pymysql和MySQLdb
MySQLdb创建mysql数据库表
其实mysqldb创建表是有限制的,要求是5.1-5.5版本
pymsql是Python中操作MySQL的模块,其使用方法和MySQLdb几乎相同。
1.下载
首先要下载下载:请到官方网站http://sourceforge.net/projects/mysql-python/或者点击链接下载http://downloads.sourceforge.net/project/mysql-python/mysql-python-test/1.2.3c1/MySQL-python-1.2.3c1.tar.gz?use_mirror=nchc
2.解压安装
解压:tar zxvf MySQL-python* 进入文件目录,运行以下命令:
python setup.py install
3. 用法
'''
# 打开数据库连接
db = MySQLdb.connect("192.168.72.131","root","","test" )
# 使用cursor()方法获取操作游标
cursor = db.cursor()
# 如果数据表已经存在使用 execute() 方法删除表。
cursor.execute("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS EMPLOYEE")
# 创建数据表SQL语句
sql = \"\"\"CREATE TABLE EMPLOYEE (
FIRST_NAME CHAR() NOT NULL,
LAST_NAME CHAR(),
AGE INT,
SEX CHAR(),
INCOME FLOAT )\"\"\"
cursor.execute(sql)
# 关闭数据库连接
db.close()
'''
pymsql
一、下载安装:
pip3 install pymysql
二、使用
1、执行SQL
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf- -*-
import pymysql # 创建连接
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=, user='root', passwd='', db='t1')
# 创建游标
cursor = conn.cursor() # 执行SQL,并返回收影响行数
effect_row = cursor.execute("update hosts set host = '1.1.1.2'") # 执行SQL,并返回受影响行数
#effect_row = cursor.execute("update hosts set host = '1.1.1.2' where nid > %s", (,)) # 执行SQL,并返回受影响行数
#effect_row = cursor.executemany("insert into hosts(host,color_id)values(%s,%s)", [("1.1.1.11",),("1.1.1.11",)]) # 提交,不然无法保存新建或者修改的数据
conn.commit() # 关闭游标
cursor.close()
# 关闭连接
conn.close()
2、获取新创建数据自增ID
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf- -*-
import pymysql conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=, user='root', passwd='', db='t1')
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.executemany("insert into hosts(host,color_id)values(%s,%s)", [("1.1.1.11",),("1.1.1.11",)])
conn.commit()
cursor.close()
conn.close() # 获取最新自增ID
new_id = cursor.lastrowid
3、获取查询数据
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)---》 这么写可以让返回的值为字典
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf- -*-
import pymysql conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=, user='root', passwd='', db='t1')
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute("select * from hosts") # 获取第一行数据
row_1 = cursor.fetchone() # 获取前n行数据
# row_2 = cursor.fetchmany()
# 获取所有数据
# row_3 = cursor.fetchall() conn.commit()
cursor.close()
conn.close()
注:在fetch数据时按照顺序进行,可以使用cursor.scroll(num,mode)来移动游标位置,如:
- cursor.scroll(1,mode='relative') # 相对当前位置移动
- cursor.scroll(2,mode='absolute') # 相对绝对位置移动
4、fetch数据类型
关于默认获取的数据是元祖类型,如果想要或者字典类型的数据,即:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf- -*-
import pymysql conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=, user='root', passwd='', db='t1') # 游标设置为字典类型
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
r = cursor.execute("call p1()") result = cursor.fetchone() conn.commit()
cursor.close()
conn.close()
5、插入数据注意的地方
li = tuple(['hrYjT71474436254', '2016-09-21 13:37:34']) #这句是重点
print li
sql = "insert INTO `222` VALUES {}".format(li)
print sql
cursor.execute(sql)
conn.commit()
自己造轮子, 二次封装pymysql
class base_pymysql(object):
def __init__(self, host, port, user, password, db_name=None):
self.db_host = host
self.db_port = int(port)
self.user = user
self.password = str(password)
self.db = db_name
self.conn = None
self.cursor = None def connect(self):
self.conn = pymysql.connect(host=self.db_host, port=self.db_port, user=self.user,
passwd=self.password, db=self.db, charset="utf8")
self.cursor = self.conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) class MyPymysql(base_pymysql):
"""
Basic Usage: ret = My_Pymysql('test1')
res = ret.selectone_sql("select * from aaa")
print(res)
ret.close()
--------------
class writer_information_tables():
def __init__(self, libname="metadata"):
self.libname = libname
self.res = MyPymysql('metadata') def insert_sql(self, data):
