BZOJ2539 Spoj 10707 Count on a tree II
题面
题解
因为这道题目我也不太会做,所以借鉴了一下大佬heyujun的博客
如果不强制在线,这道题目是树上莫队练手题
我们知道莫队是离线的,但是万一强制在线就凉凉了
于是我们就需要一些操作:树分块
看到这个图:
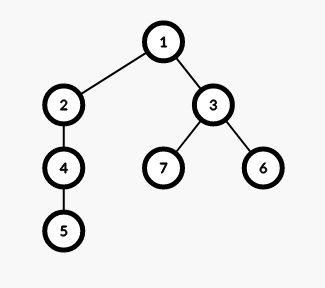
这里有\(7\)个点,我们每隔\(2\)深度分块
但是我们要保证分块的连续性,于是分成了\((1,2)(7,6,3)(4,5)\)三块
现在给了你两个将询问的点\(u,v(dep[u]>dep[v])\),分类讨论:
两个点在同一个块内
直接暴力
两个点不在同一个块内
这种情况比较复杂,记一个块的根为\(rt[i]\),则它到另外所有点的答案我们可以很轻松地
统计出来,只需要对于每个\(rt[i]\)暴力统计一遍就可以了。那么现在我们要考虑的只有\(u\)到它的块的根\(x\)路径上是否会对答案产生贡献:
对于这个,我们可以将这个分块可持久化,维护这个点的颜色在它的祖先中出现最深的位置
的深度,那么一个块只需继承上面的块,并将在这个块中颜色的答案更新,因为那个颜色如
果出现在这个位置,那么答案肯定更优。有了上面的铺垫,那我们只需对\(u\to x\)上的点暴力算它的深度是否超过\(\mathrm{LCA}(u, v)\)即可
代码
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cctype>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#define RG register
#define file(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin), freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define clear(x, y) memset(x, y, sizeof(x))
inline int read()
{
int data = 0, w = 1; char ch = getchar();
while(ch != '-' && (!isdigit(ch))) ch = getchar();
if(ch == '-') w = -1, ch = getchar();
while(isdigit(ch)) data = data * 10 + (ch ^ 48), ch = getchar();
return data * w;
}
const int maxn(40010), SQRT(210);
struct edge { int next, to; } e[maxn << 1];
int head[maxn], e_num;
inline void add_edge(int from, int to)
{
e[++e_num] = (edge) {head[from], to};
head[from] = e_num;
}
int n, m, Len, a[maxn], b[maxn], _a[maxn], r[maxn];
int P[maxn][SQRT], A[SQRT][maxn], fa[maxn], dep[maxn];
int q[maxn], belong[maxn], top, cnt, SIZE, root[maxn];
int c[maxn], Ans;
struct Block
{
int a[SQRT]; void insert(const Block&, int, int);
int &operator [] (const int &x) { return P[a[b[x]]][r[x]]; }
const int &operator [] (const int &x) const { return P[a[b[x]]][r[x]]; }
} s[maxn];
void Block::insert(const Block &rhs, int x, int d)
{
int blk = b[x], t = r[x];
memcpy(a, rhs.a, sizeof(a));
memcpy(P[++SIZE], P[a[blk]], sizeof(P[0]));
P[a[blk] = SIZE][t] = d;
}
namespace Tree
{
int belong[maxn], heavy[maxn], size[maxn];
void dfs(int x, int chain)
{
belong[x] = chain;
if(!heavy[x]) return;
dfs(heavy[x], chain);
for(RG int i = head[x]; i; i = e[i].next)
{
int to = e[i].to;
if(to == fa[x] || to == heavy[x]) continue;
dfs(to, to);
}
}
int LCA(int x, int y)
{
while(belong[x] != belong[y])
{
if(x[belong][dep] < y[belong][dep]) std::swap(x, y);
x = x[belong][fa];
}
return dep[x] < dep[y] ? x : y;
}
}
int dfs(int x, int f)
{
using Tree::size; using Tree::heavy;
fa[x] = f, size[x] = 1;
s[x].insert(s[f], a[x], dep[x] = dep[f] + 1);
q[++top] = x; int maxd = dep[x], p = top;
for(RG int i = head[x]; i; i = e[i].next)
{
int to = e[i].to; if(to == f) continue;
maxd = std::max(maxd, dfs(to, x)); size[x] += size[to];
if(size[heavy[x]] < size[to]) heavy[x] = to;
}
if(maxd - dep[x] >= Len || p == 1)
{
root[++cnt] = x;
for(RG int i = p; i <= top; i++) belong[q[i]] = cnt;
top = p - 1; return dep[x] - 1;
}
return maxd;
}
void Pre(int x, int f, int *s)
{
if(!c[a[x]]++) ++Ans; s[x] = Ans;
for(RG int i = head[x]; i; i = e[i].next) if(e[i].to != f)
Pre(e[i].to, x, s);
if(!--c[a[x]]) --Ans;
}
int Solve1(int x, int y)
{
for(top = Ans = 0; x != y; x = fa[x])
{
if(dep[x] < dep[y]) std::swap(x, y);
if(!c[q[++top] = a[x]]) c[a[x]] = 1, ++Ans;
}
for(Ans += !c[a[x]]; top;) c[q[top--]] = 0;
return Ans;
}
int Solve2(int x, int y)
{
if(dep[root[belong[x]]] < dep[root[belong[y]]]) std::swap(x, y);
int x1 = root[belong[x]], d = dep[Tree::LCA(x, y)]; Ans = A[belong[x]][y];
for(top = 0; x != x1; x = fa[x])
if(!c[a[x]] && s[x1][a[x]] < d && s[y][a[x]] < d)
c[q[++top] = a[x]] = 1, ++Ans;
while(top) c[q[top--]] = 0;
return Ans;
}
int main()
{
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("cpp.in", "r", stdin);
#endif
n = read(), m = read(), Len = sqrt(n) - 1;
for(RG int i = 1; i <= n; i++) b[i] = (i - 1) / Len + 1, r[i] = i % Len;
for(RG int i = 1; i <= n; i++) a[i] = _a[i] = read();
std::sort(_a + 1, _a + n + 1);
int tot = std::unique(_a + 1, _a + n + 1) - _a - 1;
for(RG int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
a[i] = std::lower_bound(_a + 1, _a + tot + 1, a[i]) - _a;
for(RG int i = 1, x, y; i < n; i++) x = read(), y = read(),
add_edge(x, y), add_edge(y, x);
top = 0, dfs(1, 0), Tree::dfs(1, 1);
for(RG int i = 1; i <= cnt; i++) Pre(root[i], 0, A[i]);
int ans = 0; while(m--)
{
int x = ans ^ read(), y = read();
printf("%d\n", ans = (belong[x] == belong[y] ?
