zookeeper(3) 持久化
zookeeper为了防止,系统宕机或重启导致的数据丢失,会对数据进行定时持久化。有两种持久化方式:
1.为每次事务操作记录到日志文件,这样就可以通过执行这些日志文件来恢复数据。
2.为了加快ZooKeeper恢复的速度,ZooKeeper还提供了对树结构和session信息进行数据快照持久化的操作。
日志文件
日志文件记录zookeeper服务器上的每一次事务操作。
日志文件格式:log.ZXID,ZXID非常重要,它表示该文件起始的事务id。
数据快照
数据快照用来记录zookeeper服务器上某一时刻的全量内存数据内容,并写入指定磁盘文件中。
数据快照文件格式:snapshot.ZXID,ZXID非常重要,ZooKeeper会根据ZXID来确定数据恢复的起始点。
镜像文件主要存储zookeeper的树结构和session信息。
类图
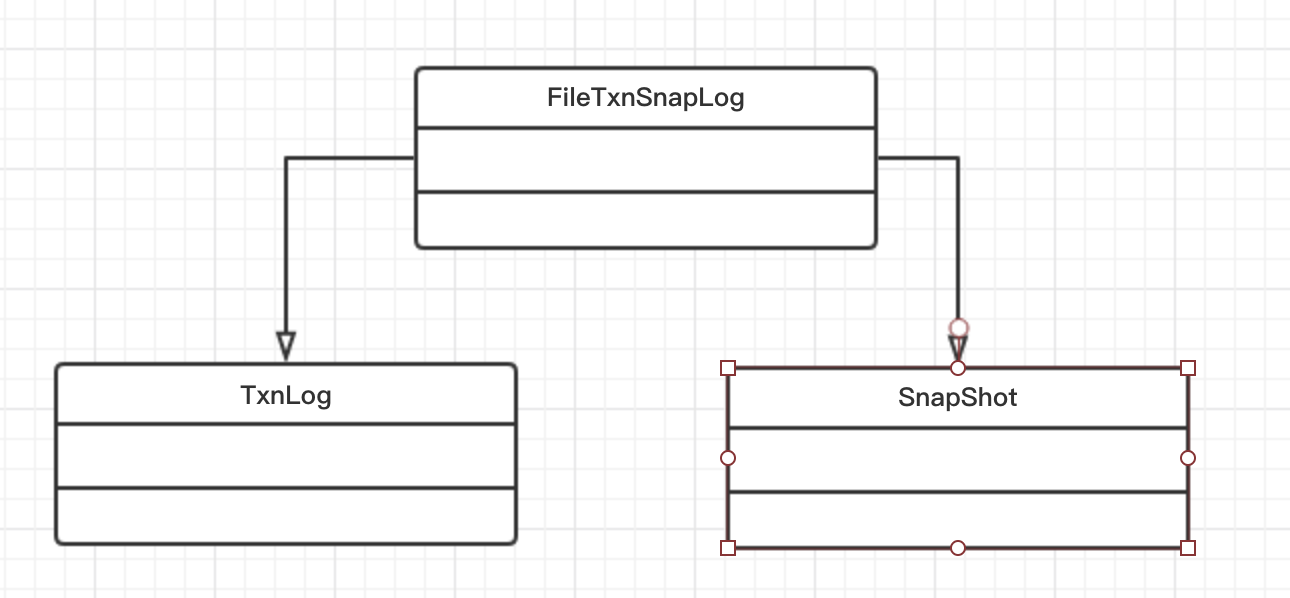
FileTxnSnapLog
是操作数据持久化的核心类,底层通过TxnLog和SnapShot来分别操作日志文件和数据快照。
存储数据快照

public void save(DataTree dataTree,
ConcurrentHashMap<Long, Integer> sessionsWithTimeouts)
throws IOException {
long lastZxid = dataTree.lastProcessedZxid;
LOG.info("Snapshotting: " + Long.toHexString(lastZxid));
File snapshot=new File(
snapDir, Util.makeSnapshotName(lastZxid));
snapLog.serialize(dataTree, sessionsWithTimeouts, snapshot); }

日志文件操作

public boolean append(Request si) throws IOException {
return txnLog.append(si.hdr, si.txn);
}
public void commit() throws IOException {
txnLog.commit();
}
public void rollLog() throws IOException {
txnLog.rollLog();
}

数据恢复

public long restore(DataTree dt, Map<Long, Integer> sessions,
PlayBackListener listener) throws IOException {
snapLog.deserialize(dt, sessions);
FileTxnLog txnLog = new FileTxnLog(dataDir);
TxnIterator itr = txnLog.read(dt.lastProcessedZxid+1);
long highestZxid = dt.lastProcessedZxid;
TxnHeader hdr;
while (true) { hdr = itr.getHeader();
...if (hdr.getZxid() < highestZxid && highestZxid != 0) {
LOG.error(highestZxid + "(higestZxid) > "
+ hdr.getZxid() + "(next log) for type "
+ hdr.getType());
} else {
highestZxid = hdr.getZxid();
}
try {
processTransaction(hdr,dt,sessions, itr.getTxn());
} catch(KeeperException.NoNodeException e) {
throw new IOException("Failed to process transaction type: " +
hdr.getType() + " error: " + e.getMessage());
}
if (!itr.next())
break;
}
return highestZxid;
}

FileTxnLog
负责维护事务日志对外的接口,包括事务日志的写入和读取等。
写入事务日志
1.如果日志文件打开,使用该日志文件;如果没有,使用该事务的zxid做为后缀,创建新的日志文件。
2.如果当前日志文件剩余空间不足4kb,对日志文件扩容到64mb,使用0来填充。预分配的原因是提高io效率。
3.对事务的头和事务体序列号
4.生成checksum
5.写入文件流。

public synchronized boolean append(TxnHeader hdr, Record txn)
throws IOException
{
if (hdr != null) {
...
if (logStream==null) {
...
logFileWrite = new File(logDir, ("log." +
Long.toHexString(hdr.getZxid())));
fos = new FileOutputStream(logFileWrite);
