大根堆的pop&remove&initialize
1. 定义
- [max(min) tree] 一棵树, 其中每个节点的值都大于 (小于) 或等于其 children (如果有) 的值.
- [max(min) heap] max(min) tree + complete binary tree.
2. 性质
- heap 是一种 隐式数据结构 (implicit data structure).
用 完全二叉树 表示的 heap 在数组中 隐式储存 (没有明确的指针或其他数据能够用来重塑这种结构).
由于没有储存 结构信息, 这种表示方法的空间利用率很高 (没有浪费任何空间); 又由于用数组形式储存, 它的时间效率也很高. - 由于是 完全二叉树, 自然满足如下性质:
- 若一颗 complete binary tree 有 \(n\) 个元素, 那么它的高度为 \(\log_2 (n+1)\) .
- 设一颗 complete binary tree 中一元素的编号为 \(i\) , \(1 \leq i \leq n\) , 则有以下关系:
- 若 \(i = 1\) , 则该元素为二叉树的 root; 若 \(i>1\) , 则其 parent 的编号为 \(\lceil i/2 \rceil\) .
- 若 \(2i>n\) , 则该元素无 left child; 否则, 其 left child 的编号为 \(2i\) .
- 若 \(2i+1>n\) , 则该元素无 right child; 否则, 其 right child 的编号为 \(2i+1\) .
3. 大根堆的 pop & remove
3.1. 核心逻辑 & 发现问题
不失一般性, 存在如下图一个大根堆.
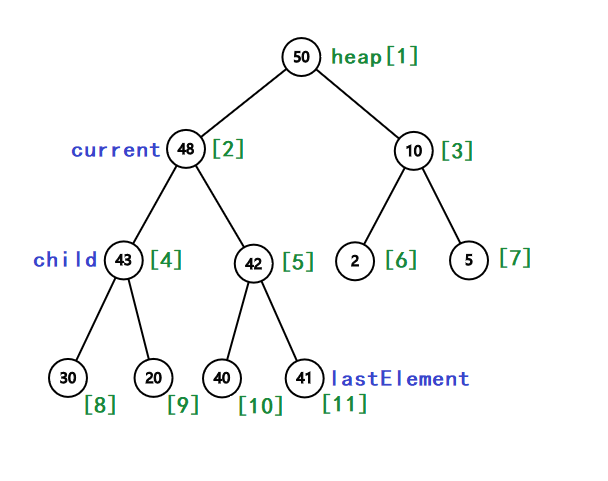
假设现在要删除 heap[current], 那么我们要做的核心步骤是:
- 将
heap[current]的 children 中较大的那个 (我们假设那个结点是heap[child]) 移动到heap[current]的位置;
这时 heap[child] 相当于 "空" 的状态,
因此顺理成章地利用递归或迭代, 再把 heap[child] 当作新的 heap[current] 而反复执行核心步骤.
应当将 child 小于 heapSize 作为限制 iteration 或 recursion 继续进行的条件.
然而, 如果我们使用上述逻辑 pop 上图中的 heap[1]:
- 48 填入
heap[1]; - 43 填入
heap[2]; - 30 填入
heap[4]; heap[8]为空;
为满足 定义 1 和 定义 2, 此时若将 lastElement = 41 填入 heap[8], 则 heap[4] = 30 小于 heap[8] = 41, 与 定义 1 产生冲突.
为什么会出现这样的问题呢?
根据 定义 1:
[max(min) tree] 一棵树, 其中每个结点的值都大于(小于)或等于其 children (如果有)的值.
我们应该明确一点:
- 整体上, 大根树中下层元素不一定大于上层元素, 而只是每个结点要大于自己所有的 descendent.
如上图, 尽管 heap[11] 在 level 4; 但仍比处于 level 2 的 heap[3] 大.
这就是为什么在 pop 或者 remove 时, 我们需要更加复杂的方法进行 重构.
3.2. 重构大根堆
2.1. 提出的问题不建议使用 recursion 解决; 因为如果用 iteration, 只要在循环体中添加一步简单的判断就即可.
再次观察前文的大根堆:

我们发现, 冲突的产生本质上是因为,
尽管 heap[4] 是 silblings 中较大的那个, 但它的 child heap[8] 并没有其 sibling (也就是 heap[5]) 的 child heap[11] = lastElement 大.
那么, 我们只要在保持核心逻辑的同时, 一旦发现 heap[current] 的较大 child 比 lastElement 小, 那就结束循环, 把 lastElement 填入 heap[current]! 后面的就不用管了!
如果没找到......那就继续循环, 循环到底, 把 lastElement 填到最下面就好.
3.3. 代码实现
- pop最顶端元素(root).
template<class T>
void maxHeap<T>::pop() {
if (heapSize == 0) throw queueEmpty();
// Delete the largest element.
heap[1].~T();
// Delete the last element and re-construct the heap.
