ASP.NET Identity 身份验证和基于角色的授权
ASP.NET Identity 身份验证和基于角色的授权
在前一篇文章中,我介绍了ASP.NET Identity 基本API的运用并创建了若干用户账号。那么在本篇文章中,我将继续ASP.NET Identity 之旅,向您展示如何运用ASP.NET Identity 进行身份验证(Authentication)以及联合ASP.NET MVC 基于角色的授权(Role-Based Authorization)。
本文的示例,你可以在此下载和预览:
探索身份验证与授权
在这一小节中,我将阐述和证明ASP.NET 身份验证和授权的工作原理和运行机制,然后介绍怎样使用Katana Middleware 和 ASP.NET Identity 进行身份验证。
1. 理解ASP.NET 表单身份验证与授权机制
谈到身份验证,我们接触的最多的可能就是表单身份验证(Form-based Authentication)。为了更好的去理解ASP.NET 表单身份验证与授权机制,我搬出几年前的一张旧图,表示HttpApplication 19个事件,它们分别在HttpModule 中被注册,这又被称为ASP.NET 管道(Pipeline)事件。通俗的讲,当请求到达服务器时,ASP.NET 运行时会依次触发这些事件:
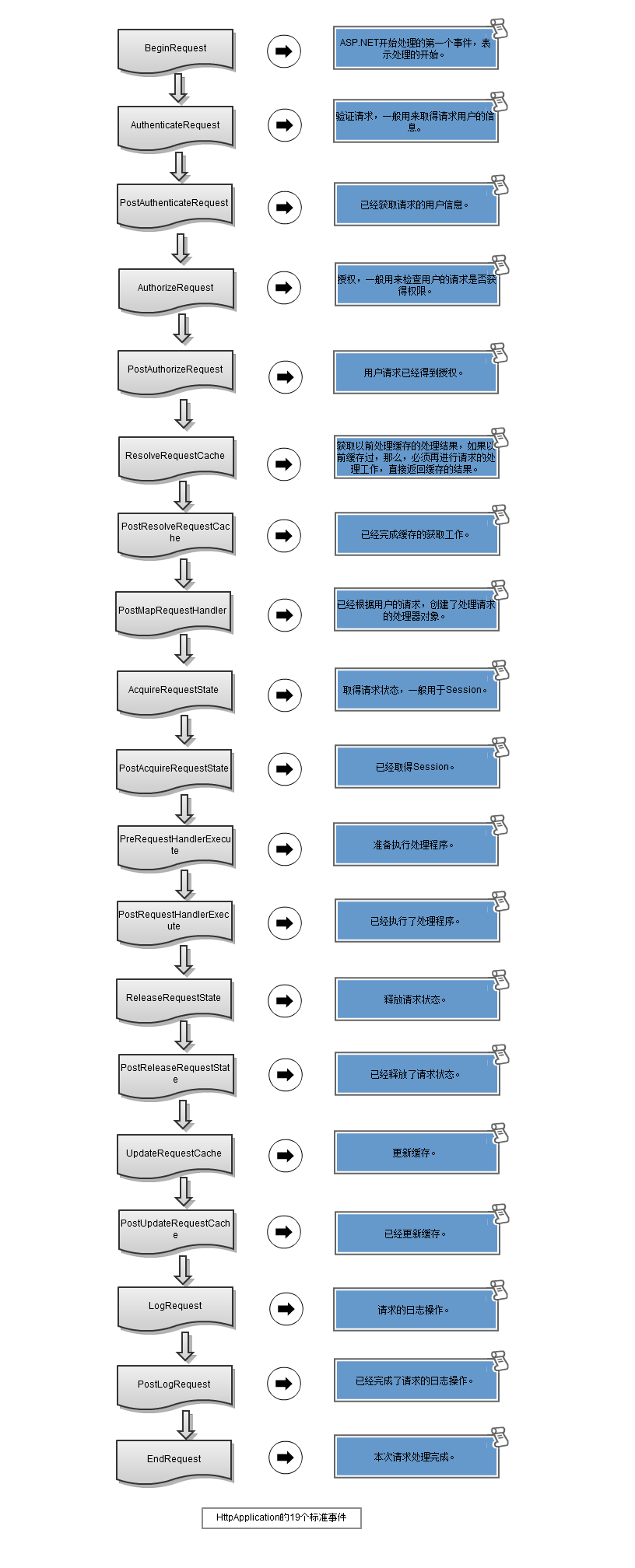
身份验证故名思义,验证的是用户提供的凭据(Credentials)。一旦验证通过,将产生唯一的Cookie标识并输出到浏览器。来自浏览器的下一次请求将包含此Cookie,对于ASP.NET 应用程序,我们熟知的FormsAuthenticationModule会对HttpApplication 的管道(Pipeline)事件AuthenticateRequest 进行注册,当请求经过ASP.NET Pipeline时,由ASP.NET Runtime 触发它,在该事件中,它会验证并解析该Cookie为对应的用户对象,它是一个实现了 IPrincipal接口的对象。PostAuthenticateRequest 事件在AuthenticateRequest 事件之后触发,表示用户身份已经检查完成 ,检查后的用户可以通过HttpContext的User属性获取并且HttpContext.User.Identity.IsAuthenticated属性为True。
