java基础-java面向对象-02-day09
1. 封装
什么是面向对象?面向对象与面向过程的区别?面向对象的好处?自查资料学习
面向对象:纪传体 《史记》 以人物为核心 讲述人物的实际 并进行评论
面向过程:编年史 以历史事件发生的时间顺序 讲述历史
封装:
把过程和数据包围起来,对于数据的访问只能通过已经定义好的接口进行访问。封装把对象所有组成部分组合在一起,使用方法将类的数据隐藏起来,控制用户对于类的修改以及数据访问程度。
private修饰符
public class Girl {
//age属性,加了private修饰符,外界对age属性的访问以及设置就收到了限制
private int age;
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
if (age >= 30) {
this.age = 18;
} else {
this.age = age;
}
}
}
练习:
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
private String sex;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
if ("男".equals(sex) || "女".equals(sex)) {
this.sex = sex;
} else {
this.sex = "错误";
}
}
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age, String sex) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
/*this.sex = sex;*/
this.setSex(sex);
}
}
package com.msb3;
/**
@Auther: jack.chen
@Date: 2023/9/10 - 09 - 10 - 11:25
@Description: com.msb3
@version: 1.0
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s = new Student();System.out.println(s.getAge());
System.out.println(s.getName());
System.out.println(s.getSex()); Student s1 = new Student("lili", 18, "女22"); System.out.println(s1.getAge());
System.out.println(s1.getName());
System.out.println(s1.getSex());
}
}

2. 继承
学生 继承 Person
package com.msb4;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/10 - 09 - 10 - 11:33
* @Description: com.msb4
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Person {
private int age;
private String name;
private double height;
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(double height) {
this.height = height;
}
public void eat(){
System.out.println("eat");
}
public void sleep(){
System.out.println("sleep");
}
}
package com.msb4;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/10 - 09 - 10 - 11:35
* @Description: com.msb4
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Student extends Person{
//学生独有的私有属性 学号sno
private int sno;
public int getSno() {
return sno;
}
public void setSno(int sno) {
this.sno = sno;
}
public void study(){
System.out.println("study");
}
}
package com.msb4;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/10 - 09 - 10 - 11:37
* @Description: com.msb4
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s = new Student();
s.setSno(1010);
s.setAge(18);
s.setName("feifei");
s.setHeight(188.9);
s.study();
s.sleep();
s.eat();
}
}
- 一个父类可以有多个子类
- 一个子类只能有一个直接父类,但是可以继承自其他的父类
- 继承具有传递性
Student-->Person --> Object
Object是所有类的祖宗,也就是所有的类都直接或者间接继承自object
权限修饰符
private 只能是同一个类才能访问
default int age;默认不写的权限 只能同一个包才能访问
protected 子类才能访问
public 都可以
写代码的一般规则:
一般属性用 private修饰
方法都用public 修饰
2.1 什么是方法的重写
对父类提供的方法不满足的时候 对父类的方法进行重写
重写父类的方法有严格限制与要求:
方法名必须一直,参数列表(个数 类型 顺序)也要一致
package com.msb5;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/10 - 09 - 10 - 11:51
* @Description: com.msb5
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Person {
public void eat(){
System.out.println("eat");
}
public void sleep(){
System.out.println("sleep");
}
}
package com.msb5;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/10 - 09 - 10 - 11:56
