elasticsearch节点间通信的基础transport
在前一篇中我们分析了cluster的一些元素。接下来的章节会对cluster的运作机制做详细分析。本节先分析一些transport,它是cluster间通信的基础。它有两种实现,一种是基于netty实现nettytransport,主要用于节点间的通信。另一种是localtransport,主要是用于同一个jvm上的节点通信。因为是同一个jvm上的网络模拟,localtransport实现上非常简单,实际用处也非常有限,这里就不过多说明。这一篇的重点是nettytransport。
transport顾名思义是集群通信的基本通道,无论是集群状态信息,还是搜索索引请求信息,都是通过transport传送。elasticsearch定义了tansport,tansportmessage,tansportchannel,tansportrequest,tansportresponse等所需的所有的基础接口。这里将以transport为主,分析过程中会附带介绍其它接口。首先看一下transport节点的定义,如下图所示:
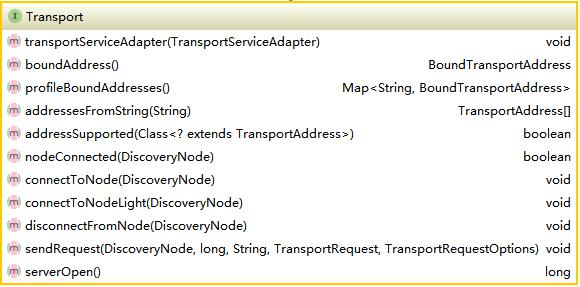
NettyTransport实现了该接口。分析NettyTransport前简单说一下Netty的用法,Netty的使用需要三个模块ServerBootStrap,ClientBootStrap(v3.x)及MessageHandler。ServerBootStrap启动服务器,ClientBootStrap启动客户端并连接服务器,MessageHandler是message处理逻辑所在,也就是业务逻辑。其它详细使用请参考Netty官方文档。NettyTransport每个在doStart()方法中启动serverBootStrap,和ClientBootStrap,并绑定ip,代码如下所示:
protected void doStart() throws ElasticsearchException {
clientBootstrap = createClientBootstrap();//根据配置启动客户端
……//省略了无关分代码
createServerBootstrap(name, mergedSettings);//启动server端
bindServerBootstrap(name, mergedSettings);//绑定ip
}
每一个节点都需要发送和接收,因此两者都需要启动,client和server的启动分别在相应的方法中,启动过程就是netty的启动过程,有兴趣可以去看相应方法。bindServerBootstrap(name, mergedSettings)将本地ip和断开绑定到netty同时设定好export host(export host的具体作业我也看明白也没有看到相关的绑定,需要进一步研究)。启动client及server的过程中将messagehandler注入到channelpipeline中。至此启动过程完成,但是client并未连接任何server,连接过程是在节点启动后,才连接到其它节点的。
首先看一下如何连接到node,方法代码如下所示:
public void connectToNode(DiscoveryNode node, boolean light) {
//transport的模块必须要启动
if (!lifecycle.started()) {
throw new ElasticsearchIllegalStateException("can't add nodes to a stopped transport");
}
//获取读锁,每个节点可以和多个节点建立连接,因此这里用读锁
globalLock.readLock().lock();
try {
//以node.id为基础获取一个锁,这保证对于每个node只能建立一次连接
connectionLock.acquire(node.id());
try {
if (!lifecycle.started()) {
throw new ElasticsearchIllegalStateException("can't add nodes to a stopped transport");
}
NodeChannels nodeChannels = connectedNodes.get(node);
if (nodeChannels != null) {
return;
}
try {
if (light) {//这里的light,就是对该节点只获取一个channel,所有类型(5种连接类型下面会说到)都使用者一个channel
nodeChannels = connectToChannelsLight(node);
} else {
nodeChannels = new NodeChannels(new Channel[connectionsPerNodeRecovery], new Channel[connectionsPerNodeBulk], new Channel[connectionsPerNodeReg], new Channel[connectionsPerNodeState], new Channel[connectionsPerNodePing]);
try {
connectToChannels(nodeChannels, node);
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.trace("failed to connect to [{}], cleaning dangling connections", e, node);
nodeChannels.close();
throw e;
}
}
// we acquire a connection lock, so no way there is an existing connection
connectedNodes.put(node, nodeChannels);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("connected to node [{}]", node);
}
transportServiceAdapter.raiseNodeConnected(node);
} catch (ConnectTransportException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ConnectTransportException(node, "general node connection failure", e);
}
} finally {
connectionLock.release(node.id());
}
} finally {
globalLock.readLock().unlock();
}
}
如果不是轻连接,每个server和clien之间都有5中连接,着5中连接承担着不同的任务。连接方法的代码如下所示:
protected void connectToChannels(NodeChannels nodeChannels, DiscoveryNode node) {
//五种连接方式,不同的连接方式对应不同的集群操作
ChannelFuture[] connectRecovery = new ChannelFuture[nodeChannels.recovery.length];
ChannelFuture[] connectBulk = new ChannelFuture[nodeChannels.bulk.length];
ChannelFuture[] connectReg = new ChannelFuture[nodeChannels.reg.length];
ChannelFuture[] connectState = new ChannelFuture[nodeChannels.state.length];
ChannelFuture[] connectPing = new ChannelFuture[nodeChannels.ping.length];
InetSocketAddress address = ((InetSocketTransportAddress) node.address()).address();
//尝试建立连接
for (int i = 0; i < connectRecovery.length; i++) {
connectRecovery[i] = clientBootstrap.connect(address);
}
