文本分类实战(五)—— Bi-LSTM + Attention模型
1 大纲概述
文本分类这个系列将会有十篇左右,包括基于word2vec预训练的文本分类,与及基于最新的预训练模型(ELMo,BERT等)的文本分类。总共有以下系列:
jupyter notebook代码均在textClassifier仓库中,python代码在NLP-Project中的text_classfier中。
2 数据集
数据集为IMDB 电影影评,总共有三个数据文件,在/data/rawData目录下,包括unlabeledTrainData.tsv,labeledTrainData.tsv,testData.tsv。在进行文本分类时需要有标签的数据(labeledTrainData),数据预处理如文本分类实战(一)—— word2vec预训练词向量中一样,预处理后的文件为/data/preprocess/labeledTrain.csv。
3 Bi-LSTM + Attention 模型
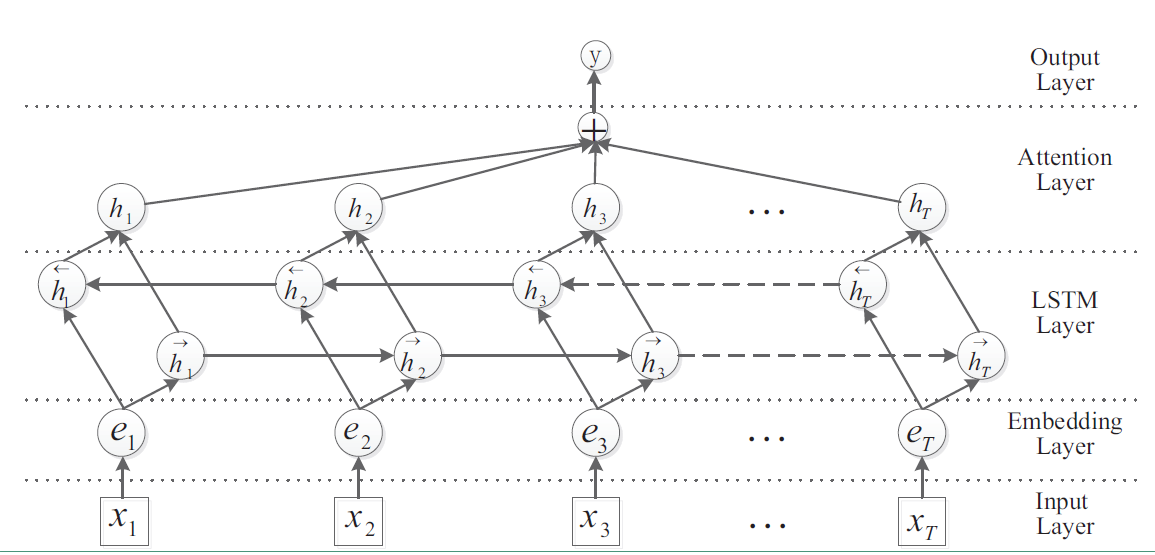
Bi-LSTM + Attention模型来源于论文Attention-Based Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory Networks for Relation Classification。关于Attention的介绍见这篇。
Bi-LSTM + Attention 就是在Bi-LSTM的模型上加入Attention层,在Bi-LSTM中我们会用最后一个时序的输出向量 作为特征向量,然后进行softmax分类。Attention是先计算每个时序的权重,然后将所有时序 的向量进行加权和作为特征向量,然后进行softmax分类。在实验中,加上Attention确实对结果有所提升。其模型结构如下图:
4 参数配置
import os
import csv
import time
import datetime
import random
import json import warnings
from collections import Counter
from math import sqrt import gensim
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score, accuracy_score, precision_score, recall_score
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
# 配置参数 class TrainingConfig(object):
epoches = 4
evaluateEvery = 100
checkpointEvery = 100
learningRate = 0.001 class ModelConfig(object):
embeddingSize = 200 hiddenSizes = [256, 128] # LSTM结构的神经元个数 dropoutKeepProb = 0.5
l2RegLambda = 0.0 class Config(object):
sequenceLength = 200 # 取了所有序列长度的均值
batchSize = 128 dataSource = "../data/preProcess/labeledTrain.csv" stopWordSource = "../data/english" numClasses = 1 # 二分类设置为1,多分类设置为类别的数目 rate = 0.8 # 训练集的比例 training = TrainingConfig() model = ModelConfig() # 实例化配置参数对象
config = Config()
5 生成训练数据
1)将数据加载进来,将句子分割成词表示,并去除低频词和停用词。
2)将词映射成索引表示,构建词汇-索引映射表,并保存成json的数据格式,之后做inference时可以用到。(注意,有的词可能不在word2vec的预训练词向量中,这种词直接用UNK表示)
3)从预训练的词向量模型中读取出词向量,作为初始化值输入到模型中。
4)将数据集分割成训练集和测试集
# 数据预处理的类,生成训练集和测试集 class Dataset(object):
def __init__(self, config):
self.config = config
self._dataSource = config.dataSource
self._stopWordSource = config.stopWordSource self._sequenceLength = config.sequenceLength # 每条输入的序列处理为定长
self._embeddingSize = config.model.embeddingSize
self._batchSize = config.batchSize
self._rate = config.rate self._stopWordDict = {} self.trainReviews = []
self.trainLabels = [] self.evalReviews = []
self.evalLabels = [] self.wordEmbedding =None self.labelList = [] def _readData(self, filePath):
"""
从csv文件中读取数据集
""" df = pd.read_csv(filePath) if self.config.numClasses == 1:
labels = df["sentiment"].tolist()
elif self.config.numClasses > 1:
labels = df["rate"].tolist() review = df["review"].tolist()
reviews = [line.strip().split() for line in review] return reviews, labels def _labelToIndex(self, labels, label2idx):
"""
将标签转换成索引表示
"""
labelIds = [label2idx[label] for label in labels]
return labelIds def _wordToIndex(self, reviews, word2idx):
"""
将词转换成索引
"""
reviewIds = [[word2idx.get(item, word2idx["UNK"]) for item in review] for review in reviews]
return reviewIds def _genTrainEvalData(self, x, y, word2idx, rate):
