NIO浅析(二)
一:前言
在(一中了解了NIO中的缓冲区和通道),通过本文章你会了解阻塞和非阻塞,选择器,管道
二:完成NIO通信的三要素
* 1.通道(Channel):负责连接
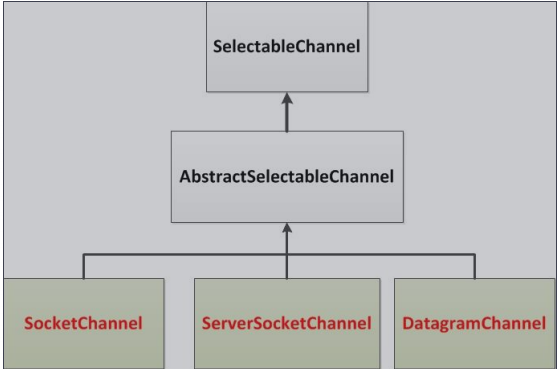
* java.nio.channels.Channel 接口:
* SelectableChannel
* //TCP
* SocketChannel
* ServerSocketChannel
* //UDP
* DatagramChannel
* Pipe.SinkChannel
* Pipe.SourceChannel
*
* 2.缓冲区:(Buffer):数据存取
* 3.选择器:(Selector):(是SelectableChannel的多路复用器)是用于监控SelectableChannel的IO状况
先使用阻塞式通信
客户端
//客户端
@Test
public void client() throws IOException {
//1.获取通道
SocketChannel sChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 9898));
FileChannel inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("1.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.READ);
//2.分配指定大小的缓冲区
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//3.读取本地文件,并发送到服务端
while (inChannel.read(buf)!=-1){
buf.flip();
sChannel.write(buf);
buf.clear();
}
//关闭通道
inChannel.close();
sChannel.close();
}
服务端
//服务端
@Test
public void server() throws IOException {
//1.获取通道
ServerSocketChannel ssChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
FileChannel outChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("4.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE, StandardOpenOption.CREATE); //2.绑定连接端口号
ssChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(9898));
//3.获取客户端的连接的通道
SocketChannel sChannel = ssChannel.accept();
//4.分配指定大小的缓冲区
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//5.接受客户端的数据并保存到本地
while (sChannel.read(buf)!=-1){
buf.flip();
outChannel.write(buf);
buf.clear();
}
sChannel.close();
outChannel.close();
ssChannel.close(); }
阻塞式通信:当一个线程调用 read() 或 write()时,该线程被阻塞,直到有一些数据被读取或写入,该线程在此期间不能执行其他任务。因此,在完成网络通信进行 IO 操作时,由于线程会阻塞,所以服务器必须为每个客户端都提供一个独立的线程进行处理,当服务器端需要处理大量客户端时,性能急剧下降。
下面使用选择器完成非阻塞式通信(TCP)
客户端
//客户端
@Test
public void client() throws IOException {
//1.获取通道
SocketChannel sChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 9898));
//2.切换成非阻塞模式
sChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//3.分配指定大小的缓冲区
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//4.发送数据到服务端
buf.put(new Date().toString().getBytes());
buf.flip();
sChannel.write(buf); //关闭通道
sChannel.close();
}
服务端
//服务端
@Test
public void server() throws IOException {
//1.获取通道
ServerSocketChannel ssChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//2.切换到非阻塞模式
ssChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//3.绑定连接
ssChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(9898));
//4.获取选择器
Selector selector = Selector.open();
//5.将通道注册到选择器上
ssChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
//6.轮询式获取选择器上面已经“准备就绪的事件”
while(selector.select()>0){
//7.获取当前选择器中所有注册的“选择键(已就绪的监听事件)”
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
//8.获取就绪事件
SelectionKey sk = iterator.next();
//9.判断具体是什么事件准备就绪
if(sk.isAcceptable()){
//10.若“接收就绪”,获取客户端连接
