[转]Enabling CRUD Operations in ASP.NET Web API 1
by Mike Wasson+
This tutorial shows how to support CRUD operations in an HTTP service using ASP.NET Web API.+
Software versions used in the tutorial
- Visual Studio 2012
- Web API 1 (also works with Web API 2)
CRUD stands for "Create, Read, Update, and Delete," which are the four basic database operations. Many HTTP services also model CRUD operations through REST or REST-like APIs.+
In this tutorial, you will build a very simple web API to manage a list of products. Each product will contain a name, price, and category (such as "toys" or "hardware"), plus a product ID.+
The products API will expose following methods.+
| Action | HTTP method | Relative URI |
|---|---|---|
| Get a list of all products | GET | /api/products |
| Get a product by ID | GET | /api/products/id |
| Get a product by category | GET | /api/products?category=category |
| Create a new product | POST | /api/products |
| Update a product | PUT | /api/products/id |
| Delete a product | DELETE | /api/products/id |
Notice that some of the URIs include the product ID in path. For example, to get the product whose ID is 28, the client sends a GET request for http://hostname/api/products/28.+
Resources
The products API defines URIs for two resource types:+
| Resource | URI |
|---|---|
| The list of all the products. | /api/products |
| An individual product. | /api/products/id |
Methods
The four main HTTP methods (GET, PUT, POST, and DELETE) can be mapped to CRUD operations as follows:+
- GET retrieves the representation of the resource at a specified URI. GET should have no side effects on the server.
- PUT updates a resource at a specified URI. PUT can also be used to create a new resource at a specified URI, if the server allows clients to specify new URIs. For this tutorial, the API will not support creation through PUT.
- POST creates a new resource. The server assigns the URI for the new object and returns this URI as part of the response message.
- DELETE deletes a resource at a specified URI.
Note: The PUT method replaces the entire product entity. That is, the client is expected to send a complete representation of the updated product. If you want to support partial updates, the PATCH method is preferred. This tutorial does not implement PATCH.+
Create a New Web API Project
Start by running Visual Studio and select New Project from the Start page. Or, from the File menu, select New and then Project.+
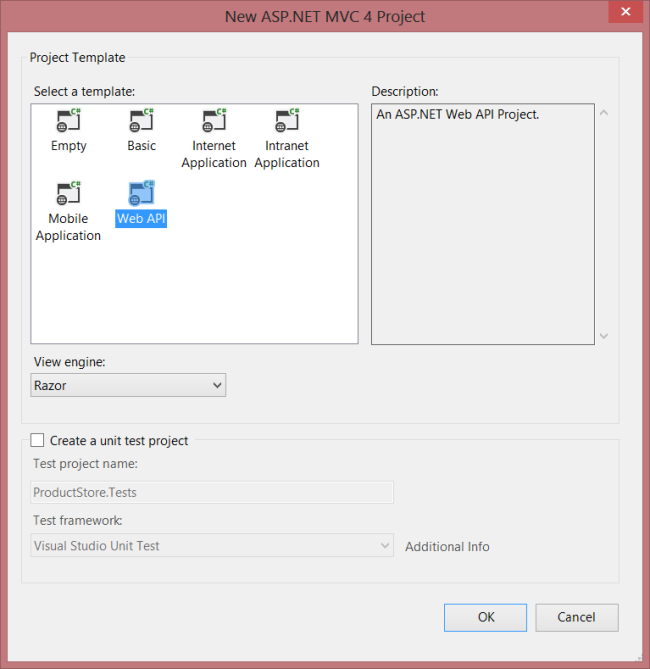
In the Templates pane, select Installed Templates and expand the Visual C# node. Under Visual C#, select Web. In the list of project templates, select ASP.NET MVC 4 Web Application. Name the project "ProductStore" and click OK.+
In the New ASP.NET MVC 4 Project dialog, select Web API and click OK.+
Adding a Model
