python入门 -- 学习笔记3
习题21:函数可以返回东西
过程解析:
1、定义函数:如def add(形参)函数
2、调用函数: add(实参) 别忘记加()
3、在函数调用的时候将实参的值传给形参,代入到函数中进行计算,return 关键字将函数计算的结果再返回给调用它的地方
代码:
def add(a, b):
print "ADDING %d + %d" % (a, b)
return a + b
def subtract(a, b):
print "SUBTRACTING %d - %d" % (a, b)
return a - b
def multiply(a, b):
print "MULTIPLYING %d * %d" % (a, b)
return a * b
def divide(a, b):
print "DIVIDING %d / %d" % (a, b)
return a / b
print "Let's do some math with just functions!"
age = add(30, 5)
height = subtract(78, 4)
weight = multiply(90, 2)
iq = divide(100, 2)
print "Age: %d, Height: %d, Weight: %d, IQ: %d" % (age, height, weight, iq)
# A puzzle for the extra credit, type it in anyway.
print "Here is a puzzle."
what = add(age, subtract(height, multiply(weight, divide(iq, 2))))
print "That becomes: ", what, "Can you do it by hand?"
结果:
习题24:更多练习
代码:
print "Let's practice everything"
print "You\'d need to know \'bout escapes with \\ that do \n newlines and \t tabs."
poem = '''
\tThe lovely world
with logic so firmly planted
cannot discern \n the needs of love
nor comprehend passion from intuition
and requires an explanation
\n\t\twhere there is none.
'''
print "---------------------"
print poem
print "---------------------"
five = 10 - 2 + 3 - 6
print "This should be five: %s" % five
def secret_formuls(started):
jelly_beans = started * 500
jars = jelly_beans / 1000
crates = jars / 100
return jelly_beans, jars, crates
start_point = 10000
beans, jars, crates = secret_formuls(start_point)
print "With a starting point of: %d" % start_point
print "We'd have %d beans, %d jars, and %d crates." % (beans, jars, crates)
start_point = start_point / 10
print "We can also do that this way:"
print "We'd have %d beans, %d jars, and %d crates." % secret_formuls(start_point)
结果:
习题27:记住逻辑关系
逻辑术语:
and 与
or 或
not 非
!= (not equal) 不等于
== (equal) 等于
>= (greater-than-equal) 大于等于
<= (less-than-equal) 小于等于
True 真
False 假
真值表:
NOT
not False True
not True False
OR
True or False True
True or True True
False or True True
False or False False
AND
True and False False
True and True True
False and True False
False and False False
NOT OR
not (True or False) False
not (True or True) False
not (False or True) False
not (False or False) True
NOT AND
not (True and False) True
not (True and True) False
not (False and True) True
not (False and False) True
!=
1 != 0 True
1 != 1 False
0 != 1 True
0 != 0 False
==
1 == 0 False
1 == 1 True
0 == 1 False
0 == 0 True
习题29:如果(if)
格式:
if 布尔表达式 : (“:”后跟一个代码块,每个语句都有4个空格的缩进)
语句(如果布尔表达式结果为真,则执行该语句,否则跳过该语句)
代码:
people = 20
cats = 30
dogs = 15
if people < cats:
print "Too many cats! The world is doomed!"
if people > cats:
print "Not many cats! The world is saved!"
if people < dogs:
print "The world is drooled on!"
if people > dogs:
print "The world id dry!"
dogs += 5
if people >= dogs:
print "People are greater than or equal to dogs."
if people <= dogs:
print "people are less than or equal to dogs."
if people == dogs:
print "People are dogs."
结果:
习题30:Else 和 If
代码:
people = 20
cars = 40
buses = 15
if cars > people:
print "We should take the cars."
elif cars < people:
print "We should not take the cars."
else:
print "We can't decide."
if buses > cars:
print "That's too many buses."
elif buses < cars:
print "Maybe we could take the buses."
else:
print "We still can't decide."
if people > buses:
print "Alright, let's just take the buses."
else:
print "Fine, let's stay home then."
