[转]Tomcat中的Session小结
什么是Session
对Tomcat而言,Session是一块在服务器开辟的内存空间,其存储结构为ConcurrentHashMap;
Session的目的
Http协议是一种无状态协议,即每次服务端接收到客户端的请求时,都是一个全新的请求,服务器并不知道客户端的历史请求记录;
Session的主要目的就是为了弥补Http的无状态特性。简单的说,就是服务器可以利用session存储客户端在同一个会话期间的一些操作记录;
实现机制
先看两个问题,如下:
1、服务器如何判断客户端发送过来的请求是属于同一个会话?
答:用Session id区分,Session id相同的即认为是同一个会话,在Tomcat中Session id用JSESSIONID表示;
2、服务器、客户端如何获取Session id?Session id在其之间是如何传输的呢?
答:服务器第一次接收到请求时,开辟了一块Session空间(创建了Session对象),同时生成一个Session id,并通过响应头的Set-Cookie:“JSESSIONID=XXXXXXX”命令,向客户端发送要求设置cookie的响应;
客户端收到响应后,在本机客户端设置了一个JSESSIONID=XXXXXXX的cookie信息,该cookie的过期时间为浏览器会话结束;
接下来客户端每次向同一个网站发送请求时,请求头都会带上该cookie信息(包含Session id);
然后,服务器通过读取请求头中的Cookie信息,获取名称为JSESSIONID的值,得到此次请求的Session id;
ps:服务器只会在客户端第一次请求响应的时候,在响应头上添加Set-Cookie:“JSESSIONID=XXXXXXX”信息,接下来在同一个会话的第二第三次响应头里,是不会添加Set-Cookie:“JSESSIONID=XXXXXXX”信息的;
而客户端是会在每次请求头的cookie中带上JSESSIONID信息;
举个例子:
以chrome浏览器为例,访问一个基于tomcat服务器的网站的时候,
浏览器第一次访问服务器,服务器会在响应头添加Set-Cookie:“JSESSIONID=XXXXXXX”信息,要求客户端设置cookie,如下图:

同时我们也可以在浏览器中找到其存储的sessionid信息,如下图

接下来,浏览器第二次、第三次...访问服务器,观察其请求头的cookie信息,可以看到JSESSIONID信息存储在cookie里,发送给服务器;且响应头里没有Set-Cookie信息,如下图:
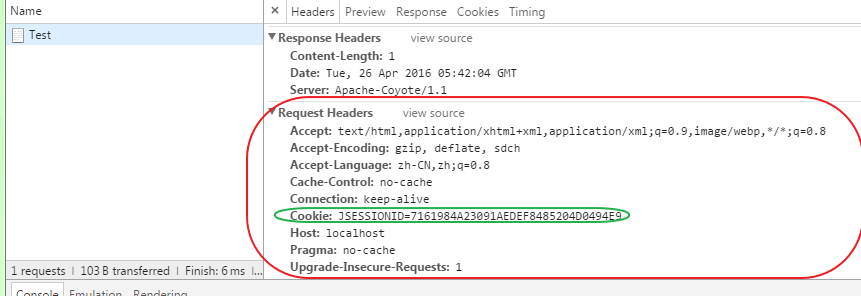
只要浏览器未关闭,在访问同一个站点的时候,其请求头Cookie中的JSESSIONID都是同一个值,被服务器认为是同一个会话。
再举个简单的例子加深印象,新建个Web工程,并写一个Servlet,在doGet中添加如下代码,主要做如下工作
首先,从session中获取key为count的值,累加,存入session,并打印;
然后,每次从请求中获取打印cookie信息,从响应中获取打印Header的Set-Cookie信息:

/**
* @see HttpServlet#doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
*/
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { if(request.getSession().getAttribute("count") == null){
request.getSession().setAttribute("count", 0);
response.getWriter().write(0+"");
}else{
int a = Integer.parseInt(request.getSession().getAttribute("count").toString());
request.getSession().setAttribute("count", ++a);
response.getWriter().write(a+"");
} Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies();
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
if(cookies!=null){
for(Cookie cookie : cookies){
sb.append(cookie.getName()+":"+cookie.getValue()+",");
}
sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length()-1);
} System.out.println("[第"+(++index)+"次访问]from client request, cookies:" + sb);
System.out.println("[第"+(index)+"次访问]from server response, header-Set-Cookie:" + response.getHeader("Set-Cookie"));;
}