logStream=new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
oa = BinaryOutputArchive.getArchive(logStream);
FileHeader fhdr = new FileHeader(TXNLOG_MAGIC,VERSION, dbId);
fhdr.serialize(oa, "fileheader");
// Make sure that the magic number is written before padding.
logStream.flush();
currentSize = fos.getChannel().position();
streamsToFlush.add(fos);
}
padFile(fos);
byte[] buf = Util.marshallTxnEntry(hdr, txn);
...
Checksum crc = makeChecksumAlgorithm();
crc.update(buf, 0, buf.length);
oa.writeLong(crc.getValue(), "txnEntryCRC");
Util.writeTxnBytes(oa, buf);
return true;
}
return false;
}

持久化本质是将内存中对象数据以二进制的方式存储到磁盘上,这个过程,底层通过jute来序列号。
序列化和反序列化的本质就是数据流与对象数据之间的变换。jute的序列化理念是让需要序列化的对象自己定义序列化协议。所以使用jute进行序列化的对象需要实现Record接口,该接口需要对象实现序列化和反序列化方法。此外jute还对序列化的流进行了抽象,OutputArchive代表输入流,InputArchive代表输入流,各种类型流的读写通过实现这两个接口实现。通过实现Record接口,对象定义序列化和反序列化的协议;通过实现OutputArchive和InputArchive,实现数据存储和读取。
Record代码:
public interface Record {
public void serialize(OutputArchive archive, String tag)
throws IOException;
public void deserialize(InputArchive archive, String tag)
throws IOException;
}
OutputArchive代码:
public interface OutputArchive {
public void writeByte(byte b, String tag) throws IOException;
public void writeBool(boolean b, String tag) throws IOException;
public void writeInt(int i, String tag) throws IOException;
public void writeLong(long l, String tag) throws IOException;
public void writeFloat(float f, String tag) throws IOException;
public void writeDouble(double d, String tag) throws IOException;
public void writeString(String s, String tag) throws IOException;
public void writeBuffer(byte buf[], String tag)
throws IOException;
public void writeRecord(Record r, String tag) throws IOException;
public void startRecord(Record r, String tag) throws IOException;
public void endRecord(Record r, String tag) throws IOException;
public void startVector(List v, String tag) throws IOException;
public void endVector(List v, String tag) throws IOException;
public void startMap(TreeMap v, String tag) throws IOException;
public void endMap(TreeMap v, String tag) throws IOException;
}
InputArchive代码:
public interface InputArchive {
public byte readByte(String tag) throws IOException;
public boolean readBool(String tag) throws IOException;
public int readInt(String tag) throws IOException;
public long readLong(String tag) throws IOException;