SocketChannel sChannel = ssChannel.accept();
//11.切换到非阻塞模式
sChannel.configureBlocking(false); //12.将该通道注册到选择器上
sChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}else if(sk.isReadable()){
//13.若读就绪,获取读就绪状态的通道
SocketChannel sChannel = (SocketChannel)sk.channel();
//14.读取数据
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int len=0;
while((len=sChannel.read(buf))>0){
buf.flip();
System.out.println(new String(buf.array(),0,len));
buf.clear();
}
}
//取消选择键SelectionKey
iterator.remove();
}
}
}
非阻塞式通信:当线程从某通道进行读写数据时,若没有数据可用时,该线程可以进行其他任务。线程通常将非阻塞 IO 的空闲时间用于在其他通道上执行 IO 操作,所以单独的线程可以管理多个输入和输出通道。因此,NIO 可以让服务器端使用一个或有限几个线程来同时处理连接到服务器端的所有客户端。
再来一个例子(DatagramChannel)UDP
客户端
@Test
public void send() throws IOException {
//通道
DatagramChannel dChannel = DatagramChannel.open();
//设置为非阻塞
dChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//设置缓冲区
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
buf.put(new Date().toString().getBytes()); buf.flip();
dChannel.send(buf,new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",9898)); dChannel.close();
}
服务端
@Test
public void receive() throws IOException {
DatagramChannel dChannel = DatagramChannel.open();
dChannel.configureBlocking(false);
dChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(9898)); Selector selector = Selector.open();
dChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
//6.轮询式获取选择器上面已经“准备就绪的事件”
while(selector.select()>0){
//7.获取当前选择器中所有注册的“选择键(已就绪的监听事件)”
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
//8.获取就绪事件
SelectionKey sk = iterator.next();
//9.判断具体是什么事件准备就绪
if(sk.isReadable()){
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
dChannel.receive(buf);
buf.flip();
System.out.println(new String(buf.array(),0,buf.limit()));
buf.clear();
}
//取消选择键SelectionKey
iterator.remove();
}
}
}
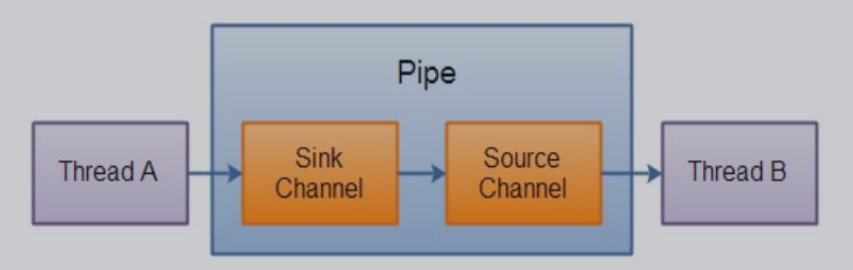
三:管道
2个线程之间的单向数据连接,管道有一个source通道和一个sink通道,数据写道sink通道,到source通道读取
@Test
public void test1() throws IOException {
//1.获取管道
Pipe pipe = Pipe.open();
//2.将缓冲区的数据写入管道
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
Pipe.SinkChannel sinkChannel = pipe.sink(); buf.put(new Date().toString().getBytes());
buf.flip();
sinkChannel.write(buf); //读取缓冲区里面的数据
Pipe.SourceChannel source = pipe.source();
buf.flip();
int len=source.read(buf);
System.out.println(new String(buf.array(),0,len)); source.close();
sinkChannel.close(); }
NIO浅析(二)的更多相关文章
- NIO(二、Buffer)
目录 NIO(一.概述) NIO(二.Buffer) Buffer 前文讲了NIO与IO的区别,那么这一章开始讲述NIO下核心类 - Buffer类 上一章就说过,NIO的核心包括三个部分:通道(Ch ...
- InnoDB的锁机制浅析(二)—探索InnoDB中的锁(Record锁/Gap锁/Next-key锁/插入意向锁)
Record锁/Gap锁/Next-key锁/插入意向锁 文章总共分为五个部分: InnoDB的锁机制浅析(一)-基本概念/兼容矩阵 InnoDB的锁机制浅析(二)-探索InnoDB中的锁(Recor ...
- EM算法浅析(二)-算法初探
EM算法浅析,我准备写一个系列的文章: EM算法浅析(一)-问题引出 EM算法浅析(二)-算法初探 一.EM算法简介 在EM算法之一--问题引出中我们介绍了硬币的问题,给出了模型的目标函数,提到了这种 ...