sql = '''insert INTO `meta_variable` SET DataTableID={}, VarValues="%s";'''.format(
data["DataTableID"])
value = (data["VarValues"])
# print(sql)
# self.res.idu_sql(sql)
self.res.insert_sql(sql, value=value)
def commit(self):
self.res.commit() def close(self):
self.res.close()
----------------
def CreateDataTableInfor(data):
sql = "insert into `meta_data_table` SET DataTableID='{}';".format(
data["DataTableID"])
ret = MyPymysql('metadata')
ret.idu_sql(sql)
ret.close()
--------------- Precautions:
Config.__init__(self, config_filename="my.cnf") """ def __init__(self, conf_name):
self.conf = Config().get_content(conf_name)
super(MyPymysql, self).__init__(**self.conf)
self.connect() def idu_sql(self, sql, value=None):
# adu: insert, delete, update的简写
# 考虑到多语句循环, try就不写在这里了
self.cursor.execute(sql, value)
self.conn.commit() def commit(self):
self.conn.commit() def rollback(self):
self.conn.rollback() def insert_sql(self, sql, value=None):
# adu: insert, delete, update的简写
# 防止sql注入
self.cursor.execute(sql, value)
def update_sql(self, sql, value=None):
# adu: insert, delete, update的简写
# 防止sql注入
self.cursor.execute(sql, value)
def delete_sql(self, sql, value=None):
# adu: insert, delete, update的简写
# 防止sql注入
self.cursor.execute(sql, value) def selectone_sql(self, sql):
self.cursor.execute(sql)
self.conn.commit()
return self.cursor.fetchone() def selectall_sql(self, sql):
self.cursor.execute(sql)
self.conn.commit()
return self.cursor.fetchall() def select_sql(self, sql, value=None):
# 防止sql注入
self.cursor.execute(sql, value)
self.conn.commit()
return self.cursor.fetchall() def close(self):
self.conn.close()
self.conn = None
self.cursor = None
自己造的轮子代码
class Config(object):
"""
# Config().get_content("user_information")
""" def __init__(self, config_filename="zk_css.cnf"):
file_path = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(__file__)), config_filename)
self.cf = configparser.ConfigParser()
self.cf.read(file_path) def get_sections(self):
return self.cf.sections() def get_options(self, section):
return self.cf.options(section) def get_content(self, section):
result = {}
for option in self.get_options(section):
value = self.cf.get(section, option)
result[option] = int(value) if value.isdigit() else value
return result
Config类
class base_pymysql(object):
def __init__(self, host, port, user, password, db_name=None, cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor):
self.db_host = host
self.db_port = int(port)
self.user = user
self.password = str(password)
self.db = db_name
self.conn = None
self.cursor = cursor def connect(self):
self.conn = pymysql.connect(host=self.db_host, port=self.db_port, user=self.user,
passwd=self.password, db=self.db, charset="utf8")
self.cursor = self.conn.cursor(cursor=self.cursor) class MyPymysql(base_pymysql):
"""
Basic Usage: ret = My_Pymysql('test1')
res = ret.selectone_sql("select * from aaa")
print(res)
ret.close()
--------------
class writer_information_tables():
def __init__(self, libname="metadata"):
self.libname = libname
self.res = MyPymysql('metadata') def insert_sql(self, data):
sql = '''insert INTO `meta_variable` SET DataTableID={}, VarValues="%s";'''.format(
data["DataTableID"])
value = (data["VarValues"])
# print(sql)
# self.res.idu_sql(sql)
self.res.insert_sql(sql, value=value)
def commit(self):
self.res.commit() def close(self):
self.res.close()
----------------
def CreateDataTableInfor(data):
sql = "insert into `meta_data_table` SET DataTableID='{}';".format(
data["DataTableID"])
ret = MyPymysql('metadata') 或者 MyPymysql('metadata', None), 返回结果将是两种不同的形态 {} 和 ()
ret.idu_sql(sql)
ret.close()
--------------- Precautions:
Config.__init__(self, config_filename="my.cnf") """ def __init__(self, conf_name, cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor):