结果:
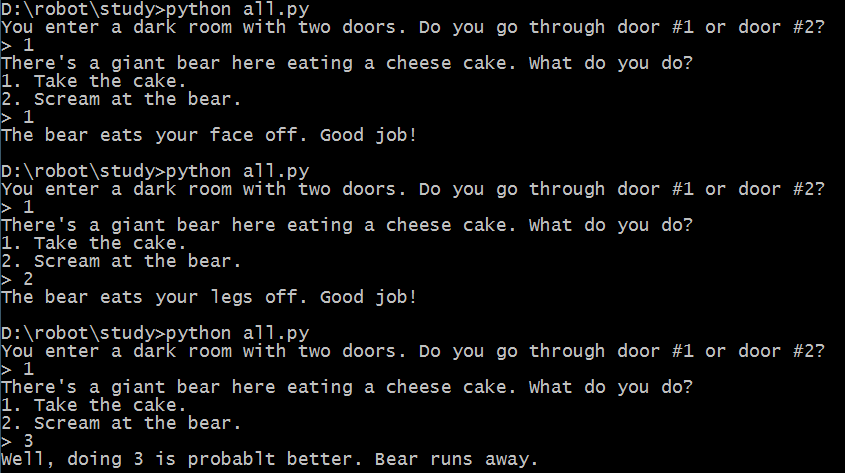
习题31:作出决定
代码:
print "You enter a dark room with two doors. Do you go through door #1 or door #2?"
door = raw_input("> ")
if door == "1":
print "There's a giant bear here eating a cheese cake. What do you do?"
print "1. Take the cake."
print "2. Scream at the bear."
bear = raw_input("> ")
if bear == "1":
print "The bear eats your face off. Good job!"
elif bear =="2":
print "The bear eats your legs off. Good job!"
else:
print "Well, doing %s is probablt better. Bear runs away." % bear
elif door == "2":
print "You stare into the endless abyss at Cthulhu's retina."
print "1. Blueberries."
print "2. Yellow jacket clothespins."
print "3. Understanding revolvers yelling melodies."
insanity = raw_input("> ")
if insanity == "1" or insanity == "2":
print "Your body survives powered by a mind of jello. Good job!"
else:
print "The insanity rots your eyes into a pool of muck. Good job!"
else:
print "You stumble around and fall on a knife and die. Good job!"
结果:
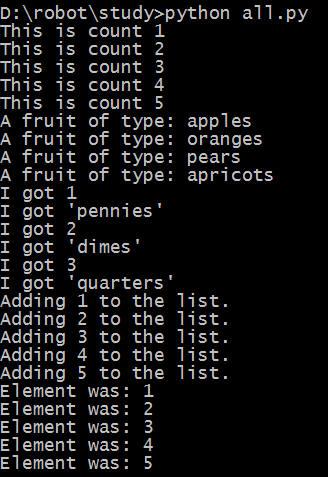
习题32:循环与列表
-- 使用刘表元素所在的位置数(基数)访问列表元素,更多列表相关可上网搜索
代码:
the_count = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
fruits = ['apples', 'oranges', 'pears', 'apricots']
change = [1, 'pennies', 2, 'dimes', 3, 'quarters']
# this first kind of for-loop goes through a list
for number in the_count:
print "This is count %d" % number
# same as above
for fruit in fruits:
print "A fruit of type: %s" % fruit
# alse we can go through mixes lists too
# notice we have to use %r since we don't know what's in it
for i in change:
print "I got %r" % i
# we can also build lists, first start with an empty one
elements = []
# then use the range function to do 0 to 5 counts
for i in range(1, 6):
print "Adding %d to the list." % i
# append is a function that lists understand
elements.append(i)
# now we can print them out too
for i in elements:
print "Element was: %d" % i
结果:
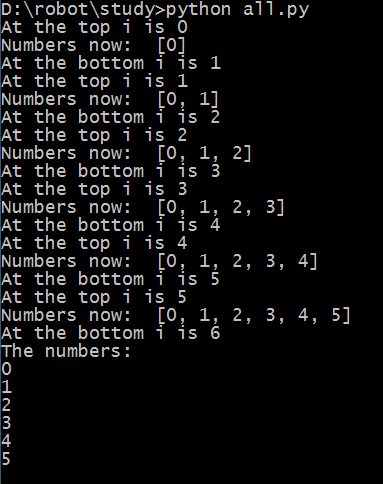
习题33:While循环 -- 尽量少用,大部分时候用for循环
代码:
i = 0
numbers = []
while i < 6:
print "At the top i is %d" % i
numbers.append(i)
i += 1
print "Numbers now: ", numbers
print "At the bottom i is %d" % i
print "The numbers: "
for num in numbers:
print num
结果:
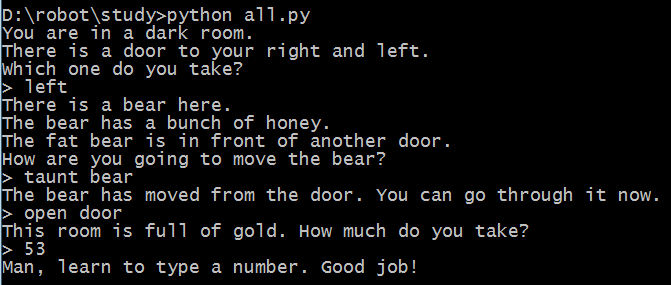
习题35:分支与函数
代码:
from sys import exit
def gold_room():
print "This room is full of gold. How much do you take?"
