JAVA并发(6)-并发队列ArrayBlockingQueue
本文讲ArrayBlockingQueue
1. 介绍
一个基于数组的有界阻塞队列,FIFO顺序。支持等待消费者和生产者线程的可选公平策略(默认是非公平的)。公平的话通常会降低吞吐量,但是可以减少可变性并避免之前被阻塞的线程饥饿。
1.1 类结构
- ArrayBlockingQueue继承关系
- ArrayBlockingQueue类图
构造器
// 默认是非公平的
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity) {
this(capacity, false);
}
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair) {
...
}
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair,
Collection<? extends E> c) {
...
}
比较重要的几个参数
// 储存元素的数组
final Object[] items;
/** items index for next take, poll, peek or remove */
// 与putIndex相互配合可以将数组变成一个可循环利用的数组,不需要扩容,后面会讲到
// 每次出队的索引
int takeIndex;
/** items index for next put, offer, or add */
// 每次入队的索引
int putIndex;
/** Number of elements in the queue */
int count;
/**
* Shared state for currently active iterators, or null if there
* are known not to be any. Allows queue operations to update
* iterator state.
*/
// 迭代的时候会用到,在后面详讲
transient Itrs itrs = null;
保证线程安全的措施
/** Main lock guarding all access */
final ReentrantLock lock;
/** Condition for waiting takes */
private final Condition notEmpty;
/** Condition for waiting puts */
private final Condition notFull;
我们可以看到ArrayBlockingQueue使用的是单锁控制线程安全,而LinkedBlockingQueue是双锁控制的, 后者的细粒度更小。
2. 源码剖析
ArrayBlockingQueue也是继承至BlockingQueue(可以去看看上面提到的那篇博客有提到BlockingQueue),它对于不同的方法不能立即满足要求的,作出的回应是不一样的。
我们分别介绍下面的方法的具体实现
- offer(E e)
- offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
- put(E e)
- poll()
- remove(Object o)
2.1 offer(E e) & poll()
插入成功就返回true;若队列满了就直接返回false,不会阻塞自己
public boolean offer(E e) {
checkNotNull(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
if (count == items.length)
return false;
else {
enqueue(e);
return true;
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
上面的代码比较简单,我们来看看入队的具体操作
private void enqueue(E x) {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;
// assert items[putIndex] == null;
final Object[] items = this.items;
items[putIndex] = x;
// 为什么putIndex+1 等于数组长度时会变成0
if (++putIndex == items.length)
putIndex = 0;
count++;
notEmpty.signal();
}
为了解答上面注释中的问题,我们先看看poll()的实现
public E poll() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return (count == 0) ? null : dequeue();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
private E dequeue() {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;
// assert items[takeIndex] != null;
final Object[] items = this.items;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E x = (E) items[takeIndex];
items[takeIndex] = null;
// takeIndex + 1等于了数组的长度也会将值置为0
if (++takeIndex == items.length)
takeIndex = 0;
count--;
if (itrs != null)
itrs.elementDequeued();
notFull.signal();
return x;
}
结合上面的入队、出队源码,我们来分析一下:
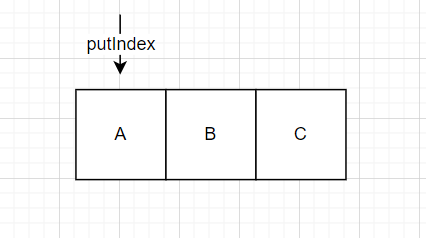
- 单线程下,首先执行
ArrayBlockingQueue<String> array = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
array.offer("A");
array.offer("B");
array.offer("C");
此时队列的状态
- 再执行
array.poll();
array.offer("D");
最后队列的状态
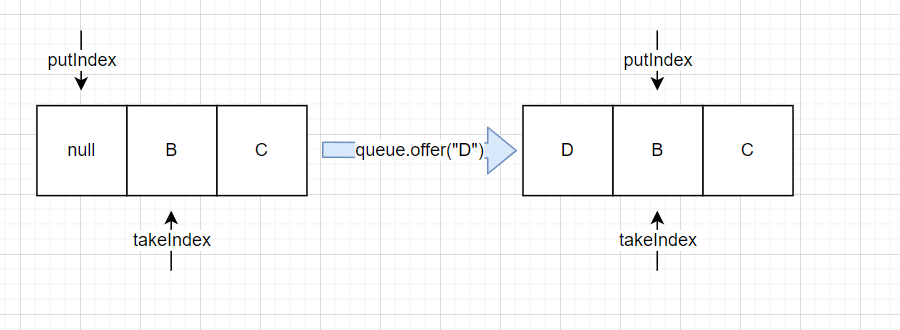
大家可能会有点疑问,上面的队列不是输出是"D B C", 咋回事? 肯定不是啦,我们看看类重写的toString就明白了。
public String toString() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
int k = count;
if (k == 0)
return "[]";
