浅析java的浅拷贝和深拷贝
Java中任何实现了Cloneable接口的类都可以通过调用clone()方法来复制一份自身然后传给调用者。一般而言,clone()方法满足:
(1) 对任何的对象x,都有x.clone() !=x,即克隆对象与原对象不是同一个对象。
(2) 对任何的对象x,都有x.clone().getClass()==x.getClass(),即克隆对象与原对象的类型一样。
(3) 如果对象x的equals()方法定义恰当,那么x.clone().equals(x)应该成立。
/**
* Creates and returns a copy of this object. The precise meaning
* of "copy" may depend on the class of the object. The general
* intent is that, for any object {@code x}, the expression:
* <blockquote>
* <pre>
* x.clone() != x</pre></blockquote>
* will be true, and that the expression:
* <blockquote>
* <pre>
* x.clone().getClass() == x.getClass()</pre></blockquote>
* will be {@code true}, but these are not absolute requirements.
* While it is typically the case that:
* <blockquote>
* <pre>
* x.clone().equals(x)</pre></blockquote>
* will be {@code true}, this is not an absolute requirement.
* <p>
* By convention, the returned object should be obtained by calling
* {@code super.clone}. If a class and all of its superclasses (except
* {@code Object}) obey this convention, it will be the case that
* {@code x.clone().getClass() == x.getClass()}.
* <p>
* By convention, the object returned by this method should be independent
* of this object (which is being cloned). To achieve this independence,
* it may be necessary to modify one or more fields of the object returned
* by {@code super.clone} before returning it. Typically, this means
* copying any mutable objects that comprise the internal "deep structure"
* of the object being cloned and replacing the references to these
* objects with references to the copies. If a class contains only
* primitive fields or references to immutable objects, then it is usually
* the case that no fields in the object returned by {@code super.clone}
* need to be modified.
* <p>
* The method {@code clone} for class {@code Object} performs a
* specific cloning operation. First, if the class of this object does
* not implement the interface {@code Cloneable}, then a
* {@code CloneNotSupportedException} is thrown. Note that all arrays
* are considered to implement the interface {@code Cloneable} and that
* the return type of the {@code clone} method of an array type {@code T[]}
* is {@code T[]} where T is any reference or primitive type.
* Otherwise, this method creates a new instance of the class of this
* object and initializes all its fields with exactly the contents of
* the corresponding fields of this object, as if by assignment; the
* contents of the fields are not themselves cloned. Thus, this method
* performs a "shallow copy" of this object, not a "deep copy" operation.
* <p>
* The class {@code Object} does not itself implement the interface
* {@code Cloneable}, so calling the {@code clone} method on an object
* whose class is {@code Object} will result in throwing an
* exception at run time.
*
* @return a clone of this instance.
* @throws CloneNotSupportedException if the object's class does not
* support the {@code Cloneable} interface. Subclasses
* that override the {@code clone} method can also
* throw this exception to indicate that an instance cannot
* be cloned.
* @see java.lang.Cloneable
*/
protected native Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException;
首先来看看浅拷贝和深拷贝的定义:
浅拷贝:使用一个已知实例对新创建实例的成员变量逐个赋值,这个方式被称为浅拷贝。
深拷贝:当一个类的拷贝构造方法,不仅要复制对象的所有非引用成员变量值,还要为引用类型的成员变量创建新的实例,并且初始化为形式参数实例值。这个方式称为深拷贝
也就是说浅拷贝只复制一个对象,传递引用,不能复制实例。而深拷贝对对象内部的引用均复制,它是创建一个新的实例,并且复制实例。
对于浅拷贝当对象的成员变量是基本数据类型时,两个对象的成员变量已有存储空间,赋值运算传递值,所以浅拷贝能够复制实例。但是当对象的成员变量是引用数据类型时,就不能实现对象的复制了。
存在一个对象Person,代码如下:

public class Person {
private String name;
private String sex;
private int age;
public Person(String name,String sex,int age){
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.age = age;
}
public Person(Person p){ //拷贝构造方法,复制对象
this.name = p.name;
this.sex = p.sex;
this.age = p.age;
}
}

上面的对象Person有三个成员变量。name、sex、age。两个构造方法。第二个的参数为该对象,它称为拷贝构造方法,它将创建的新对象初始化为形式参数的实例值,通过它可以实现对象复制功能。
又有一个对象Asian,如下:

public class Asian {
private String skin;
Person person;
public Asian(String skin,Person person){
this.skin = skin;
this.person = person; //引用赋值
}
public Asian(Asian asian){ //拷贝构造方法,复制对象
this(asian.skin,asian.person);
}
}

上面对象也存在着两个成员变量,skin 和Person对象
对于person对象有如下:
Person p1 = new Person("李四","mam",23);
Person p2 = new Person(P1);
当调用上面的语句时。P2对象将会对P1进行复制。执行情况如下如下图:

