Fragment详解
1 Fragment简介
1.1 Fragment的设计初衷
Android3.0引入Fragment的初衷是为大屏幕的设备提供更加灵活的动态UI设计,由于大屏设备可以容纳更多的UI组件,且这些UI组件之间存在交互关系。Fragment简化了大屏UI的设计,它不需要开发者guan'li管理组件包含关系的复杂变化,开发者使用Fragment对UI组件进行分组、模块化管理,可以更方便的动态更新Activity的用户界面。
1.2 Fragment特征
Fragment必须被“嵌入”Activity中使用,因此虽然Fragment也拥有自己的生命周期,但是Fragment的生命周期会受到它所在的Activity的生命周期控制:当Activity暂停时,其中所有的Fragment也暂停;当Activity被销毁时,其中所有的Fragment都会被销毁;只有当该Activity处于活动状态时,程序员可以通过方法独立操作Fragment。Fragment
具有如下特征:
- Fragment总是作为Activity界面的重要组成部分。Fragment可调用getActivity()方法获得它所在的Activity;Activity可以调用FragmentManager的findFragmentById()或者findFragmentByTag()的方法来获取Fragment
- 在Activity运行过程中,可以调用FragmentManager的add()、remove()、replace()方法动态地添加、删除或替换Fragment
- 一个Activity可以同时组合多个Fragment,反过来,一个Fragment也可以为多个Activity复用;一个Fragment也可以为同一个Activity复用
- Fragment可以响应自己的输入事件,并拥有自己的生命周期,但是他的生命周期为Activity所控制
1.3 Fragment的类继承关系
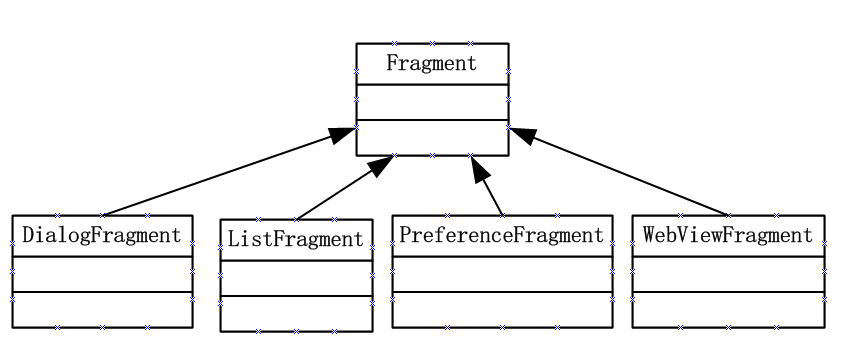
2 创建Fragment
开发Fragment与开发Activity非常相似,区别只是开发两者继承的类分别为Activity及其子类/Fragment及其子类。需要将原来写在Activity中的回调方法也需要在Fragment中实现。创建Fragment通常需要实现如下三个方法:创建时的回调方法onCreate()、绘制界面时的回调方法onCreateView()、用户离开Fragment时的回调方法onPause()
2.1 静态Fragment
使用Fragment最简单的一种方式,把Fragment当成普通的控件,直接写在Activity的布局文件中。步骤:
- 继承Fragment,重写onCreateView决定Fragemnt的布局
- 在Activity中声明此Fragment,就当和普通的View一样
2.2 动态Fragment
Activity中的Fragment可以动态的添加、删除、更新。
- <include
- android:id="@+id/id_ly_bottombar"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="55dp"
- android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
- layout="@layout/bottombar" />
注意:layout布局文件中包含子布局文件,用<include>元素
3 Fragment与Activity之间数据传输
3.1 对象的获取
将Fragment添加到Activity之后,Fragment必须与Activity交互信息,这就需要两者能在各自的空间中获取对方的对象。
- Fragment获取它所在的Activity:调用Fragment的getActivity()方法 ,即可获得它所在的Activity
- Activity获取它包含的Fragment:调用Activity关联的FragmentManager的findFragmentById(int id)或findFragmentByTag(String tag)方法即可获取指定的Fragment
3.2 数据的传递
- Activity向Fragment传递数据:在Activity中创建Bundle数据包,并调用Fragment的setArguments(Bundle bundle)方法即可将Bundle的数据包传给Fragment
- Fragment向Activity传递数据,或者是Fragment在运行中要与Activity实时通信:在Fragment中定义一个内部回调接口,再让包含该Fragment的Activity实现该回调接口,这样Fragment可以调用该回调接口将数据传给Activity
示例:
Activity文件:
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle; public class SelectBookActivity extends Activity implements
BookListFragment.Callbacks
{
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// 加载/res/layout目录下的activity_book_twopane.xml布局文件
setContentView(R.layout.activity_book_twopane);
}
//实现Callbacks接口必须实现的方法,实现此方法从Fragment取数据
@Override
public void onItemSelected(Integer id) {
///Activity向BookDetailFragment发送数据 Bundle arguments = new Bundle();
arguments.putInt(BookDetailFragment.ITEM_ID, id);
BookDetailFragment fragment = new BookDetailFragment();
// 向Fragment传入参数
fragment.setArguments(arguments);
// 使用fragment替换book_detail_container容器当前显示的Fragment
getFragmentManager().beginTransaction()
.replace(R.id.book_detail_container, fragment)
.commit();
}
}
向Activity发送数据的BookListFragment文件
import android.app.ListFragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.ArrayAdapter;
import android.widget.ListView; public class BookListFragment extends ListFragment {
