一天一个设计模式——Strategy策略模式
一、模式说明
策略模式比较好理解,就是将程序中用到的算法整体的拿出来,并有多个不同版本的算法实现,在程序运行阶段,动态的决定使用哪个算法来解决问题。
举个实际的例子:排序算法的问题,假如我们的程序中需要对数据进行排序,我们知道,不同的算法具有不同的时间复杂度和空间复杂度,因此需要在程序运行时,根据可用内存和数据特征,选用不同的算法(排序策略),这就是策略模式的使用场景之一。再举个例子,负载均衡算法:如果某个服务部署了多个冗余的实例,客户端在向服务端发送请求时,根据负载均衡算法策略,请求可能会被转发到不同的服务提供者实例来处理,如何决定某个请求转发给哪个服务实例呢,最简单的做法就是轮询,顺次将请求转发给每个服务实例进行处理。也可以采用随机方式,或者根据实际硬件环境和业务场景设置特定算法。
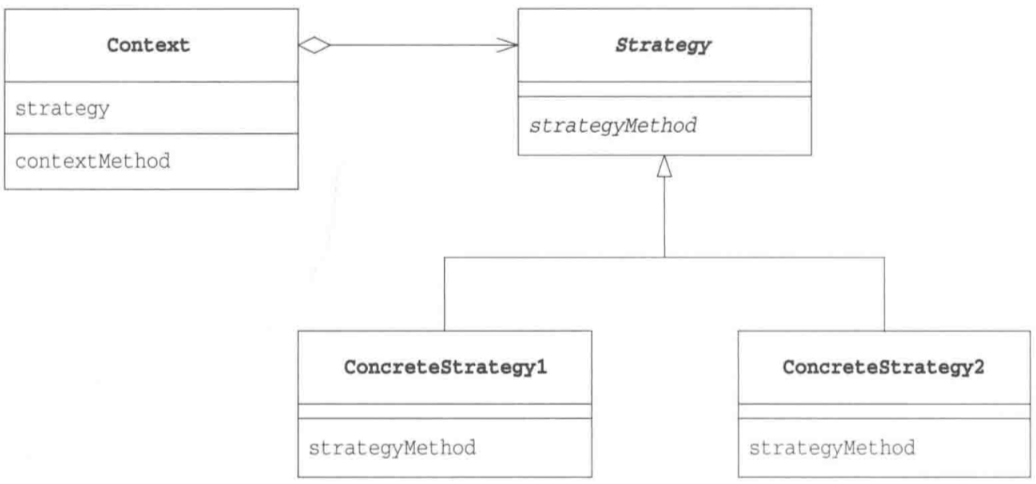
二、模式类图
三、程序示例
在下面的演示策略模式的代码示例中,我们模拟猜拳游戏——剪刀石头布,猜拳的策略有两种:如果这次猜拳赢了,则下次还出同样的手势。另一种策略就是根据以前的猜拳结果,选择胜率最高的一种手势。
1、Hand类:表示猜拳游戏中的手势,并非Strategy策略模式中的角色。
package com.designpattern.cn.strategypattern;
public class Hand {
public static final int HANDVALUE_ROCK = 0; //表示石头
public static final int HANDVALUE_SCISSORS = 1; //表示剪刀
public static final int HANDVALUE_PEPER = 2; //表示布
private static final Hand[] hand = {
new Hand(HANDVALUE_ROCK),
new Hand(HANDVALUE_SCISSORS),
new Hand(HANDVALUE_PEPER)
};
private static final String[] name = {
"石头", "剪刀", "布"
};
private int handValue;
private Hand(int handValue){
this.handValue = handValue;
}
public static Hand getHand(int handValue){
return hand[handValue];
}
public boolean isStrongerThan(Hand h){
return fight(h) == 1;
}
public boolean isWeakerThan(Hand h){
return fight(h) == -1;
}
private int fight(Hand h){
if(this == h) {
return 0;
}else if((this.handValue + 1)%3 == h.handValue){
return 1;
}else{
return -1;
}
}
public String toString(){
return name[handValue];
}
}
2、Strategy接口:
package com.designpattern.cn.strategypattern;
public interface Strategy {
public abstract Hand nextHand();
public abstract void study(boolean win);
}
3、WinningStrategy类:
package com.designpattern.cn.strategypattern;
import java.util.Random;
public class WinningStrategy implements Strategy {
private Random random;
private boolean won = false; //上一局的输赢结果
private Hand prevHand; //上一局的手势
public WinningStrategy(int seed){
random = new Random(seed);
}
public Hand nextHand(){
if(!won){
prevHand = Hand.getHand(random.nextInt(3));
}
return prevHand;
}
public void study(boolean win){
won = win;
}
}
4、ProbStrategy类:
package com.designpattern.cn.strategypattern;
import java.util.Random;
public class ProbStrategy implements Strategy {
private Random random;
private int prevHandValue = 0;
private int currentHandValue = 0;
//history[上一局的手势][这一局的手势] 表达式的值越高表示过去的胜率越高
//study方法会根据nextHand方法返回的手势胜负结果更新history字段中的值
private int[][] history = {
{1, 1, 1},
{1, 1, 1},
{1, 1, 1}
};
public ProbStrategy(int seed) {
random = new Random(seed);
}
public Hand nextHand() {
int bet = random.nextInt(getSum(currentHandValue));
int handValue = 0;
if (bet < history[currentHandValue][0]) {
handValue = 0;
}else if(bet < history[currentHandValue][1]){