* @Description: com.msb5
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Student extends Person{
public void study(){
System.out.println("study");
}
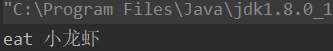
@Override
public void eat(){
System.out.println("eat 小龙虾");
}
}
package com.msb5;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/10 - 09 - 10 - 11:59
* @Description: com.msb5
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s = new Student();
s.eat();
}
}
2.2 super
- super访问父类的属性 访问父类的方法
package com.msb5;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/10 - 09 - 10 - 11:51
* @Description: com.msb5
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Person {
int age;
public void eat(){
System.out.println("eat");
}
public void sleep(){
System.out.println("sleep");
}
}
package com.msb5;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/10 - 09 - 10 - 11:56
* @Description: com.msb5
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Student extends Person{
double score;
public void study(){
System.out.println("study");
}
@Override
public void eat(){
System.out.println("eat 小龙虾");
}
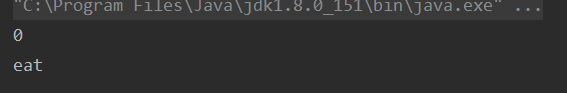
public void a(){
System.out.println(super.age);
super.eat();//调用父类的eat方法
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s = new Student();
s.a();
}
}
- 构造器中使用super()
package com.msb5;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/10 - 09 - 10 - 11:51
* @Description: com.msb5
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Person {
int age;
String name;
public Person(){
}
public Person(int age, String name){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void eat(){
System.out.println("eat");
}
public void sleep(){
System.out.println("sleep");
}
}
package com.msb5;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/10 - 09 - 10 - 11:56
* @Description: com.msb5
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Student extends Person{
double score;
public Student(){
}
public Student(int age, String name, double score){
super(age, name);//调用父类的构造器
/*this(score);*/ //构造器只能调用一个 因为实例化对象 只能实例化一个对象
this.score = score;
}
public void study(){
System.out.println("study");
}
@Override
public void eat(){
System.out.println("eat 小龙虾");
}
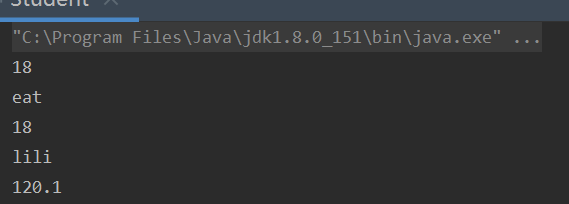
public void a(){
System.out.println(super.age);
super.eat();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s = new Student(18, "lili", 120.1);
s.a();
System.out.println(s.age);
System.out.println(s.name);
System.out.println(s.score);
}
}
- 使用idea的快捷键alt+insert快速生成构造
快捷键生成构造器 alt+insert
package com.msb6;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/10 - 09 - 10 - 21:34
* @Description: com.msb6
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Student extends Person {
double height;
double weight;
public Student(){
}
public Student(int age, String name) {
super(age, name);
}
public Student(int age, String name, double height, double weight) {
super(age, name);
this.height = height;
this.weight = weight;
}
}
2.3 object详解
object是java中一切类的根基
所有未声明其父类的class默认 extended object