T lastElement = heap[heapSize];
heap[heapSize--].~T();
// Starting from the root, find location for the last element.
int current = 1,
child = 2;
// Loop until the end.
while (child <= heapSize) {
// "child" should be the larger child of "current"
if (child < heapSize && heap[child] < heap[child + 1]) { child++; }
// IF: "current" points to a node whose child is smaller than "lastElement",
// indicating that "lastElement" can be put in "heap[current]".
if (lastElement >= heap[child]) {
// End loop.
break;
}
// OTHERWISE.
else {
heap[current] = heap[child];
current = child;
// Move "child" to its child.
child << 1;
}
}
heap[current] = lastElement;
}
- remove下标为 i 的元素.
template<class T>
T maxHeap<T>::remove(int i) {
if (heapSize == 0) throw queueEmpty;
T theDeleted = heap[i];
T lastElement = heap[heapSize];
heap[heapSize].~T();
int current = i, child = i << 1;
while (child <= heapSize) {
// Make sure "child" points to the larger one between the sublings.
if (child < heapSize && heap[child] < heap[child + 1]) {
child++;
}
// IF: "current" points to a node whose child is smaller than "lastElement",
// indicating that "lastElement" can be put in "heap[current]".
if (lastElement >= heap[child]) {
// End loop.
break;
}
// OTHERWISE.
else {
heap[current] = heap[child];
current = child;
child <<= 1;
}
}
heap[current] = lastElement;
return theDeleted;
}
3.4. 复杂度分析
对于方法 pop, 遍历只迭代至 left/right child, 因此时间复杂度为:
\]
方法 remove 的复杂度取决于目标 node 的 descendent 的数量.
4. Initialize
4.1. 逻辑分析
root 从最后一个 node 的 parent node 开始向根迭代, 直至 max heap 真正的根;
对于迭代中的每个 root, child 从其 child node 开始向 descendent 迭代 (迭代需要保证 child 指向 siblings 中较大的那个):
- 若
rootElement小于child的元素, 则child继续向 descendent 迭代, 同时将child的元素覆盖至child/2; - 若
rootElement大于等于child的元素, 则child终止迭代, 同时将rootElement存入child/2;
4.2. 代码实现
template<class T>
void maxHeap<T>::initialize(T* theHeap, int theSize)
{
delete[] heap; // Empty the memory of "T* maxHeap<T>::heap".
heap = theHeap; // Make "heap" points to "theHeap".
heapSize = theSize; // Set the "heapSize".
// 'root' would iterates from {heapSize/2 (parent of the last element)} and keep decreasing until reaches real root.
for (int root = heapSize / 2; root >= 1; root--) {
// Pick up the current element of 'root'.
T rootElement = heap[root];
int child = 2 * root;
// 'child' iterates from the child of current root to end, but cannot be larger than 'heapSize'.
for (; child <= heapSize; child *= 2) {
// Ensure 'heap[child]' is the larger one between the siblings.
if (child < heapSize && heap[child] < heap[child + 1]) { child++; }
if (rootElement >= heap[child]) { // IF: 'rootElement' can be put in 'heap[child/2]'.
break;
}
// IF: "rootElement" cannot be put in "heap[child/2]".
// Move 'heap[child]' to 'heap[child/2]'.
heap[child/2] = heap[child];
// Re-allocate the next level to 'child'.
}
heap[child / 2] = rootElement;
}
}
4.3. Complexity
假设元素个数为 \(n\), 高度为 \(h\).
- 由于外层 for 循环
root从 \(n/2\) 开始迭代, 因此从元素上看总共迭代了 \(n/2\) 次, 从层数上看总共迭代了 \(h-1\) 层. - 内层 for 循环的每次迭代, 实际上都遍历了一棵 complete binary tree, 复杂度为 \(O(h_{i})\). 其中 \(h_{i}\) 是该层 complete binary tree 的高度.
- binary tree 的第 \(j\) 层, 最多有 \(2^{j-1}\) 个 node; 而每个 node 的高度 \(h_{i}=h-j+1\).
\]
因为有 \(n\) 个元素的 complete binary tree 的高度为 \(h= \lceil \log_{2}{(n+1)} \rceil\), 因此:
\]
由于外层 for 循环从元素上看迭代了 \(n/2\) 次, 所以复杂度下限为 \(\Omega(n)\).
综上, 方法 initialize 的复杂度为:
\]
Reference | Data Structures, Algoritms, and Applications in C++, Sartaj Sahni
大根堆的pop&remove&initialize的更多相关文章
- CJOJ 2482 【POI2000】促销活动(STL优先队列,大根堆,小根堆)
CJOJ 2482 [POI2000]促销活动(STL优先队列,大根堆,小根堆) Description 促销活动遵守以下规则: 一个消费者 -- 想参加促销活动的消费者,在账单下记下他自己所付的费用 ...