self.conf = Config().get_content(conf_name)
super(MyPymysql, self).__init__(**self.conf, cursor=cursor)
self.connect() def idu_sql(self, sql, value=None):
# adu: insert, delete, update的简写
# 考虑到多语句循环, try就不写在这里了
self.cursor.execute(sql, value)
self.conn.commit() def commit(self):
self.conn.commit() def rollback(self):
self.conn.rollback() def insert_sql(self, sql, value=None):
# adu: insert, delete, update的简写
# 防止sql注入
self.cursor.execute(sql, value)
def update_sql(self, sql, value=None):
# adu: insert, delete, update的简写
# 防止sql注入
self.cursor.execute(sql, value)
def delete_sql(self, sql, value=None):
# adu: insert, delete, update的简写
# 防止sql注入
self.cursor.execute(sql, value) def selectone_sql(self, sql):
self.cursor.execute(sql)
self.conn.commit()
return self.cursor.fetchone() def selectall_sql(self, sql):
self.cursor.execute(sql)
self.conn.commit()
return self.cursor.fetchall() def select_sql(self, sql, value=None):
# 防止sql注入
self.cursor.execute(sql, value)
self.conn.commit()
return self.cursor.fetchall() def close(self):
self.conn.close()
self.conn = None
self.cursor = None
升级版, 改变返回值形态
注意:少写了一句: def close(self):里面需要增加一句: self.cursor.close() ------>忘了
class A():
def bb(self):
sql = \
"""
select * from db_metadata.meta_project limit ;
"""
data = self.pymysql.selectall_sql(sql)
return data
class DSF(A):
def __init__(self, libname="notdbMysql"):
self.libname = libname
self.pymysql = MyPymysql(self.libname)
def aa(self):
sql = \
"""
select * from db_metadata.meta_project limit ;
"""
data = self.pymysql.selectall_sql(sql)
return data
def close(self):
self.pymysql.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
ret = DSF()
print(ret.aa())
print(ret.bb())
ret.close()
model 类使用方法
class CreateProjectProduce(SelectInfo):
def __init__(self, libname="notdbMysql"):
self.libname = libname
self.pymysql = MyPymysql(self.libname) def __enter__(self):
return self def check_the_data(self, ProjectID):
'''
explain:
检查核对数据是否存在
:return:
'''
# 调用继承类方法
data = self.CatSimpleProjectProduceModel(ProjectID) return data def insert_sql(self, data):
sql = '''insert INTO `meta_variable` SET DataTableID={}, VarValues="%s";'''.format(
data["DataTableID"])
value = (data["VarValues"])
self.pymysql.insert_sql(sql, value=value) def close(self):
self.pymysql.close() def __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_val, exc_tb):
self.close()
Use Method
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import os, configparser, pymysql '''
1. Config 类的 my.cnf 需要指定路径
2. my.cnf 的文件详情
my.cnf: # -----<notdbMysql>----- #配置中没有写库的名字,这样更加灵活
[notdbMysql]
host = 192.168.2.137
port = 3306
user = root
password = python123
3. 返回值形态设置
class writer_information_tables():
def __init__(self, libname="notdbMysql"):
self.libname = libname
self.res = MyPymysql(self.libname) # --> 返回值形态是{'aid': 5, 'varlabel': 'adadsf', 'vid': 0}
# self.res = MyPymysql(self.libname, None) # --> 返回值形态是(0, 5, 'adadsf')
''' class Config(object):
"""
# Config().get_content("user_information")
""" def __init__(self, config_filename="my.cnf"):
file_path = "/opt/code/my_code/tornado_uedit/my.cnf"
self.cf = configparser.ConfigParser()
self.cf.read(file_path) def get_sections(self):
return self.cf.sections() def get_options(self, section):
return self.cf.options(section) def get_content(self, section):
result = {}
for option in self.get_options(section):
value = self.cf.get(section, option)
result[option] = int(value) if value.isdigit() else value
return result class base_pymysql(object):
def __init__(self, host, port, user, password, db_name=None, cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor):
self.db_host = host
self.db_port = int(port)
self.user = user
self.password = str(password)
self.db = db_name
self.conn = None
self.cursor = cursor def connect(self):
self.conn = pymysql.connect(host=self.db_host, port=self.db_port, user=self.user,