toString方法
package com.msb6;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/10 - 09 - 10 - 21:34
* @Description: com.msb6
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Student extends Person {
double height;
double weight;
public Student(){
}
public Student(int age, String name) {
super(age, name);
}
public Student(int age, String name, double height, double weight) {
super(age, name);
this.height = height;
this.weight = weight;
}
public String toString(){//重写toString方法
return getClass().getName() + "@" + Integer.toHexString(hashCode());
}
}
package com.msb6;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/10 - 09 - 10 - 21:34
* @Description: com.msb6
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Student extends Person {
double height;
double weight;
public Student(){
}
public Student(int age, String name) {
super(age, name);
}
public Student(int age, String name, double height, double weight) {
super(age, name);
this.height = height;
this.weight = weight;
}
public String toString(){
// return getClass().getName() + "@" + Integer.toHexString(hashCode());
return "这个是一个Student对象, 名字是"+name+"身高:"+height+"体重"+weight;
}
}
package com.msb6;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/10 - 09 - 10 - 21:41
* @Description: com.msb6
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s = new Student(18, "lili", 188.8, 68.9);
System.out.println(s.toString());
}
}

toString方法就是对象的自我介绍,
可以用快捷键生成toString方法
public class Student extends Person {
double height;
double weight;
public Student(){
}
public Student(int age, String name) {
super(age, name);
}
public Student(int age, String name, double height, double weight) {
super(age, name);
this.height = height;
this.weight = weight;
}
/* public String toString(){
// return getClass().getName() + "@" + Integer.toHexString(hashCode());
return "这个是一个Student对象, 名字是"+name+"身高:"+height+"体重"+weight;
}*/
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"height=" + height +
", weight=" + weight +
", age=" + age +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
alt+insert
2.4 equals方法
package com.msb;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/10 - 09 - 10 - 21:51
* @Description: com.msb
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Phone {
private String brand;
private double price;
private int year;
public Phone() {
}
public Phone(String brand, double price, int year) {
this.brand = brand;
this.price = price;
this.year = year;
}
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
public int getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(int year) {
this.year = year;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Phone{" +
"brand='" + brand + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
", year=" + year +
'}';
}
public boolean equals(Object obj){//重写equals方法
Phone other = (Phone) obj;//向下转型
if(this.getBrand().equals(other.getBrand())&&this.getYear()==other.getYear()){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
package com.msb;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/10 - 09 - 10 - 21:53