public float readFloat(String tag) throws IOException;
public double readDouble(String tag) throws IOException;
public String readString(String tag) throws IOException;
public byte[] readBuffer(String tag) throws IOException;
public void readRecord(Record r, String tag) throws IOException;
public void startRecord(String tag) throws IOException;
public void endRecord(String tag) throws IOException;
public Index startVector(String tag) throws IOException;
public void endVector(String tag) throws IOException;
public Index startMap(String tag) throws IOException;
public void endMap(String tag) throws IOException;
}
例如对FileHeader实现序列化,分别在serialize和deserialize方法中定义序列化协议,然后调用相应方法就可以将该对象序列化和反序列化。
public class FileHeader implements Record {
private int magic;
private int version;
private long dbid;
public void serialize(OutputArchive a_, String tag) throws java.io.IOException {
a_.startRecord(this,tag);
a_.writeInt(magic,"magic");
a_.writeInt(version,"version");
a_.writeLong(dbid,"dbid");
a_.endRecord(this,tag);
}
public void deserialize(InputArchive a_, String tag) throws java.io.IOException {
a_.startRecord(tag);
magic=a_.readInt("magic");
version=a_.readInt("version");
dbid=a_.readLong("dbid");
a_.endRecord(tag);
}
}
具体对象会序列化为什么样的数据形式以及从什么样数据形式中反序列化,取决于OutputArchive和InputArchive的实现。
二进制数据流实现:
BinaryOutputArchive:
public class BinaryOutputArchive implements OutputArchive {
private ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
private DataOutput out;
public static BinaryOutputArchive getArchive(OutputStream strm) {
return new BinaryOutputArchive(new DataOutputStream(strm));
}
public BinaryOutputArchive(DataOutput out) {
this.out = out;
}
public void writeByte(byte b, String tag) throws IOException {
out.writeByte(b);
}
public void writeBool(boolean b, String tag) throws IOException {
out.writeBoolean(b);
}
public void writeInt(int i, String tag) throws IOException {
out.writeInt(i);
}
public void writeLong(long l, String tag) throws IOException {
out.writeLong(l);
}
public void writeFloat(float f, String tag) throws IOException {
out.writeFloat(f);
}
public void writeDouble(double d, String tag) throws IOException {
out.writeDouble(d);
}
/**
* create our own char encoder to utf8. This is faster
* then string.getbytes(UTF8).
* @param s the string to encode into utf8
* @return utf8 byte sequence.
