Spring Security Architecture and Implementation(架构和实现)学习笔记
Spring Security
关于spring-security的官网文档学习笔记,主要是第8章 Architecture and Implementation(架构和实现)内容
Architecture and Implementation(架构与实现)
应用程序安全性可以归结为或多或少的两个独立问题:身份验证(您是谁)和授权(您可以做什么?)
Summary(摘要)
Spring Security的主要组成部分:
SecurityContextHolder,提供对的访问SecurityContext。SecurityContext,以保存Authentication(可能还有特定于请求的)安全信息。Authentication,以特定于Spring Security的方式表示主体。GrantedAuthority,以反映授予主体的应用程序范围的权限。UserDetails,以提供必要的信息以从应用程序的DAO或其他安全数据源构建Authentication对象。UserDetailsService,以UserDetails在传入String基于-的用户名(或证书ID等)时创建一个。
Authentication(身份验证)
What is authentication in Spring Security?
Spring Security中的身份验证:
- 获取用户名和密码,并将其组合到的一个实例
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(Authentication接口的实例)。 - 令牌会传递到的实例
AuthenticationManager进行验证。 - 成功认证后 ,
AuthenticationManager返回一个完全填充的Authentication实例。 - 通过调用
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(…)并传入返回的身份验证对象来建立安全上下文。
官网实例:
/**
*
* 身份认证实例
*
* {@link AuthenticationManager} 认证管理器,处理{@link Authentication}请求,返回一个完全填充的{@link Authentication}实例
*
* {@link GrantedAuthority} 授予的权限
*
* 参考: https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/site/docs/5.2.1.BUILD-SNAPSHOT/reference/htmlsingle/#tech-intro-authentication
*
* @author xinchen
* @version 1.0
* @date 16/10/2019 11:07
*/
public class AuthenticationExample {
private static AuthenticationManager am = new SampleAuthenticationManager();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
while (true){
System.out.println("Please enter your username:");
String name = in.readLine();
System.out.println("Please enter your password:");
String password = in.readLine();
try {
Authentication request = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(name, password);
Authentication result = am.authenticate(request);
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(result);
break;
} catch(AuthenticationException e) {
System.out.println("Authentication failed: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
System.out.println("Successfully authenticated. Security context contains: " +
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication());
}
}
class SampleAuthenticationManager implements AuthenticationManager{
static final List<GrantedAuthority> AUTHORITIES = new ArrayList<>();
static {
// 初始化角色
AUTHORITIES.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_USER"));
}
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
// authentication.getCredentials() 通常是密码
if (authentication.getName().equals(authentication.getCredentials())){
// Object principal, Object credentials, Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities
return new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(authentication.getName(), authentication.getCredentials(), AUTHORITIES);
}
throw new BadCredentialsException("Bad Credentials");
}
}
Authentication in a Web Application
考虑典型的Web应用程序的身份验证过程:
- 1.您访问主页,然后单击链接。
- 2.请求发送到服务器,服务器确定您已请求受保护的资源。
- 3.由于您目前尚未通过身份验证,因此服务器会发回响应,指示您必须进行身份验证。响应将是HTTP响应代码,或重定向到特定网页。
- 4.根据身份验证机制,您的浏览器将重定向到特定网页,以便您可以填写表格,或者浏览器将以某种方式检索您的身份(通过BASIC身份验证对话框,cookie,X.509证书等)。 )。
- 5.浏览器将响应发送回服务器。这将是包含您填写的表单内容的HTTP POST或包含身份验证详细信息的HTTP标头。
- 6.接下来,服务器将决定所提供的凭据是否有效。如果有效,则将进行下一步。如果它们无效,通常会要求您的浏览器再试一次(因此您返回到上面的第二步)。
- 7.您尝试引起身份验证过程的原始请求将被重试。希望您已获得足够授权的身份验证,以访问受保护的资源。如果您具有足够的访问权限,则请求将成功。否则,您将收到一个HTTP错误代码403,表示“禁止”。
Spring Security具有负责上述大多数步骤的不同类。
主要参与者(按照使用顺序)是ExceptionTranslationFilter,AuthenticationEntryPoint和和“Authentication Mechanism(身份验证机制)”,它们负责调用AuthenticationManager
ExceptionTranslationFilter
ExceptionTranslationFilter是一个Spring Security过滤器,它负责检测抛出的任何Spring Security异常(AccessDeniedException和AuthenticationException).
