ribbon 详解
ribbon 详解
1. 顶层架构
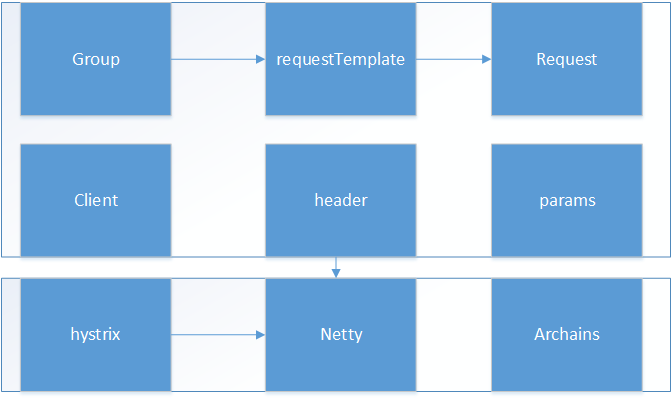
2. 简单的示例:使用ResourceTemplate方式
@Test
public void testGroup(){
HttpResourceGroup httpResourceGroup = Ribbon.createHttpResourceGroup("test",
ClientOptions.create().withMaxAutoRetries(3).
withConfigurationBasedServerList("localhost:8081,localhost:8080"));
HttpRequestTemplate<ByteBuf> recommendationsByUserIdTemplate = httpResourceGroup.newTemplateBuilder("recommendationsByUserId", ByteBuf.class)
.withMethod("GET")
.withUriTemplate("/aa/index")
.withHeader("X-Auth-Token", "abc")
//.withFallbackProvider(new RecommendationServiceFallbackHandler())
//.withResponseValidator(new RecommendationServiceResponseValidator())
.build();
RibbonRequest<ByteBuf> request = recommendationsByUserIdTemplate.requestBuilder()
.withRequestProperty("userId", "test")
.build();
ByteBuf buf = request.execute();
byte[] bytes = new byte[buf.capacity()];
buf.readBytes(bytes);
System.out.println(new String(bytes));
}
3.实现:
3.1 关键对象
public interface RibbonRequest<T> {
/**
* Blocking API that returns a single (or last element if there is a sequence of objects from the execution) element
*/
public T execute();
/**
* Non blocking API that returns a {@link Future}, where its {@link Future#get()} method is blocking and returns a
* single (or last element if there is a sequence of objects from the execution) element
*/
public Future<T> queue();
/**
* Non blocking API that returns an {@link Observable} while the execution is started asynchronously.
* Subscribing to the returned {@link Observable} is guaranteed to get the complete sequence from
* the beginning, which might be replayed by the framework. Use this API for "fire and forget".
*/
public Observable<T> observe();
/**
* Non blocking API that returns an Observable. The execution is not started until the returned Observable is subscribed to.
*/
public Observable<T> toObservable();
/**
* Create a decorated {@link RequestWithMetaData} where you can call its similar blocking or non blocking
* APIs to get {@link RibbonResponse}, which in turn contains returned object(s) and
* some meta data from Hystrix execution.
*/
public RequestWithMetaData<T> withMetadata();
}
明显,最终生成的关键对象RibbonRequest,使用的时观察者模式,底层实现肯定会使用RxJava或者Hystrix。
3.2 关键实现:HystrixObservableCommandChain
HystrixObservableCommandChain<T> createHystrixCommandChain() {
List<HystrixObservableCommand<T>> commands = new ArrayList<HystrixObservableCommand<T>>(2);
if (cacheProvider != null) {
commands.add(new CacheObservableCommand<T>(cacheProvider.getCacheProvider(), cacheProvider.getKey(), cacheHystrixCacheKey,
requestProperties, template.cacheHystrixProperties()));
}
commands.add(new HttpResourceObservableCommand<T>(client, httpRequest, hystrixCacheKey, requestProperties, template.fallbackHandler(),
template.responseValidator(), template.getClassType(), template.hystrixProperties()));
return new HystrixObservableCommandChain<T>(commands);
}
在HystrixObservableCommandChain执行toObservable的时候,会依次便利集合中所有的HystrixObservableCommand,知道其toObservable不为null。
所以,如果cacheProvider不为null会调用CacheObservableCommand的toObservable,如果cacheProvider为null,则直接调用HttpResourceObservableCommand的toObservable.
