Mybatis——Mapper解析
Mapper的注册入口在Configuration的addMapper方法中,其会调用MapperRegistry的addMapper方法。
Mapper的注册过程分为两个步骤:
1.创建MapperProxyFactory,将其与mapper的class进行映射
2.解析mapper对应xml文件和其方法上的注解,生成MappedStatement。
public class MapperRegistry {
private final Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers = new HashMap<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>>();
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
//1.创建MapperProxyFactory,将其与mapper的class进行映射
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<T>(type));
2.解析mapper对应xml文件和其方法上的注解,生成MappedStatement。
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
}
MapperAnnotationBuilder解析过程
MapperAnnotationBuilder的解析过程分为两个步骤:
1.解析xml文件
2.解析mapper方法上的注解
public void parse() {
//校验mapper是否已经解析
String resource = type.toString();
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
//1.解析xml文件
loadXmlResource();
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
assistant.setCurrentNamespace(type.getName());
parseCache();
parseCacheRef();
//2.解析mapper方法上的注解
Method[] methods = type.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
try {
// issue #237
if (!method.isBridge()) {
parseStatement(method);
}
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteMethod(new MethodResolver(this, method));
}
}
}
//3.重新解析由于首次解析因为父元素未解析导致解析的方法
parsePendingMethods();
}
xml文件解析
private void loadXmlResource() {
// Spring may not know the real resource name so we check a flag
// to prevent loading again a resource twice
// this flag is set at XMLMapperBuilder#bindMapperForNamespace
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded("namespace:" + type.getName())) {
String xmlResource = type.getName().replace('.', '/') + ".xml";
InputStream inputStream = null;
try {
inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(type.getClassLoader(), xmlResource);
} catch (IOException e) {
// ignore, resource is not required
}
if (inputStream != null) {
XMLMapperBuilder xmlParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, assistant.getConfiguration(), xmlResource, configuration.getSqlFragments(), type.getName());
xmlParser.parse();
}
}
}
xml文件的路径为:String xmlResource = type.getName().replace('.', '/') + ".xml";mapper的全路径,并将后缀改为xml,因为要求xml文件与mapper class文件位于相同的路径下。
xmlParser.parse()解析流程:
public void parse() {
//mapper节点解析
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
//解析由于父ResultMap未解析的ResultMap
parsePendingResultMaps();
parsePendingCacheRefs();
//解析由于依赖元素未解析的Insert/update/delete/select节点
parsePendingStatements();
}
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
try {
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
if (namespace == null || namespace.equals("")) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
//解析parameterMap节点为ParameterMap,存放于configuration的parameterMaps中
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));
//解析resultMap节点为ResultMap,存放于configuration的ResultMaps中
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
//解析sql片段,存放在configuration的sqlFragments中
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
//解析select|insert|update|delete节点生成MappedStatement,存放在configuration的mappedStatements中
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. The XML location is '" + resource + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
method注解解析
void parseStatement(Method method) {
