hdu 2196(Computer 树形dp)
A school bought the first computer some time ago(so this computer’s id is 1). During the recent years the school bought N-1 new computers. Each new computer was connected to one of settled earlier. Managers of school are anxious about slow functioning of the net and want to know the maximum distance Si for which i-th computer needs to send signal (i.e. length of cable to the most distant computer). You need to provide this information.
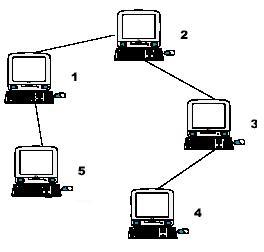
Hint: the example input is corresponding to this graph. And from the graph, you can see that the computer 4 is farthest one from 1, so S1 = 3. Computer 4 and 5 are the farthest ones from 2, so S2 = 2. Computer 5 is the farthest one from 3, so S3 = 3. we also get S4 = 4, S5 = 4.
Input
Input file contains multiple test cases.In each case there is natural number N (N<=10000) in the first line, followed by (N-1) lines with descriptions of computers. i-th line contains two natural numbers - number of computer, to which i-th computer is connected and length of cable used for connection. Total length of cable does not exceed 10^9. Numbers in lines of input are separated by a space.
Output
For each case output N lines. i-th line must contain number Si for i-th computer (1<=i<=N).
Sample Input
5
1 1
2 1
3 1
1 1
Sample Output
3
2
3
4
4
题意:
给出一棵树,求离每个节点最远的点的距离
思路:
把无根树转化成有根树分析。
对于上面那棵树,要求距结点2的最长距离,那么,就需要知道以2为顶点的子树(蓝色圈起的部分,我们叫它Tree(2)),距顶点2的最远距离L1
还有知道2的父节点1为根节点的树Tree(1)-Tree(2)部分(即红色圈起部分),距离结点1的最长距离+dist(1,2) = L2,那么最终距离结点2最远的距离就是max{L1,L2}
f[i][0],表示顶点为i的子树的,距顶点i的最长距离
f[i][1],表示Tree(i的父节点)-Tree(i)的最长距离+i跟i的父节点距离
要求所有的f[i][0]很简单,只要先做一次dfs求每个结点到叶子结点的最长距离即可。
然后要求f[i][1], 可以从父节点递推到子节点,
假设节点u有n个子节点,分别是v1,v2…vn
那么
如果vi不是u最长距离经过的节点,f[vi][1] = dist(vi,u)+max(f[u][0], f[u][1])
如果vi是u最长距离经过的节点,那么不能选择f[u][0],因为这保存的就是最长距离,要选择Tree(u)第二大距离secondDist,
可得f[vi][1] = dist(vi, u) + max(secondDist, f[u][1])
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<vector>
#include<math.h>
#include<cstdio>
#include<sstream>
#include<numeric>//STL数值算法头文件
#include<stdlib.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<functional>//模板类头文件
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 10010;
struct Node{
int v, w;
};
vector<Node>adj[MAXN];
int indeg[MAXN];
int val[MAXN];
int n, m;
int64 f[MAXN][2];
int vis[MAXN];
int64 dfs1(int u){
vis[u] = true;
f[u][0] = 0;
for(int i=0; i<adj[u].size(); ++i){
int v = adj[u][i].v;
int w = adj[u][i].w;
if(vis[v]) continue;
f[u][0] = max(f[u][0], dfs1(v)+w);
}
return f[u][0];
}
void dfs2(int u, int fa_w){
vis[u] = true;
int max1=0, v1, max2=0, v2;
for(int i=0; i<adj[u].size(); ++i){
int v = adj[u][i].v;
int w = adj[u][i].w;
if(vis[v]) continue;
int tmp = f[v][0] + w;
if(tmp > max1){
max2 = max1; v2 = v1;
max1 = tmp; v1 = v;
}else if(tmp == max1 || tmp>max2){
max2 = tmp;
v2 = v;
}
}
if(u != 1){
int tmp = f[u][1];
int v = -1;
if(tmp > max1){
max2 = max1; v2 = v1;
max1 = tmp; v1 = v;
}else if(tmp == max1 || tmp>max2){
max2 = tmp;
v2 = v;
}
}
for(int i=0; i<adj[u].size(); ++i){
int v = adj[u][i].v;
int w = adj[u][i].w;
if(vis[v]) continue;
if(v==v1){
f[v][1] = max2 + w;
}else{
f[v][1] = max1 + w;
}
dfs2(v, w);
}
}
int main(){
while(~scanf("%d", &n) && n){
for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i) adj[i].clear();
for(int u=2; u<=n; ++u){
int v, w;
scanf("%d%d", &v, &w);
adj[u].push_back((Node){v, w});
adj[v].push_back((Node){u, w});
}
memset(f, 0, sizeof(f));
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
dfs1(1);
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
dfs2(1, 0);
for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
cout << max(f[i][0], f[i][1]) << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<vector>
#include<math.h>
#include<cstdio>
#include<sstream>
#include<numeric>//STL数值算法头文件
#include<stdlib.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<functional>//模板类头文件
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int maxn=6005;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
const int N = 1e4 + 5;
int top;
int head[N];
struct Edge
{
int v,w,next;
} E[N];
void init()
{
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));
top = 0;
}
void add_edge(int u,int v,int w)
{
E[top].v = v;
E[top].w = w;
E[top].next = head[u];
head[u] = top++;
}
int dp[N][3];
void dfs1(int u)
{
int biggest = 0, bigger = 0;
for(int i=head[u]; i!=-1; i=E[i].next)
{
int v = E[i].v;
dfs1(v);
int tmp = dp[v][0]+E[i].w;
if(biggest <= tmp)
{
bigger = biggest;
biggest = tmp;
}
else if(bigger < tmp)
bigger = tmp;
}
dp[u][0] = biggest;
dp[u][1] = bigger;
}
void dfs2(int u)
{
for(int i=head[u]; i!=-1; i=E[i].next)
{
int v = E[i].v;
dp[v][2] = max(dp[u][2], dp[v][0]+E[i].w==dp[u][0] ? dp[u][1] : dp[u][0]) + E[i].w;
dfs2(v);
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
while(~scanf("%d",&n))
{
init();
for(int v=2; v<=n; v++)
{
int u,w;
scanf("%d%d",&u,&w);
add_edge(u,v,w);
}
dfs1(1);
dp[1][2] = 0;
dfs2(1);
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
printf("%d\n",max(dp[i][0],dp[i][2]));
}
return 0;
}hdu 2196(Computer 树形dp)的更多相关文章
- HDU 2196.Computer 树形dp 树的直径
Computer Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Su ...