for (int i = 0; i < connectBulk.length; i++) {
connectBulk[i] = clientBootstrap.connect(address);
}
for (int i = 0; i < connectReg.length; i++) {
connectReg[i] = clientBootstrap.connect(address);
}
for (int i = 0; i < connectState.length; i++) {
connectState[i] = clientBootstrap.connect(address);
}
for (int i = 0; i < connectPing.length; i++) {
connectPing[i] = clientBootstrap.connect(address);
}
//获取每个连接的channel存入到相应的channels中便于后面使用。
try {
for (int i = 0; i < connectRecovery.length; i++) {
connectRecovery[i].awaitUninterruptibly((long) (connectTimeout.millis() * 1.5));
if (!connectRecovery[i].isSuccess()) {
throw new ConnectTransportException(node, "connect_timeout[" + connectTimeout + "]", connectRecovery[i].getCause());
}
nodeChannels.recovery[i] = connectRecovery[i].getChannel();
nodeChannels.recovery[i].getCloseFuture().addListener(new ChannelCloseListener(node));
}
for (int i = 0; i < connectBulk.length; i++) {
connectBulk[i].awaitUninterruptibly((long) (connectTimeout.millis() * 1.5));
if (!connectBulk[i].isSuccess()) {
throw new ConnectTransportException(node, "connect_timeout[" + connectTimeout + "]", connectBulk[i].getCause());
}
nodeChannels.bulk[i] = connectBulk[i].getChannel();
nodeChannels.bulk[i].getCloseFuture().addListener(new ChannelCloseListener(node));
}
for (int i = 0; i < connectReg.length; i++) {
connectReg[i].awaitUninterruptibly((long) (connectTimeout.millis() * 1.5));
if (!connectReg[i].isSuccess()) {
throw new ConnectTransportException(node, "connect_timeout[" + connectTimeout + "]", connectReg[i].getCause());
}
nodeChannels.reg[i] = connectReg[i].getChannel();
nodeChannels.reg[i].getCloseFuture().addListener(new ChannelCloseListener(node));
}
for (int i = 0; i < connectState.length; i++) {
connectState[i].awaitUninterruptibly((long) (connectTimeout.millis() * 1.5));
if (!connectState[i].isSuccess()) {
throw new ConnectTransportException(node, "connect_timeout[" + connectTimeout + "]", connectState[i].getCause());
}
nodeChannels.state[i] = connectState[i].getChannel();
nodeChannels.state[i].getCloseFuture().addListener(new ChannelCloseListener(node));
}
for (int i = 0; i < connectPing.length; i++) {
connectPing[i].awaitUninterruptibly((long) (connectTimeout.millis() * 1.5));
if (!connectPing[i].isSuccess()) {
throw new ConnectTransportException(node, "connect_timeout[" + connectTimeout + "]", connectPing[i].getCause());
}
nodeChannels.ping[i] = connectPing[i].getChannel();
nodeChannels.ping[i].getCloseFuture().addListener(new ChannelCloseListener(node));
}
if (nodeChannels.recovery.length == 0) {
if (nodeChannels.bulk.length > 0) {
nodeChannels.recovery = nodeChannels.bulk;
} else {
nodeChannels.recovery = nodeChannels.reg;
}
}
if (nodeChannels.bulk.length == 0) {
nodeChannels.bulk = nodeChannels.reg;
}
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
// clean the futures
for (ChannelFuture future : ImmutableList.<ChannelFuture>builder().add(connectRecovery).add(connectBulk).add(connectReg).add(connectState).add(connectPing).build()) {
future.cancel();
if (future.getChannel() != null && future.getChannel().isOpen()) {
try {
future.getChannel().close();
} catch (Exception e1) {
// ignore
}
}
}
throw e;
}
}
以上就是节点建立连接的过程,每一对client和server间都会建立一定数量的不同连接。之所以要区分连接,是因为不同的操作消耗的资源不同,请求的频率也不同。对于资源消耗少请求频率高的如ping,可以建立多一些连接,来确保并发。对于消耗资源多如bulk操作,则要少建立一些连接,保证机器不被拖垮。节点的断开,这是讲相应的channel释放的过程。这里就不再做详细说明,可以参考相关源码。
总结一下nettytransport的连接过程,启动过程分别启动client和server,同时将对于的messagehandler注入,启动多次就是netty的启动过程。然后绑定server ip和断开。但是这里并没有连接,连接发送在节点启动时,节点启动会获取cluster信息,分别对集群中的节点建立上述的5种连接。这就是NettyTransport的启动和连接过程。transport还有一个很重要的功能就是发送request,及如何处理request,这些功能会在下一篇中分析。
elasticsearch节点间通信的基础transport的更多相关文章
- RAC 安装完成后 节点间通信不依赖于SSH
RAC 安装完成后,想修改ssh 的端口.google了一下.原文https://community.oracle.com/thread/2444594?tstart=0 原文说的是11g,10g也好 ...
