SALALchemy Session与scoped_session的源码分析
我们发现Session与scoped_session都有一些方法:
但是scoped_session的源码里面没有设置这些方法让我们从源码里去窥探下源码在哪里设置了这些方法:
Session里面的方法放在了public_methods里面:
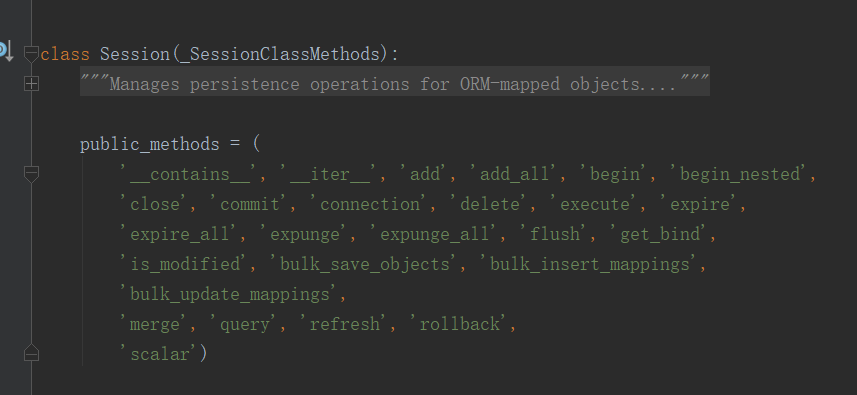
scoped_session的源码里面没有这些方法?:
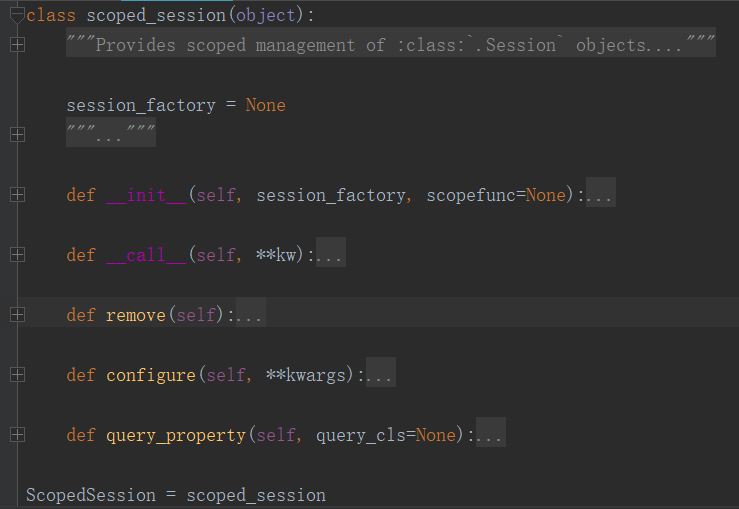
那它怎么实现这些方法的呢?
我们看到了它的构造方法:
def __init__(self, session_factory, scopefunc=None):
"""Construct a new :class:`.scoped_session`. :param session_factory: a factory to create new :class:`.Session`
instances. This is usually, but not necessarily, an instance
of :class:`.sessionmaker`.
:param scopefunc: optional function which defines
the current scope. If not passed, the :class:`.scoped_session`
object assumes "thread-local" scope, and will use
a Python ``threading.local()`` in order to maintain the current
:class:`.Session`. If passed, the function should return
a hashable token; this token will be used as the key in a
dictionary in order to store and retrieve the current
:class:`.Session`. """
self.session_factory = session_factory if scopefunc:
self.registry = ScopedRegistry(session_factory, scopefunc)
else:
self.registry = ThreadLocalRegistry(session_factory)
第一次进来时,scopefunc是空的。
走else,
self.registry = ThreadLocalRegistry(session_factory)
就会实例化:ThreadLocalRegistry。
class ThreadLocalRegistry(ScopedRegistry):
"""A :class:`.ScopedRegistry` that uses a ``threading.local()``
variable for storage. """ def __init__(self, createfunc):
self.createfunc = createfunc
self.registry = threading.local()
里面有两个对象 self.createfunc和registry:
registry是唯一标识,
session加上括号就会执行__call__方法:
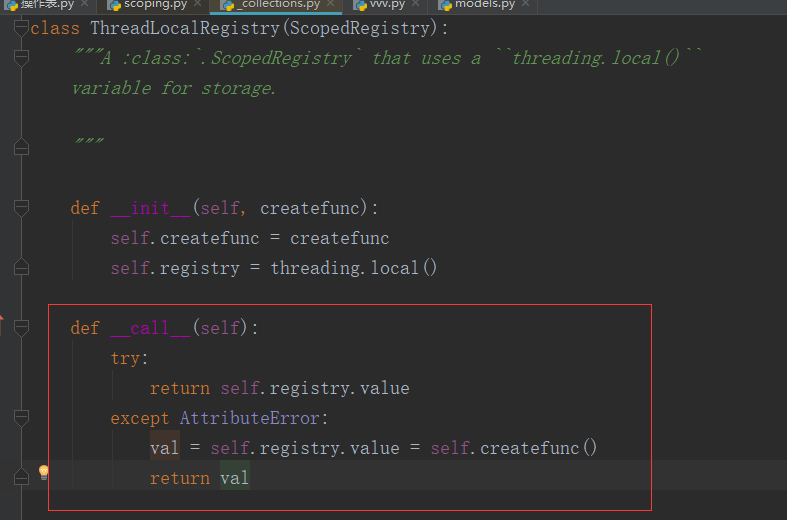
因为self.registry.value第一次进入没有值:
所以走except 就是执行self.createfunc()往前找传的值是session_factory那么session_factory是谁呢?就是我们传入的session,也就是实例化了我们的session。
就这就会走下面的方法:
def instrument(name):
def do(self, *args, **kwargs):
return getattr(self.registry(), name)(*args, **kwargs)
return do for meth in Session.public_methods:
setattr(scoped_session, meth, instrument(meth))
方法二:
我们发现
class scoped_session(object):
"""Provides scoped management of :class:`.Session` objects. See :ref:`unitofwork_contextual` for a tutorial. """ session_factory = None
"""The `session_factory` provided to `__init__` is stored in this
attribute and may be accessed at a later time. This can be useful when
a new non-scoped :class:`.Session` or :class:`.Connection` to the
database is needed.""" def __init__(self, session_factory, scopefunc=None):
"""Construct a new :class:`.scoped_session`. :param session_factory: a factory to create new :class:`.Session`
instances. This is usually, but not necessarily, an instance
of :class:`.sessionmaker`.