- HDU 2196 Computer 树形DP经典题
链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php? pid=2196 题意:每一个电脑都用线连接到了还有一台电脑,连接用的线有一定的长度,最后把全部电脑连成了一棵树,问 ...
- HDU 2196 Computer 树形DP 经典题
给出一棵树,边有权值,求出离每一个节点最远的点的距离 树形DP,经典题 本来这道题是无根树,可以随意选择root, 但是根据输入数据的方式,选择root=1明显可以方便很多. 我们先把边权转化为点权, ...
- hdu 2196 Computer(树形DP)
Computer Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Su ...
- hdu 2196 Computer 树形dp模板题
Computer Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others) Total S ...
- hdu 2196 Computer(树形DP经典)
Computer Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Su ...
- HDU 2196 Computer (树dp)
题目链接:http://acm.split.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2196 给你n个点,n-1条边,然后给你每条边的权值.输出每个点能对应其他点的最远距离是多少 ...
- HDU - 2196(树形DP)
题目: A school bought the first computer some time ago(so this computer's id is 1). During the recent ...
- hdu 2196【树形dp】
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2196 题意:找出树中每个节点到其它点的最远距离. 题解: 首先这是一棵树,对于节点v来说,它到达其它点的最远距离 ...
- HDU 2196 Compute --树形dp
Computer Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Su ...
随机推荐
- 【BZOJ】4530: [Bjoi2014]大融合
[题意]给定n个点的树,从无到有加边,过程中动态询问当前图某条边两端连通点数的乘积,n<=10^5. [算法]线段树合并+并查集 (||LCT(LCT维护子树信息 LCT维护子树信息(+启发式合 ...
- 【POJ】1222 EXTENDED LIGHTS OUT
[算法]高斯消元 [题解] 高斯消元经典题型:异或方程组 poj 1222 高斯消元详解 异或相当于相加后mod2 异或方程组就是把加减消元全部改为异或. 异或性质:00 11为假,01 10为真.与 ...
- Html5学习2(Html表格、Html列表、Html5新元素、Canvas (坐标、路径、画圆、文本、渐变、图像))
Html表格 1.表格中的表头:<th></th>.其中表头部分字体加粗,颜色深绿色 <h4>水平标题:</h4> <table border=& ...
- PAT L2-017. 人以群分
题目链接:https://www.patest.cn/contests/gplt/L2-017 题目: 社交网络中我们给每个人定义了一个“活跃度”,现希望根据这个指标把人群分为两大类,即外向型(out ...
- nyoj 15 括号匹配(二) (经典dp)
题目链接 描述 给你一个字符串,里面只包含"(",")","[","]"四种符号,请问你需要至少添加多少个括号才能使这些 ...
- Python 开发中easy_install的安装及使用
easy_install是一个python的扩展包,主要是用来简化python安装第三方安装包,在安装了easy_install之后,安装python第三方安装包就只需要在命令行中输入:easy_in ...
- Perl6 Bailador框架(1):开始
use v6; use Bailador; get '/' => sub { '<h1><center>Hello, World</center></h ...
- 某labs上传writeup-上传漏洞总结
github:https://github.com/d0ef/upload-labs 第一题:通过JS判断的直接抓包改了就ok. 第二题:只要Content-Type信息为图片的就可以 第三题:通过上 ...
- python基础===【爬虫】爬虫糗事百科首页图片代码
import requests import re import urllib.request def getHtml(url): page = requests.get(url) html = pa ...
- HIbernate学习笔记3 之 缓存和 对象的三种状态
一.hibernate一级缓存 * hibernate创建每个Session对象时,都会给该Session分配一块独立的缓冲区,用于存放Session查询出来的对象,这个分配给session的缓存区 ...