* @Description: com.msb
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Phone p1 = new Phone("小米", 199.9, 2019);
Phone p2 = new Phone("小米", 199.9, 2019);
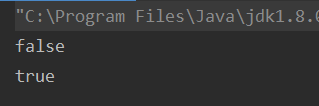
System.out.println(p1==p2); //false对于引用数据类型存储的是地址 两个不同的对象肯定不一样
System.out.println(p1.equals(p2));
}
}
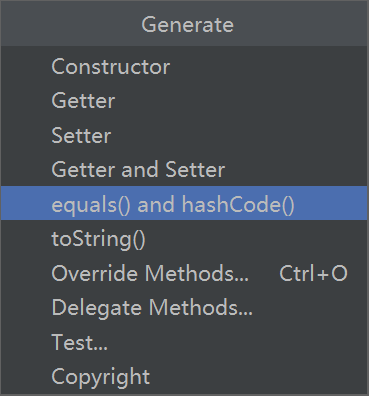
使用快捷键alt+insert生成equals方法
package com.msb;
import java.util.Objects;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/10 - 09 - 10 - 21:51
* @Description: com.msb
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Phone {
private String brand;
private double price;
private int year;
public Phone() {
}
public Phone(String brand, double price, int year) {
this.brand = brand;
this.price = price;
this.year = year;
}
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
public int getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(int year) {
this.year = year;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Phone{" +
"brand='" + brand + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
", year=" + year +
'}';
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (!(o instanceof Phone)) return false;
Phone phone = (Phone) o;
return Double.compare(phone.getPrice(), getPrice()) == 0 &&
getYear() == phone.getYear() &&
Objects.equals(getBrand(), phone.getBrand());
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(getBrand(), getPrice(), getYear());
}
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;//如果是自己 返回true
if (!(o instanceof Phone)) return false; //如果不是同一个类实例化出来的 返回false
Phone phone = (Phone) o;//使同一个类实例化的 将o这个对象 向下转型成Phone对象
return Double.compare(phone.getPrice(), getPrice()) == 0 &&
getYear() == phone.getYear() &&
Objects.equals(getBrand(), phone.getBrand());
//浮点数的比较用Double.compare
//int类型 直接 ==比较 这里都省略了this.
//字符串的比较用Objects.equals()
}
类之间的关系
package com.msb2;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/10 - 09 - 10 - 22:23
* @Description: com.msb2
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Boy {
String name;
int age;
public Boy(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void buy(){
System.out.println("买买买!!");
}
}
package com.msb2;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/10 - 09 - 10 - 22:22
* @Description: com.msb2
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Girl {
String name;
double weight;
Mom m;//女生的妈妈是谁 了解下丈母娘的背景!!!
public Girl(String name, double weight) {
this.name = name;
this.weight = weight;
}
public void love(Boy b){
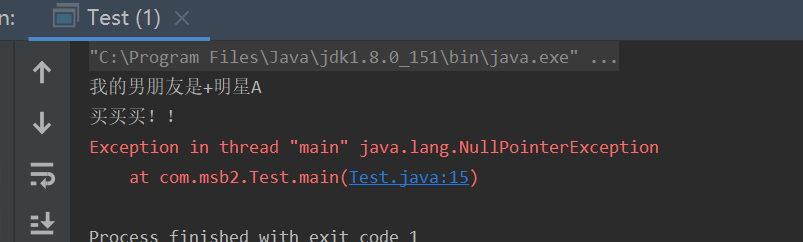
System.out.println("我的男朋友是+"+b.name);
b.buy();
}
}
package com.msb2;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/10 - 09 - 10 - 22:27
* @Description: com.msb2
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Mom {
public void say(){
System.out.println("妈妈总是唠唠叨叨");
}
}
package com.msb2;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/10 - 09 - 10 - 22:25
* @Description: com.msb2
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Boy b = new Boy("明星A", 18);
