Spring (IOC)配置
就是这个东西,里面的不同标签,所代表的不同含义

beans 里面有很多的bean ,每一个bean都是容器里面的一个对象
1.别名alias (另外的一个名字)


XML
<alias name="cons_01" alias="constructor01"/> java
// Constructor_01 cons_01 = (Constructor_01)context.getBean("cons_01");
Constructor_01 cons_01 = (Constructor_01)context.getBean("constructor01");
2.bean的配置
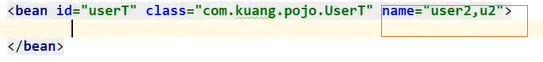
id :唯一的标识符
class :bean对象所对应的全限定名(包名+类名)
name :也是别名,更高级,可以取多个名字 (可以通过空格和逗号和分号分割)
3.import(一般用于团队开发,可以将多个配置文件导入合并为一个)
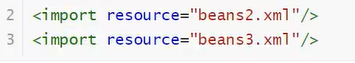
多个人开发,不同的类,需要注册在不同的beans(任意名)中,可以利用import将所有人的beans.xml合并为一个总的 ,最后使用总的就行
重名的话后面导入的会覆盖前面的
依赖注入

1.构造器注入(利用构造器[无参或有参]创建对象)
2.Set方式注入[重点] 依赖注入
依赖:bean对象的创建依赖于容器
注入:bean对象中的所有属性,由容器来注入(相关的xml 的配置文件)


<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="adress" class="com.ljm.pojo.Address">
<!-- 不写的话就为null-->
<property name="address" value="银河街道866号"/> </bean>
<!-- p命名控件注入,可以直接注入属性的值 (property)-->
<bean id="user" class="com.ljm.pojo.User" p:age="18" p:name="小明"/> <bean id="student" class="com.ljm.pojo.Student">
<!-- 普通值注入 依靠set方法注入 -->
<property name="name" value="鸣人"/>
<!-- bean注入使用ref-->
<property name="address" ref="adress"/>
<!-- 数组注入-->
<property name="books">
<array>
<value>红楼梦</value>
<value>西游记</value>
<value>三国演义</value>
</array>
</property>
<!--List-->
<property name="hobbys">
<list>
<value>唱</value>
<value>跳</value>
<value>rap</value>
</list>
</property>
<!-- map-->
<property name="card">
<map>
<entry key="农业银行" value="123"/>
<entry key="平安银行" value="456"/>
<entry key="招商银行" value="789"/>
</map>
</property>
<!-- set-->
<property name="games">
<set>
<value>LOL</value>
<value>DNF</value>
<value>CF</value>
</set>
</property>
<!-- 空字符串value="" ; null则是下面的方法-->
<property name="wife">
<null/>
</property>
<!-- Properties key=value-->
<property name="info">
<props>
<prop key="学号">215845244</prop>
<prop key="性别">男</prop>
<prop key="姓名">里番</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean> <!-- more bean definitions go here --> </beans>
44
3.利用p命名空间:可以直接给属性赋值


<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean name="john-classic" class="com.example.Person">
<property name="name" value="John Doe"/>
<property name="spouse" ref="jane"/>
</bean>
<!-- 还可以ref引用其他bean对象-->
<bean name="john-modern"
class="com.example.Person"
p:name="John Doe"
p:spouse-ref="jane"/> <bean name="jane" class="com.example.Person">
<property name="name" value="Jane Doe"/>
</bean>
</beans>
4.利用c命名空间:可以利用构造器注入