3.3 http请求:
Observable<HttpClientResponse<ByteBuf>> httpResponseObservable = httpClient.submit(httpRequest);
Observable<T> o =
(server == null ? selectServer() : Observable.just(server))
.concatMap(new Func1<Server, Observable<T>>() {
@Override
// Called for each server being selected
public Observable<T> call(Server server) {
context.setServer(server);
final ServerStats stats = loadBalancerContext.getServerStats(server);
// Called for each attempt and retry
Observable<T> o = Observable
.just(server)
.concatMap(new Func1<Server, Observable<T>>() {
...
});
if (maxRetrysSame > 0)
o = o.retry(retryPolicy(maxRetrysSame, true));
return o;
}
}
if (maxRetrysSame > 0)
o = o.retry(retryPolicy(maxRetrysSame, true));
return o;
会调用统一服务器n次,后调用下一个服务器m次(n,m为设定的最大调用次数)。
4.简单示例:使用注解方式
public interface AAIndex {
@Http( method = Http.HttpMethod.GET,
uri = "http://localhost:8080/aa/index")
RibbonRequest<ByteBuf> index();
}
@Test
public void testRibbonAnnotation(){
AAIndex aaIndex = Ribbon.from(AAIndex.class);
ByteBuf buf = aaIndex.index().execute();
byte[] bytes = new byte[buf.capacity()];
buf.readBytes(bytes);
System.out.println(new String(bytes));
}
5.实现:
5.1 动态代理:
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(),
new Class[]{clientInterface, ProxyLifeCycle.class},
new RibbonDynamicProxy<T>(clientInterface, resourceGroupFactory, configFactory, transportFactory, processors)
);
使用JDK自带的代理类实现,代理了client接口,和ProxyLifeCycle,其实现具体类为RibbonDynamicProxy。
5.2 支持的注解:
static void registerAnnotationProcessors(AnnotationProcessorsProvider processors) {
processors.register(new HttpAnnotationProcessor());
processors.register(new HystrixAnnotationProcessor());
processors.register(new CacheProviderAnnotationProcessor());
processors.register(new ClientPropertiesProcessor());
}
最终的实现跟非注解方式的实现是一致的。
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <O> RibbonRequest<O> executeFromTemplate(Object[] args) {
HttpRequestBuilder<?> requestBuilder = httpRequestTemplateBuilder.build().requestBuilder();
withParameters(requestBuilder, args);
withContent(requestBuilder, args);
return (RibbonRequest<O>) requestBuilder.build();
}
ribbon 详解的更多相关文章
- Ribbon详解
转自Ribbon详解 简介 Spring Cloud Ribbon是一个基于HTTP和TCP的客户端负载均衡工具,它基于Netflix Ribbon实现.通过Spring Cloud的封装,可以让 ...
- Spring Cloud:使用Ribbon实现负载均衡详解(下)
在上一篇文章(Spring Cloud:使用Ribbon实现负载均衡详解(上))中,我对 Ribbon 做了一个介绍,Ribbon 可以实现直接通过服务名称对服务进行访问.这一篇文章我详细分析一下如何 ...
- VC++ 2010 创建高级Ribbon界面详解(1)
运用 VC++ 2010 创建高级 Ribbon 界面详解,包括 Ribbon 界面的结构层次.Ribbon 控件的使用等,ribbon 用户界面,ribbon interface ,ribbon 高 ...
- (2-3)Eureka详解
基础架构 服务注册中心 服务提供者 服务消费者 服务治理 服务提供者 服务注册.在服务注册时,需要确认一下eureka.client.registerwith-eurek=ture参数是否正确,默认是 ...