如果将身份验证看作是"开门"的话,主人邀请你进屋,但这并不意味着你可以进入到卧室或者书房,可能你的活动场所仅限书房——这就是授权。在PostAuthenticateRequest事件触发过后,会触发AuthorizeRequest 事件,它在UrlAuthorizationModule 中被注册(题外插一句:UrlAuthorizationModule 以及上面提到的FormsAuthenticationModule你可以在IIS 级别的.config文件中找到,这也是ASP.NET 和 IIS紧耦合关系的体现)。在该事件中,请求的URL会依据web.config中的authorization 配置节点进行授权,如下所示授予Kim以及所有Role为Administrator的成员具有访问权限,并且拒绝John以及匿名用户访问。
- <authorization>
- <allow users="Kim"/>
- <allow roles="Administrator"/>
- <deny users="John"/>
- <deny users="?"/>
- </authorization>
通过身份验证和授权,我们可以对应用程序敏感的区域进行受限访问,这确保了数据的安全性。
2.使用Katana进行身份验证
到目前为止,你可能已经对OWIN、Katana 、 Middleware 有了基本的了解,如果不清楚的话,请移步到此浏览。
使用Katana,你可以选择几种不同类型的身份验证方式,我们可以通过Nuget来安装如下类型的身份验证:
- 表单身份验证
- 社交身份验证(Twitter、Facebook、Google、Microsoft Account…)
- Windows Azure
- Active Directory
- OpenID
其中又以表单身份验证用的最为广泛,正如上面提到的那样,传统ASP.NET MVC 、Web Form 的表单身份验证实际由FormsAuthenticationModule 处理,而Katana重写了表单身份验证,所以有必要比较一下传统ASP.NET MVC & Web Form 下表单身份验证与OWIN下表单身份验证的区别:
|
Features |
ASP.NET MVC & Web Form Form Authentication |
OWIN Form Authentication |
|
Cookie Authentication |
√ |
√ |
|
Cookieless Authentication |
√ |
× |
|
Expiration |
√ |
√ |
|
Sliding Expiration |
√ |
√ |
|
Token Protection |
√ |
√ |
|
Claims Support |
× |
√ |
|
Unauthorized Redirection |
√ |
√ |
从上表对比可以看出,Katana几乎实现了传统表单身份验证所有的功能,那我们怎么去使用它呢?还是像传统那样在web.config中指定吗?