Girl g = new Girl("xiaotong", 65);
g.love(b);
//girl的妈妈 属性为赋值 报错
g.m.say();
}
}
package com.msb2;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/10 - 09 - 10 - 22:25
* @Description: com.msb2
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Boy b = new Boy("明星A", 18);
Girl g = new Girl("xiaotong", 65);
g.love(b);
g.m = new Mom();//给girl对象赋值妈妈属性
g.m.say();
}
}

类与类之间的关系:
常见的:继承 实现
组合>聚合>关联>依赖 可baidu了解
3. 多态
多态指的是 不同的子类 重写父类的方法 从而有了不同的实现方式也就是 方法的多态
package com.msb3;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/10 - 09 - 10 - 22:50
* @Description: com.msb3
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Dog extends Animal {
public void shout(){
System.out.println("旺旺汪");
}
public void guard(){
System.out.println("看门");
}
}
package com.msb3;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/10 - 09 - 10 - 22:48
* @Description: com.msb3
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Cat extends Animal {
public void shout(){
System.out.println("喵喵喵");
}
public void scratch(){
System.out.println("我是小猫 我可以 抓 ");
}
}
package com.msb3;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/10 - 09 - 10 - 22:50
* @Description: com.msb3
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Dog extends Animal {
public void shout(){
System.out.println("旺旺汪");
}
public void guard(){
System.out.println("看门");
}
}
package com.msb3;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/10 - 09 - 10 - 22:52
* @Description: com.msb3
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Girl {
public void play(Animal an){
an.shout();
}
}
package com.msb3;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/10 - 09 - 10 - 22:51
* @Description: com.msb3
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Pig extends Animal {
public void shout(){
System.out.println("我是小猪 enenen 是我的叫声");
}
public void eat(){
System.out.println("吃吃吃");
}
}
package com.msb3;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/10 - 09 - 10 - 22:53
* @Description: com.msb3
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Girl g = new Girl();
Pig p = new Pig();
Animal an = p; // 父类的应用指向子类的对象
g.play(an);
Animal an1 = new Cat(); // 与上面是相同的
g.play(an1);
Dog d = new Dog();
g.play(d); // 父类的应用指向子类的对象 传参的时候有转换
}
}
什么是向下转型 与 向上转型
package com.msb3;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/10 - 09 - 10 - 22:53
* @Description: com.msb3
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Girl g = new Girl();
Pig p = new Pig();
Animal an = p; // 父类的应用指向子类的对象 向上转型
g.play(an);
Animal an1 = new Cat(); // 与上面是相同的
g.play(an1);
Dog d = new Dog();
g.play(d); // 父类的应用指向子类的对象 传参的时候有转换
//向下转型
Pig p1 = (Pig) an; //转成pig之后才有weight age属性
p1.eat();
p1.weight = 10;
p1.age = 20;
}
}
简单的工厂模式
static 提供getAnimal方法
package com.msb3;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/10 - 09 - 10 - 23:09
* @Description: com.msb3
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class PetStore {
public static Animal getAnimal(String petName){
Animal an = null;
if ("猫".equals(petName)){
an = new Cat();
}
if ("猪".equals(petName)){
an = new Pig();