对于Asian对象有:
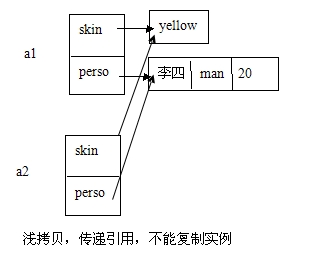
Asian a1 = new Asian("yellow",new Person("李四","mam",23));
Asian a2 = new Asian(a1);
New Asian(a1)执行Asian类的拷贝构造方法,由于对象赋值是引用赋值。使得a1和a2引用同一个对象
如下图:
当a1执行某条可以改变该值的语句时,那么a1将会通过这个语句也可以改变a2对象的成员变量
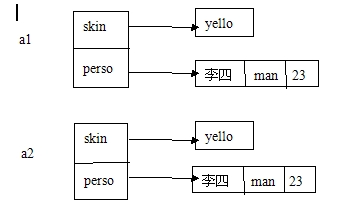
如果执行以下语句:a2.name = new Person(a1.name)
这时将会创建一个新的Person对象
如下图:
http://www.cnblogs.com/chenssy/p/3308489.html
浅析java的浅拷贝和深拷贝的更多相关文章
- Java的浅拷贝与深拷贝
Java的浅拷贝与深拷贝 Java中,所有的类都继承Object,Object中有clone方法,它被声明为了 protected ,所以我们但是如果要使用该方法就得重写且声明为public,必须在要 ...
- Java的浅拷贝与深拷贝总结
Java中的对象拷贝(Object Copy)指的是将一个对象的所有属性(成员变量)拷贝到另一个有着相同类类型的对象中去.举例说明:比如,对象A和对象B都属于类S,具有属性a和b.那么对对象A进行拷贝 ...
- 渐析java的浅拷贝和深拷贝
首先来看看浅拷贝和深拷贝的定义: 浅拷贝:使用一个已知实例对新创建实例的成员变量逐个赋值,这个方式被称为浅拷贝. 深拷贝:当一个类的拷贝构造方法,不仅要复制对象的所 ...
- Java中浅拷贝和深拷贝的区别
浅拷贝和深拷贝的定义: 浅拷贝: 被复制对象的所有变量都含有与原来的对象相同的值,而所有的对其他对象的引用仍然指向原来的对象.即对象的浅拷贝会对"主"对象进行拷贝,但不会复制主对象 ...
- 初始JAVA中浅拷贝和深拷贝
1. 简单变量的复制 public static void main(String[] args) { int a = 5; int b = a; System.out.println(a); Sys ...
- Java之浅拷贝与深拷贝
----?浅拷贝 --- 概念 被复制对象的所有变量都含有与原来的对象相同的值,而所有的对其他对象的引用仍然指向原来的对象.简单说,浅拷贝就是只复制所考虑的对象,而不复制它所引用的对象 --- 实现方 ...
- Java之浅拷贝和深拷贝
[概述] Java中的对象拷贝 ( Object Copy ) 是指将一个对象的所有属性(成员变量)拷贝到另一个有着相同类类型的对象中去.例如,对象 A 和对象 B 都属于类 S,具有属性 a 和 b ...
- java的浅拷贝和深拷贝(待解决)
1.什么是浅拷贝,什么是深拷贝? 2.storm的并行度问题,需要使用全局变量static ConcorrentHashMap,因为加了static,所有的线程只能拷贝该全局变量的一个唯一的副本,进行 ...
- 浅析java的深拷贝与浅拷贝
(转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/chenssy/p/3308489.html) 首先来看看浅拷贝和深拷贝的定义: 浅拷贝:使用一个已知实例对新创建实例的成员变量逐个赋值,这个方式 ...
随机推荐
- JS给元素增加className
function(element,value) //给元素添加className { if(!element.className) { element.className=value; } else{ ...
- oschina程序开发
程序开发 102脚本编程语言 36地图相关 7Epub电子图书工具 109UI组件库 16代码生成工具 25SVG开发包 17推荐引擎 3指纹识别 23拼音转换工具包 24蓝牙开发 295GUI开发框 ...
- C++中的智能指针(auto_ptr)
实际上auto_ptr 仅仅是C++标准库提供的一个类模板,它与传统的new/delete控制内存相比有一定优势.使用它不必每次都手动调用delete去释放内存.当然有利也有弊,也不是全然完美的. 本 ...
- iOS开发中关于本地数据中SQLite数据库常用的SQL语句
创建表 CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS "student" ("number" INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCRE ...
- C语言中关于scanf函数的用法
scanf()函数的控制串 函数名: scanf 功 能: 执行格式化输入 用 法: int scanf(char *format[,argument,...]); scanf()函数是通用终端格式化 ...
- uva 10330 - Power Transmission(网络流)
uva 10330 - Power Transmission 题目大意:最大流问题. 解题思路:増广路算法. #include <stdio.h> #include <string. ...
- 闲扯 Javascript 00
引言 Javascript 的作用在此就不阐述了,相信你已经知道它的用途!那我说点什么呢? 不如就和大家先扯一把,后面的工作 随后后展开吧! 首先声明:我个人对Javascript 认识,我只知道它 ...
- CentOS安装postgresql 9.4
第一步:在CentOS6.5下安装Postgresql 1. 安装PostgreSQL源 # yum install http://yum.postgresql.org/9.4/redhat/rhel ...
- 三、IF...ELSE和缩进
IF...ELSE和缩进 根据用户输入的不同做不同的事情 注意语法结尾的冒号. 例1: name = input("Please input your name:") if nam ...
- 一天一个类--ArrayList之二
继续我的小激动--- 1.看看构造一个ArrayList 有两种方式 一个指定大小,一个不指定.我们知道他其实使用数组来实现了,数组肯定要有大小,那么他没指定大小,默认的是多少呢???追踪源码---开 ...