非也非也,Katana 完全抛弃了FormsAuthenticationModule,实际上是通过Middleware来实现身份验证。默认情况下,Middleware在HttpApplication的PreRequestHandlerExecute 事件触发时链式执行,当然我们也可以将它指定在特定的阶段执行,通过使用UseStageMarker方法,我们可以在AuthenticateRequest 阶段执行Middleware 进行身份验证。
那我们要怎样去实现呢?幸运的是,Katana已经帮助我们封装好了一个扩展方法,如下所示,
- app.UseCookieAuthentication(new CookieAuthenticationOptions
- {
- AuthenticationType = DefaultAuthenticationTypes.ApplicationCookie,
- LoginPath = new PathString("/Account/Login")
- });
app.UseCookieAuthentication 是一个扩展方法,它的内部帮我们做了如下几件事:
- 使用app.Use(typeof(CookieAuthenticationMiddleware), app, options) 方法,将CookieAuthenticationMiddleware 中间件注册到OWIN Pipeline中
- 通过app.UseStageMarker(PipelineStage.Authenticate)方法,将前面添加的CookieAuthenticationMiddleware指定在 ASP.NET 集成管道(ASP.NET integrated pipeline)的AuthenticateRequest阶段执行
当调用(Invoke)此Middleware时,将调用CreateHandler方法返回CookieAuthenticationHandler对象,它包含 AuthenticateCoreAsync方法,在这个方法中,读取并且验证Cookie,然后通过AddUserIdentity方法创建ClaimsPrincipal对象并添加到Owin环境字典中,可以通过OwinContext对象Request.User可以获取当前用户。
这是一个典型Middleware中间件使用场景,说白了就是去处理Http请求并将数据存储到OWIN环境字典中进行传递。而CookieAuthenticationMiddleware所做的事其实和FormsAuthenticationModule做的事类似。
那我们怎么产生Cookie呢?使用ASP.NET Identity 进行身份验证,如果验证通过,产生Cookie并输出到客户端浏览器, 这样一个闭环就形成了,我将在下一小节实施这一步骤。
3.使用Authorize特性进行授权
ASP.NET Identity已经集成到了ASP.NET Framework中,在ASP.NET MVC 中,我们可以使用Authorize 特性进行授权,如下代码所示:
- [Authorize]
- public ActionResult Index()
- {
- return View();
- }
上述代码中,Index Action 已被设置了受限访问,只有身份验证通过才能访问它,如果验证不通过,返回401.0 – Unauthorized,然后请求在EndRequest 阶段被 OWIN Authentication Middleware 处理,302 重定向到/Account/Login 登录。

使用ASP.NET Identity 身份验证
有了对身份验证和授权机制基本了解后,那么现在就该使用ASP.NET Identity 进行身份验证了。
1. 实现身份验证所需的准备工作
当我们匿名访问授权资源时,会被Redirect 到 /Account/Login 时,此时的URL结构如下:
http://localhost:60533/Account/Login?ReturnUrl=%2Fhome%2Findex
因为需要登陆,所以可以将Login 设置为允许匿名登陆,只需要在Action的上面添加 [AllowAnonymous] 特性标签,如下所示:
- [AllowAnonymous]
- public ActionResult Login(string returnUrl)
- {
- //如果登录用户已经Authenticated,提示请勿重复登录
- if (HttpContext.User.Identity.IsAuthenticated)
- {
- return View("Error", new string[] {"您已经登录!"});
- }
- ViewBag.returnUrl = returnUrl;
- return View();
- }
注意,在这儿我将ReturnUrl 存储了起来,ReturnUrl 顾名思义,当登录成功后,重定向到最初的地址,这样提高了用户体验。
由于篇幅的限制,Login View 我不将代码贴出来了,事实上它也非常简单,包含如下内容:
- 用户名文本框
- 密码框
- 存储ReturnUrl的隐藏域
- @Html.AntiForgeryToken(),用来防止CSRF跨站请求伪造
2.添加用户并实现身份验证
当输入了凭据之后,POST Form 表单到/Account/Login 下,具体代码如下:
- [HttpPost]
- [AllowAnonymous]
- [ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
- public async Task<ActionResult> Login(LoginModel model,string returnUrl)
- {
- if (ModelState.IsValid)
- {
- AppUser user = await UserManager.FindAsync(model.Name, model.Password);
- if (user==null)
- {
- ModelState.AddModelError("","无效的用户名或密码");
- }
- else
- {
- var claimsIdentity =
