LeetCode 987. Vertical Order Traversal of a Binary Tree
原题链接在这里:https://leetcode.com/problems/vertical-order-traversal-of-a-binary-tree/
题目:
Given a binary tree, return the vertical order traversal of its nodes values.
For each node at position (X, Y), its left and right children respectively will be at positions (X-1, Y-1) and (X+1, Y-1).
Running a vertical line from X = -infinity to X = +infinity, whenever the vertical line touches some nodes, we report the values of the nodes in order from top to bottom (decreasing Y coordinates).
If two nodes have the same position, then the value of the node that is reported first is the value that is smaller.
Return an list of non-empty reports in order of X coordinate. Every report will have a list of values of nodes.
Example 1:
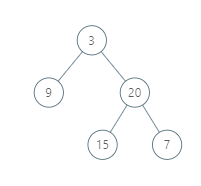
Input: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: [[9],[3,15],[20],[7]]
Explanation:
Without loss of generality, we can assume the root node is at position (0, 0):
Then, the node with value 9 occurs at position (-1, -1);
The nodes with values 3 and 15 occur at positions (0, 0) and (0, -2);
The node with value 20 occurs at position (1, -1);
The node with value 7 occurs at position (2, -2).
Example 2:
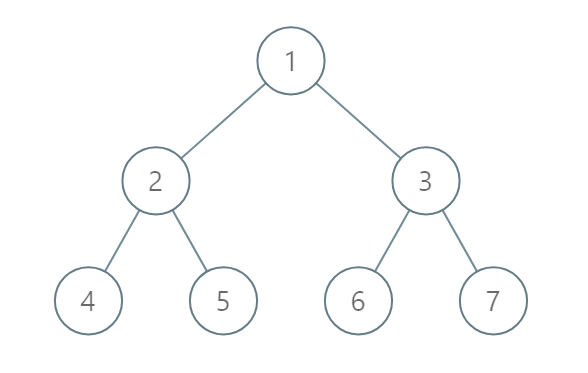
Input: [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
Output: [[4],[2],[1,5,6],[3],[7]]
Explanation:
The node with value 5 and the node with value 6 have the same position according to the given scheme.
However, in the report "[1,5,6]", the node value of 5 comes first since 5 is smaller than 6.
Note:
- The tree will have between 1 and
1000nodes. - Each node's value will be between
0and1000.
题解:
For vertical order, we need a HashMap to maintain key as column.
When there is same column, they should be put into same value collection.
Here is one more extra constraint, that is to for same column and same row, have smaller value come first.
Thus when coming out the HashMap, sort the values first based on row, then based on value.
Time Complexity: O(n + logn*loglogn). n is the number of nodes. Thus the longest list is the height of tree m = logn. sort takes O(mlogm).
Space: O(n).
AC Java:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> verticalTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null){
return res;
} HashMap<Integer, List<Pair>> hm = new HashMap<>();
LinkedList<Pair> que = new LinkedList<>();
que.add(new Pair(0, 0, root));
int min = 0;
int max = 0; while(!que.isEmpty()){
Pair cur = que.poll();
min = Math.min(min, cur.x);
max = Math.max(max, cur.x);
hm.putIfAbsent(cur.x, new ArrayList<>());
hm.get(cur.x).add(cur); if(cur.node.left != null){
que.add(new Pair(cur.x-1, cur.y-1, cur.node.left));
} if(cur.node.right != null){
que.add(new Pair(cur.x+1, cur.y-1, cur.node.right));
}
} for(int i = min; i<=max; i++){
List<Pair> list = hm.get(i);
Collections.sort(list, (a, b) -> a.y == b.y ? a.node.val-b.node.val : b.y-a.y); List<Integer> item = new ArrayList<>();
for(Pair p : list){
item.add(p.node.val);
} res.add(item);
} return res;
}
} class Pair{
int x;
int y;
TreeNode node;
public Pair(int x, int y, TreeNode node){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.node = node;
} public String toString(){
return "" + this.x + "^" + this.y + "^" + this.node.val;
}
}
类似Binary Tree Vertical Order Traversal.