passwd=self.password, db=self.db, charset="utf8")
self.cursor = self.conn.cursor(cursor=self.cursor) class MyPymysql(base_pymysql):
"""
Basic Usage: ret = My_Pymysql('test1')
res = ret.selectone_sql("select * from aaa")
print(res)
ret.close()
--------------
class writer_information_tables():
def __init__(self, libname="metadata"):
self.libname = libname
self.res = MyPymysql('metadata') def insert_sql(self, data):
sql = '''insert INTO `meta_variable` SET DataTableID={}, VarValues="%s";'''.format(
data["DataTableID"])
value = (data["VarValues"])
# print(sql)
# self.res.idu_sql(sql)
self.res.insert_sql(sql, value=value)
def commit(self):
self.res.commit() def close(self):
self.res.close()
----------------
def CreateDataTableInfor(data):
sql = "insert into `meta_data_table` SET DataTableID='{}';".format(
data["DataTableID"])
ret = MyPymysql('metadata') 或者 MyPymysql('metadata', None), 返回结果将是两种不同的形态 {} 和 ()
ret.idu_sql(sql)
ret.close()
--------------- Precautions:
Config.__init__(self, config_filename="my.cnf") """ def __init__(self, conf_name, cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor):
self.conf = Config().get_content(conf_name)
super(MyPymysql, self).__init__(**self.conf, cursor=cursor)
self.connect() def idu_sql(self, sql, value=None):
# adu: insert, delete, update的简写
# 考虑到多语句循环, try就不写在这里了
self.cursor.execute(sql, value)
self.conn.commit() def commit(self):
self.conn.commit() def rollback(self):
self.conn.rollback() def insert_sql(self, sql, value=None):
# adu: insert, delete, update的简写
# 防止sql注入
self.cursor.execute(sql, value) def update_sql(self, sql, value=None):
# adu: insert, delete, update的简写
# 防止sql注入
self.cursor.execute(sql, value) def delete_sql(self, sql, value=None):
# adu: insert, delete, update的简写
# 防止sql注入
self.cursor.execute(sql, value) def selectone_sql(self, sql):
self.cursor.execute(sql)
self.conn.commit()
return self.cursor.fetchone() def selectall_sql(self, sql):
self.cursor.execute(sql)
self.conn.commit()
return self.cursor.fetchall() def select_sql(self, sql, value=None):
# 防止sql注入
self.cursor.execute(sql, value)
self.conn.commit()
return self.cursor.fetchall() def close(self):
self.conn.close()
self.conn = None
self.cursor = None class writer_information_tables():
def __init__(self, libname="notdbMysql"):
self.libname = libname
self.res = MyPymysql(self.libname) # --> 返回值形态是{'aid': 5, 'varlabel': 'adadsf', 'vid': 0}
# self.res = MyPymysql(self.libname, None) # --> 返回值形态是(0, 5, 'adadsf') def insert_sql(self):
sql = "select * from myTest.a1"
data = self.res.selectone_sql(sql)
return data def commit(self):
self.res.commit() def close(self):
self.res.close() if __name__ == '__main__':
pym_obj = writer_information_tables()
print(pym_obj.insert_sql())
pym_obj.close()
Use Method
Pymysql 进行事务回滚
#!/usr/bin/env python
import MySQLdb def connect_mysql():
db_config = {
'host': '127.0.0.1',
'port': ,
'user': 'root',
'passwd': 'pzk123'
}
c = MySQLdb.connect(**db_config)
return c if __name__ == '__main__':
c = connect_mysql() # 首先连接数据库
cus = c.cursor() # 生成游标对象
sql = 'drop database test;' # 定义要执行的SQL语句
try:
cus.execute(sql) # 执行SQL语句
c.commit() # 如果执行成功就提交事务
except Exception as e:
c.rollback() # 如果执行失败就回滚事务
raise e
finally:
c.close() # 最后记得关闭数据库连接
mysqldb的
PYMYSQL防止sql注入问题
1.寻找到SQL注入的位置
2.判断服务器类型和后台数据库类型
3.针对不通的服务器和数据库特点进行SQL注入攻击
案例:
1、字符串拼接查询,造成注入
import pymysql conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='', db='User')
cursor = conn.cursor()
username=input()
password =input()
# 正常构造语句的情况
sql = "select user,pwd from User where user='%s' and pwd='%s'" % (username,password) row_count = cursor.execute(sql)
row_1 = cursor.fetchone()
print(row_count, row_1)
conn.commit()
cursor.close()
conn.close()
案例
其实用户可以这样输入实现免帐号登录:
username: ‘or 1 = 1 –-
password:
如若没有做特殊处理,那么这个非法用户直接登陆进去了.