final Object[] items = this.items;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append('[');
// 主要代码
for (int i = takeIndex; ; ) {
Object e = items[i];
sb.append(e == this ? "(this Collection)" : e);
if (--k == 0)
return sb.append(']').toString();
sb.append(',').append(' ');
if (++i == items.length)
i = 0;
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
思考一下,就会明白了。
通过上面的分析,我们看出了数组就像一个循环数组一样,每个地址都被重复使用。我们也知道了基于数组的队列如何实现的。
offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) 与 put(E e)实现都比较简单,大家看看源码即可。
2.2 remove(Object o)
若o存在则移除,返回true;反之。这个操作会改变队列的结构,但是该方法一般很少使用
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) return false;
final Object[] items = this.items;
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
if (count > 0) {
final int putIndex = this.putIndex;
int i = takeIndex;
do {
if (o.equals(items[i])) {
// 主要删除逻辑
removeAt(i);
return true;
}
if (++i == items.length)
i = 0;
} while (i != putIndex);
}
return false;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
void removeAt(final int removeIndex) {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;
// assert items[removeIndex] != null;
// assert removeIndex >= 0 && removeIndex < items.length;
final Object[] items = this.items;
if (removeIndex == takeIndex) {
// removing front item; just advance
items[takeIndex] = null;
if (++takeIndex == items.length)
takeIndex = 0;
count--;
if (itrs != null)
itrs.elementDequeued();
} else {
// an "interior" remove
// slide over all others up through putIndex.
// 此时removeIndex != takeIndex
// 为啥要执行下面的代码,大家可以按照上面图片的最后状态,
// 按照下面代码走一下,就明白了.主要是设置putIndex
final int putIndex = this.putIndex;
for (int i = removeIndex;;) {
int next = i + 1;
if (next == items.length)
next = 0;
if (next != putIndex) {
items[i] = items[next];
i = next;
} else {
items[i] = null;
this.putIndex = i;
break;
}
}
count--;
if (itrs != null)
itrs.removedAt(removeIndex);
}
notFull.signal();
}
2.3 解释解释Itrs
// 当前活动迭代器的共享状态; 允许队列操作更新迭代器的状态;
transient Itrs itrs = null;
这个变量可以理解成,在一个线程使用迭代器时,其他的线程可以对队列进行更新操作的一个保障。
源码注释中对Itrs的描述,迭代器和它们的队列之间共享数据,允许在删除元素时修改队列以更新迭代器。 我们可以看到对队列进行了删除操作时,队列都会执行下面的语句
if (itrs != null)
itrs.removedAt(removeIndex);
初始化该值是在使用迭代器时
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Itr();
}
...
Itr() {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 0;
lastRet = NONE;
final ReentrantLock lock = ArrayBlockingQueue.this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
...
itrs = new Itrs(this);
...
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
3. 总结
ArrayBlockingQueue的实现整体不难,使用ReetrantLock保证了线程安全,putIndex与takeIndex分别维护入队与出队的位置,一起构成一个循环数组
JAVA并发(6)-并发队列ArrayBlockingQueue的更多相关文章
- Java中的阻塞队列-ArrayBlockingQueue(一)
最近在看一些java基础的东西,看到了队列这章,打算对复习的一些知识点做一个笔记,也算是对自己思路的一个整理,本章先聊聊java中的阻塞队列 参考文章: http://ifeve.com/java-b ...
- java并发:阻塞队列
第一节 阻塞队列 1.1 初识阻塞队列 队列以一种先进先出的方式管理数据,阻塞队列(BlockingQueue)是一个支持两个附加操作的队列,这两个附加的操作是:在队列为空时,获取元素的线程会等待队列 ...
- 聊聊并发(七)——Java中的阻塞队列
3. 阻塞队列的实现原理 聊聊并发(七)--Java中的阻塞队列 作者 方腾飞 发布于 2013年12月18日 | ArchSummit全球架构师峰会(北京站)2016年12月02-03日举办,了解更 ...
- Java并发编程-阻塞队列(BlockingQueue)的实现原理
背景:总结JUC下面的阻塞队列的实现,很方便写生产者消费者模式. 常用操作方法 常用的实现类 ArrayBlockingQueue DelayQueue LinkedBlockingQueue Pri ...