"""
生成训练集和验证集
"""
reviews = []
for review in x:
if len(review) >= self._sequenceLength:
reviews.append(review[:self._sequenceLength])
else:
reviews.append(review + [word2idx["PAD"]] * (self._sequenceLength - len(review))) trainIndex = int(len(x) * rate) trainReviews = np.asarray(reviews[:trainIndex], dtype="int64")
trainLabels = np.array(y[:trainIndex], dtype="float32") evalReviews = np.asarray(reviews[trainIndex:], dtype="int64")
evalLabels = np.array(y[trainIndex:], dtype="float32") return trainReviews, trainLabels, evalReviews, evalLabels def _genVocabulary(self, reviews, labels):
"""
生成词向量和词汇-索引映射字典,可以用全数据集
""" allWords = [word for review in reviews for word in review] # 去掉停用词
subWords = [word for word in allWords if word not in self.stopWordDict] wordCount = Counter(subWords) # 统计词频
sortWordCount = sorted(wordCount.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True) # 去除低频词
words = [item[0] for item in sortWordCount if item[1] >= 5] vocab, wordEmbedding = self._getWordEmbedding(words)
self.wordEmbedding = wordEmbedding word2idx = dict(zip(vocab, list(range(len(vocab))))) uniqueLabel = list(set(labels))
label2idx = dict(zip(uniqueLabel, list(range(len(uniqueLabel)))))
self.labelList = list(range(len(uniqueLabel))) # 将词汇-索引映射表保存为json数据,之后做inference时直接加载来处理数据
with open("../data/wordJson/word2idx.json", "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
json.dump(word2idx, f) with open("../data/wordJson/label2idx.json", "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
json.dump(label2idx, f) return word2idx, label2idx def _getWordEmbedding(self, words):
"""
按照我们的数据集中的单词取出预训练好的word2vec中的词向量
""" wordVec = gensim.models.KeyedVectors.load_word2vec_format("../word2vec/word2Vec.bin", binary=True)
vocab = []
wordEmbedding = [] # 添加 "pad" 和 "UNK",
vocab.append("PAD")
vocab.append("UNK")
wordEmbedding.append(np.zeros(self._embeddingSize))
wordEmbedding.append(np.random.randn(self._embeddingSize)) for word in words:
try:
vector = wordVec.wv[word]
vocab.append(word)
wordEmbedding.append(vector)
except:
print(word + "不存在于词向量中") return vocab, np.array(wordEmbedding) def _readStopWord(self, stopWordPath):
"""
读取停用词
""" with open(stopWordPath, "r") as f:
stopWords = f.read()
stopWordList = stopWords.splitlines()
# 将停用词用列表的形式生成,之后查找停用词时会比较快
self.stopWordDict = dict(zip(stopWordList, list(range(len(stopWordList))))) def dataGen(self):
"""
初始化训练集和验证集
""" # 初始化停用词
self._readStopWord(self._stopWordSource) # 初始化数据集
reviews, labels = self._readData(self._dataSource) # 初始化词汇-索引映射表和词向量矩阵
word2idx, label2idx = self._genVocabulary(reviews, labels) # 将标签和句子数值化
labelIds = self._labelToIndex(labels, label2idx)
reviewIds = self._wordToIndex(reviews, word2idx) # 初始化训练集和测试集
trainReviews, trainLabels, evalReviews, evalLabels = self._genTrainEvalData(reviewIds, labelIds, word2idx, self._rate)
self.trainReviews = trainReviews
self.trainLabels = trainLabels self.evalReviews = evalReviews
self.evalLabels = evalLabels data = Dataset(config)