- await UserManager.CreateIdentityAsync(user, DefaultAuthenticationTypes.ApplicationCookie);
- AuthManager.SignOut();
- AuthManager.SignIn(new AuthenticationProperties {IsPersistent = false}, claimsIdentity);
- return Redirect(returnUrl);
- }
- }
- ViewBag.returnUrl = returnUrl;
- return View(model);
- }
上述代码中,首先使用 ASP.NET Identity 来验证用户凭据,这是通过 AppUserManager 对象的FindAsync 方法来实现,如果你不了解ASP.NET Identity 基本API ,请参考我这篇文章。
- AppUser user = await UserManager.FindAsync(model.Name, model.Password);
FindAsync 方法接受两个参数,分别是用户名和密码,如果查找到,则返回AppUser 对象,否则返回NULL。
如果FindAsync 方法返回AppUser 对象,那么接下来就是创建Cookie 并输出到客户端浏览器,这样浏览器的下一次请求就会带着这个Cookie,当请求经过AuthenticateRequest 阶段时,读取并解析Cookie。也就是说Cookie 就是我们的令牌, Cookie如本人,我们不必再进行用户名和密码的验证了。
使用ASP.NET Identity 产生Cookie 其实很简单,就3行代码,如下所示:
- var claimsIdentity =
- await UserManager.CreateIdentityAsync(user, DefaultAuthenticationTypes.ApplicationCookie);
- AuthManager.SignOut();
- AuthManager.SignIn(new AuthenticationProperties {IsPersistent = false}, claimsIdentity);
对代码稍作分析,第一步创建了用来代表当前登录用户的ClaimsIdentity 对象,ClaimsIndentity 是 ASP.NET Identity 中的类,它实现了IIdentity 接口。
ClaimsIdentity 对象实际上由AppUserManager 对象的CreateIdentityAsync 方法创建,它需要接受一个AppUser 对象和身份验证类型,在这儿选择ApplicationCookie。
接下来,就是让已存在的Cookie 失效,并产生新Cookie。我预先定义了一个AuthManager 属性,它是IAuthenticationManager 类型的对象,用来做一些通用的身份验证操作。它 包含如下重要的操作:
- SignIn(options,identity) 故名思意登录,用来产生身份验证过后的Cookie
- SignOut() 故名思意登出,让已存在的Cookie 失效
SignIn 需要接受两个参数,AuthenticationProperties 对象和ClaimsIdentity 对象,AuthticationProperties 有众多属性,我在这儿只设置IsPersistent=true ,意味着Authentication Session 被持久化保存,当开启新Session 时,该用户不必重新验证了。
最后,重定向到ReturnUrl:
- return Redirect(returnUrl);
使用角色进行授权
在前一小节中,使用了Authorize 特性对指定区域进行受限访问,只有被身份验证通过后才能继续访问。在这一小节将更细粒度进行授权操作,在ASP.NET MVC Framework 中,Authorize 往往结合User 或者 Role 属性进行更小粒度的授权操作,正如如下代码所示:
- [Authorize(Roles = "Administrator")]
- public class RoleController : Controller
- {
- }
1.使用ASP.NET Identity 管理角色
对Authorize 有了基本的了解之后,将关注点转移到角色Role的管理上来。ASP.NET Identity 提供了一个名为RoleManager<T> 强类型基类用来访问和管理角色,其中T 实现了IRole 接口,IRole 接口包含了持久化Role 最基础的字段(Id和Name)。
Entity Framework 提供了名为IdentityRole 的类,它实现了IRole 接口,所以它不仅包含Id、Name属性,还增加了一个集合属性Users。IdentityRole重要的属性如下所示:
|
Id |
定义了Role 唯一的Id |
|
Name |
定义了Role的名称 |
|
Users |
返回隶属于Role的所有成员 |
我不想在应用程序中直接使用IdentityRole,因为我们还可能要去扩展其他字段,故定义一个名为AppRole的类,就像AppUser那样,它继承自IdentityRole:
- public class AppRole:IdentityRole
- {
- public AppRole() : base() { }
- public AppRole(string name) : base(name) { }
- // 在此添加额外属性
- }
同时,再定义一个AppRoleManager 类,如同AppUserManager 一样,它继承RoleManager<T>,提供了检索和持久化Role的基本方法:
- public class AppRoleManager:RoleManager<AppRole>
- {
- public AppRoleManager(RoleStore<AppRole> store):base(store)
- {
- }