A model is an object that represents the data in your application. In ASP.NET Web API, you can use strongly typed CLR objects as models, and they will automatically be serialized to XML or JSON for the client.+
For the ProductStore API, our data consists of products, so we'll create a new class named Product.+
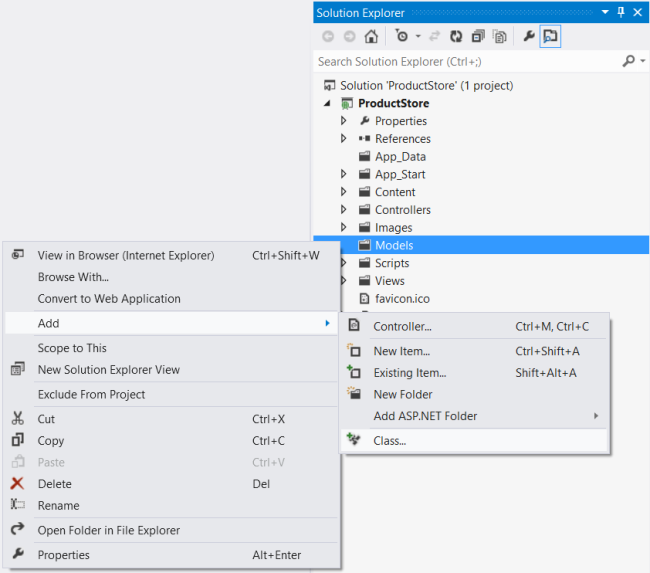
If Solution Explorer is not already visible, click the View menu and select Solution Explorer. In Solution Explorer, right-click the Models folder. From the context meny, select Add, then select Class. Name the class "Product".+
Add the following properties to the Product class.+
namespace ProductStore.Models
{
public class Product
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Category { get; set; }
public decimal Price { get; set; }
}
}
Adding a Repository
We need to store a collection of products. It's a good idea to separate the collection from our service implementation. That way, we can change the backing store without rewriting the service class. This type of design is called the repository pattern. Start by defining a generic interface for the repository.+
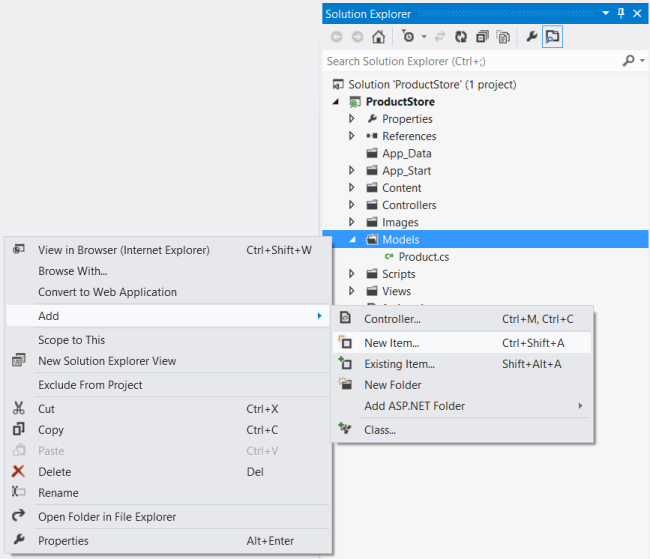
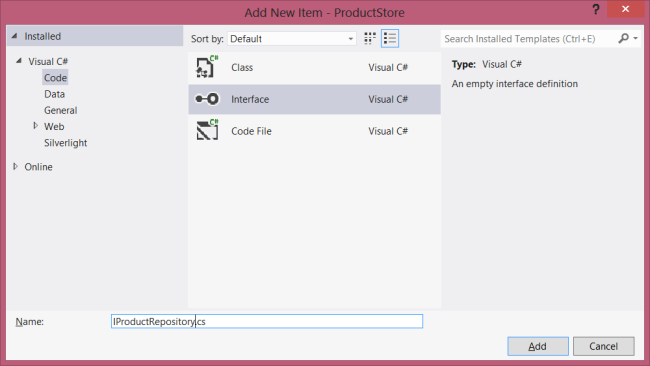
In Solution Explorer, right-click the Models folder. Select Add, then select New Item.+
In the Templates pane, select Installed Templates and expand the C# node. Under C#, select Code. In the list of code templates, select Interface. Name the interface "IProductRepository".+
Add the following implementation:+
namespace ProductStore.Models
{
public interface IProductRepository
{
IEnumerable<Product> GetAll();
Product Get(int id);
Product Add(Product item);
void Remove(int id);
bool Update(Product item);
}
}
Now add another class to the Models folder, named "ProductRepository." This class will implement the IProductRespository interface. Add the following implementation:+
namespace ProductStore.Models
{
public class ProductRepository : IProductRepository
{
private List<Product> products = new List<Product>();
private int _nextId = 1;
public ProductRepository()
{
Add(new Product { Name = "Tomato soup", Category = "Groceries", Price = 1.39M });
Add(new Product { Name = "Yo-yo", Category = "Toys", Price = 3.75M });
Add(new Product { Name = "Hammer", Category = "Hardware", Price = 16.99M });
}
public IEnumerable<Product> GetAll()
{
return products;
}
public Product Get(int id)
{
return products.Find(p => p.Id == id);
}
public Product Add(Product item)
{
if (item == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("item");
}
item.Id = _nextId++;
products.Add(item);
return item;
}
public void Remove(int id)
{
products.RemoveAll(p => p.Id == id);
}
public bool Update(Product item)
{
if (item == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("item");
}