- poppo大根堆的原理与实现。
大根堆的定义:1 大根堆是一个大根树 2 大根堆是一个完全二叉树 所以大根堆用数组表示是连续的,不会出现空白字段. 对于大根堆的插入 对于大根堆的插入,可以在排序前确定大根堆的形状,可以确定元素5从位 ...
- bzoj 1577: [Usaco2009 Feb]庙会捷运Fair Shuttle——小根堆+大根堆+贪心
Description 公交车一共经过N(1<=N<=20000)个站点,从站点1一直驶到站点N.K(1<=K<=50000)群奶牛希望搭乘这辆公交车.第i群牛一共有Mi(1& ...
- 51nod K 汽油补给 大根堆+小根堆....
题目传送门 用优先队列瞎搞... 想着在每个地方 先算上一个点到这一个点要花费多少钱 这个用小根堆算就好 然后在这个地方加油 把油钱比自己多的替代掉 这个用大根堆维护一下 然后两个堆之间信息要保持互通 ...
- bzoj 5495: [2019省队联测]异或粽子【可持久化trie+大根堆】
和bzoj4504差不多,就是换了个数据结构 像超级钢琴一样把五元组放进大根堆,每次取一个出来拆开,(d,l,r,p,v)表示右端点为d,左端点区间为(l,r),最大区间和值为v左端点在p上 关于怎么 ...
- bzoj 4504: K个串【大根堆+主席树】
像超级钢琴一样把五元组放进大根堆,每次取一个出来拆开,(d,l,r,p,v)表示右端点为d,左端点区间为(l,r),最大区间和值为v左端点在p上 关于怎么快速求区间和,用可持久化线段树维护(主席树?) ...
- TJOI2013 奖学金—大根堆实现(洛谷P3963)
奖学金 题目描述 小张学院有 \(c\) 名学生,第 \(i\) 名学生的成绩为 \(ai\) ,要获得的奖学金金额为 \(bi\) . 要从这 \(c\) 名学生中挑出 \(n\) 名学生发奖学金 ...
- priority_queue()大根堆和小根堆(二叉堆)
#include<iostream> #include <queue> using namespace std; int main() { //对于基础类型 默认是大顶堆 pr ...
- AtCoder Beginner Contest 249 F - Ignore Operations // 贪心 + 大根堆
传送门:F - Keep Connect (atcoder.jp) 题意: 给定长度为N的操作(ti,yi). 给定初值为0的x,对其进行操作:当t为1时,将x替换为y:当t为2时,将x加上y. 最多 ...
随机推荐
- windows如何结束某个端口的进程
netstat -ano | findstr 端口号 (查询端口号被哪个进程占用) tasklist | findstr 进程PID (根据PID找到进程名称) taskkill -PID 进程PID ...
- 手写一个模拟的ReentrantLock
package cn.daheww.demo.juc.reentrylock; import sun.misc.Unsafe; import java.lang.reflect.Field; impo ...
- React报错之Cannot find name
正文从这开始~ .tsx扩展名 为了在React TypeScript中解决Cannot find name报错,我们需要在使用JSX文件时使用.tsx扩展名,在你的tsconfig.json文件中把 ...
- 使用python3.7和opencv4.1来实现人脸识别和人脸特征比对以及模型训练
原文转载自「刘悦的技术博客」https://v3u.cn/a_id_126 OpenCV4.1已经发布将近一年了,其人脸识别速度和性能有了一定的提高,这里我们使用opencv来做一个实时活体面部识别的 ...
- 【PMP学习笔记】第4章 项目整合管理
[PMP学习笔记]第4章 项目整合管理 一.项目整合管理 什么是项目整合管理? 项目整合管理由项目经理负责.虽然其他知识领域可以由相关专家(如成本分析专家.进度规划专家.风险管理专家)管理,但是项目整 ...
- 论语音社交视频直播平台与 Apache DolphinScheduler 的适配度有多高
在 Apache DolphinScheduler& Apache ShenYu(Incubating) Meetup 上,YY 直播 软件工程师 袁丙泽 为我们分享了<YY直播基于Ap ...
- BZOJ4569 [Scoi2016]萌萌哒(并查集,倍增)
类似\(ST表\)的思想,倍增\(log(n)\)地合并 你是我家的吗?不是就来呀啦啦啦.还有要来的吗?没了!那有多少个家就映射多少答案呀 倍增原来这么好玩 #include <iostream ...
- Redis 09 基数
参考源 https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1S54y1R7SB?spm_id_from=333.999.0.0 版本 本文章基于 Redis 6.2.6 概述 Redi ...
- Spring 02 控制反转
简介 IOC IOC(Inversion of Control),即控制反转. 这不是一项技术,而是一种思想. 其根本就是对象创建的控制权由使用它的对象转变为第三方的容器,即控制权的反转. DI DI ...
- 神器 利器 Typora
用typora编辑真的实在太爽了! gooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooood! 支持html可以实现好看的排版! 支持latex实在是太棒了! 不过默认不支持,要去首选项里 ...