部署到tomcat后,连续访问该servlet,观察控制台输出,如下,客户端第一次访问服务器的时候,在服务端的响应头里添加了JSESSIONID信息,且接下来客户端的每次访问都会带上该JSESSIONID:
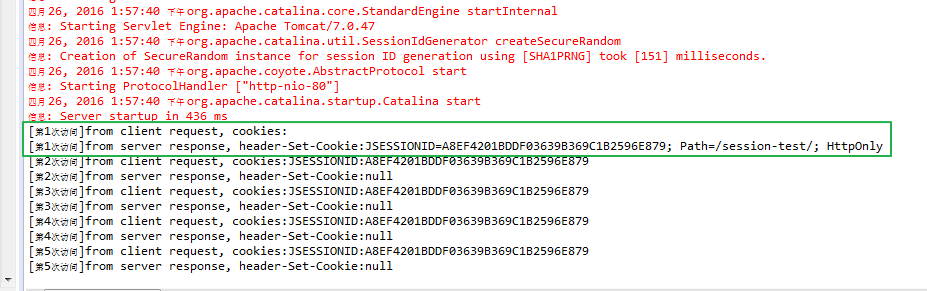
其实这里有一个问题,session劫持
只要用户知道JSESSIONID,该用户就可以获取到JSESSIONID对应的session内容,还是以上面这个例子为例,
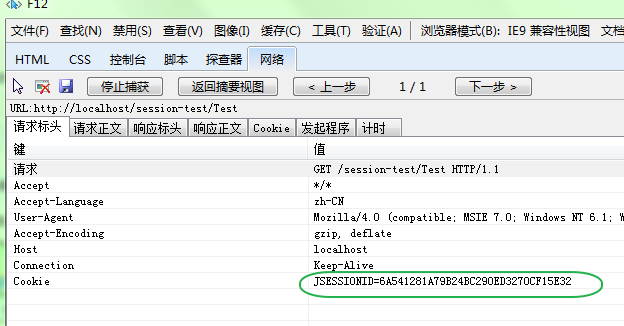
我先用IE浏览器访问该站点,比如连续访问了5次,此时,session中的count值为:

查看该会话的Session id,为6A541281A79B24BC290ED3270CF15E32
接下来打开chrome控制台,将IE浏览器获取过来的JSESSIONID信息(“6A541281A79B24BC290ED3270CF15E32”)写入到cookie中,如下
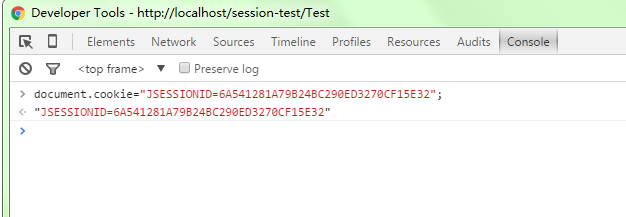
接着删除其中的一个,只留下JSESSIONID为“6A541281A79B24BC290ED3270CF15E32”的cookie;

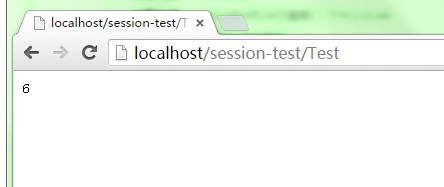
刷新页面,发现我们从session获取的count值已经变成6了,说明此次chrome浏览器的请求劫持了IE浏览器会话中的session,
Tomcat中的session实现
Tomcat中一个会话对应一个session,其实现类是StandardSession,查看源码,可以找到一个attributes成员属性,即存储session的数据结构,为ConcurrentHashMap,支持高并发的HashMap实现;
/**
* The collection of user data attributes associated with this Session.
*/
protected Map<String, Object> attributes = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object>();
那么,tomcat中多个会话对应的session是由谁来维护的呢?ManagerBase类,查看其代码,可以发现其有一个sessions成员属性,存储着各个会话的session信息:
/**
* The set of currently active Sessions for this Manager, keyed by
* session identifier.
*/
protected Map<String, Session> sessions = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Session>();
接下来,看一下几个重要的方法,
服务器查找Session对象的方法
客户端每次的请求,tomcat都会在HashMap中查找对应的key为JSESSIONID的Session对象是否存在,可以查看Request的doGetSession方法源码,如下源码:

protected Session doGetSession(boolean create) {
// There cannot be a session if no context has been assigned yet
Context context = getContext();
if (context == null) {
return (null);
}
// Return the current session if it exists and is valid
if ((session != null) && !session.isValid()) {
session = null;
}
if (session != null) {
return (session);
}
// Return the requested session if it exists and is valid
Manager manager = context.getManager();
if (manager == null) {
return null; // Sessions are not supported
}
if (requestedSessionId != null) {
try {
session = manager.findSession(requestedSessionId);
} catch (IOException e) {
session = null;
}
if ((session != null) && !session.isValid()) {
session = null;
}
if (session != null) {
session.access();
return (session);
}
}
// Create a new session if requested and the response is not committed
if (!create) {
return (null);
}
if ((context != null) && (response != null) &&
context.getServletContext().getEffectiveSessionTrackingModes().
contains(SessionTrackingMode.COOKIE) &&
response.getResponse().isCommitted()) {
throw new IllegalStateException
(sm.getString("coyoteRequest.sessionCreateCommitted"));
}
// Re-use session IDs provided by the client in very limited
// circumstances.
String sessionId = getRequestedSessionId();
if (requestedSessionSSL) {
// If the session ID has been obtained from the SSL handshake then
// use it.
} else if (("/".equals(context.getSessionCookiePath())
&& isRequestedSessionIdFromCookie())) {
/* This is the common(ish) use case: using the same session ID with
* multiple web applications on the same host. Typically this is
* used by Portlet implementations. It only works if sessions are
* tracked via cookies. The cookie must have a path of "/" else it
* won't be provided to for requests to all web applications.
*
* Any session ID provided by the client should be for a session
* that already exists somewhere on the host. Check if the context
* is configured for this to be confirmed.
*/
if (context.getValidateClientProvidedNewSessionId()) {
boolean found = false;
for (Container container : getHost().findChildren()) {
Manager m = ((Context) container).getManager();
if (m != null) {
try {
if (m.findSession(sessionId) != null) {
found = true;
break;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// Ignore. Problems with this manager will be
// handled elsewhere.
}
}
}
if (!found) {
sessionId = null;
}
sessionId = getRequestedSessionId();
}
} else {
sessionId = null;
}
session = manager.createSession(sessionId);
// Creating a new session cookie based on that session
if ((session != null) && (getContext() != null)
&& getContext().getServletContext().
getEffectiveSessionTrackingModes().contains(
SessionTrackingMode.COOKIE)) {
Cookie cookie =
ApplicationSessionCookieConfig.createSessionCookie(
context, session.getIdInternal(), isSecure());
response.addSessionCookieInternal(cookie);
}
if (session == null) {
return null;
}
session.access();
return session;
}

先看doGetSession方法中的如下代码,这个一般是第一次访问的情况,即创建session对象,session的创建是调用了ManagerBase的createSession方法来实现的; 另外,注意response.addSessionCookieInternal方法,该方法的功能就是上面提到的往响应头写入“Set-Cookie”信息;最后,还要调用session.access方法记录下该session的最后访问时间,因为session是可以设置过期时间的;

session = manager.createSession(sessionId);
// Creating a new session cookie based on that session
if ((session != null) && (getContext() != null)
&& getContext().getServletContext().
getEffectiveSessionTrackingModes().contains(
SessionTrackingMode.COOKIE)) {
Cookie cookie =
ApplicationSessionCookieConfig.createSessionCookie(
context, session.getIdInternal(), isSecure());
response.addSessionCookieInternal(cookie);
}
if (session == null) {
return null;
}
session.access();
return session;

再看doGetSession方法中的如下代码,这个一般是第二次以后访问的情况,通过ManagerBase的findSession方法查找session,其实就是利用map的key从ConcurrentHashMap中拿取对应的value,这里的key即requestedSessionId,也即JSESSIONID,同时还要调用session.access方法,记录下该session的最后访问时间;

if (requestedSessionId != null) {
try {
session = manager.findSession(requestedSessionId);
} catch (IOException e) {
session = null;
}
if ((session != null) && !session.isValid()) {
session = null;
}
if (session != null) {
session.access();
return (session);
}
}