data.dataGen()
6 生成batch数据集
采用生成器的形式向模型输入batch数据集,(生成器可以避免将所有的数据加入到内存中)
# 输出batch数据集 def nextBatch(x, y, batchSize):
"""
生成batch数据集,用生成器的方式输出
""" perm = np.arange(len(x))
np.random.shuffle(perm)
x = x[perm]
y = y[perm] numBatches = len(x) // batchSize for i in range(numBatches):
start = i * batchSize
end = start + batchSize
batchX = np.array(x[start: end], dtype="int64")
batchY = np.array(y[start: end], dtype="float32") yield batchX, batchY
7 Bi-LSTM + Attention模型
# 构建模型
class BiLSTMAttention(object):
"""
Text CNN 用于文本分类
"""
def __init__(self, config, wordEmbedding): # 定义模型的输入
self.inputX = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [None, config.sequenceLength], name="inputX")
self.inputY = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [None], name="inputY") self.dropoutKeepProb = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, name="dropoutKeepProb") # 定义l2损失
l2Loss = tf.constant(0.0) # 词嵌入层
with tf.name_scope("embedding"): # 利用预训练的词向量初始化词嵌入矩阵
self.W = tf.Variable(tf.cast(wordEmbedding, dtype=tf.float32, name="word2vec") ,name="W")
# 利用词嵌入矩阵将输入的数据中的词转换成词向量,维度[batch_size, sequence_length, embedding_size]
self.embeddedWords = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(self.W, self.inputX) # 定义两层双向LSTM的模型结构
with tf.name_scope("Bi-LSTM"):
for idx, hiddenSize in enumerate(config.model.hiddenSizes):
with tf.name_scope("Bi-LSTM" + str(idx)):
# 定义前向LSTM结构
lstmFwCell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.DropoutWrapper(tf.nn.rnn_cell.LSTMCell(num_units=hiddenSize, state_is_tuple=True),
output_keep_prob=self.dropoutKeepProb)
# 定义反向LSTM结构
lstmBwCell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.DropoutWrapper(tf.nn.rnn_cell.LSTMCell(num_units=hiddenSize, state_is_tuple=True),
output_keep_prob=self.dropoutKeepProb) # 采用动态rnn,可以动态的输入序列的长度,若没有输入,则取序列的全长
# outputs是一个元祖(output_fw, output_bw),其中两个元素的维度都是[batch_size, max_time, hidden_size],fw和bw的hidden_size一样
# self.current_state 是最终的状态,二元组(state_fw, state_bw),state_fw=[batch_size, s],s是一个元祖(h, c)
outputs_, self.current_state = tf.nn.bidirectional_dynamic_rnn(lstmFwCell, lstmBwCell,
self.embeddedWords, dtype=tf.float32,
scope="bi-lstm" + str(idx)) # 对outputs中的fw和bw的结果拼接 [batch_size, time_step, hidden_size * 2], 传入到下一层Bi-LSTM中
self.embeddedWords = tf.concat(outputs_, 2) # 将最后一层Bi-LSTM输出的结果分割成前向和后向的输出
outputs = tf.split(self.embeddedWords, 2, -1) # 在Bi-LSTM+Attention的论文中,将前向和后向的输出相加
with tf.name_scope("Attention"):
H = outputs[0] + outputs[1] # 得到Attention的输出
output = self.attention(H)
outputSize = config.model.hiddenSizes[-1] # 全连接层的输出
with tf.name_scope("output"):
outputW = tf.get_variable(
"outputW",
shape=[outputSize, config.numClasses],
initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer()) outputB= tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[config.numClasses]), name="outputB")
l2Loss += tf.nn.l2_loss(outputW)
l2Loss += tf.nn.l2_loss(outputB)
self.logits = tf.nn.xw_plus_b(output, outputW, outputB, name="logits") if config.numClasses == 1:
self.predictions = tf.cast(tf.greater_equal(self.logits, 0.0), tf.float32, name="predictions")
elif config.numClasses > 1:
self.predictions = tf.argmax(self.logits, axis=-1, name="predictions") # 计算二元交叉熵损失
with tf.name_scope("loss"): if config.numClasses == 1:
losses = tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=self.logits, labels=tf.cast(tf.reshape(self.inputY, [-1, 1]),
dtype=tf.float32))
elif config.numClasses > 1:
losses = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=self.logits, labels=self.inputY) self.loss = tf.reduce_mean(losses) + config.model.l2RegLambda * l2Loss def attention(self, H):
"""
利用Attention机制得到句子的向量表示
"""
# 获得最后一层LSTM的神经元数量
hiddenSize = config.model.hiddenSizes[-1] # 初始化一个权重向量,是可训练的参数
W = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([hiddenSize], stddev=0.1)) # 对Bi-LSTM的输出用激活函数做非线性转换
M = tf.tanh(H) # 对W和M做矩阵运算,W=[batch_size, time_step, hidden_size],计算前做维度转换成[batch_size * time_step, hidden_size]
# newM = [batch_size, time_step, 1],每一个时间步的输出由向量转换成一个数字
newM = tf.matmul(tf.reshape(M, [-1, hiddenSize]), tf.reshape(W, [-1, 1])) # 对newM做维度转换成[batch_size, time_step]
restoreM = tf.reshape(newM, [-1, config.sequenceLength]) # 用softmax做归一化处理[batch_size, time_step]
self.alpha = tf.nn.softmax(restoreM) # 利用求得的alpha的值对H进行加权求和,用矩阵运算直接操作
r = tf.matmul(tf.transpose(H, [0, 2, 1]), tf.reshape(self.alpha, [-1, config.sequenceLength, 1])) # 将三维压缩成二维sequeezeR=[batch_size, hidden_size]
sequeezeR = tf.reshape(r, [-1, hiddenSize]) sentenceRepren = tf.tanh(sequeezeR) # 对Attention的输出可以做dropout处理
output = tf.nn.dropout(sentenceRepren, self.dropoutKeepProb) return output
8 定义计算metrics的函数
"""
定义各类性能指标
""" def mean(item: list) -> float:
"""
计算列表中元素的平均值
:param item: 列表对象
:return:
"""
res = sum(item) / len(item) if len(item) > 0 else 0
return res def accuracy(pred_y, true_y):
"""
计算二类和多类的准确率
:param pred_y: 预测结果
:param true_y: 真实结果
:return:
"""
if isinstance(pred_y[0], list):
pred_y = [item[0] for item in pred_y]
corr = 0
for i in range(len(pred_y)):
if pred_y[i] == true_y[i]:
corr += 1
acc = corr / len(pred_y) if len(pred_y) > 0 else 0
return acc def binary_precision(pred_y, true_y, positive=1):
"""
二类的精确率计算
:param pred_y: 预测结果
:param true_y: 真实结果
:param positive: 正例的索引表示
:return:
"""
corr = 0
pred_corr = 0
for i in range(len(pred_y)):
if pred_y[i] == positive:
pred_corr += 1
if pred_y[i] == true_y[i]:
corr += 1 prec = corr / pred_corr if pred_corr > 0 else 0
return prec def binary_recall(pred_y, true_y, positive=1):
"""
二类的召回率
:param pred_y: 预测结果
:param true_y: 真实结果
:param positive: 正例的索引表示
:return:
"""
corr = 0
true_corr = 0
for i in range(len(pred_y)):
if true_y[i] == positive:
true_corr += 1
if pred_y[i] == true_y[i]:
corr += 1 rec = corr / true_corr if true_corr > 0 else 0
return rec def binary_f_beta(pred_y, true_y, beta=1.0, positive=1):
"""
二类的f beta值
:param pred_y: 预测结果
:param true_y: 真实结果
:param beta: beta值
:param positive: 正例的索引表示
:return:
"""
precision = binary_precision(pred_y, true_y, positive)
recall = binary_recall(pred_y, true_y, positive)