private Callbacks mCallbacks; // 定义一个回调接口,该Fragment所在Activity需要实现该接口
// 该Fragment将通过该接口与它所在的Activity交互
public interface Callbacks {
void onItemSelected(Integer id);
} @Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// 为该ListFragment设置Adapter
setListAdapter(new ArrayAdapter<>(getActivity(),
android.R.layout.simple_list_item_activated_1,
android.R.id.text1, BookContent.itemList));
} // 当该Fragment从它所属的Activity中被删除时回调该方法
@Override
public void onDetach() {
super.onDetach();
// 将mCallbacks赋为null。
mCallbacks = null;
} // 当用户点击某列表项时激发该回调方法
@Override
public void onListItemClick(ListView listView
, View view, int position, long id) {
super.onListItemClick(listView, view, position, id);
// 获取Activity对象,以调用Callbacks回调方法
mCallbacks = (Callbacks) getActivity();
mCallbacks.onItemSelected((int)id);
}
}
从Activity接收数据的BookDetailFragment文件
import android.app.Fragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.TextView; public class BookDetailFragment extends Fragment {
public static final String ITEM_ID = "item_id";
BookContent.Book book;
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View rootView = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_book_detail, container, false);
//Fragment接收Activity传输过来的数据
Bundle bd = getArguments();
book = BookContent.itemList.get(bd.getInt(ITEM_ID));
((TextView) rootView.findViewById(R.id.book_title)).setText(book.title);
((TextView) rootView.findViewById(R.id.book_desc)).setText(book.desc);
return rootView;
}
}
Activity布局文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!-- 定义一个水平排列的LinearLayout,并指定使用中等分隔条 -->
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_marginLeft="16dp"
android:layout_marginRight="16dp"
android:divider="?android:attr/dividerHorizontal"
android:showDividers="middle">
<!-- 添加一个Fragment -->
<fragment
android:name="com.example.penghuster.fragmenttest.BookListFragment"
android:id="@+id/book_list"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1" />`
<!-- 添加一个FrameLayout容器 -->
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/book_detail_container"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="2" />
</LinearLayout>
DetailFragment布局文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<!-- 定义一个TextView来显示图书标题 -->
<TextView
android:id="@+id/book_title"
style="?android:attr/textAppearanceLarge"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="哈地方"
android:padding="16dp" />
<!-- 定义一个TextView来显示图书描述 -->
<TextView
android:id="@+id/book_desc"
style="?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:padding="16dp" />
</LinearLayout>
4 Fragment管理与Fragment事物
4.1 FragmentManager
- 使用Activity关联的FragmentManager的findFragmentById(int id)或findFragmentByTag(String tag)方法即可获取指定的Fragment
- 调用popBackStack()方法将Fragment从后台中弹出(模拟用户按下Back按钮)
- 调用addOnBackStackChangeListener()注册一个监听器,用于监听后台的变化
4.2FragmentTransaction
如果需要添加,删除,替换Fragment,则需要通过FragmentTransaction对象
5 Fragment的生命周期
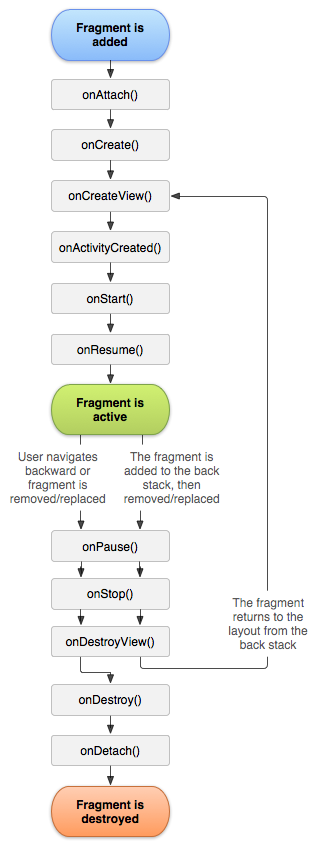
Fragment详解的更多相关文章
- Fragment详解之三——管理Fragment(1)
相关文章: 1.<Fragment详解之一--概述>2.<Fragment详解之二--基本使用方法>3.<Fragment详解之三--管理Fragment(1)>4 ...