此类异常通常由AbstractSecurityInterceptor授权服务的主要提供者抛出
AuthenticationEntryPoint
AuthenticationEntryPoint(认证入口点)主要负责上述步骤中的第3步.
主要是在ExceptionTranslationFilter中通过捕获到AuthenticationException异常后,
调用handleSpringSecurityException(...)在此方法中的sendStartAuthentication(...)开启认证方案
Authentication Mechanism
Authentication Mechanism(身份验证机制),
一旦您的浏览器提交了身份验证凭据(authentication credentials)(作为HTTP表单帖子或HTTP标头
,服务器上就需要有一些东西来“收集”这些身份验证详细信息。到目前为止,我们位于上述列表的第6步.
在Spring Security中,我们有一个特殊的名称,用于从用户代理(通常是Web浏览器)收集身份验证详细信息的功能,将其称为Authentication Mechanism(身份验证机制)。
从用户代理收集到身份验证详细信息后,Authentication便会构建一个“请求”对象,然后将其呈现给AuthenticationManager
Authentication Mechanism(身份验证机制)收到完整的Authentication(从AuthenticationManager中返回)对象后,
它将认为请求有效,将Authentication放入SecurityContextHolder,
并导致重试原始请求(上述步骤7)。
另一方面,如果AuthenticationManager拒绝了请求,
则认证机制将要求用户代理重试(上面的第2步)。
通常AuthenticationManager中的返回:
- 如果它可以验证输入是否代表有效的主体,则返回
Authentication(通常为authenticated=true) - 如果它认为输入代表无效的主体,则抛出一个
AuthenticationException - 如果无法决定,则返回
null
Storing the SecurityContext between requests
在请求之间如何存储SecurityContext?根据应用程序的类型,可能需要制定一种策略来存储用户操作之间的安全上下文。在典型的Web应用程序中,用户登录一次,然后通过其会话ID(session id)进行标识。
有效期取决于服务器session的过期时间.
在Spring Security中,存储SecurityContext请求之间的责任落在SecurityContextPersistenceFilter,
默认情况下,将上下文存储为HttpSessionHTTP请求之间的属性(将设置request.setAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED, Boolean.TRUE);保证值执行一次)。
它将上下文SecurityContextHolder还原到每个请求,并且至关重要的是,当请求完成时清除SecurityContextHolder
SecurityContextPersistenceFilter中真正存储由SecurityContextRepository完成,通过调用loadContext(...)加载其中:
NullSecurityContextRepository实际上是每次都生成新的SecurityContextHolder.createEmptyContext()HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository实际上是存储在HttpSession中,默认属性值为SPRING_SECURITY_CONTEXT,可以通过修改springSecurityContextKey自定义该值
许多其他类型的应用程序(例如,无状态RESTful Web服务)不使用HTTP会话,并且将在每个请求上重新进行身份验证。
但是,仍然必须确保链中包含SecurityContextPersistenceFilter,以确保SecurityContextHolder在每次请求后清除。
Access-Control (Authorization) in Spring Security
在Spring Security中负责做出访问控制决策的主要接口是AccessDecisionManager。它具有一种decide方法,该方法采用Authentication代表请求访问的主体的对象,“secure object(安全对象)”(请参见下文)以及适用于该对象的安全元数据属性列表(例如授予访问权限所需的角色列表) )。
Security and AOP Advice
您可以选择使用AspectJ或Spring AOP执行方法授权,也可以选择使用过滤器执行Web请求授权,Spring Security中主要是AbstractSecurityInterceptor的继承类FilterSecurityInterceptor贯穿整个周期
Secure Objects and the AbstractSecurityInterceptor
那么,什么是 “secure object(安全对象)”?Spring Security使用该术语来指代任何可以对其应用安全性(例如授权决策)的对象。最常见的示例是方法调用和Web请求。
每个受支持的安全对象类型都有其自己的拦截器类(AbstractSecurityInterceptor的子类),
重要的是,当AbstractSecurityInterceptor被调用时,如果principal(主体)已通过身份验证,
SecurityContextHolder则将包含有效Authentication的内容。
AbstractSecurityInterceptor 提供用于处理安全对象请求的一致工作流,通常是:
- 1.查找与当前请求关联的
“configuration attributes(配置属性)” - 2.将安全对象,当前
Authentication属性和配置属性提交AccessDecisionManager给授权决策 - 3.(可选)更改
Authentication调用的依据 - 4.允许进行安全对象调用(假设已授予访问权限)
- 5.调用返回后如果配置了
AfterInvocationManager,则调用。一旦调用引发了异常,AfterInvocationManager则不会调用。
注,关于步骤
2,可查看AbstractSecurityInterceptor中的this.accessDecisionManager.decide(authenticated, object, attributes);
What are Configuration Attributes(配置属性)?