//获取parameterType,如果有多个参数为ParamMap,单个参数为参数类型
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = getParameterType(method);
LanguageDriver languageDriver = getLanguageDriver(method);
//解析@Select|Update|Delete|Insert中的value值,或者@SelectProvider|@UpdateProvider|@DeleteProvider|@InsertProvider的方法,生成SqlSource
SqlSource sqlSource = getSqlSourceFromAnnotations(method, parameterTypeClass, languageDriver);
if (sqlSource != null) {
//解析@Options
Options options = method.getAnnotation(Options.class);
final String mappedStatementId = type.getName() + "." + method.getName();
Integer fetchSize = null;
Integer timeout = null;
StatementType statementType = StatementType.PREPARED;
ResultSetType resultSetType = ResultSetType.FORWARD_ONLY;
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = getSqlCommandType(method);
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
boolean flushCache = !isSelect;
boolean useCache = isSelect;
//解析@SelectKey生成KeyGenerator
KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
String keyProperty = "id";
String keyColumn = null;
if (SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType) || SqlCommandType.UPDATE.equals(sqlCommandType)) {
// first check for SelectKey annotation - that overrides everything else
SelectKey selectKey = method.getAnnotation(SelectKey.class);
if (selectKey != null) {
keyGenerator = handleSelectKeyAnnotation(selectKey, mappedStatementId, getParameterType(method), languageDriver);
keyProperty = selectKey.keyProperty();
} else if (options == null) {
keyGenerator = configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() ? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
} else {
keyGenerator = options.useGeneratedKeys() ? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
keyProperty = options.keyProperty();
keyColumn = options.keyColumn();
}
} else {
keyGenerator = NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
}
if (options != null) {
if (FlushCachePolicy.TRUE.equals(options.flushCache())) {
flushCache = true;
} else if (FlushCachePolicy.FALSE.equals(options.flushCache())) {
flushCache = false;
}
useCache = options.useCache();
fetchSize = options.fetchSize() > -1 || options.fetchSize() == Integer.MIN_VALUE ? options.fetchSize() : null; //issue #348
timeout = options.timeout() > -1 ? options.timeout() : null;
statementType = options.statementType();
resultSetType = options.resultSetType();
}
//解析@ResultMap获取ResultMapId,或者解析@Resutls生成ResultMap
String resultMapId = null;
ResultMap resultMapAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(ResultMap.class);
if (resultMapAnnotation != null) {//解析@ResultMap获取ResultMapId
String[] resultMaps = resultMapAnnotation.value();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (String resultMap : resultMaps) {
if (sb.length() > 0) {
sb.append(",");
}
sb.append(resultMap);
}
resultMapId = sb.toString();
} else if (isSelect) {//解析@Resutls生成ResultMap
resultMapId = parseResultMap(method);
}
//根据上面解析得到的ResultMap、ParamterType、SqlSource等生成MapperStatement
assistant.addMappedStatement(
mappedStatementId,
sqlSource,
statementType,
sqlCommandType,
fetchSize,
timeout,
// ParameterMapID
null,
parameterTypeClass,
resultMapId,
getReturnType(method),
resultSetType,
flushCache,
useCache,
// TODO gcode issue #577
false,
keyGenerator,
keyProperty,
keyColumn,
// DatabaseID
null,