当输入了上面的用户名和密码,服务端的sql就变成:
sql = "select user,pwd from User where user=‘'or 1 = 1 –-' and pwd='%s'"
因为条件后面username=”or 1=1 用户名等于 ” 或1=1 那么这个条件一定会成功;然后后面加两个-,这意味着注释,它将后面的语句注释,让他们不起作用,这样语句永远都能正确执行,用户轻易骗过系统,获取合法身份。
解决方法:
注意:一定要用"%s" 而不是‘%s’
#! /usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import pymysql conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='', db='User')
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
username= input()
password =input() #执行参数化查询
row_count=cursor.execute("select user,pwd from User where user='%s' and pwd='%s'" ,(username,password))
#execute()函数本身就有接受SQL语句变量的参数位,只要正确的使用(直白一点就是:使用”逗号”,而不是”百分号”)就可以对传入的值进行correctly转义,从而避免SQL注入的发生。 #内部执行参数化生成的SQL语句,对特殊字符进行了加\转义,避免注入语句生成。
# sql=cursor.mogrify("select user,pwd from User where user='%s' and pwd='%s'" ,(username,password))
# print (sql) row_1 = cursor.fetchone()
print(row_count,row_1) conn.commit()
cursor.close()
conn.close()
防sql注入问题2
报错:TypeError: %d format: a number is required, not str"
cursor.execute("""
insert into tree (id,parent_id,level,description,code,start,end)
values (%d,%d,%d,%s,%s,%f,%f)
""", (1,1,1,'abc','def',1,1)
)
如果这么写报错
对应mysql表类型
id int(),
parent_id int(),
level int(),
description varchar(),
code varchar(),
start decimal(,),
end decimal(,)
" File "/usr/lib/pymodules/python2./MySQLdb/cursors.py", line 151, in execute query = query % db.literal(args) TypeError: %d format: a number is required, not str"
解决办法:
The format string is not really a normal Python format string. You must always use %s for all fields.
防sql注入问题3
pymysql防sql注入必须是"%s", 可以这种%s形式的
from collections import OrderedDict
from common.Base import MyPymysql d = {'is_top': '', 'input_data_text': 'adfadf', 'is_comment': '', 'title': 'adsf', 'tag': ';分离', 'input_data_html': , 'is_release': '', 'input_data_content': '<p>adfadf<br/></p>', 'is_homepage': '', 'Password': '', 'edit_category': '', 'is_password': ''} def AddArticleModel(info):
sql = """
INSERT INTO blog.text
SET
ArticleTitle="%s", Release=%s ----> 这样是错的, pymysql防sql注入必须是"%s", 不能用这种%s形式的,包括数据是int都不行《---可以%s,留着这句话,看看当时因为release关键字让自己写的傻逼笔记 """
ret = MyPymysql('notdbMysql')
value = (
info["title"], # ArticleTitle int(info["is_release"]), # Release )
ret.idu_sql(sql, value=value)
ret.close() if __name__ == '__main__':
AddArticleModel(d)
三、错误集锦
1.
查看mysql单个库大小容量的命令(单位为字节,得到多少M需要除以1048576)
SELECT sum(DATA_LENGTH)+sum(INDEX_LENGTH) FROM information_schema.TABLES where TABLE_SCHEMA='数据库名';
2.
变量名为关键字(尤其前朝余孽留下的坑,特别注意了需要加``)
update `test` set a='' where `index`=; 这个index耗费了我2个小时,下午5点头晕沉沉的
3.
那么转换一下,上次是测试的语句,下面就直接换正式的了, %s也加引号,视情况而定
sql2 = "update `%s` set a10b1j='%s' where `index`='%s'" % (table_name, li[j], j)
4.