next = raw_input("> ")
if "0" in next or "1" in next:
how_much = int(next)
else:
dead("Man, learn to type a number.")
if how_much < 50:
print "Nice, you're not greedy, you win!"
exit(0)
else:
dead("You greedy bastard!")
def bear_room():
print "There is a bear here."
print "The bear has a bunch of honey."
print "The fat bear is in front of another door."
print "How are you going to move the bear?"
bear_moved = False
while True:
next = raw_input("> ")
if next == "take honey":
dead("The bear looks at you then slaps your face off.")
elif next == "taunt bear" and not bear_moved:
print "The bear has moved from the door. You can go through it now."
bear_moved = True
elif next == "taunt bear" and bear_moved:
dead("The bear gets pissed off and chews your leg off.")
elif next == "open door" and bear_moved:
gold_room()
else:
print "I got no idea what that means."
def cthulhu_room():
print "Hear you see the great evil Cthulhu."
print "He, it, whatever stares at you and you go insane."
print "Do you flee for your life or eat your head?"
next = raw_input("> ")
if "flee" in next:
start()
elif "head" in next:
dead("Well that was tasty!")
else:
cthulhu_room()
def dead(why):
print why, "Good job!"
exit(0)
def start():
print "You are in a dark room."
print "There is a door to your right and left."
print "Which one do you take?"
next = raw_input("> ")
if next == "left":
bear_room()
elif next == "right":
cthulhu_room()
else:
dead("You stumble around the room until you starve.")
start()
结果:(路径之一)
习题36:设计与调试
If 语句的规则
1. 每一个“if 语句”必须包含一个 else.
2. 如果这个 else 永远都不应该被执行到,因为它本身没有任何意义,那你必须在 else 语句后面
使用一个叫做 die 的函数,让它打印出错误信息并且死给你看,这和上一节的习题类似,这样你
可以找到很多的错误。
3. “if 语句”的嵌套不要超过 2 层,最好尽量保持只有 1 层。 这意味着如果你在 if 里边又有了
一个 if,那你就需要把第二个 if 移到另一个函数里面。
4. 将“if 语句”当做段落来对待,其中的每一个 if, elif, else 组合就跟一个段落的句子组
合一样。在这种组合的最前面和最后面留一个空行以作区分。
5. 你的布尔测试应该很简单,如果它们很复杂的话,你需要将它们的运算事先放到一个变量里,并
且为变量取一个好名字。
循环的规则
1. 只有在循环永不停止时使用“while 循环”,这意味着你可能永远都用不到。这条只有 Python
中成立,其他的语言另当别论。
2. 其他类型的循环都使用“for 循环”,尤其是在循环的对象数量固定或者有限的情况下。
调试(debug)的小技巧
1. 不要使用 “debugger”。 Debugger 所作的相当于对病人的全身扫描。你并不会得到某方面的
有用信息,而且你会发现它输出的信息态度,而且大部分没有用,或者只会让你更困惑。
2. 最好的调试程序的方法是使用 print 在各个你想要检查的关键环节将关键变量打印出来,从而
检查哪里是否有错。
3. 让程序一部分一部分地运行起来。不要等一个很长的脚本写完后才去运行它。写一点,运行一点,
再修改一点。
习题37:复习各种符号
Keywords(关键字)
• and
• del
• from
• not
• while
• as
• elif
• global
• or
• with
• assert
• else
• if
• pass
• yield
• break
• except
• import
• print
• class
• exec
• in
• raise
• continue
• finally
• is
• return
• def
• for
• lambda
• try
数据类型
• True
• False
• None
• strings
• numbers
• floats
• lists
字符串转义序列(Escape Sequences)
• \\
• \'
• \"
• \a
• \b
• \f
• \n
• \r
• \t
• \v
字符串格式化(String Formats)
• %d
• %i
• %o
• %u
• %x
• %X
• %e
• %E
• %f
• %F
• %g
• %G
• %c
• %r
• %s
• %%
操作符号
• +
• -
• *
• **
• /
• //
• %
• <
• >
• <=
• >=
• ==
• !=
• <>
• ( )
• [ ]
• { }
• @
• ,
• :
• .