}
if ("狗".equals(petName)){
an = new Dog();
}
return an;
}
}
调用
Animal an2 = PetStore.getAnimal("狗");
g.play(an2);
4. final修饰符
final的意思就是没有下文了到我这里截止
变量不能再赋值
类的method不能被子类重写
类被final修饰 则代表没有子类 (理解 断子绝孙 )
- 修饰变量
package com.msb4;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/13 - 09 - 13 - 20:14
* @Description: com.msb4
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 修饰变量
final int A = 10;
//A = 20; 不能在赋值
final Dog d = new Dog();//final修饰引用数据类型 地址就不可以在改变
// d = new Dog(); 不能再赋值修改
a(d);//可以
final Dog d2 = new Dog();
b(d2);
}
public static void a(Dog d){
d = new Dog();
}
public static void b(final Dog d){
//d = new Dog(); //提示final变量不能再赋值
}
}
- 修饰方法则该方法不能被该类的子类 重写
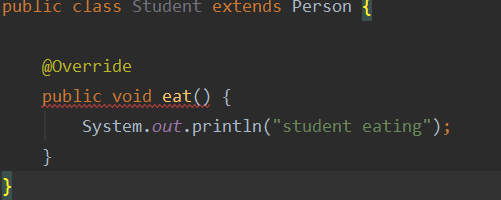
修饰类
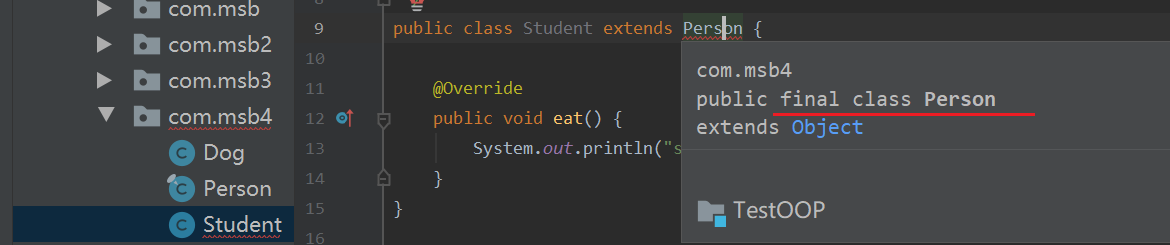
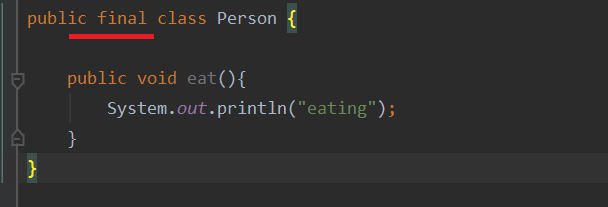
出现的案例
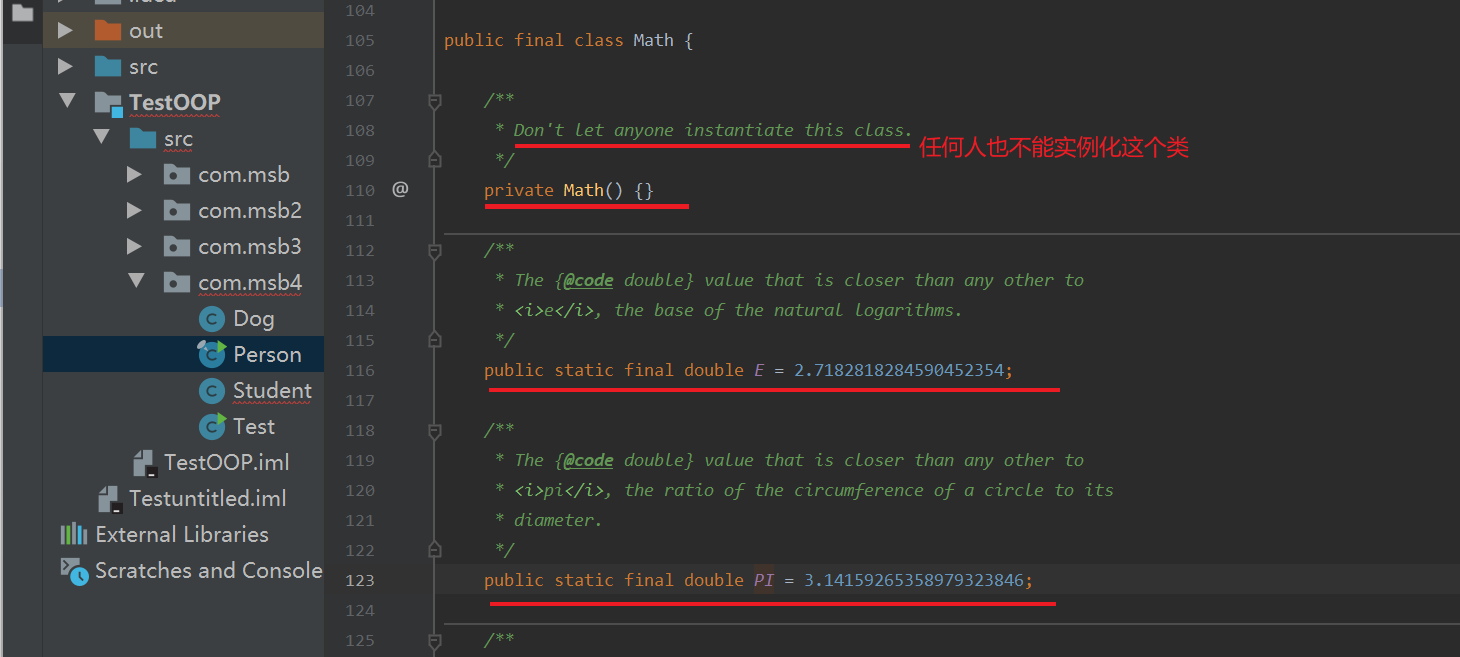
jdk源码里面
package java.lang;
public final class MAth{}
相当于这里面的东西不允许你修改 这是java语言提供的公共实现方法
例如pai=3.14
外面是不能
Math m = new Math();
被final修饰的类的方法全都被static修饰不能让外面修改
5.抽象类
作用是给子类提供一个通用的模板,子列的父类的基础上进行开发,重写父类的方法,扩展自己的内容,避免了子类的随意性
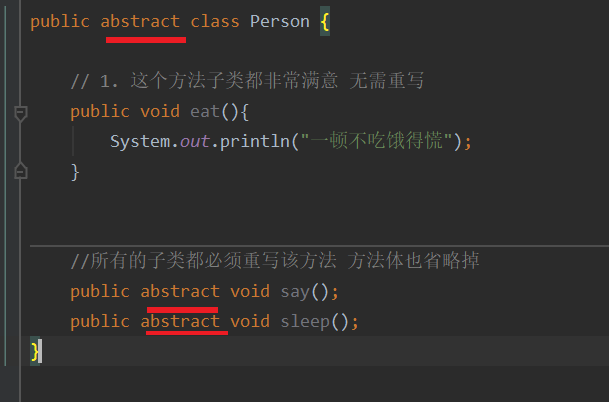
只要有一个抽象方法 这个类就必须变成抽象类
子类继承了抽象类就必须重写抽象类里面的方法
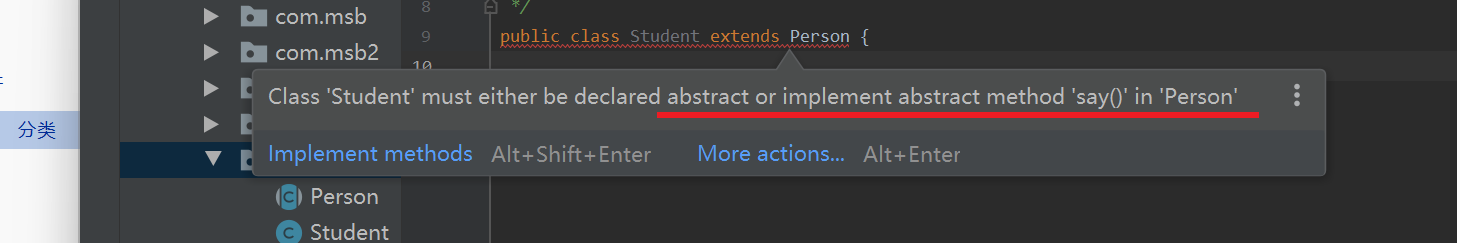
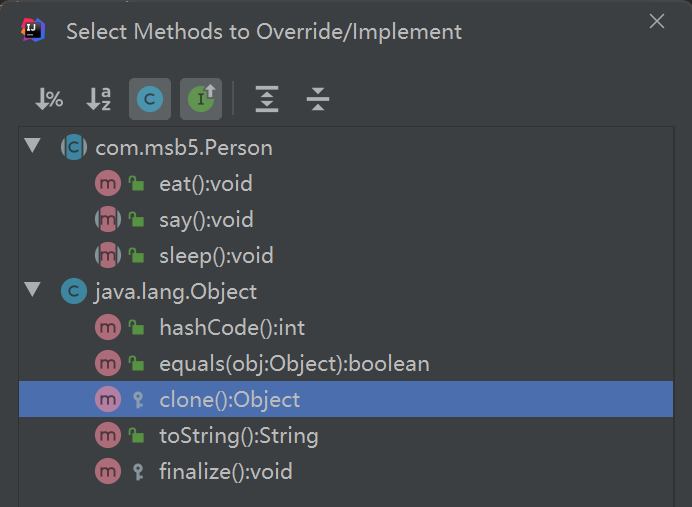
子类如果没有实现抽象类的方法 自己可以变成一个抽象类
抽象类是不可以创建对象的
6. 接口
接口是接口 类是类 他们是同层次的概念
接口没有构造器
格式:
[修饰符] interface 接口名 [extends 父接口1, 父接口2] {
常量;
方法;
}
注:
方法前面默认都是 public abstract 可以不写
常量前面默认public static final 可以不写
package com.msb6;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/17 - 09 - 17 - 9:25
* @Description: com.msb6
* @version: 1.0
*/
public interface TestInterface01 {
int Num = 1;
public abstract void a();
void b();
int c(String name);
}
类是接口的实现 -- 接口与类的关系
实现类要重写接口中的全部方法
如果没有全部重写 这个类可以变成抽象类
java只有单继承 但是有多实现
例如:
public class Person {
int age;
String name;
public void sleep(){
System.out.println("sleeping");
}
}
package com.msb6;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/17 - 09 - 17 - 9:32
* @Description: com.msb6
* @version: 1.0
*/
//一个类只能直接继承一个类
//实现类实现接口的话 可以实现多个接口
public class Student extends Person implements TestInterface01,TestInterface02{
@Override
public void a() {
System.out.println("----1");
}
@Override
public void b() {
System.out.println("----2");
}
@Override
public int c(String name) {
return 0;
}
@Override
public void e() {
System.out.println("----3");
}
@Override
public void f() {
System.out.println("----4");
}
}
package com.msb6;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/17 - 09 - 17 - 9:25
* @Description: com.msb6
* @version: 1.0
*/
public interface TestInterface01 {
public static final int Num = 1;
int Num2 = 2;
public abstract void a();
void b();
int c(String name);
}
package com.msb6;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/17 - 09 - 17 - 9:29
* @Description: com.msb6
* @version: 1.0
*/
public interface TestInterface02 {
void e();
void f();
}
package com.msb6;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/17 - 09 - 17 - 9:39
* @Description: com.msb6
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TestInterface01 t1 = new TestInterface01(); // 接口类不能创建对象