handValue = 1;
}else{
handValue = 2;
}
prevHandValue = currentHandValue;
currentHandValue = handValue;
return Hand.getHand(handValue);
}
private int getSum(int hv){
int sum = 0;
for (int i : history[hv]
) {
sum += i;
}
return sum;
}
public void study(boolean win){
if(win){
history[prevHandValue][currentHandValue]++;
}else{
history[prevHandValue][(currentHandValue+1)%3]++;
history[prevHandValue][(currentHandValue+2)%3]++;
}
}
}
5、Player类:
package com.designpattern.cn.strategypattern;
public class Player {
private String name;
private Strategy strategy;
private int wincount;
private int losecount;
private int gamecount;
public Player(String name, Strategy strategy){
this.name = name;
this.strategy = strategy;
}
public Hand nextHand(){
return strategy.nextHand();
}
public void win(){
strategy.study(true);
wincount++;
gamecount++;
}
public void lose(){
strategy.study(false);
losecount++;
gamecount++;
}
public void even(){
gamecount++;
}
public String toString(){
return "[" + name + ":" + gamecount + " games, " + wincount +
" win, " + losecount + " lose" + "]";
}
}
6、Main类与运行结果:
package com.designpattern.cn.strategypattern;
import java.util.Random;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
int seed1 = ((new Random()).nextInt(500))*(1+(new Random()).nextInt(500));
int seed2 = seed1 * (new Random()).nextInt(500);
Player player1 = new Player("Taro", new WinningStrategy(seed1));
Player player2 = new Player("Hana", new ProbStrategy(seed2));
for(int i = 0; i < 100000; i++){
Hand nextHand1 = player1.nextHand();
Hand nextHand2 = player2.nextHand();
if(nextHand1.isStrongerThan(nextHand2)){
System.out.println("Winner: " + player1);
player1.win();
player2.lose();
}else if(nextHand2.isStrongerThan(nextHand1)){
System.out.println("Winner: " + player2);
player2.win();
player1.lose();
}else{
System.out.println("Even...");
player1.even();
player2.even();
}
}
System.out.println("Total result:");
System.out.println(player1.toString());
System.out.println(player2.toString());
}
}
四、Strategy策略模式中的角色
- Strategy策略:负责定义实现策略必须的接口方法
- ConcreteStrategy具体的策略:实现Strategy角色的接口,如程序中的WinningStrategy和ProbStrategy
- Context上下文:负责使用Strategy策略,如示例程序中的player。
五、相关的设计模式
- Flyweight享元模式:通过使用享元模式,让多个地方共用ConcreteStrategy角色;
- Abstract Factory抽象工厂:策略模式整体替换算法,抽象工厂整体替换具体的工厂,零件和产品;
- State状态模式:状态模式和策略模式都可以替换被委托对象,而且类之间的关系也相似,只是两种模式目的不同。strategy策略模式替换被委托对象的类;状态模式中,每次状态发生变化时,被委托的对象必定会被替换。
一天一个设计模式——Strategy策略模式的更多相关文章
- Java的设计模式----strategy(策略模式)
设计模式: 一个程序员对设计模式的理解: “不懂”为什么要把很简单的东西搞得那么复杂.后来随着软件开发经验的增加才开始明白我所看到的“复杂”恰恰就是设计模式的精髓所在,我所理解的“简单”就是一把钥匙开 ...
- C++设计模式-Strategy策略模式
Strategy策略模式作用:定义了算法家族,分别封装起来,让他们之间可以互相替换,此模式让算法的变化,不会影响到使用算法的客户. UML图: Strategy模式将逻辑(算法)封装到一个类(Cont ...