*/
final private ByteBuffer stringToByteBuffer(CharSequence s) {
bb.clear();
final int len = s.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (bb.remaining() < 3) {
ByteBuffer n = ByteBuffer.allocate(bb.capacity() << 1);
bb.flip();
n.put(bb);
bb = n;
}
char c = s.charAt(i);
if (c < 0x80) {
bb.put((byte) c);
} else if (c < 0x800) {
bb.put((byte) (0xc0 | (c >> 6)));
bb.put((byte) (0x80 | (c & 0x3f)));
} else {
bb.put((byte) (0xe0 | (c >> 12)));
bb.put((byte) (0x80 | ((c >> 6) & 0x3f)));
bb.put((byte) (0x80 | (c & 0x3f)));
}
}
bb.flip();
return bb;
}
public void writeString(String s, String tag) throws IOException {
if (s == null) {
writeInt(-1, "len");
return;
}
ByteBuffer bb = stringToByteBuffer(s);
writeInt(bb.remaining(), "len");
out.write(bb.array(), bb.position(), bb.limit());
}
public void writeBuffer(byte barr[], String tag)
throws IOException {
if (barr == null) {
out.writeInt(-1);
return;
}
out.writeInt(barr.length);
out.write(barr);
}
public void writeRecord(Record r, String tag) throws IOException {
r.serialize(this, tag);
}
public void startRecord(Record r, String tag) throws IOException {}
public void endRecord(Record r, String tag) throws IOException {}
public void startVector(List v, String tag) throws IOException {
if (v == null) {
writeInt(-1, tag);
return;
}
writeInt(v.size(), tag);
}
public void endVector(List v, String tag) throws IOException {}
public void startMap(TreeMap v, String tag) throws IOException {
writeInt(v.size(), tag);
}
public void endMap(TreeMap v, String tag) throws IOException {}
}
BinaryInputArchive:
public class BinaryInputArchive implements InputArchive {
private DataInput in;
static public BinaryInputArchive getArchive(InputStream strm) {
return new BinaryInputArchive(new DataInputStream(strm));
}
static private class BinaryIndex implements Index {
private int nelems;
BinaryIndex(int nelems) {
this.nelems = nelems;
}
public boolean done() {
return (nelems <= 0);
}
public void incr() {
nelems--;
}
}
/** Creates a new instance of BinaryInputArchive */
public BinaryInputArchive(DataInput in) {
this.in = in;
}
public byte readByte(String tag) throws IOException {
return in.readByte();
}
public boolean readBool(String tag) throws IOException {
return in.readBoolean();
}
public int readInt(String tag) throws IOException {
return in.readInt();
}
public long readLong(String tag) throws IOException {
return in.readLong();
}
public float readFloat(String tag) throws IOException {
return in.readFloat();
}
public double readDouble(String tag) throws IOException {
return in.readDouble();
}
public String readString(String tag) throws IOException {
int len = in.readInt();
if (len == -1) return null;
byte b[] = new byte[len];
in.readFully(b);
return new String(b, "UTF8");
}
static public final int maxBuffer = determineMaxBuffer();
private static int determineMaxBuffer() {
String maxBufferString = System.getProperty("jute.maxbuffer");
try {
return Integer.parseInt(maxBufferString);
} catch(Exception e) {
return 0xfffff;
}
}
public byte[] readBuffer(String tag) throws IOException {
int len = readInt(tag);
if (len == -1) return null;
if (len < 0 || len > maxBuffer) {
throw new IOException("Unreasonable length = " + len);
}
byte[] arr = new byte[len];
in.readFully(arr);
return arr;
}
public void readRecord(Record r, String tag) throws IOException {
r.deserialize(this, tag);
}
public void startRecord(String tag) throws IOException {}
public void endRecord(String tag) throws IOException {}
public Index startVector(String tag) throws IOException {
int len = readInt(tag);
if (len == -1) {
return null;
}
return new BinaryIndex(len);
}
public void endVector(String tag) throws IOException {}
public Index startMap(String tag) throws IOException {
return new BinaryIndex(readInt(tag));
}
public void endMap(String tag) throws IOException {}
}
其他的实现还有,cvs文件(CsvInputArchive,CsvOutputArchive);xml文件(XmlInputArchive,XmlOutputArchive)。
zookeeper(3) 持久化的更多相关文章
- Zookeeper(四))持久化日志文件
Zookeeper(四))持久化日志文件 持久化用途 存储两种文件 snapshot:内存快照 log:事务日志,类似MySQL的binlog,存储数据节点的操作日志 问题 序列化的本质其实就是将原数 ...
- Zookeeper(五)持久化快照
Zookeeper(五)持久化快照 用途 快照文件是指定时间间隔对zookeeper服务器上的节点数据的序列化后备份到磁盘中,快照文件不一定是最新的 如果zk集群挂了,可能会用到它来复原 基本术语 D ...
- 详解 ZooKeeper 数据持久化
本文作者:HelloGitHub-老荀 Hi,这里是 HelloGitHub 推出的 HelloZooKeeper 系列,免费开源.有趣.入门级的 ZooKeeper 教程,面向有编程基础的新手. 项 ...
- 【Zookeeper】源码分析之持久化--FileTxnLog
一.前言 前一篇已经分析了序列化,这篇接着分析Zookeeper的持久化过程源码,持久化对于数据的存储至关重要,下面进行详细分析. 二.持久化总体框架 持久化的类主要在包org.apache.zook ...
