Longest Increasing Subsequences(最长递增子序列)的两种DP实现
/**
@description: Longest Increasing Subsequence
@author: seiyagoo
@create: 2013.10.25
@modified: 2013.10.26
**/
int LIS_1(int A[], int size){ int *LIS = new int[size];
vector<int> *vec = new vector<int>[size]; /* Compute optimized LIS values in bottom up manner */
for(int i=; i < size; i++){
LIS[i]=; //初始化默认长度
int max_j=, flag=;
for(int j=; j < i; j++){ //查表,找出前面最长的序列, 若将A[i]加入LIS[j](LIS[j]+1的含义)的递增子序列比当前的LIS[i]更长, 则更新LIS[i]
if(A[i] > A[j] && LIS[i] < LIS[j]+){
LIS[i] = LIS[j]+;
max_j=j;
flag=;
}
}
if(flag) //copy前面最长子序列到vec[i]
vec[i].insert(vec[i].end(), vec[max_j].begin(), vec[max_j].end());
vec[i].push_back(A[i]); //最后放入A[i]
} /*Show LIS of the current state*/
vector<int>::iterator it;
cout<<left;
for(int i=; i<size; i++){
cout<<setw()<<A[i]<< " --> ";
for(it = vec[i].begin(); it!=vec[i].end(); it++)
cout<<*it<<" ";
cout<<endl;
} /* Pick maximum of all LIS values, namely max{LIS[i]} */
int max_len=;
for(int i = ; i < size; i++ )
if( max_len < LIS[i] )
max_len = LIS[i]; delete[] LIS;
delete[] vec; return max_len;
}
/**
@description: Longest Increasing Subsequence
@author: seiyagoo
@create: 2013.10.25
@modified: 2013.10.26
**/ // Binary search (note boundaries in the caller)
// A[] is ceilIndex in the caller
int CeilIndex(int A[], int l, int r, int key) {
int m; while( r - l > ) {
m = l + (r - l)/;
(A[m] >= key ? r : l) = m; // ternary expression returns an l-value
} return r;
} int LIS_2(int A[], int size) {
// boundary case: when array size is one
if( == size ) return ; int *tailTable = new int[size];
vector<int> *vec = new vector<int>[size];
int len; // always points empty slot //memset(tailTable, INT_MAX, sizeof(tailTable[0])*size); @bug for(int i = ; i < size; i++)
tailTable[i] = INT_MAX; tailTable[] = A[]; //tailTable[0] store the smallest value
vec[].push_back(A[]); len = ;
for( int i = ; i < size; i++ ) {
if( A[i] < tailTable[] ) { //case 1: new smallest value
tailTable[] = A[i]; /*discard and create*/
vec[].clear();
vec[].push_back(A[i]);
}
else if( A[i] > tailTable[len-] ) { //case 2: A[i] wants to extend largest subsequence
tailTable[len++] = A[i]; /*clone and extend*/
vec[len-] = vec[len-];
vec[len-].push_back(A[i]);
}
else { //case 3: A[i] wants to be current end candidate of an existing subsequence, It will replace ceil value in tailTable
int ceilIndex = CeilIndex(tailTable, -, len-, A[i]);
tailTable[ceilIndex] = A[i]; /*discard, clone and extend*/
vec[ceilIndex].clear();
vec[ceilIndex] = vec[ceilIndex-];
vec[ceilIndex].push_back(A[i]);
} /*Printf all the active lists*/
vector<int>::iterator it;
cout<<left;
cout<<"A["<<i<<"] = "<<A[i]<<endl<<endl;
cout<<"active lists:"<<endl;
for(int i=; i<len; i++){
for(it = vec[i].begin(); it!=vec[i].end(); it++)
cout<<*it<<" ";
cout<<endl;
} /*Printf end elements of all the active lists*/
cout<<endl<<"end elements array:"<<endl;
for(int i = ; i < size; i++)
if(tailTable[i] != INT_MAX)
cout<<tailTable[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
cout<<"-------------------------"<<endl;
} delete[] tailTable;
delete[] vec; return len;
}
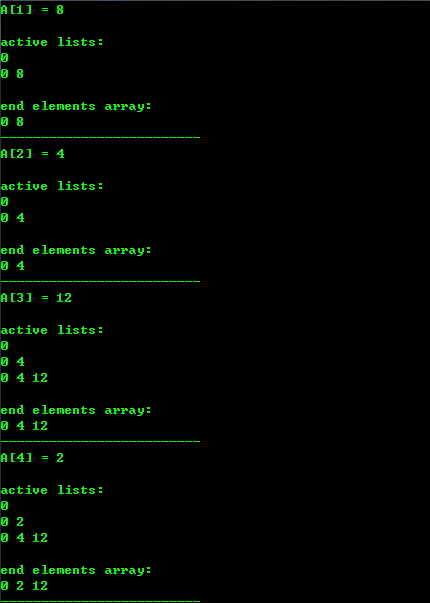
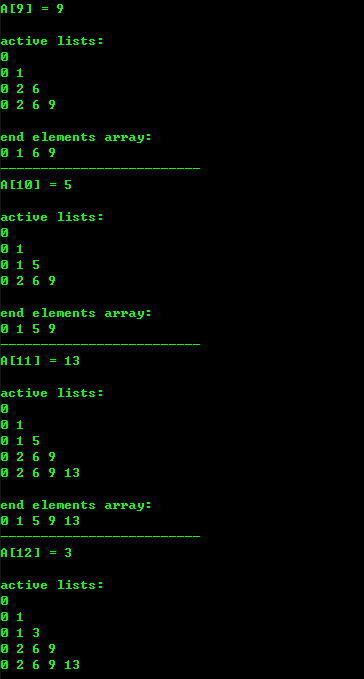
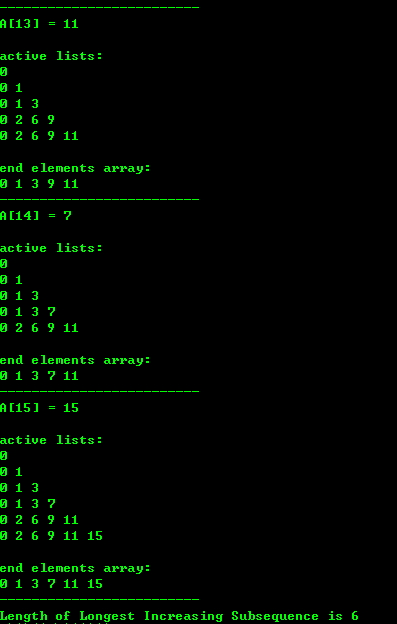
五、运行结果
example:


Longest Increasing Subsequences(最长递增子序列)的两种DP实现的更多相关文章
- leetcode300. Longest Increasing Subsequence 最长递增子序列 、674. Longest Continuous Increasing Subsequence
Longest Increasing Subsequence 最长递增子序列 子序列不是数组中连续的数. dp表达的意思是以i结尾的最长子序列,而不是前i个数字的最长子序列. 初始化是dp所有的都为1 ...