可以将“configuration attribute(配置属性)”视为一个String,它对所有AbstractSecurityInterceptor使用的类具有特殊的含义.
它们由框架内的接口ConfigAttribute表示。它们可以是简单的角色名称,也可以具有更复杂的含义,具体取决于AccessDecisionManager的具体实现。
AbstractSecurityInterceptor配置了SecurityMetadataSource来查找安全对象的属性。通常,此配置将对用户隐藏。
配置属性将作为安全方法的注释或安全URL的访问属性输入.
例如,当我们配置<intercept-url pattern='/secure/**' access='ROLE_A,ROLE_B'/>,这表示配置属性ROLE_A和ROLE_B适用于与给定模式匹配的网络请求。
实际上,使用默认AccessDecisionManager配置,这意味着GrantedAuthority将允许具有这两个属性之一匹配的任何人访问。
严格来说,它们只是属性,其解释取决于AccessDecisionManager的实现。
前缀的使用ROLE_是一个标记,以指示这些属性是角色,并且应由Spring Security的RoleVoter消费.
这仅AccessDecisionManager在使用基于投票者的情况下才有意义。
RunAsManager
假设AccessDecisionManager决定允许该请求,AbstractSecurityInterceptor通常将继续进行该请求。
但是有可能用户希望用不同的Authentication替换处于SecurityContext中已经通过AccessDecisionManager处理返回的Authentication,这个时候可以使用RunAsManager.
当服务层方法(Service layer)需要调用远程系统并显示不同的标识(不同的安全属性等)时,这可能会有有用.
因为Spring Security会自动将安全身份从一台服务器传播到另一台服务器(假设您使用的是正确配置的RMI或HttpInvoker远程协议客户端)
AfterInvocationManager
当安全对象(secure object)调用和返回,这可能意味着方法调用完成或过滤器链继续进行,AbstractSecurityInterceptor最终有机会处理该调用。
在这个阶段,AbstractSecurityInterceptor可以修改返回对象.
我们可能希望发生这种情况,因为无法在安全对象调用的“途中”做出授权决定。
由于高度可插拔,因此AbstractSecurityInterceptor将控制权传递给AfterInvocationManager以便在需要时实际修改对象。
此类甚至可以完全替换对象,或者引发异常,也可以按照其选择的任何方式对其进行更改。
调用后检查仅在调用成功的情况下执行。如果发生异常,将跳过其他检查。
Security interceptors and the "secure object" model
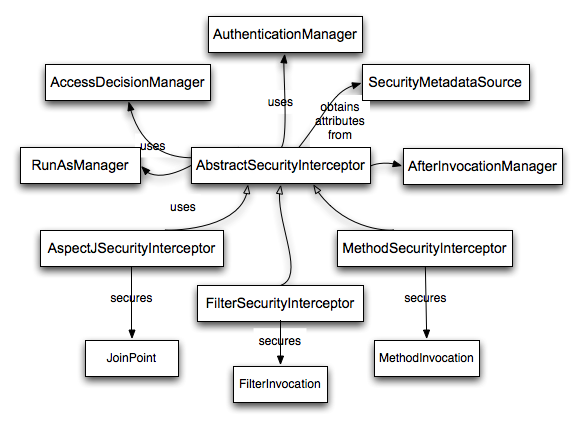
Extending the Secure Object Model
只有打算采用全新的拦截和授权请求方式的开发人员才需要直接使用安全对象。
例如,有可能建立一个新的安全对象以保护对消息系统的呼叫。
任何需要安全性并且还提供拦截呼叫的方式的东西(例如,围绕建议语义的AOP)都可以成为安全对象。
话虽如此,大多数Spring应用程序将完全透明地使用当前支持的三种安全对象类型(AOP Alliance MethodInvocation,AspectJ JoinPoint和Web request FilterInvocation)。
Core Services(核心服务)
现在,我们对Spring Security的架构和核心类的高度概括,让我们来仔细看看一个或两个核心接口及其实现的,
特别是AuthenticationManager,UserDetailsService和AccessDecisionManager。
AuthenticationManager,ProviderManager和AuthenticationProvider

AuthenticationManager只是一个接口,这样实现可以让我们选择,但它是如何在实践中运作?