languageDriver,
// ResultSets
options != null ? nullOrEmpty(options.resultSets()) : null);
}
}
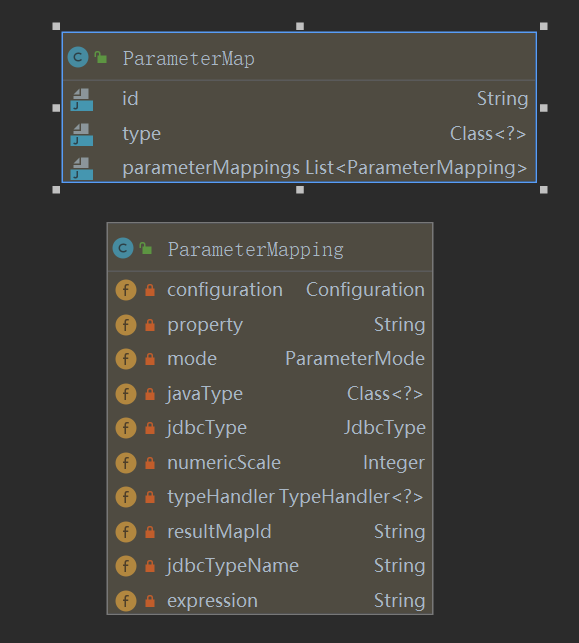
ParameterMap解析
ParameterMap结构:
ParameterMap映射节点:
<parameterMap id="BaseParameterMap" type="com.example.demo.User">
<parameter property="id" javaType="long" jdbcType="BIGINT"/>
<parameter property="username" javaType="string" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
<parameter property="password" javaType="string" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
</parameterMap>
parameterMap对应上面xml配置节点,该节点转换的parameterMap会注册到configuration中。解析逻辑在org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.XMLMapperBuilder#parameterMapElement中。
此外还有select|insert|update|delete的parameter节点的parameterType属性,method注解的参数都是转换为parameterMap,但是只有id和type属性,且不会注册到configuration中,只会存放于mappedStatement中。生成逻辑位于org.apache.ibatis.builder.MapperBuilderAssistant#getStatementResultMaps中
ResultMap解析
resultMap映射节点:
xml
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="com.example.demo.User">
<id column="id" property="id" />
<result column="username" property="username" />
<result column="password" property="password" />
</resultMap>
注解
@Results(id = "BaseResultMap2",
value = {
@Result(property = "id", column = "id"),
@Result(property = "username", column = "username"),
@Result(property = "password", column = "password"),
}
)
xml解析逻辑位于org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.XMLMapperBuilder#resultMapElement(org.apache.ibatis.parsing.XNode, java.util.List<org.apache.ibatis.mapping.ResultMapping>)
注解解析逻辑位于org.apache.ibatis.builder.annotation.MapperAnnotationBuilder#parseResultMap
解析结果会注册到Configuration的resultMaps中
SqlSource解析
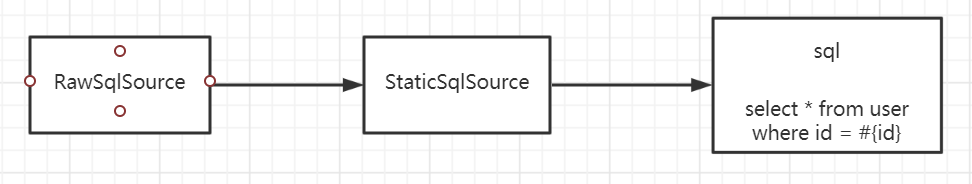
1.RawSqlSource:纯sql语句,不包含动态判断节点,例如:
select * from user where id = #{id}
创建过程如下为:
@Test
public void testRawSqlSource(){
RawSqlSource rawSqlSource = new RawSqlSource(new Configuration(), "select * from user where id = #{id}", Long.class);
System.out.println(rawSqlSource.getBoundSql(1L).getSql());
}
2.DynamicSqlSource:动态sql语句,例如:
select * from user where
<if test="id != null">
id = #{id}
</if>
创建过程如下为:
@Test
public void testDynamicSqlSource(){
List<SqlNode> contents = new ArrayList<>();
contents.add(new StaticTextSqlNode("select * from user where 1=1"));
contents.add(new IfSqlNode(new StaticTextSqlNode("and id = #{id}"), "id != null"));
MixedSqlNode mixedSqlNode = new MixedSqlNode(contents);
DynamicSqlSource dynamicSqlSource = new DynamicSqlSource(new Configuration(), mixedSqlNode);
BoundSql boundSql = dynamicSqlSource.getBoundSql(null);
System.out.println(boundSql.getSql());
MapperMethod.ParamMap<Object> objectParamMap = new MapperMethod.ParamMap<>();
objectParamMap.put("id", 1);
System.out.println(dynamicSqlSource.getBoundSql(objectParamMap).getSql());
}
3.ProviderSqlSource:@SelectProvider|@UpdateProvider|@DeleteProvider|@InsertProvider修饰注解方法,例如:
@Results(id = "BaseResultMap2",
value = {
@Result(property = "id", column = "id"),
@Result(property = "username", column = "username"),
@Result(property = "password", column = "password"),
}
)
@SelectProvider(type = UserSelectProvider.class, method = "selectById")
User selectById2(@Param("id") Long id);
public class UserSelectProvider{
public String selectById(){
return new SQL().SELECT("username", "password")
.FROM("user")
.WHERE("id = #{id}").toString();