在session对象中查找和设置key-value的方法
这个我们一般调用getAttribute/setAttribute方法:
getAttribute方法很简单,就是根据key从map中获取value;
setAttribute方法稍微复杂点,除了设置key-value外,如果添加了一些事件监听(HttpSessionAttributeListener)的话,还要通知执行,如beforeSessionAttributeReplaced, afterSessionAttributeReplaced, beforeSessionAttributeAdded、 afterSessionAttributeAdded。。。
session存在的问题
- 安全性,session劫持,这个前面已经举过例子了;
- 增加服务器压力,因为session是直接存储在服务器的内存中的;
- 如果存在多台服务器的话,还存在session同步问题,当然如果只有一台tomcat服务器的话,也就没有session同步的事情了,然而现在一般的应用都会用到多台tomcat服务器,通过负载均衡,同一个会话有可能会被分配到不同的tomcat服务器,因此很可能出现session不一致问题;解决session同步问题,实际上主要是保证能够抽离出一块共享空间存放session信息,且这块空间不同的tomcat服务器都可以访问到;一般这块共享的空间可以是数据库,或者某台服务器的内存空间,甚至硬盘空间,或者客户端的cookie也是可以的;
(原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/chenpi/p/5434537.html)
[转]Tomcat中的Session小结的更多相关文章
- Tomcat中的Session小结
什么是Session 对Tomcat而言,Session是一块在服务器开辟的内存空间,其存储结构为ConcurrentHashMap: Session的目的 Http协议是一种无状态协议,即每次服务端 ...
- 【Web】Tomcat中利用Session识别用户的基本原理
HTTP无状态的特性与Session.Cookie的存在 HTTP有一个特性:无状态的,就是前后两个HTTP事务它们并不知道对方的信息. 而为了维护会话信息或用户信息,一般可用Cookie或Sessi ...
- How Tomcat works — 八、tomcat中的session管理
在使用shiro的session的时候感觉对于tomcat中session的管理还不是特别清楚,而且session管理作为tomcat中比较重要的一部分还是很有必要学习的. 目录 概述 session ...
- Tomcat 中的 Session 和 Cookie
HTTP 是一种无状态通信协议,每个请求之间相互独立,服务器不能识别曾经来过的请求.而对于 Web 应用,它的活动都是依赖某个状态的,比如用户登录,此时使用 HTTP 就需要它在一次登录请求后,有为后 ...
- [转]tomcat中的session管理
转载地址:http://blog.csdn.net/iloveqing/article/details/1544958 当一个sesson开始时,Servlet容器会创建一个HttpSession对象 ...
- Tomcat中的session实现
Tomcat中一个会话对应一个session,其实现类是StandardSession,查看源码,可以找到一个attributes成员属性,即存储session的数据结构,为ConcurrentHas ...
- Tomcat 集群中 实现session 共享的三种方法
前两种均需要使用 memcached 或 redis 存储 session ,最后一种使用 terracotta 服务器共享. 建议使用 redis ,不仅仅因为它可以将缓存的内容持久化,还因为它支持 ...
- Nginx+tomcat集群中,session的共享
nginx,tomcat集群后多个session分配到同一个应用 单节点低负荷的情况下,我们通常把一个WEB应用打成WAR包放WEB应用服务器,如TOMCAT下运行就行了(如图1).但随着用户量的增加 ...
- Tomcat使用Memcached Session Manager管理Session
Tomcat使用Memcached Session Manager管理Session 废话不多说,直接进入主题.项目使用阿里云负载均衡+ECS服务器集群进行部署,Tomcat使用8.5版本.阿里云负载 ...
随机推荐
- python——从datetime模块探索python的数据架构
问题出现于我试图向自建网页中加入实时时间开始. 我之前已经知道python中有有关事件和日期的模块datetime.以下导入datetime并作实验. >>> import date ...
- Struts2学习笔记四:深入拦截器
一:拦截器的工作原理 拦截器的执行过程可以类比filter过滤器,ActionInvocation实例执行过程中,先执行action实例上引用的拦截器们,然后才执行action实例处理请求,返回res ...
- 早前阅读live555源码做的笔记
早前阅读live555源码的时候做了一些简单的笔记.现在看来那个时候对C++的理解还是不够,还有很多不足.当时对很多名词也不是很熟悉,对一些类的描述也很生硬,所以笔记中有一些不通畅之处. 阅读live ...
- Linux下ls与cp命令
Linux熟练的应用命令,才可以随心所欲~ ls 注意: ls -1 //每次只列出1个文件 cp 注意: cp -u xxx xxx //注意修改时间的先后
- 体验cygwin纪实
在windows快速体验linux,借助Cygwin很不错的体验(占用空间小),win10应用商店目前集成ubuntu.fedora...系统... 00.安装源,直接下载的是init(仅仅是下载器) ...
- Arduino通过I2C(SSD1306)驱动0.96寸12864OLED
I2C驱动的128x64 OLED I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit) 集成电路总线是I2CBus的简称, 是一种串行通信总线, 使用多主从架构. 飞利浦公司在1980年代为 ...
- PL/SQL Developer 中文乱码问题的解决
分三个步骤解决: 1.检查server编码: 运行SQL语法: select * from v$nls_parameters; 2.设置本地client编码: 进入 ...
- adjustResize和adjustPan的比较
在下面的描述中,编辑框的maxLine都设定为10. 在信息列表界面中,编辑框在RelativeLayout中定义.编辑框上边(above)的列表组件的高度不会缩小为0,导致显示出现一点问题. 当信息 ...
- BigDecimal去除末尾多余的0
Java有自带的 stripTrailingZeros() 方法用于去除末尾多余的0 BigDecimal num = new BigDecimal("100.000"); Big ...
- CentOS设置开机自动启动某服务
CentOS设置开机自动启动某服务 这里以启动sshd服务为例: 查看sshd是否已经是系统服务: # chkconfig --list |grep sshd 会显示: sshd ...