- 【Zookeeper】源码分析之持久化(一)之FileTxnLog
一.前言 前一篇已经分析了序列化,这篇接着分析Zookeeper的持久化过程源码,持久化对于数据的存储至关重要,下面进行详细分析. 二.持久化总体框架 持久化的类主要在包org.apache.zook ...
- Zookeeper基本配置
前面两篇文章介绍了Zookeeper是什么和可以干什么,那么接下来我们就实际的接触一下Zookeeper这个东西,看看具体如何使用,有个大体的感受,后面再描述某些地方的时候也能在大脑中有具体的印象.本 ...
- Zookeeper集群的安装和使用
Apache Zookeeper 由 Apache Hadoop 的 Zookeeper 子项目发展而来,现已经成为 Apache 的顶级项目,它是一个开放源码的分布式应用程序协调服务,是Google ...
- zookeeper 配置详解
http://blog.csdn.net/shenlan211314/article/details/6185176 因博主原创,所以不能转载 下面是更为详细的配置说明: 前面两篇文章介绍了Zook ...
- zookeeper配置
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/yuyijq/p/3438829.html 前面两篇文章介绍了Zookeeper是什么和可以干什么,那么接下来我们就实际的接触一下Zookee ...
随机推荐
- Vue3.0数据响应式原理
在vue2版本中响应式使用的是ES5对象的操作,通过遍历对象Object.defineProperty属性值的变化,实现监听数据 在3.0中使用的ES6版本的Proxy代理对象方式来实现数据的监听,省 ...
- Ubuntu图形桌面切换到命令行界面
Ubuntu提供两种进入方式,一个是我们平常最熟悉的图形界面形式,还有一种是纯命令行方式. 1.按 Ctrl + Alt + (F1~F6中的任意一个)即可进入纯命令行模式. 进入后,需要输入用户名, ...
- 虚拟化技术之kvm虚拟机创建工具qemu-kvm
在前边的博客中我们介绍了如何创建kvm虚拟机,以及一些常用的工具的介绍和使用,今天我们来了解下kvm原始工具qemu-kvm:为什么说qemu-kvm是一个原始的工具呢,如果你用kvm虚拟机,心细的你 ...
- Linux两台服务器mysql数据库同步
我们在做web系统部署的时候往往涉及到两台甚至多台数据库的备份,为了数据安全考虑(虽然说到底不过是一堆0 1,但是价值千金啊),所以我们还是乖乖做同步把! 1.准备两台Linux服务器(主.从) 2. ...
- C++字符串与指针
字符串初始化 在C++中基本数据类型并不包括string,string类型其实是一种类类型,通过STL函数库中的模板类basic_string 实例化得到. int main () { // stri ...
- 我们真的需要JWT吗?
JWT(JSON Web Token)是目前最流行的认证方案之一.博客园.各种技术公众号隔三差五就会推一篇JWT相关的文章,真的多如牛毛.但我对JWT有点困惑,今天写出来跟大家探讨探讨,不要喷哈. J ...
- day42:HTML标签和CSS选择器
目录 1.HTML 1.1 文档结构 1.2 head标签 1.3 body标签 1.3.1 h1-h6标签 1.3.2.br标签:换行 1.3.3.hr标签:一行横线 1.3.4 a标签:超链接标签 ...
- 高可用集群corosync+pacemaker之crmsh使用(一)
上一篇博客我们聊了下高可用集群corosync+pacemaker的相关概念以及corosync的配置,回顾请参考https://www.cnblogs.com/qiuhom-1874/p/13585 ...
- SpringCloud入门 消息总线 Bus
消息总线 1.概述 使用SpringCloud Bus配和Spring Cloud Config使用实现配置的动态刷新 Bus只支持消息处理:RabbitMQ和Kafaka. 能干嘛 能管理和传播分布 ...
- ajax发送请求的时候url为空或者undefined会发生什么
$.ajax()里的url为空,ajax请求发送到当前自己的页面. 例如index.html里$.ajax()的url为空就发送到index.html