:param scopefunc: optional function which defines
the current scope. If not passed, the :class:`.scoped_session`
object assumes "thread-local" scope, and will use
a Python ``threading.local()`` in order to maintain the current
:class:`.Session`. If passed, the function should return
a hashable token; this token will be used as the key in a
dictionary in order to store and retrieve the current
:class:`.Session`. """
self.session_factory = session_factory if scopefunc:
self.registry = ScopedRegistry(session_factory, scopefunc)
else:
self.registry = ThreadLocalRegistry(session_factory)
如果我们给
scopefunc传值就会走if语句,
class ScopedRegistry(object):
"""A Registry that can store one or multiple instances of a single
class on the basis of a "scope" function. The object implements ``__call__`` as the "getter", so by
calling ``myregistry()`` the contained object is returned
for the current scope. :param createfunc:
a callable that returns a new object to be placed in the registry :param scopefunc:
a callable that will return a key to store/retrieve an object.
""" def __init__(self, createfunc, scopefunc):
"""Construct a new :class:`.ScopedRegistry`. :param createfunc: A creation function that will generate
a new value for the current scope, if none is present. :param scopefunc: A function that returns a hashable
token representing the current scope (such as, current
thread identifier). """
self.createfunc = createfunc
self.scopefunc = scopefunc
self.registry = {} def __call__(self):
key = self.scopefunc()
try:
return self.registry[key]
except KeyError:
return self.registry.setdefault(key, self.createfunc())
我们看到如果对象加括号就会走__call__方法:
第一次没有值,就会走except,设置并且实例化session。
往下方法和方式一一样啦。
在执行到最后我们要加上一句:
session.remove()
我们来看下这句话做了什么?
def remove(self):
"""Dispose of the current :class:`.Session`, if present. This will first call :meth:`.Session.close` method
on the current :class:`.Session`, which releases any existing
transactional/connection resources still being held; transactions
specifically are rolled back. The :class:`.Session` is then
discarded. Upon next usage within the same scope,
the :class:`.scoped_session` will produce a new
:class:`.Session` object. """ if self.registry.has():
self.registry().close()
self.registry.clear()
我们进入has看下:
def has(self):
return hasattr(self.registry, "value")
如果有值就执行close方法。
然后在执行clear方法:
def clear(self):
try:
del self.registry.value
except AttributeError:
pass
SALALchemy Session与scoped_session的源码分析的更多相关文章
- SqlAlchemy 中操作数据库时session和scoped_session的区别(源码分析)
原生session: from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker from sqlalchemy import create_engine from sqlalch ...