- java nio 通道(二)
本文章来源于我的个人博客: java nio 通道(二) 一,文件通道 文件通道总是堵塞式的,因此不能被置于非堵塞模式. FileChannel对象是线程安全的.多个进程能够在同一个实例上并发调用方法 ...
- Java NIO浅析 转至 美团技术团队
出处: Java NIO浅析 NIO(Non-blocking I/O,在Java领域,也称为New I/O),是一种同步非阻塞的I/O模型,也是I/O多路复用的基础,已经被越来越多地应用到大型应用服 ...
- 深入理解NIO(二)—— Tomcat中对NIO的应用
深入理解NIO(二)—— Tomcat中对NIO的应用 老哥行行好,转载和我说一声好吗,我不介意转载的,但是请把原文链接贴大点好吗 Tomcat大致架构 先贴两张图大致看一眼Tomcat的架构 Tom ...
- JAVA NIO学习二:通道(Channel)与缓冲区(Buffer)
今天是2018年的第三天,真是时光飞逝,2017年的学习计划还没有学习完成,因此继续开始研究学习,那么上一节我们了解了NIO,那么这一节我们进一步来学习NIO相关的知识.那就是通道和缓冲区.Java ...
- ReentrantLock和condition源码浅析(二)
转载请注明出处... 接着上一篇的ReentrantLock和condition源码浅析(一),这篇围绕着condition 一.condition的介绍 在这里为了作对比,引入Object类的两个方 ...
- Java基础——NIO(二)非阻塞式网络通信与NIO2新增类库
一.NIO非阻塞式网络通信 1.阻塞与非阻塞的概念 传统的 IO 流都是阻塞式的.也就是说,当一个线程调用 read() 或 write() 时,该线程被阻塞,直到有一些数据被读取或写入,该线程在 ...
随机推荐
- GET和POST区别及缓存问题
2.就是get和post区别的缓存问题. 首先要了解什么是缓存. HTTP缓存的基本目的就是使应用执行的更快,更易扩展,但是HTTP缓存通常只适用于idempotent request(可以理解为查询 ...
- T1219:马走日
[题目描述] 马在中国象棋以日字形规则移动. 请编写一段程序,给定n×m大小的棋盘,以及马的初始位置(x,y),要求不能重复经过棋盘上的同一个点,计算马可以有多少途径遍历棋盘上的所有点. [输入] 第 ...
- Digital Root 的推导
背景 在LeetCode上遇到这道题:Add Digits 大意是给一个数,把它各位数字相加得到一个数,如果这个数小于10就返回,不然继续 addDigits(这个相加得到的数). 题目很简单,但是如 ...
- exsi 回收虚拟机磁盘
用客户端登陆服务端,用下面命令停止虚拟机机器 esxcli vm process list 用如下命令关闭一台虚拟机: esxcli vm process kill --type=[soft,h ...
- 分布式ID的雪花算法及坑
分布式ID生成是目前系统的常见刚需,其中以Twitter的雪花算法(Snowflake)比较知名,有Java等各种语言的版本及各种改进版本,能生成满足分布式ID,返回ID为Long长整数 但是这里有一 ...
- (十二)Bind读取配置到C#实例
继续上一节的,接下来用Options或者Bind把json文件里的配置转成C#的实体,相互之间映射起来.首先新建一个asp.net core mvc项目OptionsBindSample Startu ...
- IIS Express 不允许的父路径
IIS Express 启动一个asp的网站,出现一个错误 Active Server Pages 错误 'ASP 0131' 不允许的父路径 对于IIS可以在可视化的IIS Manager中配置: ...
- java.nio.Buffer 中的 flip()方法
在Java NIO编程中,对缓冲区操作常常需要使用 java.nio.Buffer中的 flip()方法. Buffer 中的 flip() 方法涉及到 Buffer 中的capacity.posi ...
- 2018-2-13-win10-UWP-九幽登录
title author date CreateTime categories win10 UWP 九幽登录 lindexi 2018-2-13 17:23:3 +0800 2018-2-13 17: ...
- js 输入整数
1.我用 /^\+?[1-9][0-9]*$/ 貌似不对(小数也可以输入) 2.输入整数 n = /^[1-9]\d*$/; . -]\d*$/; //判断字符串是否为数字 if (!value) ...