如果我们需要检查多个身份验证数据库或不同身份验证服务(例如数据库和LDAP服务器)的组合,该怎么办?
Spring Security中的默认实现是ProviderManager,而不是处理身份验证请求本身,
它委托给已配置的AuthenticationProviders列表,依次查询每个,以查看其是否可以执行身份验证。
每个provider都会引发异常或者返回一个完全填充的Authentication对象.
验证身份验证请求的最常见方法是加载相应UserDetails的密码,并对照用户输入的密码检查已加载的密码。
这是DaoAuthenticationProvider(见下文)使用的方法。加载的UserDetails对象-尤其是GrantedAuthority包含的对象-
当成功认证时,会构建一个完全填充的Authentication对象返回,并且存储到SecurityContext环境上下文中.
<bean id="authenticationManager"
class="org.springframework.security.authentication.ProviderManager">
<constructor-arg>
<list>
<!-- 这些bean都是AuthenticationProvider的实现类 -->
<ref local="daoAuthenticationProvider"/>
<ref local="anonymousAuthenticationProvider"/>
<ref local="ldapAuthenticationProvider"/>
</list>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
在上面的示例中,我们有三个提供程序。它们按照所示的顺序进行尝试.
每个提供程序都可以尝试进行身份验证,也可以通过简单地返回来跳过身份验证null。
如果所有实现均返回null,ProviderManager则将抛出ProviderNotFoundException。
诸如Web表单登录处理过滤器之类的身份验证机制,其注入了对ProviderManager的引用,并将调用它来处理其身份验证请求。
你需要的providers有时候可能会被认证机制(authentication mechanisms)调用,而其他时候,它们将取决于特定的身份验证机制(a specific authentication mechanism)。
例如,DaoAuthenticationProvider和LdapAuthenticationProvider与提交简单的用户名/密码身份验证请求的任何机制都兼容,因此,通常和基于表单的登录认证或HTTP Basic身份验证一起使用.
另一方面,某些身份验证机制会创建一个身份验证请求对象,该对象只能由一种类型的AuthenticationProvider。
一个示例就是JA-SIG CAS,它使用服务票证的概念,因此只能由进行身份验证CasAuthenticationProvider。
Erasing Credentials on Successful Authentication
默认情况下(从Spring Security 3.1开始),ProviderManager它将尝试从Authentication成功的身份验证请求返回的对象中清除所有敏感的凭据信息。这样可以防止将密码之类的信息保留的时间过长。
例如,在使用用户对象的缓存来提高无状态应用程序的性能时,这可能会导致问题。
如果Authentication包含对缓存中某个对象(例如UserDetails实例)的引用,并且已删除其凭据,则将无法再针对缓存的值进行身份验证.
如果使用缓存,则需要考虑到这一点。
一个明显的解决方案是先在高速缓存实现中,或在AuthenticationProvider创建返回Authentication的对象中,首先创建对象的副本。
或者,您可以在ProviderManager禁用该eraseCredentialsAfterAuthentication属性。
DaoAuthenticationProvider
Spring Security中最简单的AuthenticationProvider实现方法是DaoAuthenticationProvider.也是框架最早支持的方法之一。
它利用UserDetailsService(作为DAO)查找用户名,密码和GrantedAuthority
只需将比较UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken提交的密码与UserDetailsService加载的密码,即可对用户进行身份验证
<beans>
<bean id="daoAuthenticationProvider"
class="org.springframework.security.authentication.dao.DaoAuthenticationProvider">
<property name="userDetailsService" ref="inMemoryDaoImpl"/>
<property name="passwordEncoder" ref="passwordEncoder"/>
</bean>
<bean id="inMemoryDaoImpl"
class="org.springframework.security.provisioning.InMemoryUserDetailsManager" >
....