- android——fragment详解
在android开发过程中,如果使用到了导航栏.那么不可避免的就需要使用fragment来处理界面.闲着没事,就详解一下Framgent的使用方法吧. 难得写一次.本人 shoneworn shone ...
- Android面试收集录4 Fragment详解
1.什么是Fragment? 你可以简单的理解为,Fragment是显示在Activity中的Activity. 它可以显示在Activity中,然后它也可以显示出一些内容. 因为它拥有自己的生命周期 ...
- Android 开发 之 Fragment 详解
本文转载于 : http://blog.csdn.net/shulianghan/article/details/38064191 本博客代码地址 : -- 单一 Fragment 示例 : http ...
- 5. Fragment详解
onCreateView是Fragment生命周期方法中最重要的一个.因为在该 方法中会创建在Fragment中显示的View. public View onCreateView(LayoutInfl ...
- Android Fragment详解
一.什么是Fragment Android在3.0中引入了fragments的概念,主要目的是用在大屏幕设备上--例如平板电脑上,支持更加动态和灵活的UI设计.平板电脑的屏幕要比手机的大得多,有更多的 ...
- Android Fragment 详解(一)
Android从3.0开始引入fragment,主要是为了支持更动态更灵活的界面设计,比如在平板上的应用.平板机上拥有比手机更大的屏幕空间来组合和交互界面组件们.Fragment使你在做那样的设计时, ...
- Android Fragment详解(二):Fragment创建及其生命周期
Fragments的生命周期 每一个fragments 都有自己的一套生命周期回调方法和处理自己的用户输入事件. 对应生命周期可参考下图: 创建片元(Creating a Fragment) To c ...
- Android Fragment详解(一):概述
Fragment是activity的界面中的一部分或一种行为.你可以把多个Fragment们组合到一个activity中来创建一个多面界面并且你可以在多个activity中重用一个Fragment.你 ...
随机推荐
- PNG优化/压缩
我们总是希望 PNG 图像的容量能够小些.小些.再小些.优化 PNG 图像,可以用以下几个工具: 1.Optipng Optipng 是命令行工具,直接在其后追加所需优化的 PNG 图像即可 2.Pn ...
- IntelliJ idea 中使用Git
1.要使用GitHub,首先你需要下载一个Git(地址:http://windows.github.com/)这里使用的是for Windows,然后安装完成会得到如下的一个目录:
- RedMine项目管理系统邮件推送设置(Windows环境)
RedMine项目管理系统有邮箱推送功能,当Bug,安全漏洞等内容被修改.解决.评论的时候,系统会通过邮件 及时的通知你的团队和客户.邮件通知的环节.形式.时间.接受人均可定制,功能十分实用. 下面是 ...
- 理解 PHP 中的 Streams
Streams 是PHP提供的一个强有力的工具,我们常常在不经意会使用到它,如果善加利用将大大提高PHP的生产力. 驾驭Streams的强大力量后,应用程序将提升到一个新的高度. 下面是PHP手册中对 ...
- 信息学院第九届ACM程序设计竞赛题解
A: 信号与系统 Time Limit: 1000 MS Memory Limit: 65536 KBTotal Submit: 238 Accepted: 44 Page View: 69 Des ...
- system CPU占用率过高与91助手的关系
今天正在认真工作,忽然发现电脑越来越慢. 按 CTRL+ALT+DEL打开任务管理器看了下CPU使用率.其中system占用率居然达到了64%.不对劲儿,按照平时习惯,system根本占用了不要这么多 ...
- 在Oracle中更新数据时,抛出:ORA-01008: not all variables bound
在Oracle中更新数据时,抛出了一个 :ORA-01008 not all variables bound, 我的理解是不是所有的变量/参数都有边界,不懂: 后来知道了,原来是“不是所有变量/参数都 ...
- MySQL 存储过程删除大表
1.权限问题 alter routine 编辑或删除存储过程 create routine 建立存储过程 execute 创建存储过程 2.存储过程相关的一些命令 show procedure sta ...
- visual studio 2012 update3
http://www.microsoft.com/zh-cn/download/confirmation.aspx?id=39305
- Datatable转成Json方式两则
1, Asp.net C# 使用Newtonsoft.Json 实现DataTable转Json格式数据 1.这里下载:http://www.newtonsoft.com/products/json/ ...