- Spring Cloud Zuul 限流详解(附源码)(转)
在高并发的应用中,限流往往是一个绕不开的话题.本文详细探讨在Spring Cloud中如何实现限流. 在 Zuul 上实现限流是个不错的选择,只需要编写一个过滤器就可以了,关键在于如何实现限流的算法. ...
- Zuul之Filter详解
Zuul详解 官方文档:https://github.com/Netflix/zuul/wiki/How-it-Works Zuul的中心是一系列过滤器,能够在HTTP请求和响应的路由过程中执行一系列 ...
- Spring Cloud限流详解
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/tracy38/article/details/78685707 在高并发的应用中,限流往往是一个绕不开的话题.本文详细探讨在Spring Cloud ...
- springcloud中Feign配置详解
Spring Cloud中Feign配置详解 到目前为止,小伙伴们对Feign的使用已经掌握的差不多了,我们在前文也提到Feign是对Ribbon和Hystrix的整合,那么在Feign中,我们要如何 ...
- Spring Cloud(十二):Spring Cloud Zuul 限流详解(附源码)(转)
前面已经介绍了很多zuul的功能,本篇继续介绍它的另一大功能.在高并发的应用中,限流往往是一个绕不开的话题.本文详细探讨在Spring Cloud中如何实现限流. 在 Zuul 上实现限流是个不错的选 ...
随机推荐
- .net core实现redisClient
引言 最近工作上有需要使用redis,于是便心血来潮打算自己写一个C#客户端.经过几天的努力,目前该客户端已经基本成型,下面简单介绍一下. 通信协议 要想自行实现redisClient,则必须先要了解 ...
- OpenStack中部署glance的步骤
OpenStack中部署glance的步骤(基于Ubuntu14.04系统) author:headsen chen 2017-10-13 08:34:35 个人原创,转载请注明作者,出处, ...
- 浅析C#之委托、Action、Func
一.委托 1.1 委托的定义 delegate(委托)是一种可用于封装命名方法或匿名方法的引用类型, 委托类似于 C++ 中的函数指针: .Net通过委托来提供回调函数机制. 声明一个委托类型 int ...
- 新华三H3C服务器安装系统问题
服务器装系统出现如下问题: 解决: 1)先点击Install Centos7进入系统盘系统,查看对应路径的盘符标识: 2)重启按e进入编辑界面修改对应的读取路径: 3)Ctrl+x继续进入,开始正常系 ...
- Go基础之锁的初识
当我们的程序就一个线程的时候是不需要用到锁的,但是通常我们实际的代码不会是单个线程的,所有这个时候就需要用到锁了,那么关于锁的使用场景主要涉及到哪些呢? 当我们多个线程在读相同的数据的时候则是需要加锁 ...
- 13.HashMap TreeMap HashTable LinkedHashMap 的区别
数据库基本连接equals和hashCode详解 http://www.cnblogs.com/XMMDMW/p/6502355.html
- poj-1207 THE 3n+1 problem
Description Problems in Computer Science are often classified as belonging to a certain class of pro ...
- 【Python】 Web开发框架的基本概念与开发的准备工作
Web框架基本概念 现在再来写这篇文章显然有些马后炮的意思.不过正是因为已经学习了Flask框架, 并且未来计划学习更加体系化的Django框架,在学习过程中碰到的很多术语等等,非常有必要通过这样一篇 ...
- hosts文件路径及文件介绍
路径:WINDOWS/system32/drivers/etc/hosts 内容127.0.0.1 localhost 一. Hosts文件的位置 很多用户都知道在Window系统中有个H ...
- JavaScript 通过队列实现异步流控制
知乎上面看到一个面试题. 某个应用模块由文本框 input,以及按钮 A,按钮 B 组成.点击按钮 A,会向地址 urlA 发出一个 ajax 请求,并将返回的字符串填充到 input 中(覆盖 in ...