- public static AppRoleManager Create(IdentityFactoryOptions<AppRoleManager> options, IOwinContext context)
- {
- return new AppRoleManager(new RoleStore<AppRole>(context.Get<AppIdentityDbContext>()));
- }
- }
最后,别忘了在OWIN Startup类中初始化该实例,它将存储在OWIN上下文环境字典中,贯穿了每一次HTTP请求:
- app.CreatePerOwinContext(AppIdentityDbContext.Create);
- app.CreatePerOwinContext<AppUserManager>(AppUserManager.Create);
- app.CreatePerOwinContext<AppRoleManager>(AppRoleManager.Create);
2.创建和删除角色
使用ASP.NET Identity 创建和删除角色很简单,通过从OWIN 上下文中获取到AppRoleManager,然后Create 或者 Delete,如下所示:
- [HttpPost]
- public async Task<ActionResult> Create(string name)
- {
- if (ModelState.IsValid)
- {
- IdentityResult result = await RoleManager.CreateAsync(new AppRole(name));
- if (result.Succeeded)
- {
- return RedirectToAction("Index");
- }
- else
- {
- AddErrorsFromResult(result);
- }
- }
- return View(name);
- }
- [HttpPost]
- public async Task<ActionResult> Delete(string id)
- {
- AppRole role = await RoleManager.FindByIdAsync(id);
- if (role != null)
- {
- IdentityResult result = await RoleManager.DeleteAsync(role);
- if (result.Succeeded)
- {
- return RedirectToAction("Index");
- }
- else
- {
- return View("Error", result.Errors);
- }
- }
- else
- {
- return View("Error", new string[] { "无法找到该Role" });
- }
- }
3.管理角色 MemberShip
要对用户授权,除了创建和删除角色之外,还需要对角色的MemberShip 进行管理,即通过Add /Remove 操作,可以向用户添加/删除角色。
为此,我添加了两个ViewModel,RoleEditModel和RoleModificationModel,分别代表编辑时展示字段和表单 Post时传递到后台的字段:
- public class RoleEditModel
- {
- public AppRole Role { get; set; }
- public IEnumerable<AppUser> Members { get; set; }
- public IEnumerable<AppUser> NonMembers { get; set; }
- }
- public class RoleModificationModel
- {
- public string RoleName { get; set; }
- public string[] IDsToAdd { get; set; }
- public string[] IDsToDelete { get; set; }
- }
在对角色进行编辑时,获取所有隶属于Role的成员和非隶属于Role的成员:
- /// <summary>
- /// 编辑操作,获取所有隶属于此Role的成员和非隶属于此Role的成员
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="id"></param>
- /// <returns></returns>
- public async Task<ActionResult> Edit(string id)
- {
- AppRole role = await RoleManager.FindByIdAsync(id);
- string[] memberIDs = role.Users.Select(x => x.UserId).ToArray();
- IEnumerable<AppUser> members = UserManager.Users.Where(x => memberIDs.Any(y => y == x.Id));
- IEnumerable<AppUser> nonMembers = UserManager.Users.Except(members);
- return View(new RoleEditModel()
- {
- Role = role,
- Members = members,
- NonMembers = nonMembers
- });
- }
最终呈现的视图如下所示:

当点击保存,提交表单时,通过模型绑定,将数据Post 到Edit Action,实现了对角色的MemberShip 进行管理,即通过Add /Remove 操作,可以向用户添加/删除角色。
,如下所示:
- [HttpPost]
- public async Task<ActionResult> Edit(RoleModificationModel model)
- {
- IdentityResult result;
- if (ModelState.IsValid)
- {
- foreach (string userId in model.IDsToAdd??new string[] {})
- {