System.out.println(TestInterface01.Num);
System.out.println(Student.Num);
Student s = new Student();
System.out.println(s.name);
System.out.println(s.Num);
TestInterface01 t2 = new Student(); //多态父类对象指向子类的实现
System.out.println(t2.Num2);
}
}
接口的作用:
定义规则 接口定义好规则 实现类负责实现
与抽象类的区别:
接口是接口 类是类
继承:
子类对父类的继承 extends
实现:
实现类对于接口的实现
举例:
手机不是照相机
如果用继承来写
手机 extends 照相机
前面讲过:继承 可以理解为 is a的关系 手机 is a 照相机 逻辑上不通
所以这个写法不好
实现:
手机 implements 照相机 has a的关系 手机 has a照相机的功能
其他案例:
飞机 小鸟 风筝
飞机是小鸟 小鸟 是风筝 都不通
只能是提取出公共的功能 具体的实现类区实现
定义一个接口 Flyable
多态:
- 父类当做方法的形参 传入的是具体的子类对象
- 父类当做方法的返回值 参会具体的子类对象
- 接口仿作方法的形参 传入具体的实现类的对象
- 接口当做方法的返回值 返回的具体的实现类的对象
7. 内部类
类的组成:
属性 方法 构造器 代码块 + 内部类
非静态的成员内部类
package com.msb7;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/17 - 09 - 17 - 10:07
* @Description: com.msb7
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class TestOuter {
//非静态 成员内部类
public class D{
int age = 20;
String name;
public void method(){
//内部类可以访外部类的内容(方法 属性)
System.out.println(age);
a();
int age = 30;
//内部 和外部类 属性重名是 如何调用
System.out.println(age);
System.out.println(this.age);
System.out.println(TestOuter.this.age);
}
}
//静态 成员内部类
static public class E{
public void method(){
//静态 内部内 只能访问 外部类中 被static修饰的内容
// System.out.println(age);
// a();
System.out.println(height);
b();
}
}
int age = 10;//属性
static int height = 188;
static public void b(){
System.out.println("static b method");
}
//方法 a
public void a(){
System.out.println("a method");
}
static {
System.out.println("静态块");
}
//构造器
public TestOuter() {
}
public TestOuter(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
package com.msb7;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/17 - 09 - 17 - 10:12
* @Description: com.msb7
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestOuter testOuter = new TestOuter();
testOuter.a();
//静态内部类 创建对象
TestOuter.E e = new TestOuter.E();
// 非静态成员内部类创建对象
TestOuter t = new TestOuter();
TestOuter.D d = t.new D();
d.method();
}
}
静态 成员 内部类
非静态成员内部类
实例化对象的区别:

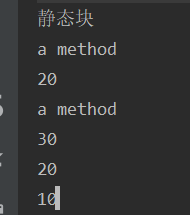
运行结果:
局部内部类
package com.msb08;
/**
* @Auther: jack.chen
* @Date: 2023/9/17 - 09 - 17 - 10:41
* @Description: com.msb08
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class TestOuter {
public void method(){
final int num = 1;
class A{
public void a(){
System.out.println(num);
}
}
}
//类B在真个项目中只使用一次 没必要单独创建一个类
public Comparable method2(){
class B implements Comparable{
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
return 100;
}
}
return new B();
}
// B的名字都不要了 匿名内部类
public Comparable method3(){
return new Comparable() {
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
return 0;
}
};
}
public void test(){
Comparable c = new Comparable() {
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
return 0;
}
};
System.out.println(c.compareTo("aaa"));
}
}
8. 面向对象 项目作业 饮料售货机--待续
java基础-java面向对象-02-day09的更多相关文章
- Java基础-初识面向对象编程(Object-Oriented-Programming)
Java基础-初识面向对象编程(Object-Oriented-Programming) 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. Java是一门面向对象的程序设计语言.那么什 ...