try:
f_b = (1 + beta * beta) * precision * recall / (beta * beta * precision + recall)
except:
f_b = 0
return f_b def multi_precision(pred_y, true_y, labels):
"""
多类的精确率
:param pred_y: 预测结果
:param true_y: 真实结果
:param labels: 标签列表
:return:
"""
if isinstance(pred_y[0], list):
pred_y = [item[0] for item in pred_y] precisions = [binary_precision(pred_y, true_y, label) for label in labels]
prec = mean(precisions)
return prec def multi_recall(pred_y, true_y, labels):
"""
多类的召回率
:param pred_y: 预测结果
:param true_y: 真实结果
:param labels: 标签列表
:return:
"""
if isinstance(pred_y[0], list):
pred_y = [item[0] for item in pred_y] recalls = [binary_recall(pred_y, true_y, label) for label in labels]
rec = mean(recalls)
return rec def multi_f_beta(pred_y, true_y, labels, beta=1.0):
"""
多类的f beta值
:param pred_y: 预测结果
:param true_y: 真实结果
:param labels: 标签列表
:param beta: beta值
:return:
"""
if isinstance(pred_y[0], list):
pred_y = [item[0] for item in pred_y] f_betas = [binary_f_beta(pred_y, true_y, beta, label) for label in labels]
f_beta = mean(f_betas)
return f_beta def get_binary_metrics(pred_y, true_y, f_beta=1.0):
"""
得到二分类的性能指标
:param pred_y:
:param true_y:
:param f_beta:
:return:
"""
acc = accuracy(pred_y, true_y)
recall = binary_recall(pred_y, true_y)
precision = binary_precision(pred_y, true_y)
f_beta = binary_f_beta(pred_y, true_y, f_beta)
return acc, recall, precision, f_beta def get_multi_metrics(pred_y, true_y, labels, f_beta=1.0):
"""
得到多分类的性能指标
:param pred_y:
:param true_y:
:param labels:
:param f_beta:
:return:
"""
acc = accuracy(pred_y, true_y)
recall = multi_recall(pred_y, true_y, labels)
precision = multi_precision(pred_y, true_y, labels)
f_beta = multi_f_beta(pred_y, true_y, labels, f_beta)
return acc, recall, precision, f_beta
9 训练模型
在训练时,我们定义了tensorBoard的输出,并定义了两种模型保存的方法。
# 训练模型 # 生成训练集和验证集
trainReviews = data.trainReviews
trainLabels = data.trainLabels
evalReviews = data.evalReviews
evalLabels = data.evalLabels wordEmbedding = data.wordEmbedding
labelList = data.labelList # 定义计算图
with tf.Graph().as_default(): session_conf = tf.ConfigProto(allow_soft_placement=True, log_device_placement=False)
session_conf.gpu_options.allow_growth=True
session_conf.gpu_options.per_process_gpu_memory_fraction = 0.9 # 配置gpu占用率 sess = tf.Session(config=session_conf) # 定义会话
with sess.as_default():
lstm = BiLSTMAttention(config, wordEmbedding) globalStep = tf.Variable(0, name="globalStep", trainable=False)
# 定义优化函数,传入学习速率参数
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(config.training.learningRate)
# 计算梯度,得到梯度和变量
gradsAndVars = optimizer.compute_gradients(lstm.loss)
# 将梯度应用到变量下,生成训练器
trainOp = optimizer.apply_gradients(gradsAndVars, global_step=globalStep) # 用summary绘制tensorBoard
gradSummaries = []
for g, v in gradsAndVars:
if g is not None:
tf.summary.histogram("{}/grad/hist".format(v.name), g)
tf.summary.scalar("{}/grad/sparsity".format(v.name), tf.nn.zero_fraction(g)) outDir = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.path.curdir, "summarys"))