- kibana访问多个 Elasticsearch 节点间的负载均衡
如果 Elasticsearch 集群有多个节点,分发 Kibana 节点之间请求的最简单的方法就是在 Kibana 机器上运行一个 Elasticsearch 协调(Coordinating onl ...
- 使用WebSocket帮助应用程序群集节点间通信
[序列化message传输方式]两种方式都是转成二进制. 1.使用Java序列化器,ObjectXXXputStream 2.使用ByteBuffer.wrap(bytes). 在一个标准群集场景中, ...
- TinyOS节点间通信相关接口和组件介绍
一.基本通信接口: Packet:提供了对message_t抽象数据类型的基本访问.这个接口的命令有:清空消息内容,获得消息的有效载荷区长度,获得消息有效载荷区的指针. //tos/interfa ...
- BFT-SMaRt:用Java做节点间的可靠信道
目录 一.引子 二.名词统一 1. 节点id 2. 节点 3. 本地节点 4. 配置域 5. TTP 6. 陌生域 三.节点服务类 四.节点通信系统概览 五.节点通信层准备 1. 创建socket服务 ...
- Blazor入门笔记(6)-组件间通信
1.环境 VS2019 16.5.1.NET Core SDK 3.1.200Blazor WebAssembly Templates 3.2.0-preview2.20160.5 2.简介 在使用B ...
- 集群节点间网络通信TIPC
1. TIPC背景介绍 TIPC主要是用于集群网络环境之中,它这个协议有一些前提假设包括: 协议发送的大部分message都是直接到达目的地(无路由): message的传输时间都很短; messag ...
- Cassandra1.2文档学习(2)——节点间通信协议之gossip协议
参考文档:http://www.datastax.com/documentation/cassandra/1.2/webhelp/index.html#cassandra/architecture/a ...
- 源码分析Android Handler是如何实现线程间通信的
源码分析Android Handler是如何实现线程间通信的 Handler作为Android消息通信的基础,它的使用是每一个开发者都必须掌握的.开发者从一开始就被告知必须在主线程中进行UI操作.但H ...
随机推荐
- Docker安装配置教程
Docker公开课 1 Docker介绍 1.1 Docker是什么 云计算\云服务 IAAS(基础设施即服务).PAAS(平台即服务).SAAS(软件即服务) Docker到底是什么呢? Docke ...
- vuex requires a Promise polyfill in this browser.--ie-vue-兼容处理日记
1.ie9+报错vuex requires a Promise polyfill in this browser. 解决如下: npm install --save-dev -polyfill 修改c ...
- Jetty 类载入问题处理
前几日使用 Jetty (9.2)部署公司一个 web 项目,这个项目原本部署在 Tomcat server上,一切正常,可是部署到 Jetty 后,启动报错.关键错误信息为"java.la ...
- es68对象的解构赋值
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
- RadioButton的check改变的时候
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/8095256/asp-net-radio-button-change You'll need to specify the a ...
- Inception V3 的 tensorflow 实现
tensorflow 官方给出的实现:models/inception_v3.py at master · tensorflow/models · GitHub 1. 模型结构 首先来看 Incept ...
- Android webview 运行时不调用系统自带浏览器
WebView mobView = new WebView(this); mobView.loadUrl("http://www.csdn.net"); WebSettings w ...
- IntelliJ IDEA基于maven构建的web项目找不到jar包
基于maven构建的springMVC项目,下载好jar包import后,运行提示ClassNotFoundException: java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: o ...
- 一个简单RPC框架是怎样炼成的(II)——制定RPC消息
开局篇我们说了,RPC框架的四个核心内容 RPC数据的传输. RPC消息 协议 RPC服务注冊 RPC消息处理 以下,我们先看一个普通的过程调用 class Client(object): def _ ...
- Javascript:存储和读取cookie
Cookie是网页开发中的一项重要技术,用于在本地存储一些信息(如username,password.登录状态)以便用户下一次訪问时使用(或在其他页面使用). cookie的格式是键值对,多个键值对之 ...