</bean>
</beans>
PasswordEncoder是可选的。PasswordEncoder提供对UserDetails从配置的返回的对象中提供的密码进行编码和解码UserDetailsService。
UserDetailsService Implementations
大多数身份验证提供程序都利用UserDetails和UserDetailsService接口.UserDetailsService只是一个简单的方法:
UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException;
返回的UserDetails是一个接口,该接口提供了获取器,该获取器保证以非空方式提供身份验证信息,例如用户名,密码,已授予的权限以及用户帐户是启用还是禁用。
大多数身份验证提供程序(providers)会使用UserDetailsService,即使用户名和密码实际上没有用作身份验证决策的一部分.
他们使用UserDetailsService作为返回,可能仅仅只是为了获取GrantedAuthority信息,因为某些其他系统(例如LDAP或X.509或CAS等)承担了实际验证凭据的责任。
UserDetailsService可以很轻松的实现,因此用户应该使用自己选择的持久性策略轻松检索身份验证信息。Spring Security包含一些有用的基本实现.
In-Memory Authentication
创建自定义UserDetailsService实现,从持久化引擎中提取用户信息很简单,但是许多应用程序不需要这种复杂性.
如果你正在构建原型或刚刚开始集成Spring Security,而又不花时间配置数据库或者自定义一个UserDetailsService实现,则可采用下列配置
<user-service id="userDetailsService">
<!-- Password is prefixed with {noop} to indicate to DelegatingPasswordEncoder that
NoOpPasswordEncoder should be used. This is not safe for production, but makes reading
in samples easier. Normally passwords should be hashed using BCrypt -->
<user name="jimi" password="{noop}jimispassword" authorities="ROLE_USER, ROLE_ADMIN" />
<user name="bob" password="{noop}bobspassword" authorities="ROLE_USER" />
</user-service>
也支持使用外部属性文件:
<user-service id="userDetailsService" properties="users.properties"/>
属性文件应包含以下形式的条目
username=password,grantedAuthority[,grantedAuthority][,enabled|disabled]
例如
jimi=jimispassword,ROLE_USER,ROLE_ADMIN,enabled
bob=bobspassword,ROLE_USER,enabled
JdbcDaoImpl
Spring Security还包括一个UserDetailsService可从JDBC数据源获取身份验证信息的。
在内部使用Spring JDBC,因此它避免了仅用于存储用户详细信息的功能齐全的对象关系映射器(ORM)的复杂性。
如果您的应用程序确实使用了ORM工具,则您可能更愿意编写一个自定义UserDetailsService来重用您可能已经创建的映射文件。
返回JdbcDaoImpl,示例配置如下所示:
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="org.hsqldb.jdbcDriver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:hsqldb:hsql://localhost:9001"/>
<property name="username" value="sa"/>
<property name="password" value=""/>
</bean>
<bean id="userDetailsService"
class="org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.jdbc.JdbcDaoImpl">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
您可以通过修改DriverManagerDataSource上面显示的内容使用不同的关系数据库管理系统。
您还可以使用从JNDI获得的全局数据源,就像其他任何Spring配置一样。
Authority Groups
默认情况下,JdbcDaoImpl假设权限直接映射到用户,则为单个用户加载权限。
另一种方法是将权限划分为组,然后将组分配给用户。有些人喜欢使用这种方法来管理用户权限。
Spring Security Architecture and Implementation(架构和实现)学习笔记的更多相关文章
- 图灵学院JAVA互联网架构师专题学习笔记
图灵学院JAVA互联网架构师专题学习笔记 下载链接:链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1xbxDzmnQudnYtMt5Ce1ONQ 密码: fbdj如果失效联系v:itit11 ...
- 字节跳动内部微服务架构-Docker实战学习笔记分享 真香
前言 基于 Spring Cloud 的微服务设计和开发,已经越来越多地得到了更多企业的推广和应用,而 Spring Cloud 社区也在不断的迅速发展壮大之中,近几年时间,Spring Cloud ...