int index = products.FindIndex(p => p.Id == item.Id);
if (index == -1)
{
return false;
}
products.RemoveAt(index);
products.Add(item);
return true;
}
}
}
The repository keeps the list in local memory. This is OK for a tutorial, but in a real application, you would store the data externally, either a database or in cloud storage. The repository pattern will make it easier to change the implementation later.+
Adding a Web API Controller
If you have worked with ASP.NET MVC, then you are already familiar with controllers. In ASP.NET Web API, a controller is a class that handles HTTP requests from the client. The New Project wizard created two controllers for you when it created the project. To see them, expand the Controllers folder in Solution Explorer.+
- HomeController is a traditional ASP.NET MVC controller. It is responsible for serving HTML pages for the site, and is not directly related to our web API.
- ValuesController is an example WebAPI controller.
Go ahead and delete ValuesController, by right-clicking the file in Solution Explorer and selecting Delete. Now add a new controller, as follows:+
In Solution Explorer, right-click the the Controllers folder. Select Add and then select Controller.+
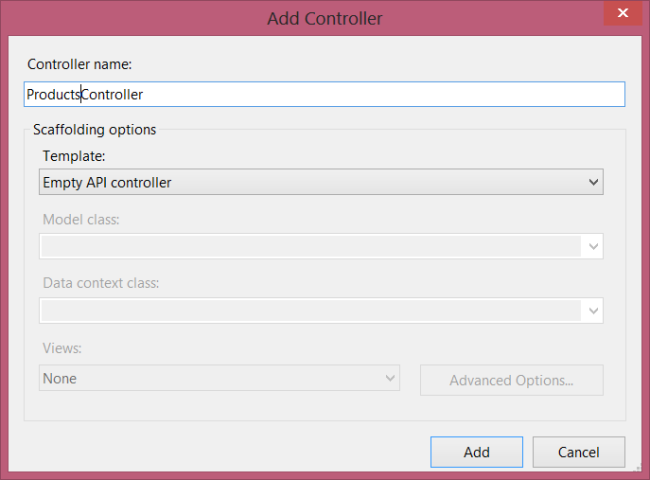
In the Add Controller wizard, name the controller "ProductsController". In the Template drop-down list, select Empty API Controller. Then click Add.+
Note+
It is not necessary to put your contollers into a folder named Controllers. The folder name is not important; it is simply a convenient way to organize your source files.+
The Add Controller wizard will create a file named ProductsController.cs in the Controllers folder. If this file is not open already, double-click the file to open it. Add the following using statement:+
using ProductStore.Models;
Add a field that holds an IProductRepository instance.+
public class ProductsController : ApiController
{
static readonly IProductRepository repository = new ProductRepository();
}
Note+
Calling new ProductRepository() in the controller is not the best design, because it ties the controller to a particular implementation of IProductRepository. For a better approach, see Using the Web API Dependency Resolver.+
Getting a Resource
The ProductStore API will expose several "read" actions as HTTP GET methods. Each action will correspond to a method in the ProductsController class.+
| Action | HTTP method | Relative URI |
|---|---|---|
| Get a list of all products | GET | /api/products |
| Get a product by ID | GET | /api/products/id |
| Get a product by category | GET | /api/products?category=category |
To get the list of all products, add this method to the ProductsController class:+
public class ProductsController : ApiController
{
public IEnumerable<Product> GetAllProducts()
{
return repository.GetAll();
}
// ....