- result = await UserManager.AddToRoleAsync(userId, model.RoleName);
- if (!result.Succeeded)
- {
- return View("Error", result.Errors);
- }
- }
- foreach (var userId in model.IDsToDelete??new string[] {})
- {
- result = await UserManager.RemoveFromRoleAsync(userId, model.RoleName);
- if (!result.Succeeded)
- {
- return View("Error", result.Errors);
- }
- }
- return RedirectToAction("Index");
- }
- return View("Error",new string[] {"无法找到此角色"});
- }
在上述代码中,你可能注意到了UserManager 类,它包含了若干与角色相关的操作方法:
|
AddToRoleAsync(string userId,string role) |
添加用户到指定的角色中 |
|
GetRolesAsync(string userId) |
获取User对应的角色列表 |
|
IsInRoleAsync(string userId,string role) |
判断用户是否隶属于指定的角色 |
|
RemoveFromRoleAsync(string userId,string role) |
将用户从指定角色中排除 |
初始化数据,Seeding 数据库
在上一小节中,通过Authorize 标签将Role 控制器受限访问,只有Role=Administrator的用户才能访问和操作。
- [Authorize(Roles = "Administrator")]
- public class RoleController : Controller
- {
- }
但当我们的应用程序部署到新环境时,是没有具体的用户数据的,这就导致我们无法访问Role Controller。这是一个典型的 "鸡生蛋还是蛋生鸡"问题。
要解决这个问题,我们一般是在数据库中内置一个管理员角色,这也是我们熟知的超级管理员角色。通过Entity Framework Seed,我们可以轻松实现数据的初始化:
- public class IdentityDbInit
- : DropCreateDatabaseIfModelChanges<AppIdentityDbContext>
- {
- protected override void Seed(AppIdentityDbContext context)
- {
- PerformInitialSetup(context);
- base.Seed(context);
- }
- public void PerformInitialSetup(AppIdentityDbContext context)
- {
- // 初始化
- AppUserManager userMgr = new AppUserManager(new UserStore<AppUser>(context));
- AppRoleManager roleMgr = new AppRoleManager(new RoleStore<AppRole>(context));
- string roleName = "Administrators";
- string userName = "Admin";
- string password = "Password2015";
- string email = "admin@jkxy.com";
- if (!roleMgr.RoleExists(roleName))
- {
- roleMgr.Create(new AppRole(roleName));
- }
- AppUser user = userMgr.FindByName(userName);
- if (user == null)
- {
- userMgr.Create(new AppUser { UserName = userName, Email = email },
- password);
- user = userMgr.FindByName(userName);
- }
- if (!userMgr.IsInRole(user.Id, roleName))
- {
- userMgr.AddToRole(user.Id, roleName);
- }
- }
- }
在这儿实例化了AppUserManager和AppRoleManager实例,这是因为PerformInitialSetup 方法比OWIN 配置先执行。
小结
在这篇文章中,探索了使用ASP.NET Identity 进行身份验证以及联合ASP.NET MVC 基于角色的授权。最后实现了对角色的管理。在下一篇文章中,继续ASP.NET Identity之旅,探索ASP.NET Identity 的高级应用——基于声明的授权。
ASP.NET Identity 身份验证和基于角色的授权的更多相关文章
- ASP.NET MVC 随想录——探索ASP.NET Identity 身份验证和基于角色的授权,中级篇
在前一篇文章中,我介绍了ASP.NET Identity 基本API的运用并创建了若干用户账号.那么在本篇文章中,我将继续ASP.NET Identity 之旅,向您展示如何运用ASP.NET Ide ...
- ASP.NET Core 2.1中基于角色的授权
ASP.NET Core 2.1中基于角色的授权 授权是来描述用户能够做什么的过程.例如,只允许管理员用户可以在电脑上进行软件的安装以及卸载.而非管理员用户只能使用软件而不能进行软件的安装以及卸载.它 ...
- 坎坷路:ASP.NET 5 Identity 身份验证(上集)
之所以为上集,是因为我并没有解决这个问题,写这篇博文的目的是纪录一下我所遇到的问题,以免自己忘记,其实已经忘了差不多了,写的过程也是自己回顾的过程,并且之前收集有关 ASP.NET 5 身份验证的书签 ...