Solve1(x, y) : Solve2(x, y)));
}
return 0;
}
BZOJ2539 Spoj 10707 Count on a tree II的更多相关文章
- 【BZOJ2589】 Spoj 10707 Count on a tree II
BZOJ2589 Spoj 10707 Count on a tree II Solution 吐槽:这道题目简直...丧心病狂 如果没有强制在线不就是树上莫队入门题? 如果加了强制在线怎么做? 考虑 ...
- bzoj2589: Spoj 10707 Count on a tree II
Description 给定一棵N个节点的树,每个点有一个权值,对于M个询问(u,v),你需要回答u xor lastans和v这两个节点间有多少种不同的点权.其中lastans是上一个询问的答案,初 ...
- [BZOJ]2589: Spoj 10707 Count on a tree II
Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 400 MB Description 给定一棵N个节点的树,每个点有一个权值,对于M个询问(u,v),你需要回答u xor last ...
- 【SPOJ】Count On A Tree II(树上莫队)
[SPOJ]Count On A Tree II(树上莫队) 题面 洛谷 Vjudge 洛谷上有翻译啦 题解 如果不在树上就是一个很裸很裸的莫队 现在在树上,就是一个很裸很裸的树上莫队啦. #incl ...
- spoj COT2 - Count on a tree II
COT2 - Count on a tree II http://www.spoj.com/problems/COT2/ #tree You are given a tree with N nodes ...
- SPOJ COT2 - Count on a tree II(LCA+离散化+树上莫队)
COT2 - Count on a tree II #tree You are given a tree with N nodes. The tree nodes are numbered from ...
- SPOJ COT2 Count on a tree II(树上莫队)
题目链接:http://www.spoj.com/problems/COT2/ You are given a tree with N nodes.The tree nodes are numbere ...
- SPOJ COT2 Count on a tree II (树上莫队)
题目链接:http://www.spoj.com/problems/COT2/ 参考博客:http://www.cnblogs.com/xcw0754/p/4763804.html上面这个人推导部分写 ...
- spoj COT2 - Count on a tree II 树上莫队
题目链接 http://codeforces.com/blog/entry/43230树上莫队从这里学的, 受益匪浅.. #include <iostream> #include < ...
随机推荐
- 使用yii AR 完成单个表的CURD操作
什么是AR(ActiveRecord) Active Record (活动记录,以下简称AR)提供了一个面向对象的接口, 用以访问数据库中的数据.一个 AR 类关联一张数据表, 每个 AR 对象对应表 ...
- session更换存储,实现在多台服务器共享
场景 web服务器有多台,每台服务器都会存贮自己的session,session无法在多台服务器共享.所以就需要更换session的存贮空间,存贮在一个共用的空间.通常为了读写速度,我们会选择存贮在内 ...
- September 30th 2017 Week 39th Saturday
The simplest answer is often the correct one. 最简单的答案通常是最正确的答案. Simplest is always best. Sometimes yo ...
- September 21st 2017 Week 38th Thursday
What fire does not destroy, it hardens. 烈火摧毁不了的东西,只会变得更坚固. The true gold can stand the test of fire, ...
- n = 3 , while n , continue
- 重复文件查找工具:Duplicate Cleaner V4.11绿色免费版
Duplicate Cleaner 是一款可以帮助你在你的计算机上找到并且快速查找出重复文件并标记出不同的颜色,让你轻松查阅处理.你可以立即搜索多个文件夹结构并且设置识别副本文件的标准.你可以选择使用 ...
- MyISAM和innoDB对比,覆盖索引简单回顾
MyISAM Myisam是Mysql的默认存储引擎,当create创建新表时,未指定新表的存储引擎时,默认使用Myisam. 它不支持事务,也不支持外键,尤其是访问速度快,对事务完整性没有要求或者以 ...
- 4种Java日志管理方法
java开发中常见的几种日志管理方案有以下4种: 1. Commons-logging + log4j 2. log4j 3. slf4j + log4j + commmons-logging 4. ...
- 本地项目关联git仓库
Command line instructions Git global setup git config --global user.name "zhoushuo" git co ...
- 1.5 Community and Conferences(社区和讨论组)+ 私货
1.5 Community and Conferences(社区和讨论组)+ 私货 下面是一些和科学计算,数据处理相关的Python社群和讨论组,如果有什么问题可以进行提问: pydata: A Go ...