}
The method name starts with "Get", so by convention it maps to GET requests. Also, because the method has no parameters, it maps to a URI that does not contain an "id" segment in the path.+
To get a product by ID, add this method to the ProductsController class:+
public Product GetProduct(int id)
{
Product item = repository.Get(id);
if (item == null)
{
throw new HttpResponseException(HttpStatusCode.NotFound);
}
return item;
}
This method name also starts with "Get", but the method has a parameter named id. This parameter is mapped to the "id" segment of the URI path. The ASP.NET Web API framework automatically converts the ID to the correct data type (int) for the parameter.+
The GetProduct method throws an exception of type HttpResponseException if id is not valid. This exception will be translated by the framework into a 404 (Not Found) error.+
Finally, add a method to find products by category:+
public IEnumerable<Product> GetProductsByCategory(string category)
{
return repository.GetAll().Where(
p => string.Equals(p.Category, category, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase));
}
If the request URI has a query string, Web API tries to match the query parameters to parameters on the controller method. Therefore, a URI of the form "api/products?category=category" will map to this method.+
Creating a Resource
Next, we'll add a method to the ProductsController class to create a new product. Here is a simple implementation of the method:+
// Not the final implementation!
public Product PostProduct(Product item)
{
item = repository.Add(item);
return item;
}
Note two things about this method:+
- The method name starts with "Post...". To create a new product, the client sends an HTTP POST request.
- The method takes a parameter of type Product. In Web API, parameters with complex types are deserialized from the request body. Therefore, we expect the client to send a serialized representation of a product object, in either XML or JSON format.
This implementation will work, but it is not quite complete. Ideally, we would like the HTTP response to include the following:+
- Response code: By default, the Web API framework sets the response status code to 200 (OK). But according to the HTTP/1.1 protocol, when a POST request results in the creation of a resource, the server should reply with status 201 (Created).
- Location: When the server creates a resource, it should include the URI of the new resource in the Location header of the response.
ASP.NET Web API makes it easy to manipulate the HTTP response message. Here is the improved implementation:+
public HttpResponseMessage PostProduct(Product item)
{
item = repository.Add(item);
var response = Request.CreateResponse<Product>(HttpStatusCode.Created, item);
string uri = Url.Link("DefaultApi", new { id = item.Id });
response.Headers.Location = new Uri(uri);
return response;
}
Notice that the method return type is now HttpResponseMessage. By returning an HttpResponseMessage instead of a Product, we can control the details of the HTTP response message, including the status code and the Location header.+
The CreateResponse method creates an HttpResponseMessage and automatically writes a serialized representation of the Product object into the body fo the response message.+
Note+
This example does not validate the Product. For information about model validation, see Model Validation in ASP.NET Web API.+
Updating a Resource
Updating a product with PUT is straightforward:+
public void PutProduct(int id, Product product)
{
product.Id = id;
if (!repository.Update(product))
{
throw new HttpResponseException(HttpStatusCode.NotFound);
}
}
The method name starts with "Put...", so Web API matches it to PUT requests. The method takes two parameters, the product ID and the updated product. The id parameter is taken from the URI path, and the product parameter is deserialized from the request body. By default, the ASP.NET Web API framework takes simple parameter types from the route and complex types from the request body.+
Deleting a Resource
To delete a resourse, define a "Delete..." method.+
public void DeleteProduct(int id)
{
Product item = repository.Get(id);
if (item == null)
{
throw new HttpResponseException(HttpStatusCode.NotFound);
}
repository.Remove(id);
}
If a DELETE request succeeds, it can return status 200 (OK) with an entity-body that describes the status; status 202 (Accepted) if the deletion is still pending; or status 204 (No Content) with no entity body. In this case, the DeleteProduct method has a void return type, so ASP.NET Web API automatically translates this into status code 204 (No Content).
[转]Enabling CRUD Operations in ASP.NET Web API 1的更多相关文章
- Enabling Cross-Origin Requests in ASP.NET Web API 2
Introduction This tutorial demonstrates CORS support in ASP.NET Web API. We’ll start by creating two ...
- 杂项:ASP.NET Web API
ylbtech-杂项:ASP.NET Web API ASP.NET Web API 是一种框架,用于轻松构建可以访问多种客户端(包括浏览器和移动设备)的 HTTP 服务. ASP.NET Web A ...
- CRUD Operations In ASP.NET MVC 5 Using ADO.NET
Background After awesome response of an published by me in the year 2013: Insert, Update, Delete In ...