- 坎坷路:ASP.NET Core 1.0 Identity 身份验证(中集)
上一篇:<坎坷路:ASP.NET 5 Identity 身份验证(上集)> ASP.NET Core 1.0 什么鬼?它是 ASP.NET vNext,也是 ASP.NET 5,以后也可能 ...
- Asp.net Mvc 身份验证、异常处理、权限验证(拦截器)实现代码
本问主要介绍asp.net的身份验证机制及asp.net MVC拦截器在项目中的运用.现在让我们来模拟一个简单的流程:用户登录>权限验证>异常处理 1.用户登录 验证用户是否登录成功步骤直 ...
- ASP.NET中身份验证的三种方法
Asp.net的身份验证有有三种,分别是"Windows | Forms | Passport",其中又以Forms验证用的最多,也最灵活.Forms 验证方式对基于用户的验证授权 ...
- ASP.NET Forms 身份验证
ASP.NET Forms 身份验证 在开发过程中,我们需要做的事情包括: 1. 在 web.config 中设置 Forms 身份验证相关参数.2. 创建登录页. 登录页中的操作包括: 1. 验证用 ...
- Forms身份验证和基于Role的权限验证
Forms身份验证和基于Role的权限验证 从Membership到SimpleMembership再到ASP.NET Identity,ASP.NET每一次更换身份验证的组件,都让我更失望.Memb ...
- Asp.Net MVC 身份验证-Forms
Asp.Net MVC 身份验证-Forms 在MVC中对于需要登录才可以访问的页面,只需要在对应的Controller或Action上添加特性[Authorize]就可以限制非登录用户访问该页面.那 ...
随机推荐
- WPF对于xml的简单操作(下下)插入节点并排序
正如T所说,下下,这个方法不堪入目, ̄□ ̄|| 贴上再说 //先搞个struct声明 private struct datastruct { public string x; public strin ...
- simplePagination API
simplePagination API simplePagination.js 一个简单的jQuery分页插件,主题和Bootstrap支持CSS 3 分页button样式 "light- ...
- OGG-01008 Extract displays Discarding bad record (discard recs=1) when using filter or where clause
因为在extract參数文件里使用了where语句,而where后面的的条件列又不是主键,没有为update.delete操作记录日志,因此会报1008错误. Applies to: Oracle G ...
- php  性能优化
基础优化 1 不要随便复制变量. 有时候为了使 PHP 代码更加整洁,一些 PHP 新手(包含我)会把提前定义好的变量拷贝到一个名字更简短的变量中,事实上这样做的结果是添加了一倍的内存消耗,仅仅会使程 ...
- Google Maps Android API v2 (1)- 入门
才可以开始工作的API,你将需要下载的API,并确保你有一个谷歌地图Android的API V2关键.API和关键是免费提供的. 概观 获得谷歌地图Android的API V2 谷歌地图API密钥 显 ...
- Android KitKat 4.4 Wifi移植AP模式和网络共享的调试日志
Tethering技术在移动平台上已经运用的越来越广泛了.它能够把移动设备当做一个接入点,其它的设备能够通过Wi-Fi.USB或是Bluetooth等方式连接到此移动设备.在Android中能够将Wi ...
- mysql回想一下基础知识
创建数据库 creat table test( #整数通常用于int test_id int, #十进制通常使用decimal test_price decimal, #普通文本通常使用.并使用Def ...
- C. Captain Marmot (Codeforces Round #271)
C. Captain Marmot time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard in ...
- c# 获取某个对象的[公有属性]的名称,类型,值
/// <summary> /// 获取某个对象的[公有属性]的名称,类型,值 /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="T&qu ...
- Mono for Andriod学习与实践(1)— 初体验
对于Andriod的开发者来说,相信Java语言是第一选择,可是对于.Net开发者来说,要想利用C#在Andriod平台上开发,Mono提供了相应的开发平台来实现,Mono for Andriod就是 ...