- [LintCode] Longest Increasing Subsequence 最长递增子序列
Given a sequence of integers, find the longest increasing subsequence (LIS). You code should return ...
- [LeetCode] Longest Increasing Subsequence 最长递增子序列
Given an unsorted array of integers, find the length of longest increasing subsequence. For example, ...
- 673. Number of Longest Increasing Subsequence最长递增子序列的数量
[抄题]: Given an unsorted array of integers, find the number of longest increasing subsequence. Exampl ...
- [LeetCode] 300. Longest Increasing Subsequence 最长递增子序列
Given an unsorted array of integers, find the length of longest increasing subsequence. Example: Inp ...
- [leetcode]300. Longest Increasing Subsequence最长递增子序列
Given an unsorted array of integers, find the length of longest increasing subsequence. Example: Inp ...
- poj 2533 Longest Ordered Subsequence 最长递增子序列
作者:jostree 转载请注明出处 http://www.cnblogs.com/jostree/p/4098562.html 题目链接:poj 2533 Longest Ordered Subse ...
- [LeetCode] Number of Longest Increasing Subsequence 最长递增序列的个数
Given an unsorted array of integers, find the number of longest increasing subsequence. Example 1: I ...
- POJ 2533 - Longest Ordered Subsequence - [最长递增子序列长度][LIS问题]
题目链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=2533 Time Limit: 2000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Description A numeric se ...
- [LeetCode] 673. Number of Longest Increasing Subsequence 最长递增序列的个数
Given an unsorted array of integers, find the number of longest increasing subsequence. Example 1: I ...
随机推荐
- XML学习总结(1)——XML入门
一.XML语法学习 学习XML语法的目的就是编写XML 一个XML文件分为如下几部分内容: 文档声明 元素 属性 注释 CDATA区 .特殊字符 处理指令(processing instruction ...
- dlopen 方式调用 Linux 的动态链接库
在dlopen()函数以指定模式打开指定的动态链接库文件.并返回一个句柄给 dlsym()的调用进程. 使用 dlclose()来卸载打开的库. 功能:打开一个动态链接库,并返回动态链接库的句柄 包括 ...
- 有关cascade的结构体
/* internal cascade classifier */ typedef struct CvCascadeHaarClassifier { CV_INT_HAAR_CLASSIFIER_FI ...
- POJ 题目1145/UVA题目112 Tree Summing(二叉树遍历)
Tree Summing Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 8132 Accepted: 1949 Desc ...
- Chrome不能在网易网盘中上传文件的解决办法
Chrome不能在网易网盘中上传文件的解决办法1. 安装 Adobe Flash Player PPAPI,设置flash插件 chrome://settings/content/flash,许可[* ...
- Multiple CPUs,Multiple Cores、Hyper-Threading
CPU Basics: Multiple CPUs, Cores, and Hyper-Threading Explained 现在多数的家用电脑,仍然使用的是 Single CPU,Multiple ...
- MYSQL存储过程中 使用变量 做表名--转
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/business122/article/details/7528859 今天写一个对数据库做快照的存储过程,用到了动态表名,突然发现MYSQL不支持 ...
- $.post()提交了数据,return不给跳转
本来Controller接到普通请求,return “somePage”,这样就跳转了.前台用$.post()提交了数据(不需要回调),我了个大草,return那里就不给跳转了这样怎么解决? ajax ...
- Java学习笔记二.1
和其他高级语言类似,Java也具有以下部分 1.关键字:见下表,注意Java严格区分大小写,关键字都是小写 2.标识符:见下图 3.注释.有两种://(单行注释)和/**/(多行注释).还有一种文档注 ...
- HTTP浅谈
HTTP浅谈 1···什么是HTTP? HTTP协议就是超文本传输协议(HyperText Transfer Protocol),通俗理解是浏览器和web服务器传输数据格式的协议,HTTP协议是一个应 ...