}
}
创建过程如下:
@Test
public void testProviderSqlSource() {
Method[] methods = UserMapper.class.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
SelectProvider selectProvider = method.getAnnotation(SelectProvider.class);
if(selectProvider != null) {
ProviderSqlSource providerSqlSource = new ProviderSqlSource(new Configuration(), selectProvider, UserMapper.class, method);
System.out.println(providerSqlSource.getBoundSql(null).getSql());
}
}
}
4.StaticSqlSource:静态sqlSource,内部String类型的sql语句,上述3种最终都会转换为该SqlSource
解析逻辑位于org.apache.ibatis.scripting.xmltags.XMLScriptBuilder#parseScriptNode
MappedStatement解析
mappedStatement映射节点:
xml
<select id="selectById" resultType="com.example.demo.User" parameterType="long"> select * from user where id = #{id};
</select>
注解
@Results(id = "BaseResultMap2",
value = {
@Result(property = "id", column = "id"),
@Result(property = "username", column = "username"),
@Result(property = "password", column = "password"),
}
)
@Select("select * from user")
@Options(fetchSize = 10)
User selectById2(@Param("id") Long id);
mappedStatement的主要字段:
1.sqlCommandType:由使用的标签Select|Insert|Update|Delete等决定
2.parameterMap:传入参数,由属性parameterType|parameterMap决定
3.resultMaps:返回结果集,由属性resultMap|resultType决定
4.sqlSource:标签包围的sql节点,即:select * from user where id = #{id}
xml解析逻辑位于org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.XMLStatementBuilder#parseStatementNode
注解解析逻辑位于org.apache.ibatis.builder.annotation.MapperAnnotationBuilder#parseStatement
整体创建一个MappedStatement如下:
<select id="selectById" resultType="com.example.demo.User" parameterType="long"> select * from user where id = #{id};
</select>
@Test
public void testMappedStatement() {
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = new ArrayList<ParameterMapping>();
ParameterMap parameterMap = new ParameterMap.Builder(
configuration,
"selectById-Inline",
Long.class,
parameterMappings).build();
ResultMap inlineResultMap = new ResultMap.Builder(
configuration,
"selectById-Inline",
User.class,
new ArrayList<ResultMapping>(),
null).build();
RawSqlSource rawSqlSource = new RawSqlSource(configuration, "select * from user where id = #{id}", Long.class);
MappedStatement.Builder builder = new MappedStatement
.Builder(configuration, "selectById", rawSqlSource, SqlCommandType.SELECT);
builder.parameterMap(parameterMap);
builder.resultMaps(Collections.singletonList(inlineResultMap));
MappedStatement mappedStatement = builder.build();
configuration.addMappedStatement(mappedStatement);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
System.out.println(sqlSession.selectOne("selectById", 18L));
}
Mybatis——Mapper解析的更多相关文章
- mybatis源码-解析配置文件(四-1)之配置文件Mapper解析(cache)
目录 1. 简介 2. 解析 3 StrictMap 3.1 区别HashMap:键必须为String 3.2 区别HashMap:多了成员变量 name 3.3 区别HashMap:key 的处理多 ...
- MyBatis mapper文件中的变量引用方式#{}与${}的差别
MyBatis mapper文件中的变量引用方式#{}与${}的差别 #{},和 ${}传参的区别如下:使用#传入参数是,sql语句解析是会加上"",当成字符串来解析,这样相比于$ ...
- mybatis mapper namespace
http://www.mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/sqlmap-xml.html#insert_update_and_delete org.apache.ibatis.excep ...
- XML CDATA(Mybatis mapper and XML)
Tip:must be followed by either attribute specifications, ">" or "/>". 所有 X ...
- [DB][mybatis]MyBatis mapper文件引用变量#{}与${}差异
MyBatis mapper文件引用变量#{}与${}差异 默认,使用#{}语法,MyBatis会产生PreparedStatement中.而且安全的设置PreparedStatement參数,这个过 ...