<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="thingOne" class="x.y.ThingTwo"/>
<bean id="thingTwo" class="x.y.ThingThree"/> <!-- traditional declaration -->
<bean id="thingOne" class="x.y.ThingOne">
<constructor-arg ref="thingTwo"/>
<constructor-arg ref="thingThree"/>
<constructor-arg value="[emailprotected]"/>
</bean> <!-- c-namespace declaration -->
<bean id="thingOne" class="x.y.ThingOne" c:thingTwo-ref="thingTwo" c:thingThree-ref="thingThree" c:email="[emailprotected]"/> </beans>
Bean的自动装配
自动装配是Spring满足bean依赖的一种方式
Spring会在上下文中自动寻找,并自动给bean装配属性
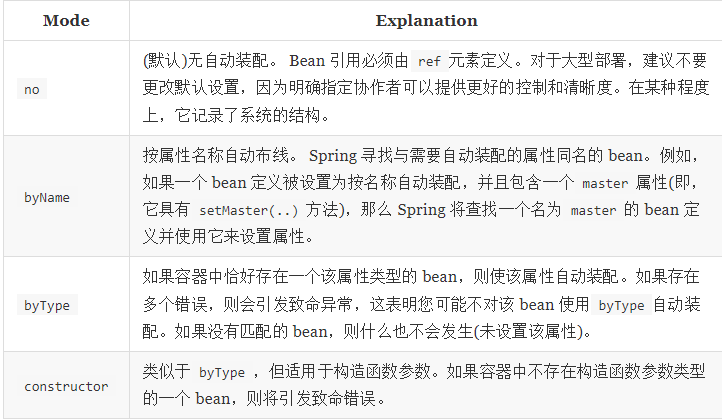
3种装配的方式
1.在XML中显示的配置
2.在java中显示配置
3.隐式的自动装配 [重要的]
基于上下文来判断


<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="cat" class="com.ljm.pojo.Cat"/>
<bean id="dog" class="com.ljm.pojo.Dog"/>
<bean id="people" class="com.ljm.pojo.People" autowire="byType">
<property name="name" value="银河"/>
</bean>
</beans>

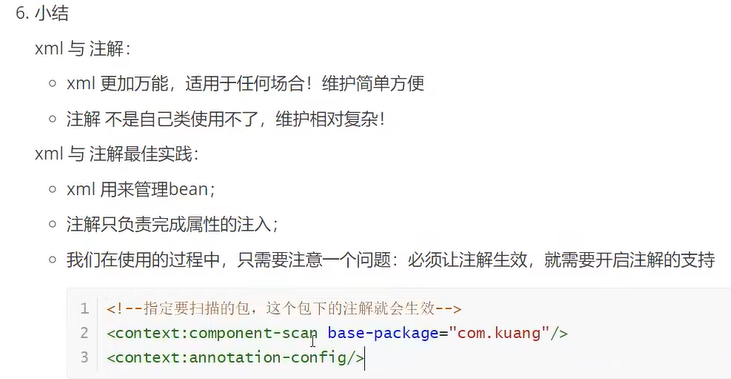
1.9使用注解实现自动装配(满足bytype和byname任意一方就行)
jdk 1.5 支持的注解 Spring2.5就支持注解
需要aop的包
Spring 允许以非侵入方式使用 注解,而无需接触目标组件的源代码,并且就工具而言,Spring 工具套件支持所有配置样式。


<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <context:annotation-config/> </beans>
具体实现, 因为是用反射机制赋予值, set方法可以省略(自动装配的属性在IOC[spring]容器中存在)


XML
<context:annotation-config/> <bean id="cat" class="com.ljm.pojo.Cat"/>
<bean id="dog" class="com.ljm.pojo.Dog"/>
<bean id="people" class="com.ljm.pojo.People"/> .java
//spring的注解 (常用)
@Autowired
@Qualifier(value = "cat15")
// 当自动装配的2个条件都不满足时.可以指定容器中的某个id
private Cat cat;
@Autowired(required = false)
//对象可以为空 容器中可以不装配相关对象 ,默认是true不为空
private Dog dog; //java的注解 (功能差不多)
@Resource
private Cat cat;
//多个id匹配最像的那个 cat √ cat11 ×
@Resource (name="cat2")
// 当自动装配的2个条件都不满足时.可以指定容器中的某个id
private Cat cat;
可以使用在属性上,也可以在set方法上