• =
• ;
• +=
• -=
• *=
• /=
• //=
• %=
• **=
python入门 -- 学习笔记3的更多相关文章
- Python入门学习笔记4:他人的博客及他人的学习思路
看其他人的学习笔记,可以保证自己不走弯路.并且一举两得,即学知识又学方法! 廖雪峰:https://www.liaoxuefeng.com/wiki/0014316089557264a6b348958 ...
- Python入门学习笔记
了解 一下Python中的基本语法,发现挺不适应的,例如变量经常想去指定类型或者if加个括号之类的.这是在MOOC中学习到的知识中一点简单的笔记. Python的变量和数据类型: 1.Python这种 ...
- python入门学习笔记(三)
10.函数 求绝对值的函数 abs(x) 也可以在交互式命令行通过 help(abs) 查看abs函数的帮助信息.调用 abs 函数:>>> abs(100)100>>& ...
- Python入门 学习笔记 (二)
今天学习了一些简单的语法规则,话不多说,开始了: 二.数据类型 常用数据类型中的整形和浮点型就不多说了. 1.字符串 ...
- python入门 -- 学习笔记1
学习资料:笨方法学Python 准备: 安装环境----请自行网络搜索(Windows安装很简单,和其他安装程序一样) 找一个自己习惯的编辑器(比如:sublime text 3) 创建一个专门的目录 ...
- Python入门 学习笔记 (一)
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/lujianwenance/p/5939786.html 说到学习一门语言第一步就是先选定使用的工具(环境).因为本人是个小白,所以征求了一下同 ...
- python入门学习笔记(二)
6.6替换元素 7.tuple类型 7.1创建tuple 7.2创建单元素tuple 7.3"可变"的tuple 8.条件判断和循环 8.1,if语句 8.2,if... ...
- python入门学习笔记(一)
写在开头: A:python的交互式环境 ...
- python入门 -- 学习笔记4
习题38:列表的操作 当你看到像 mystuff.append('hello') 这样的代码时,你事实上已经在 Python 内部激发了一个连锁反应.以下是它的工作原理: 1. Python 看到你用 ...
随机推荐
- 通过GUID确保winform运行唯一实例
通过程序生成的GUIDwinform唯一实例 using System.Threading;bool createdNew; Guid ownGUID = new Guid(((GuidAttribu ...
- alpha冲刺(3/10)
前言 队名:旅法师 作业链接 队长博客 燃尽图 会议 会议照片 会议内容 陈晓彬(组长) 今日进展: 召开会议 安排任务 博客撰写 制定计划 问题困扰: 前后端的交互沟通有点缺失,以至后端进度很慢,需 ...
- spring boot 1.4 整合 mybatis druid
http://www.jianshu.com/p/cef49ad91ba9spring boot 1.4 整合 mybatis druid
- C# 调用打印机 打印 Excel
打印 Excel 模板 大体思路,通过NPOI操作Excel文件,通过Spire将Excel转成图片,将图片传给系统打印. Spire是收费工具,在微软库中下载Free版本. #region 打印所用 ...
- golang 写日志到syslog
应用程序可以通过 UNIX domain sockets, UDP or TCP,向syslog守护进程发送日志.syslog守护进程可以在远端. 这样,就可以不用单独收集应用程序的日志了. gola ...
- PostgreSQL获取所有表名、字段名、字段类型、注释
转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/cicon/article/details/51577655 获取表名及注释: select relname as tabname,cast(obj_ ...
- 秒懂,Java 注解 (Annotation)你可以这样学 - CSDN博客
https://blog.csdn.net/briblue/article/details/73824058 文章开头先引入一处图片. 这处图片引自老罗的博客.为了避免不必要的麻烦,首先声明我个人比较 ...
- DataTable.Select 处理关联表数据
DataSet.Clone 会拷贝表结构,关联关系也会拷贝, 用Select 筛选后ImportRow 导入新的DataTable,然后处理关联DataTable DataSet ds2 = dsS ...
- sequelize查询数据的日期格式化
首先确定时区 const sequelize = new Sequelize(config.database, config.username, config.password, { host: co ...
- 减小delphi体积的方法
1.关闭RTTI反射机制 自从Delphi2010中引入了新的RTTI反射机制后,编译出来的程序会变得很大,这是因为默认情况下 Delphi2010 给所有类都加上了反射机制.而我们的工程并不每每都 ...