- Mybatis Mapper接口是如何找到实现类的-源码分析
KeyWords: Mybatis 原理,源码,Mybatis Mapper 接口实现类,代理模式,动态代理,Java动态代理,Proxy.newProxyInstance,Mapper 映射,Map ...
- 基于注解的Mybatis mapper 接口注意事项
基于注解的Mybatis mapper 接口功能没有mapper xml配置文件丰富,并且动态sql语句的灵活性不能和xml配置相比. 这里仅仅说一下基于注解的动态sql注意事项: Mybatis提供 ...
- ][mybatis]MyBatis mapper文件中的变量引用方式#{}与${}的差别
转自https://blog.csdn.net/szwangdf/article/details/26714603 MyBatis mapper文件中的变量引用方式#{}与${}的差别 默认情况下,使 ...
- Mybatis的解析和运行原理
Mybatis的解析和运行原理 Mybatis的运行过程大致分为两大步:第一步,读取配置文件缓存到Configuration对象,用以创建 SqlSessionFactory:第二步,SqlSessi ...
随机推荐
- 搞定ReentrantReadWriteLock 几道小小数学题就够了
| 好看请赞,养成习惯 你有一个思想,我有一个思想,我们交换后,一个人就有两个思想 If you can NOT explain it simply, you do NOT understand it ...
- ThinkPHP5使用阿里云OSS图片上传
1.下载OSS文件放在网站根目录下(OSS文件下载地址:https://gitee.com/jth1234/oss_files.git) 2.在入口文件中加载OSS 3.config文件配置oss信息 ...
- nginx使用热部署添加新模块
简介 当初次编译安装nginx时,http_ssl_module 模块默认是不编译进nginx的二进制文件当中,如果需要添加 ssl 证书.也就是使用 https协议.那么则需要添加 http_ssl ...
- python冷知识(续)
python 冷知识 1.交互式中修改最大递归深度 大家都知道使用递归是有风险的,递归深度过深容易导致堆栈的溢出. 那到底,默认递归次数限制是多少呢? 可以使用sys这个库来查看 >>&g ...
- python递归函数实现阶乘函数
实现的效果如下: 参考www.cnblogs.com/yuanchenqi/articles/5828233.html f(5)=5*4*3*2*1=120 f(7)=7*6*5*4*3*2*1= ...
- 记一次服务器被植入挖矿木马cpu飙升200%解决过程
线上服务器用的是某讯云的,欢快的完美运行着Tomcat,MySQL,MongoDB,ActiveMQ等程序.突然一则噩耗从前线传来:网站不能访问了. 此项目是我负责,我以150+的手速立即打开了服务器 ...
- 利用搭载好的工控机环境跑yolov3-tiny
辛辛苦苦搭载好GPU环境现在要开始测试下效果 1,准备好数据集 2,测试开始 (1),如果尚未安装Darknet,则应先进行安装 git clone https://github.com/pjredd ...
- node实现文件属性批量修改(文件名)
前言 书接上回,我们实现了批量修改文件的时间,但是却没有实现文件名称的批量修改,是因为我也说过,没有界面的话直接在命令行实现显得有点繁琐,所以我们就通过接口+界面的方式来实现我们这个小需求吧.所以,闲 ...
- Linux高并发网络编程开发——10-Linux系统编程-第10天(网络编程基础-socket)
在学习Linux高并发网络编程开发总结了笔记,并分享出来.有问题请及时联系博主:Alliswell_WP,转载请注明出处. 10-Linux系统编程-第10天(网络编程基础-socket) 在学习Li ...
- SCOI 2016 萌萌哒
SCOI 2016 萌萌哒 solution 有点线段树的味道,但是并不是用线段树来做,而是用到另外一个区间修改和查询的利器--ST表 我们可以将一个点拆成\(logN\)个点,分别代表从点\(i\) ...