- Java设计模式---Strategy策略模式
参考于 : 大话设计模式 马士兵设计模式视频 1.场景介绍 购物网站上有一个产品,有三个字段,档次,价格,重量. 有些同学喜欢轻的,有些手头紧,想要便宜的,有些喜欢档次高的. 那么我们为了提高网站用户 ...
- [C++设计模式] strategy 策略模式
依照陈硕老师的观点.c++里有面向过程编程.面向对象编程,基于对象编程(面向接口编程)和泛型编程.四种思路都各有其适用场景. 面向过程编程是沿袭C的结构化编程思路,OOP是C++的核心,也是现代高级编 ...
- 设计模式:Strategy 策略模式 -- 行为型
设计模式 策略模式Strategy(对象行为型) 这是几年前写的文字(转载做的笔记更准确些),发觉还是废话多了点. 其实,核心就是5.结构中的UML图 5.1 和 5.2(新增).现在看这张图就觉得一 ...
- 乐在其中设计模式(C#) - 策略模式(Strategy Pattern)
原文:乐在其中设计模式(C#) - 策略模式(Strategy Pattern) [索引页][源码下载] 乐在其中设计模式(C#) - 策略模式(Strategy Pattern) 作者:webabc ...
- 设计模式22:Strategy 策略模式(行为型模式)
Strategy 策略模式(行为型模式) 动机(Motivation) 在软件构建过程中,某些对象使用的算法可能多种多样,经常改变,如果将这些算法都编码到对象中,将会使对象变得异常复杂:而且有时候支持 ...
- 设计模式之策略模式和状态模式(strategy pattern & state pattern)
本文来讲解一下两个结构比较相似的行为设计模式:策略模式和状态模式.两者单独的理解和学习都是比较直观简单的,但是实际使用的时候却并不好实践,算是易学难用的设计模式吧.这也是把两者放在一起介绍的原因,经过 ...
- 设计模式:策略模式(Strategy)
定 义:它定义了算法家族,分别封装起来,让它们之间可以互相替换,此模式让算法的变化, 不会影响到使用算法的客户. 示例:商场收银系统,实现正常收费.满300返100.打8折.......等不同收费 ...
随机推荐
- alsa-utils 的使用
ref : https://blog.csdn.net/outstanding_yzq/article/details/8126350 一.alsa-utils介绍 ALSA是kernel中的一个声 ...
- docker中mysql数据库
在docker中安装mysql数据库,直接上代码,pull 并run 补充20190809=============== 如果要挂载数据库实现数据持久化到本地的时候,会出现权限问题,这个原因是: 在执 ...
- Tasks、 activity 及 activity stack - 人间奇迹(转)
http://www.cnblogs.com/yaozhongxiao/p/3365345.html Activity之间的跳转,或者说加载一个新的Activity,一般对于开发者来说,都不是一个 ...
- 文献阅读报告 - Social BiGAT + Cycle GAN
原文文献 Social BiGAT : Kosaraju V, Sadeghian A, Martín-Martín R, et al. Social-BiGAT: Multimodal Trajec ...
- input中name和id的区别
一直很困惑,表单里面input标签有id和name,它们之间到底有什么区别自己很少去想,只知道一般的场景该怎么使用,今天就在网上搜索了一下,自己也总结一下.为什么有了ID还要有Name呢?其实ID就像 ...
- leetcode1162 As Far from Land as Possible
""" Given an N x N grid containing only values and , represents water and represents ...
- mpvue + Vant weapp + 微信云服务 打造小程序应用
写在前面的话: 从事小程序开发已经大半年的时间了,但是一直都是再用原生写项目.一直想着用框架自己写一个小程序,但苦于一直没有时间.正好最近项目搁置,有了空闲时间,就研究了下mpvue + Vant w ...
- IDEA快速定位一个文件到项目目录
第一步:快捷键搜索java文件关键字 快捷键Ctrl+N,如果设置为Eclipse版本快捷键为Ctrl+Shift+R 第二步:定位文件到项目目录中 1.在当前文件下 2.点击定位按钮 3.定位到项目 ...
- 【pwnable.kr】input
这道题是一道一遍一遍满足程序需求的题. 网上其他的题解都是用了C语言或者python语言的本地调用,我想联系一下pwntools的远程调用就写了下面的脚本, 执行效果可以通过1~4的检测,到最后soc ...
- Docker Yearning + Inception SQL审核平台搭建
[一]安装[1.1]系统环境系统环境:CentOS Linux release 7.6.1708 (Core)系统内存:4G系统内核:1Python:3.6.4关闭iptables and selin ...