@Component


Spring (IOC)配置的更多相关文章
- Spring学习笔记之三----基于Annotation的Spring IOC配置
使用Annotation 来创建Bean有两种方式 在配置类中创建bean(配置类是指标注为@Configuration的类),在配置类中每一个创建bean的方法都应该标注为@Bean,可以在@Bea ...
- Spring学习笔记之一----基于XML的Spring IOC配置
1. 在spring配置文件中,如果对一个property进行直接赋值,可使用<value>元素,spring负责将值转化为property指定的类型:也可以直接在property元素上使 ...
- Spring IOC配置与应用
1. FAQ:不给提示: a) window – preferences – myeclipse – xml – xml catalog b) User Specified E ...
- 小马哥讲Spring栈核心编程思想 Spring IoC+Bean+Framework
小马哥出手的Spring栈核心编程思想课程,可以说是非常专业和权威的Spring课程.课程主要的方向与核心是Spring Framework总览,带领同学们重新认识重新认识IoC,Spring IoC ...
- [原创]java WEB学习笔记101:Spring学习---Spring Bean配置:IOC容器中bean的声明周期,Bean 后置处理器
本博客的目的:①总结自己的学习过程,相当于学习笔记 ②将自己的经验分享给大家,相互学习,互相交流,不可商用 内容难免出现问题,欢迎指正,交流,探讨,可以留言,也可以通过以下方式联系. 本人互联网技术爱 ...
- Spring IOC的配置使用(转)
转:http://www.cnblogs.com/linjiqin/p/3408306.html Spring IOC的配置使用 1.1.1 XML配置的结构一般配置文件结构如下: <beans ...
- Spring IOC之基于JAVA的配置
基础内容:@Bean 和 @Configuration 在Spring中新的支持java配置的核心组件是 @Configuration注解的类和@Bean注解的方法. @Bean注解被用于表明一个方法 ...
- Spring IOC之基于注解的容器配置
Spring配置中注解比XML更好吗?基于注解的配置的介绍提出的问题是否这种途径比XML更好.简单来说就是视情况而定. 长一点的答案是每一种方法都有自己的长处也不足,而且这个通常取决于开发者决定哪一种 ...
- Spring IOC的配置使用
1.1.1 XML配置的结构一般配置文件结构如下: <beans> <import resource=”resource1.xml” /> <bean id=”bean1 ...
随机推荐
- dp:最长非递减序列
#include <iostream.h> void main() { int i,j,a[14]={5,6,-6,-1,9,10,-5,-3,16,4,3,-4,-3,5}; int d ...
- Java时间处理类LocalDate和LocalDateTime常用方法
Java时间处理类LocalDate和LocalDateTime常用方法 https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42579074/article/details/93721757
- MySQL 获取每月多少日的sql写法
# 写法1 指定 年月 的共有多少日 select DATEDIFF(DATE_ADD(CONCAT( 2020, '-', '03','-','01'),INTERVAL 1 MONTH),CONC ...
- gradle构建scala
1. 在目录下创建build.gradle文件,内容为: apply plugin: 'idea' apply plugin: 'scala' repositories { mavenLocal() ...
- java-doc注释详解
注释的分类 // 注释一行/* ...... */ 注释若干行/** ...... */ 注释若干行,并写入 javadoc 文档 列子 /** * show 方法的简述. * <p>sh ...
- 常见算法的时间复杂度(大O计数法)
定义 对于不同的机器环境而言,确切的单位时间是不同的,但是对于算法进行多少个基本操作(即花费多少时间单位)在规模数量级上却是相同的,由此可以忽略机器环境的影响而客观的反应算法的时间效率. 对于算法 ...
- 学习 Haproxy (四)
一. haproxy 的安装配置 # cat /etc/redhat-release CentOS release 6.6 (Final) # uname -r 2.6.32-504.el6.i686 ...
- Netty学习摘记 —— 单元测试
本文参考 本篇文章是对<Netty In Action>一书第九章"单元测试"的学习摘记,主要内容为使用特殊的 Channel 实现--EmbeddedChannel来 ...
- Numpy怎样给数组增加一个维度
Numpy怎样给数组增加一个维度 背景:很多数据计算都是二维或三维的,对于一维的数据输入为了形状匹配,经常需升维变成二维 需要:在不改变数据的情况下,添加数组维度:(注意观察这个例子,维度变了,但数据 ...
- Blog Ideas
Blog Ideas How-to Post Case Studies Product + Service Updates Product Reviews Content Survey Current ...