2.7存入mysql以后unicode的转义解决办法
"""
import pymysql
conn = pymysql.connect(host='112.126.70.69', port=, user='datapl', passwd='Rome78Uj', db='data_index_test')
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
cursor.execute("select cid FROM data_bak")
row_3 = cursor.fetchall()
li = [i[] for i in row_3]
err_li = []
for i in range(len(li)):
try:
print i
a, json_sumdata = VSummary().do_(, li[i])
sql = "INSERT INTO data_cid_json SET cid='%s', json_sumdata='%s'" % (li[i], pymysql.escape_string(json_sumdata))
cursor.execute(sql)
conn.commit()
except Exception as e:
err_li.append(li[i])
continue
cursor.close() conn.close() """
5.
调用oracle的时候需要注意的问题
他说一直是编码的问题,其实是oracle的问题

6.

解决办法
在创建连接的时候设置一下编码,如: conn = MySQLdb.connect(host="localhost", user="root", passwd="root", db="db", charset="utf8")
7. 注意一定要用"%s", 而不能用'%s'
8. 在pymysql里面防sql要注意, 例如: update `%s` 这个时候会把表名也转义, 所以报错
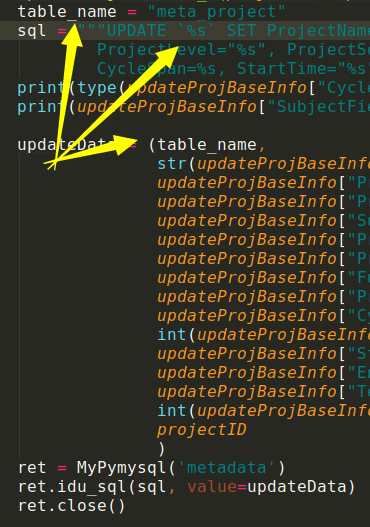
会变成update `\'meta_project\' set ....这样就找不到表名
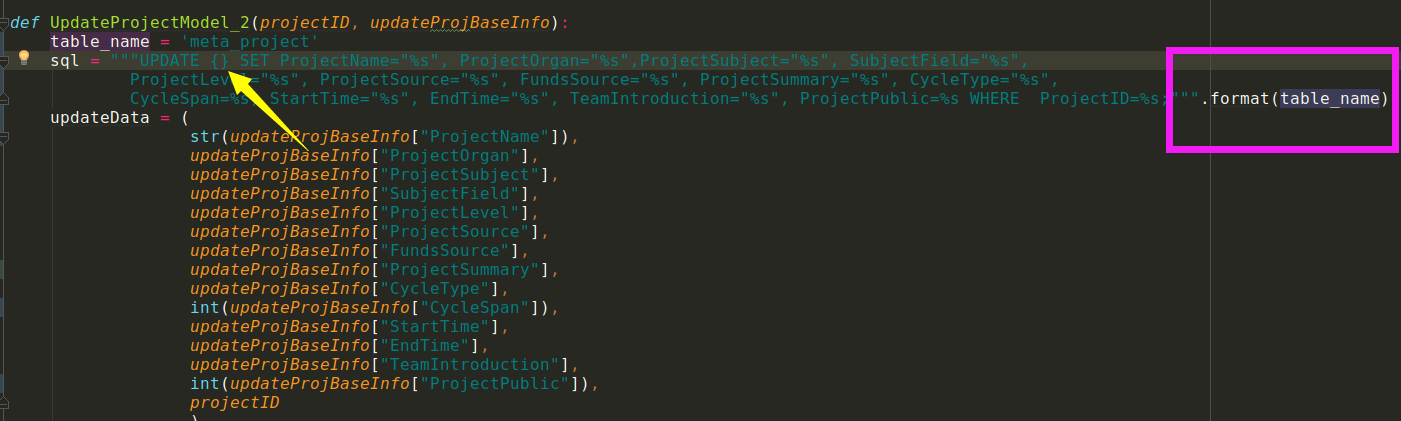
之前这么写的
pymysql和MySQLdb的更多相关文章
- MySQL、sqlalchemy、pymysql、mysqldb、DBAPI之间关系梳理(终于明白了)
MySQL.sqlalchemy.pymysql.mysqldb.DBAPI之间关系梳理(终于明白了) python3不再支持mysqldb 请用pymysql和mysql.connector 问题背 ...
