枚大将,我们无时无刻都在看着它,只要是你盯屏幕上的任何一个地方都会有文字.地铁上无时无刻都在盯着屏幕上的人对于文字更为敏感,太大不行,太小TN又看不清上面到底在说什么,有时候车 ...
- css3——webkit-animation动画
-webkit-animation:仍旧是一个复合属性, -webkit-animation: name duration timing-function delay iteration_coun ...
- win8VPN
上一章已经讲过Windows2008RT搭建VPN服务器搭建过程,接下来说一下win8的VPN登录 这里是win2008的VPN连接过程 先说win8的VPN登录过程.同样也很简单步骤和2008的差不 ...
- vb 添加状态栏
1.新建一工程2.添加"部件" ms windows common controls 6.03.将StatusBar控件加至窗体中4.右键点击该控件,选"属性" ...
- Android NOTE
一些小的点就记在这里吧…… MultiDex打包时zip错误 我遇到的是 Execution failed for task ':excelSior:packageAllDebugClassesFor ...
- vs指定QT的工作目录(其它项目也是如此)
当一个工程依赖第三方动态库时,这时vs编译出来后,运行会提示缺少动态库.解决方法: 项目->属性->调试: 工作目录:指定程序运行时的目录 环境:指定程序运行时的环境变量 我们可以在环境变 ...
- 柯南君:看大数据时代下的IT架构(2)消息队列之RabbitMQ-基础概念详细介绍
一.基础概念详细介绍 1.引言 你是否遇到过两个(多个)系统间需要通过定时任务来同步某些数据?你是否在为异构系统的不同进程间相互调用.通讯的问题而苦恼.挣扎?如果是,那么恭喜你,消息服务让你可以很轻松 ...