- springMVC源码分析--国际化实现Session和Cookie(二)
上一篇博客springMVC源码分析--国际化LocaleResolver(一)中我们介绍了springMVC提供的国际化的解决方案,接下来我们根据springMVC提供的解决方案来简单的实现一个多语 ...
- [asp.net core 源码分析] 01 - Session
1.Session文档介绍 毋庸置疑学习.Net core最好的方法之一就是学习微软.Net core的官方文档:https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/aspnet/cor ...
- TOMCAT8源码分析——SESSION管理分析(上)
前言 对于广大java开发者而已,对于J2EE规范中的Session应该并不陌生,我们可以使用Session管理用户的会话信息,最常见的就是拿Session用来存放用户登录.身份.权限及状态等信息.对 ...
- Tomcat源码分析——Session管理分析(下)
前言 在<TOMCAT源码分析——SESSION管理分析(上)>一文中我介绍了Session.Session管理器,还以StandardManager为例介绍了Session管理器的初始化 ...
- Tomcat源码分析——Session管理分析(上)
前言 对于广大java开发者而已,对于J2EE规范中的Session应该并不陌生,我们可以使用Session管理用户的会话信息,最常见的就是拿Session用来存放用户登录.身份.权限及状态等信息.对 ...
- 一个由正则表达式引发的血案 vs2017使用rdlc实现批量打印 vs2017使用rdlc [asp.net core 源码分析] 01 - Session SignalR sql for xml path用法 MemCahe C# 操作Excel图形——绘制、读取、隐藏、删除图形 IOC,DIP,DI,IoC容器
1. 血案由来 近期我在为Lazada卖家中心做一个自助注册的项目,其中的shop name校验规则较为复杂,要求:1. 英文字母大小写2. 数字3. 越南文4. 一些特殊字符,如“&”,“- ...
- Flask框架(三)—— 请求扩展、中间件、蓝图、session源码分析
Flask框架(三)—— 请求扩展.中间件.蓝图.session源码分析 目录 请求扩展.中间件.蓝图.session源码分析 一.请求扩展 1.before_request 2.after_requ ...
- Flask框架(五) —— session源码分析
Flask框架(五) —— session源码分析 目录 session源码分析 1.请求来了,执行__call__方法 2.__call__方法 3.调用__call__方法 3.1.ctx = s ...
随机推荐
- Java基础系列--ArrayList集合
原创作品,可以转载,但是请标注出处地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/V1haoge/p/8494618.html 一.概述 ArrayList是Java集合体系中最常使用,也是最简单 ...
- xshell远程终端操作Ubuntu server安装LAMP环境之最详细笔记之二PHP开发环境配置
前言: 昨天学会了安装server,今天试着通过远程终端xshell来安装LAMP,搭配一下开发环境,也有集成环境可以一键安装使用,还是瞎折腾一下,手动一步一步搭建一下这个开发环境. 接上一篇:ubu ...
- 分布式版本控制系统GIT的使用
一.什么是Git Git是一个分布式版本控制系统,Git 和其他版本控制系统的主要差别在于,Git 只关心文件数据的整体是否发生变化,而大多数其他系统则只关心文件内容的具体差异(如CVS.Subver ...
- element split 将多个单号分隔
const condeid = this.formData.WayBillCode; var item = ""; const codes = condeid.split(&quo ...
- MVC四大筛选器—ActionFilter&ResultedFilter
AuthorizeFilter筛选器 在Action的执行中包括两个重要的部分,一个是Action方法本身逻辑代码的执行,第二个就是Action方法的筛选器的执行. MVC4中筛选器都是以AOP(面向 ...
- Placement of class definition and prototype
When I create a function, I can put the code for it after main if I put the prototype above main. Fo ...
- Android线程
1.引言 在Android中,几乎完全采用了Java的线程机制,由于Android的特性,主线程只处理和界面相关的事情,子线程处理耗时操作.Android中扮演线程角色的有Thread.AsyncTa ...
- Django Rest framework 之 权限
django rest framework 之 认证(一) django rest framework 之 权限(二) django rest framework 之 节流(三) django res ...
- csharp: FTP Client Library using System.Net.FtpWebRequest
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.D ...
- spring配置log4j
1.引入log4j-xxx.jar包,buildpath. 2.在项目的根目录下新建resources名的文件夹,注意是source folder,并新建log4j.properties文件 3.在l ...