- 【ASP.NET Web API教程】2.1 创建支持CRUD操作的Web API
原文 [ASP.NET Web API教程]2.1 创建支持CRUD操作的Web API 2.1 Creating a Web API that Supports CRUD Operations2.1 ...
- 通过Knockout.js + ASP.NET Web API构建一个简单的CRUD应用
REFERENCE FROM : http://www.cnblogs.com/artech/archive/2012/07/04/Knockout-web-api.html 较之面向最终消费者的网站 ...
- Asp.Net Web API 2(CRUD操作)第二课
Asp.Net Web API 2(CRUD操作)第二课 Asp.Net Web API 导航 Asp.Net Web API第一课:入门http://www.cnblogs.com/aehyok ...
- ASP.NET Web API 基本操作(CRUD)
上一篇介绍了ASP.NET Web API的基本知识和原理,这一篇我们通过一个更直观的实例,对产品进行CRUD操作(Create/Read/Update/Delete)来继续了解一下它的基本应用. 创 ...
- 基于ASP.NET WEB API实现分布式数据访问中间层(提供对数据库的CRUD)
一些小的C/S项目(winform.WPF等),因需要访问操作数据库,但又不能把DB连接配置在客户端上,原因有很多,可能是DB连接无法直接访问,或客户端不想安装各种DB访问组件,或DB连接不想暴露在客 ...
- 适用于app.config与web.config的ConfigUtil读写工具类 基于MongoDb官方C#驱动封装MongoDbCsharpHelper类(CRUD类) 基于ASP.NET WEB API实现分布式数据访问中间层(提供对数据库的CRUD) C# 实现AOP 的几种常见方式
适用于app.config与web.config的ConfigUtil读写工具类 之前文章:<两种读写配置文件的方案(app.config与web.config通用)>,现在重新整理一 ...
随机推荐
- kylin的clube合并后清理hbase中产生的相关历史表
kylin的clube合并后清理hbase中产生的相关历史表 kylin 的clube 历史的每次构建,都会产生一个hbase的表:虽然可以设置按照一定策略合并,但是合并后hbase 历史表不会被自动 ...
- Android开源库集合(控件)
RecycleView: RecycleView功能增强 https://github.com/Malinskiy/SuperRecyclerView RecycleView功能增强(拖拽,滑动删除, ...
- .net core获取服务器本地IP及Request访问端口
string str = (Request.HttpContext.Connection.LocalIpAddress.MapToIPv4().ToString() + ":" + ...
- WPF之坑——surface触控失灵之谜
本次又遇到了WPF编写触控程序的一个问题,虽然已解决,但原因确搞不太明白,希望有大神看到这篇文章帮我解答. 在项目中实现了自己定义的icommandsource,因为需要对触控有特殊需求,控件对鼠标与 ...
- Kotlin 初体验
本文由作者邹丽萍授权网易云社区发布. 背景 Kotlin 是 JetBrains 公司(著名的 IntelliJ IDEA 正是由这家公司开发的,Android Studio 也是基于 IDEA 的) ...
- Day 12 作业.(完成)
1,将装饰器的所有知识点总结完成,将这几天的作业再整理一遍,还是不会的,就抄代码,一遍不行就三遍,直到所有知识点,所有题都整明白. 2,有时间就画流程图,梳理知识点. 3,上面两项完成的写以下作业. ...
- CEPH 创建 RPM 安装包
1.安装依赖环境 yum install gcc make python-devel openssl-devel graphviz autoconf automake rpm-build redhat ...
- Java 8 LocalDateTime 初使用
LocalTime : 只包括时间 LocalDate : 只包括日期 LocalDateTime : 包括日期和时间 JDBC映射 LocalTime 对应 time LocalDate 对应 d ...
- Android应用安全防护和逆向分析 ——apk反编译
概述 最近一直在学习Android应用安全相关和逆向分析的知识.现在移动app在安全方面是越来越重视了,特别是那些巨头企业涉及到钱的应用,那加密程度,简直是丧心病狂,密密麻麻.从这里可以看出,对于应用 ...
- [Swift实际操作]七、常见概念-(9)使用定时组件Timer执行定时任务
本文将为你演示计时器的使用,使用计时器可以每隔一定时间执行某个函数. 在左侧的项目导航区,打开视图控制器的代码文件:ViewController.swift现在开始编写代码,实现任务定时的功能.定义一 ...