- Java编程的逻辑 (76) - 并发容器 - 各种队列
本系列文章经补充和完善,已修订整理成书<Java编程的逻辑>,由机械工业出版社华章分社出版,于2018年1月上市热销,读者好评如潮!各大网店和书店有售,欢迎购买,京东自营链接:http: ...
- Java并发编程——阻塞队列BlockingQueue
Java 并发编程系列文章 Java 并发基础——线程安全性 Java 并发编程——Callable+Future+FutureTask java 并发编程——Thread 源码重新学习 java并发 ...
- 【Java并发】并发队列与线程池
并发队列 阻塞队列与非阻塞队 ConcurrentLinkedQueue BlockingQueue ArrayBlockingQueue LinkedBlockingQueue PriorityBl ...
- Java并发编程笔记之ArrayBlockingQueue源码分析
JDK 中基于数组的阻塞队列 ArrayBlockingQueue 原理剖析,ArrayBlockingQueue 内部如何基于一把独占锁以及对应的两个条件变量实现出入队操作的线程安全? 首先我们先大 ...
- [Java并发] AQS抽象队列同步器源码解析--锁获取过程
要深入了解java并发知识,AbstractQueuedSynchronizer(AQS)是必须要拿出来深入学习的,AQS可以说是贯穿了整个JUC并发包,例如ReentrantLock,CountDo ...
- [Java并发] AQS抽象队列同步器源码解析--独占锁释放过程
[Java并发] AQS抽象队列同步器源码解析--独占锁获取过程 上一篇已经讲解了AQS独占锁的获取过程,接下来就是对AQS独占锁的释放过程进行详细的分析说明,废话不多说,直接进入正文... 锁释放入 ...
随机推荐
- 从苏宁电器到卡巴斯基(后传)第05篇:聊聊我对WannaCry产生的感慨
这几天看到网上对WannaCry勒索病毒讨论得沸沸扬扬,不免有些感触. 其实该病毒的这次爆发,完全可以类比N年前"熊猫烧香"爆发的情况.也就是国内杀软纷纷歇菜,让本来就没什么技术含 ...
- NetBIOS名称欺骗和LLMNR欺骗
目录 LLMNR和NetBios 攻击原理 Responder 攻击过程 LLMNR和NetBios 什么是LLMNR和NetBIOS名称服务器广播? 当DNS名称服务器请求失败时,Microsoft ...
- Python数模笔记-Sklearn(1) 介绍
1.SKlearn 是什么 Sklearn(全称 SciKit-Learn),是基于 Python 语言的机器学习工具包. Sklearn 主要用Python编写,建立在 Numpy.Scipy.Pa ...
- linux跨文件复制粘贴
跨文件是这样的: 复制a.txt的第20行至第30行到b.txt中vi a.txt:2010yy:e b.txtp
- UVa OJ 455 Periodic Strings
Periodic Strings A character string is said to have period k if it can be formed by concatenating ...
- [MySQL数据库之事务、读现象、数据库锁机制、多版本控制MVCC、事务隔离机制]
[MySQL数据库之事务.读现象.数据库锁机制.多版本控制MVCC.事务隔离机制] 事务 1.什么是事务: 事务(Transaction),顾名思义就是要做的或所做的事情,数据库事务指的则是作为单个逻 ...
- [面向对象之继承应用(在子类派生重用父类功能(super),继承实现原理(继承顺序、菱形问题、继承原理、Mixins机制),组合]
[面向对象之继承应用(在子类派生重用父类功能(super),继承实现原理(继承顺序.菱形问题.继承原理.Mixins机制),组合] 继承应用 类与类之间的继承指的是什么'是'什么的关系(比如人类,猪类 ...
- 记一次golang内存泄露
记一次golang内存泄露 最近在QA环境上验证功能时,发现机器特别卡,查看系统内存,发现可用(available)内存仅剩200多M,通过对进程耗用内存进行排序,发现有一个名为application ...
- [Web] 计算机网络课程(一)
局域网 覆盖范围小,自己花钱买设备,自己单位维护 线长不超过100米,带宽固定(10M 100M 1000M) 星形结构,上层交换机口少,但每个口带宽高 广域网 距离远 如在家通过ADSL拨号上网,或 ...
- sed 's/AA/BB/' file # 将文件中的AA替换成BB,只替换一行中第一次出现的AA,替换后的结果输出到屏幕 sed 's/AA/BB/g' file # 将文件中的所有AA都替换成BB,替换后的结果输出到屏幕
生信人的自我修养:Linux命令速查手册 简佐义 四川大学 生物信息学硕士 科学求真 赢 10 万奖金 · 院士面对面 209 人赞同了该文章 许多人做生物信息学,要么不重视Linux,要么不知道 ...