LeetCode 987. Vertical Order Traversal of a Binary Tree的更多相关文章
- 【LeetCode】987. Vertical Order Traversal of a Binary Tree 解题报告(C++ & Python)
作者: 负雪明烛 id: fuxuemingzhu 个人博客: http://fuxuemingzhu.cn/ 目录 题目描述 题目大意 解题方法 DFS BFS 日期 题目地址:https://le ...
- 【leetcode】987. Vertical Order Traversal of a Binary Tree
题目如下: Given a binary tree, return the vertical order traversal of its nodes values. For each node at ...
- LC 987. Vertical Order Traversal of a Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, return the vertical order traversal of its nodes values. For each node at posit ...
- [Swift]LeetCode987. 二叉树的垂序遍历 | Vertical Order Traversal of a Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, return the vertical order traversal of its nodes values. For each node at posit ...
- LeetCode Binary Tree Vertical Order Traversal
原题链接在这里:https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-vertical-order-traversal/ 题目: Given a binary tree, ...
- LeetCode 314. Binary Tree Vertical Order Traversal
原题链接在这里:https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-vertical-order-traversal/ 题目: Given a binary tree, ...
- Binary Tree Vertical Order Traversal -- LeetCode
Given a binary tree, return the vertical order traversal of its nodes' values. (ie, from top to bott ...
- [Locked] Binary Tree Vertical Order Traversal
Binary Tree Vertical Order Traversal Given a binary tree, return the vertical order traversal of its ...
- [LeetCode] Binary Tree Vertical Order Traversal 二叉树的竖直遍历
Given a binary tree, return the vertical order traversal of its nodes' values. (ie, from top to bott ...
随机推荐
- Scala字符串插值 - StringContext
翻译自:STRING INTERPOLATION 简介 自2.10.0版本开始,Scala提供了一种新的机制来根据数据生成字符串:字符串插值.字符串插值允许使用者将变量引用直接插入处理过的字面字符中. ...
- mysql数据库备份工具xtrabackup
1.下载二进制安装包 其他高版本测试缺少依赖 2.xtrabackup参数说明 简介: Xtrabackup是一个对InnoDB做数据备份的工具,支持在线热备份(备份时不影响数据读写),是商业备份工 ...
- fiddler抓包-1-安装与快速上手
前言 fiddler作为一个中间商协议代理,众所周知,有请求就会有响应,那没有响应呢?那就是哪个环节出现问题了.通过代理就可以查看到所有请求信息.与响应信息.举个例子,以前上学时有没有写过情书?或者给 ...
- 释放mac磁盘空间
转发自:https://www.jianshu.com/p/722093bc3dea Mac清理磁盘空间主要讲述在Mac上工作清理磁盘空间的小技巧,本节主要讲述作为一名使用Mac开发的iOS工程师,需 ...
- FFT(快速傅里叶变换)
FFT(快速傅里叶变换) 前置知识 \(1.复数\) \(2.单位根\) \(3.循环结构\) \(4.C++\) 1.复数 \(定义:形如a+bi的数,其中i^2=-1\) \(计算:1.(a+bi ...
- Laravel手动分页的方法
use Illuminate\Pagination\LengthAwarePaginator; public function index(Request $request){ $list =[... ...
- linux内核树的建立(Ubuntu)
博客地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/zengjianrong/p/3178874.html 1.搜索源码 2.下载源码,下载路径可设为:/usr/src/ 3.解压源码 4.进入源 ...
- KVM 学习笔记
查看虚拟化环境 (1)查看虚拟机环境 (2)查看kvm模块支持 (3)查看虚拟工具版本 (4)查看网桥
- java8 Lambda 表达式和函数式接口快速理解
前言 接上篇文章 java8 新特性 由于上篇过于庞大,使得重点不够清晰,本篇单独拿出 java8 的 Lambda 表达式和函数式接口说明. Lambda 表达式 lambda 表达式其实就是使用了 ...
- C#安全类型转换基于convert
using Newtonsoft.Json; using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Globalization; n ...