print("Writing to {}\n".format(outDir)) lossSummary = tf.summary.scalar("loss", lstm.loss)
summaryOp = tf.summary.merge_all() trainSummaryDir = os.path.join(outDir, "train")
trainSummaryWriter = tf.summary.FileWriter(trainSummaryDir, sess.graph) evalSummaryDir = os.path.join(outDir, "eval")
evalSummaryWriter = tf.summary.FileWriter(evalSummaryDir, sess.graph) # 初始化所有变量
saver = tf.train.Saver(tf.global_variables(), max_to_keep=5) # 保存模型的一种方式,保存为pb文件
savedModelPath = "../model/bilstm-atten/savedModel"
if os.path.exists(savedModelPath):
os.rmdir(savedModelPath)
builder = tf.saved_model.builder.SavedModelBuilder(savedModelPath) sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) def trainStep(batchX, batchY):
"""
训练函数
"""
feed_dict = {
lstm.inputX: batchX,
lstm.inputY: batchY,
lstm.dropoutKeepProb: config.model.dropoutKeepProb
}
_, summary, step, loss, predictions = sess.run(
[trainOp, summaryOp, globalStep, lstm.loss, lstm.predictions],
feed_dict)
timeStr = datetime.datetime.now().isoformat() if config.numClasses == 1:
acc, recall, prec, f_beta = get_binary_metrics(pred_y=predictions, true_y=batchY) elif config.numClasses > 1:
acc, recall, prec, f_beta = get_multi_metrics(pred_y=predictions, true_y=batchY,
labels=labelList) trainSummaryWriter.add_summary(summary, step) return loss, acc, prec, recall, f_beta def devStep(batchX, batchY):
"""
验证函数
"""
feed_dict = {
lstm.inputX: batchX,
lstm.inputY: batchY,
lstm.dropoutKeepProb: 1.0
}
summary, step, loss, predictions = sess.run(
[summaryOp, globalStep, lstm.loss, lstm.predictions],
feed_dict) if config.numClasses == 1: acc, precision, recall, f_beta = get_binary_metrics(pred_y=predictions, true_y=batchY)
elif config.numClasses > 1:
acc, precision, recall, f_beta = get_multi_metrics(pred_y=predictions, true_y=batchY, labels=labelList) evalSummaryWriter.add_summary(summary, step) return loss, acc, precision, recall, f_beta for i in range(config.training.epoches):
# 训练模型
print("start training model")
for batchTrain in nextBatch(trainReviews, trainLabels, config.batchSize):
loss, acc, prec, recall, f_beta = trainStep(batchTrain[0], batchTrain[1]) currentStep = tf.train.global_step(sess, globalStep)
print("train: step: {}, loss: {}, acc: {}, recall: {}, precision: {}, f_beta: {}".format(
currentStep, loss, acc, recall, prec, f_beta))
if currentStep % config.training.evaluateEvery == 0:
print("\nEvaluation:") losses = []
accs = []
f_betas = []
precisions = []
recalls = [] for batchEval in nextBatch(evalReviews, evalLabels, config.batchSize):
loss, acc, precision, recall, f_beta = devStep(batchEval[0], batchEval[1])
losses.append(loss)
accs.append(acc)
f_betas.append(f_beta)
precisions.append(precision)
recalls.append(recall) time_str = datetime.datetime.now().isoformat()
print("{}, step: {}, loss: {}, acc: {},precision: {}, recall: {}, f_beta: {}".format(time_str, currentStep, mean(losses),
mean(accs), mean(precisions),
mean(recalls), mean(f_betas))) if currentStep % config.training.checkpointEvery == 0:
# 保存模型的另一种方法,保存checkpoint文件
path = saver.save(sess, "../model/Bi-LSTM-atten/model/my-model", global_step=currentStep)
print("Saved model checkpoint to {}\n".format(path)) inputs = {"inputX": tf.saved_model.utils.build_tensor_info(lstm.inputX),
"keepProb": tf.saved_model.utils.build_tensor_info(lstm.dropoutKeepProb)} outputs = {"predictions": tf.saved_model.utils.build_tensor_info(lstm.binaryPreds)} prediction_signature = tf.saved_model.signature_def_utils.build_signature_def(inputs=inputs, outputs=outputs,
method_name=tf.saved_model.signature_constants.PREDICT_METHOD_NAME)
legacy_init_op = tf.group(tf.tables_initializer(), name="legacy_init_op")
builder.add_meta_graph_and_variables(sess, [tf.saved_model.tag_constants.SERVING],
signature_def_map={"predict": prediction_signature}, legacy_init_op=legacy_init_op) builder.save()
10 预测代码
x = "this movie is full of references like mad max ii the wild one and many others the ladybug´s face it´s a clear reference or tribute to peter lorre this movie is a masterpiece we´ll talk much more about in the future" # 注:下面两个词典要保证和当前加载的模型对应的词典是一致的
with open("../data/wordJson/word2idx.json", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
word2idx = json.load(f) with open("../data/wordJson/label2idx.json", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
label2idx = json.load(f)
idx2label = {value: key for key, value in label2idx.items()} xIds = [word2idx.get(item, word2idx["UNK"]) for item in x.split(" ")]
if len(xIds) >= config.sequenceLength:
xIds = xIds[:config.sequenceLength]
else:
xIds = xIds + [word2idx["PAD"]] * (config.sequenceLength - len(xIds)) graph = tf.Graph()
with graph.as_default():
gpu_options = tf.GPUOptions(per_process_gpu_memory_fraction=0.333)
session_conf = tf.ConfigProto(allow_soft_placement=True, log_device_placement=False, gpu_options=gpu_options)
sess = tf.Session(config=session_conf) with sess.as_default():
checkpoint_file = tf.train.latest_checkpoint("../model/Bi-LSTM-atten/model/")
saver = tf.train.import_meta_graph("{}.meta".format(checkpoint_file))
saver.restore(sess, checkpoint_file) # 获得需要喂给模型的参数,输出的结果依赖的输入值
inputX = graph.get_operation_by_name("inputX").outputs[0]
dropoutKeepProb = graph.get_operation_by_name("dropoutKeepProb").outputs[0] # 获得输出的结果
predictions = graph.get_tensor_by_name("output/predictions:0") pred = sess.run(predictions, feed_dict={inputX: [xIds], dropoutKeepProb: 1.0})[0] pred = [idx2label[item] for item in pred]
print(pred)
文本分类实战(五)—— Bi-LSTM + Attention模型的更多相关文章
- 文本分类实战(八)—— Transformer模型
1 大纲概述 文本分类这个系列将会有十篇左右,包括基于word2vec预训练的文本分类,与及基于最新的预训练模型(ELMo,BERT等)的文本分类.总共有以下系列: word2vec预训练词向量 te ...
- 文本分类实战(六)—— RCNN模型
1 大纲概述 文本分类这个系列将会有十篇左右,包括基于word2vec预训练的文本分类,与及基于最新的预训练模型(ELMo,BERT等)的文本分类.总共有以下系列: word2vec预训练词向量 te ...
- 文本分类实战(四)—— Bi-LSTM模型
1 大纲概述 文本分类这个系列将会有十篇左右,包括基于word2vec预训练的文本分类,与及基于最新的预训练模型(ELMo,BERT等)的文本分类.总共有以下系列: word2vec预训练词向量 te ...
- 文本分类实战(三)—— charCNN模型
1 大纲概述 文本分类这个系列将会有十篇左右,包括基于word2vec预训练的文本分类,与及基于最新的预训练模型(ELMo,BERT等)的文本分类.总共有以下系列: word2vec预训练词向量 te ...