- 用pymysql代替MySQLdb
在我刚开始学python的时候,用的是python2.7,那时候连接mysql用的库是MySQLdb(很诡异的大小写,初学者经常因为记不住大小写导致“No module named xxx”).燃鹅, ...
- PyMySQL和MySQLdb的区别
网上很多关于Scrapy存入MySQL的教程,都会发现又这么一个包的引入: import MySQLdb import MySQLdb.cursors 聪明的你或许已经算到,需要安装MySQLdb ...
- pyhton 自动化pymysql操作mysqldb数据库增删改查封装
# coding=utf-8 import pymysql import os import configparser """ /* @:param: python ve ...
- python peewee.ImproperlyConfigured: MySQLdb or PyMySQL must be installed.
最近在学习Python,打算先看两个在线教程,再在github上找几个开源的项目练习一下,在学到“被解放的姜戈”时遇到django同步数据库时无法执行的错误,记录一下. 错误现象: 执行python ...
- Python3出现"No module named 'MySQLdb'"问题-以及使用PyMySQL连接数据库
Python3 与 Django 连接数据库,出现了报错:Error loading MySQLdb module: No module named 'MySQLdb'.原因如下:在 python2 ...
- Python 3.x 连接数据库(pymysql 方式)
==================pymysql=================== 由于 MySQLdb 模块还不支持 Python3.x,所以 Python3.x 如果想连接MySQL需要安装 ...
- python pymysql和orm
pymsql是Python中操作MySQL的模块,其使用方法和MySQLdb几乎相同. 1. 安装 管理员打开cmd,切换到python的安装路径,进入到Scripts目录下(如:C:\Users\A ...
- Python 3.5 连接Mysql数据库(pymysql 方式)
由于 MySQLdb 模块还不支持 Python3.x,官方的Mysql连接包只支持到3.4,所以 Python3.5 如果想连接MySQL需要安装 pymysql 模块. pymysql 模块可以通 ...
随机推荐
- 使用JSR-303进行后台数据校验
一.在SringMVC中使用 使用注解 1.准备校验时使用的JAR validation-api-1.0.0.GA.jar:JDK的接口: hibernate-validator-4.2.0.Fina ...
- 菜鸟学EJB(一)——第一个实例
EJB用了那么长时间了,从来没写过关于它的东西,挺对不住它的.今天先写一个简单的小实例,虽然小但是却能体现出EJB的核心——分布式.我们可以将业务逻辑的接口跟实现部署到一台机器上,将调用它们的客户端部 ...
- C++中的static 成员变量的一些注意点
C++中的static成员变量主要用来为多个对象共享数据 例: #include <iostream> using namespace std; class Student{ public ...
- 破解Linux系统root用户密码
linux系统的启动过程 在介绍破解Linux系统root密码之前先了解一下linux系统的启动过程 开机自检(POST),初始化部分硬件 搜素可用于引导的启动设备(如磁盘的MBR) 读取并将控制权 ...
- iOS开发如何学习前端(1)
iOS开发如何学习前端(1) 我为何学前端?因为无聊. 概念 前端大概三大块. HTML CSS JavaScript 基本上每个概念在iOS中都有对应的.HTML请想象成只能拉Autolayout或 ...
- Secure gRPC with TLS/SSL
摘自:http://bbengfort.github.io/programmer/2017/03/03/secure-grpc.html Secure gRPC with TLS/SSL 03 Mar ...
- Oracle生成流水号函数
一.参考 1:日期范围上 smalldatetime的有效时间范围1900/1/1~2079/6/6 datetime的有效时间范围1753/1/1~9999/12/31 2:精准度上 smallda ...
- C语言字符串格式化显示
符号 作用 ────────────────────────── %d 十进制有符号整数 %i 输 ...
- 命令行todo神器taskwarrior使用简介
简介 taskwarrior是一个命令行的任务管理神器,同时也有服务端,支持同步. 语法规则为 安装 Linux上可以直接软件包管理器安装 Window可以用cygwin Mac可以用homebrew ...
- spring boot模仿reponseBody注解,自定义注解,返回值加上元数据
简介 ResponseBody是通过RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor起作用的. 我们的做法是写一个包装类,替换掉他 问题:怎么替换呢? 取出 Spring的List ...