- Java基础-Java中23种设计模式之常用的设计模式
Java基础-Java中23种设计模式之常用的设计模式 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一.设计模式分类 设计模式是针对特定场景给出的专家级的解决方案.总的来说设 ...
- Java基础-JAVA中常见的数据结构介绍
Java基础-JAVA中常见的数据结构介绍 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一.什么是数据结构 答:数据结构是指数据存储的组织方式.大致上分为线性表.栈(Stack) ...
- java基础---->java中正则表达式二
跟正则表达式相关的类有:Pattern.Matcher和String.今天我们就开始Java中正则表达式的学习. Pattern和Matcher的理解 一.正则表达式的使用方法 一般推荐使用的方式如下 ...
- Java基础-Java中的堆内存和离堆内存机制
Java基础-Java中的堆内存和离堆内存机制 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任.
- Java基础-Java中的内存分配与回收机制
Java基础-Java中的内存分配与回收机制 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一. 二.
- Java基础-Java中的并法库之重入读写锁(ReentrantReadWriteLock)
Java基础-Java中的并法库之重入读写锁(ReentrantReadWriteLock) 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 在学习Java的之前,你可能已经听说过读 ...
- Java基础-Java中的并法库之线程池技术
Java基础-Java中的并法库之线程池技术 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一.什么是线程池技术 二.
- Java基础-Java数据类型
Java基础-Java数据类型 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一.数据类型的作用 数据类型就是一组值,以及这一组值上的操作,数据类型可以决定数据的存储方式,取值范围 ...
- 黑马程序员——【Java基础】——面向对象(二)异常机制、包(Package)
---------- android培训.java培训.期待与您交流! ---------- 一.异常机制 (一)异常概述 1.异常:就是程序在运行时出现不正常情况. 2.异常类:程序在运行时,出现的 ...
随机推荐
- LeetCode5716:好因子的最大数目(数学、快速幂)
解题思路:因为primeFactors比较大,所以需要使用快速幂. class Solution: def quick_pow(self,base,x): ans = 1 while x>0: ...
- MySQL运维14-管理及监控工具Mycat-web的安装配置
一.Mycat-web介绍 Mycat-web(现改名为Mycat-eye)是对Mycat-server提供监控服务,通过JDBC连接对Mycat,MySQL监控,监控远程服务器的cpu,内存,网络, ...
- 数字孪生和GIS的融合能够为智慧水务带来什么帮助?
数字孪生和地理信息系统(GIS)的融合在智慧水务领域有着重要的应用前景.让我们一起探讨数字孪生和GIS如何合作,为智慧水务系统带来了哪些帮助. GIS系统提供了准确的地理数据,包括水资源.管道网络.水 ...
- python tkinter 使用(六)
python tkinter 使用(六) 本文主要讲述tkinter中进度条的使用. 1:确定的进度条 progressbar = tkinter.ttk.Progressbar(root, mode ...
- 神经网络优化篇:详解归一化输入(Normalizing inputs)
归一化输入 训练神经网络,其中一个加速训练的方法就是归一化输入.假设一个训练集有两个特征,输入特征为2维,归一化需要两个步骤: 零均值 归一化方差: 希望无论是训练集和测试集都是通过相同的\(μ\)和 ...
- 前端 Git 使用约定
前端 Git 使用约定 背景 开发前端项目,有以下困惑: 使用哪个分支开发,哪个分支发布 修复线上bug的流程是什么,如何避免修复完了下次却又出现了 cms分支有十多个,是否都有用 如何快速找到之前某 ...
- cp {,bak}用法(转载)
cp filename{,bak} cp filename{,.bak} 这个命令是用来把filename备份成filename.bak的 等同于命令 cp filename filename.bak ...
- 从0开始学微信逆向开发(android版)——第一栏
首先给大家普及一下啥叫微信逆向开发,以及微信逆向开发能做什么: 场景1:小明是做微商的,他每天需要加很多很多的好友.然后他会通过微信的各种渠道去添加好友,比如(附近的人.摇一摇.漂流瓶.手机号搜索等) ...
- 如何用axios加后端数据库传值给前端
小杰笔记: 如何用axios : 第一步:编写数据库实体类 @Data @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor public class User { priva ...
- Typecho 反向代理 http 访问强制启用生成 https 链接
问题描述 微酷是使用Nginx反向代理内网的Typecho站点,为了效率内网访问不需要使用https,这样Typecho接收到的请求是http协议的,于是网站内部资源链接被修改成了http. 解决方案 ...