- Spring security (一)架构框架-Component、Service、Filter分析
“致"高级"工程师(BUG工程师) 一颗折腾的心
- ARMv8 架构与指令集.学习笔记
目 录 第1章 ARMv8简介. 3 1.1基础认识. 3 1.2 相关专业名词解释. 3 第2章 Execution State 4 2.1 提供两种Execution State 4 2.2 决定 ...
- .NET 云原生架构师训练营(权限系统 RGCA 架构设计)--学习笔记
目录 项目核心内容 实战目标 RGCA 四步架构法 项目核心内容 无代码埋点实现对所有 API Action 访问控制管理 对 EF Core 实体新增.删除.字段级读写控制管理 与 Identity ...
- 《精通Spring 4.x 企业应用开发实战》学习笔记
第四章 IoC容器 4.1 IoC概述 IoC(Inverse of Control 控制反转),控制是指接口实现类的选择控制权,反转是指这种选择控制权从调用类转移到外部第三方类或容器的手中. 也就是 ...
- Spring Security(三十二):10. Core Services
Now that we have a high-level overview of the Spring Security architecture and its core classes, let ...
- Spring Security(一):官网向导翻译
原文出自 https://spring.io/guides/topicals/spring-security-architecture Spring Security Architecture ...
- 44. Spring Security FAQ春季安全常见问题
第44.1节,“一般问题” 第44.2节,“常见问题” 第44.3节,“春季安全架构问题” 第44.4节,“常见”如何“请求 44.1 General Questions 第44.1.1节,“Spri ...
随机推荐
- 树莓派3B+红外配置
sudo apt-get install lirc /etc/lirc/lirc_options.conf #driver = devinput driver = default #device = ...
- 转载【MySQL】MySQL5.X常用日志配置及5.7和5.6主从复制的区别
转载:https://blog.csdn.net/zyb378747350/article/details/78728886 2)MySQL5.7和5.6主从复制的区别: . 5.6之后默认binlo ...
- django orm 分页(paginator)取数据出现警告manage.py:1: UnorderedObjectListWarning: Pagination may yield inconsistent results with an unordered object_list: <class 'sign.models.Guest'> QuerySet.
使用django的orm做分页(Paginator)时出现了下面的警告 In [19]: p=Paginator(guest_list,2) manage.py:1: UnorderedObjectL ...
- [原]使用global mapper 修改影像数据DOM的投影变换(将数据转换成osgearth支持的投影)
osgearth默认使用的投影基准面为: Geographic(Latitude/Longitude)的 WGS84 有这样一份数据需要修改: 1.在菜单栏种选择“工具”---->“配置” 2. ...
- Java学习-057-Jsoup爬虫获取中国所有的三级行政区划数据(二),并生成数据库 SQL 脚本插入语句
多不废话,直接上马,小主您稳着... package com.fanfengping.zeus.uitl; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject; import ...
- Android Studio 3.0——unable to resolve dependency for cordovalib
Android Studio 3.0 更新了gradle后,项目竟然开始报错unable to resolve dependency for cordovalib...打开build.gradle看了 ...
- C# 发送Post请求(带参数)
此处内容传输都是用UTF-8编码 1.不带参数发送Post请求 /// <summary> /// 指定Post地址使用Get 方式获取全部字符串 /// </summary> ...
- ETF计算公司:现金差额
T日现金差额=T日最小申赎单位的基金净值-(申购.赎回清单中必须现金替代的替代金额+申购.赎回清单中可以现金替代成份证券的数量与T日收盘价之和+申购.赎回清单中禁止现金替代成份证券的数量与T日收盘价之 ...
- ORA-01126: 数据库必须已装载到此实例并且不在任何实例中打开
原因:修改归档模式的操作只能在 mount 状态下进行,不能处于 open 状态. SQL> alter database archivelog;alter database archivelo ...
- Gerrit - 一些基本用法
1 - 主配置文件 主配置文件位于$GERRIT_SITE/etc/gerrit.config目录 [gerrit@mt101 ~]$ cat gerrit_testsite/etc/gerrit.c ...