- 文本分类实战(二)—— textCNN 模型
1 大纲概述 文本分类这个系列将会有十篇左右,包括基于word2vec预训练的文本分类,与及基于最新的预训练模型(ELMo,BERT等)的文本分类.总共有以下系列: word2vec预训练词向量 te ...
- 文本分类实战(七)—— Adversarial LSTM模型
1 大纲概述 文本分类这个系列将会有十篇左右,包括基于word2vec预训练的文本分类,与及基于最新的预训练模型(ELMo,BERT等)的文本分类.总共有以下系列: word2vec预训练词向量 te ...
- 文本分类实战(十)—— BERT 预训练模型
1 大纲概述 文本分类这个系列将会有十篇左右,包括基于word2vec预训练的文本分类,与及基于最新的预训练模型(ELMo,BERT等)的文本分类.总共有以下系列: word2vec预训练词向量 te ...
- 文本分类实战(九)—— ELMO 预训练模型
1 大纲概述 文本分类这个系列将会有十篇左右,包括基于word2vec预训练的文本分类,与及基于最新的预训练模型(ELMo,BERT等)的文本分类.总共有以下系列: word2vec预训练词向量 te ...
- Python 1行代码实现文本分类(实战笔记),含代码详细说明及运行结果
Python 1行代码实现文本分类(实战笔记),含代码详细说明及运行结果 一.详细说明及代码 tc.py =============================================== ...
随机推荐
- React Native (二) ios打包到真机
每当在模拟器上完成了开发,都想到真机上试试,正好前段时候淘了一个imac. 这里就以打包rndemo到iphone为例,讲一下react ntive ios打包到真机的流程. 一.前置 1.有个iph ...
- RxJS 实现摩斯密码(Morse) 【内附脑图】
参加 2018 ngChina 开发者大会,特别喜欢 Michael Hladky 奥地利帅哥的 RxJS 分享,现在拿出来好好学习工作坊的内容(工作坊Demo地址),结合这个示例,做了一个改进版本, ...
- Linux基础知识第一讲,基本目录结构与基本命令
目录 一丶Window 与 Linux的目录结构 1.Windows 与 Linux目录简介 2.Linux目录主要作用 3.任务栏与菜单栏,与关闭按钮 二丶Linux终端与常见命令学习 1.终端中的 ...
- CAN总线学习记录之四:位定时与同步
一.位定时 1.1 比特率和波特率 1)位速率:又叫做比特率(bit rata).信息传输率,表示的是单位时间内,总线上传输的信息量,即每秒能够传输的二进制位的数量,单位是bit per second ...
- Shell编程(week4_day2)--技术流ken
本节内容 1. shell变量简介 2. 定义变量 3. 使用变量 4. 修改变量的值 5. 单引号和双引号的区别 6. 将命令的结果赋值给变量 7. 删除变量 8. 变量类型 9. 特殊变量列表 1 ...
- Python之文件和目录操作
1.文件基本操作 python内置了打开文件的函数open(),使用规则如下: File_object=open(filename[,access_mode][,buffering]) Filen ...
- 谈下WebSocket介绍,与Socket的区别
这个话题应该是面试中出现频率比较高的吧....不管咋样还是有必要深入了解下两者之间的关联.废话不多说,直接入题吧: WebSocket介绍与原理 目的:即时通讯,替代轮询 网站上的即时通讯是很常见的, ...
- Java开发笔记(六十二)如何定义函数式接口
前面介绍了Lambda表达式的用法,从实践中发现它确实极大地方便了开发者,然而不管是匿名内部类还是Lambda表达式,所举的例子都离不开各类数组的排序方法,倘使Lambda表达式仅能用于sort方法, ...
- Java中的锁——锁的分类
Java中有各种各样的锁,例如公平锁.乐观锁等等,这篇文章主要介绍一下各种锁的分类. 按照其性质分类 公平锁/非公平锁 公平锁是指多个线程按照申请锁的顺序来获取锁. 非公平锁是指多个线程获取锁的顺序并 ...
- 如何保证MongoDB的安全性?
上周写了个简短的新闻<MongoDB裸奔,2亿国人求职简历泄漏!>: 根据安全站点HackenProof的报告,由于MongoDB数据库没有采取任何安全保护措施,导致共计202,730,4 ...
