python 之字符串的使用
在python中,字符串是最常用的数据类型,通常由单引号(' ')、双引号(" ")、三重引号(''' ''',""" """)引起来。
# 字符串的创建
str1 = "hello world"
str2 = 'sunlight'
str3 = '''On a new day,
the sun rises in the East
'''
str4 = """On a new day,
the sun rises in the East"""
str5 = "What's this?"
使用单引号、双引号、三重引号创建的字符串是无区别的,验证如下
str1 = 'sunlight'
str2 = "sunlight"
str3 = """sunlight"""
str4 = '''sunlight'''
print(str1 == str2 == str3 == str4) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py
True Process finished with exit code 0
三重引号的使用场景一般用于类、函数等注释,或者定义含有多行的字符串
字符串是一个由独立字符组成的序列,意味着可以
1.获取字符串长度
# 获取字符串长度
str1 = 'sunlight'
print(len(str1)) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py
8 Process finished with exit code 0
2、通过下标读取其中的某个字符
# 通过下标读取字符
str1 = 'sunlight'
print(str1[1])
print(str1[0])
print(str1[-1]) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py
u
s
t Process finished with exit code 0
3、通过切片方式读取字符串片段
# 切片方式读取片段
str1 = 'sunlight'
print(str1[2:4])
print(str1[-4:-1]) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py
nl
igh
4.字符串拼接
# 字符串拼接
str1 = 'sunlight'
str2 = 'hello ' print(str2 + str1)
print(str1[2:4] + str2[1:3]) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py
hello sunlight
nlel
5.遍历字符串
# 遍历字符串
str1 = 'sunlight'
for i in str1:
print(i) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py
s
u
n
l
i
g
h
t Process finished with exit code 0
python中的转义字符:就是用反斜杠开头的字符串,表示特定的意义,常见的转义字符如表中所示
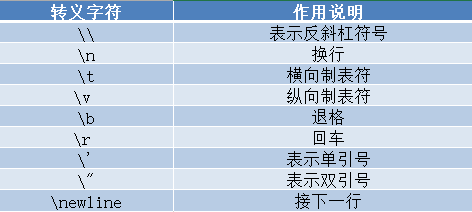
# 转义示例
str4 = """On a new day,the sun rises in the East"""
str5 = 'what\t do\b you \v do'
str6 = 'What\'s this?'
str7 = "It's \"cat\""
print(str4, "\n", str5, "\n", str6, "\n", str7) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py
On a new day,the sun rises in the East
what d you do
What's this?
It's "cat" Process finished with exit code 0
python中字符串常用的运算符
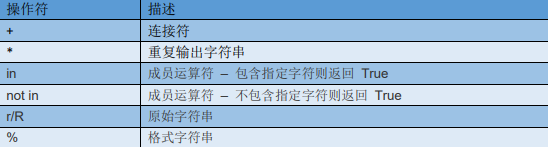
# 运算符示例
str1 = 'sun' + 'light '
s = "r" in str1
t = "r" not in str1
w = r'\n' + R'\t'
z = 3.14159 print(str1, str1*3 + "\n", s, t, "\n" + w)
print("Π的值是%s:" % z) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py
sunlight sunlight sunlight sunlight
False True
\n\t
Π的值是3.14159: Process finished with exit code 0
改变字符串:
在数组中可以通过下标直接更改值,但是字符串中同样的操作会提示“'str' object does not support item assignment”
# 变更字符串
str1 = 'sunlight'
str1[0] = "D"
print(str) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "D:/demo/str_1.py", line 52, in <module>
str1[0] = "D"
TypeError: 'str' object does not support item assignment Process finished with exit code 1
通过创建新的字符串间接更改
# 创建新的字符串间接更改
str1 = 'sunlight'
s = "S" + str1[1:]
t = str1.replace("s", "S")
str1 = s
print(str1, t) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py
Sunlight Sunlight Process finished with exit code 0
通过符号 += 更改
# 通过 += 符号 更改
str1 = 'sun'
str1 += 'light'
print(str1) info = "start "
for s in str1:
info += s
print(info) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py
sunlight
start sunlight Process finished with exit code 0
python中的字符串格式化
字符串格式化可以理解为将实际值插入模板中
# 使用%实现字符串格式化
student = {"张三": 19, "李四": 20, "王五": 20}
for info in student:
print("学生 %s的年龄为 %s" % (info, student[info])) # 使用string.format()方法实现字符串格式化
prices = {"apple": 8.99, "banana": 6.99, "orange": 7.99}
for price in prices:
print("水果 {}的单价为 {}".format(price, prices[price])) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py
学生 张三的年龄为 19
学生 李四的年龄为 20
学生 王五的年龄为 20
水果 apple的单价为 8.99
水果 banana的单价为 6.99
水果 orange的单价为 7.99 Process finished with exit code 0
常用字符串内建函数
string.split(sep, maxsplit):maxsplit给定值max,sep在字符串中出现的次数为num, 且给定的值0<= max <=num,以sep作为分隔符进行切片字符串,则分割max+1个字符串,若max不传(不传时默认为-1)或者传入的值大于num,则默认分割num+1个字符串,并返回由字符串组成的数组
str1 = 'sunlight'
r = str1.split("l") # maxsplit不传时,默认为-1,返回1+1个字符
s = str1.split("l", 0) # maxsplit传入0则返回0+1个字符
t = str1.split("l", 3) # maxsplit传入值大于分隔符出现的次数,返回1+1个字符
w = str1.split() # sep 不传时,默认为空白字符
print(r, "\n", s, "\n", t, "\n", w) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py
['sun', 'ight']
['sunlight']
['sun', 'ight']
['sunlight'] Process finished with exit code 0
string.strip(chars): 从起始至末尾去掉指定的chars,若不指定默认去除字符串左边空格和末尾空格(相当于执行了string.lstrip()和string.rstrip()),并返回去除后的字符串
# 常用内建函数
str1 = ' sunlight '
t = str1.strip()
w = str1.strip("t ")
print(t)
print(str1)
print(w) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py
sunlight
sunlight
sunligh Process finished with exit code 0
string.rstrip(chars): 右起去掉指定的chars,若不指定默认去除字符串末尾空格,并返回去除后的字符串
# 常用内建函数
str1 = ' sunlight '
x = str1.rstrip()
y = str1.rstrip("t ")
print(str1)
print(x)
print(y) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py
sunlight
sunlight
sunligh Process finished with exit code 0
string.lstrip(chars): 左起删除指定的chars,若不指定默认去除字符串左边空格,并返回去除后的字符串
# 常用内建函数
str1 = ' sunlight '
z = str1.lstrip()
t = str1.lstrip(' su')
print(z)
print(t) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py
sunlight
nlight Process finished with exit code 0
string.find(sub, start, end):检测字符串中是否包含指定字符串sub,如果包含则返回首次出现的位置索引值,否则返回-1,start、end非必填,若指定start、end则在指定范围内查找
# 常用内建函数
str1 = 'sunlightn'
a = str1.find("n") # 字符串中含有n,返回首次出现的位置索引值2
b = str1.find("n", 3) # 从索引为3开始检测,返回首次出现的位置索引值8
c = str1.find("n", 0, 2) # 从索引[0, 2)开始检测,检测不到返回-1
print(a, b, c) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py
2 8 -1 Process finished with exit code 0
string.rfind(sub, start, end):用法与find类似,区别在返回指定sub最后出现的位置索引值,否则返回-1
# 常用内建函数
str1 = 'sunlightn'
e = str1.rfind("n") # 字符串中含有n,返回最后出现的位置索引值8
f = str1.rfind("n", 0, 3) # 从索引[0, 3)开始检测
print(e, f) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py
8 2 Process finished with exit code 0
string.count(sub, start, end):返回指定sub在字符串中出现的次数,若指定start、end则在指定范围内统计
# 常用内建函数
str1 = ' sunlight '
j = str1.count(" ")
k = str1.count(" ", 2, 9)
print(j, k) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py
5 2 Process finished with exit code 0
python 之字符串的使用的更多相关文章
- Python格式化字符串~转
Python格式化字符串 在编写程序的过程中,经常需要进行格式化输出,每次用每次查.干脆就在这里整理一下,以便索引. 格式化操作符(%) "%"是Python风格的字符串格式化操作 ...
- python学习--字符串
python的字符串类型为str 定义字符串可以用 ‘abc' , "abc", '''abc''' 查看str的帮助 在python提示符里 help(str) python基于 ...
- Python格式化字符串和转义字符
地址:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-20794157-id-3038417.html Python格式化字符串的替代符以及含义 符 号 说 明 ...
- [转载] python 计算字符串长度
本文转载自: http://www.sharejs.com/codes/python/4843 python 计算字符串长度,一个中文算两个字符,先转换成utf8,然后通过计算utf8的长度和len函 ...
- Python基础-字符串格式化_百分号方式_format方式
Python的字符串格式化有两种方式: 百分号方式.format方式 百分号的方式相对来说比较老,而format方式则是比较先进的方式,企图替换古老的方式,目前两者并存.[PEP-3101] This ...
- python判断字符串
python判断字符串 s为字符串s.isalnum() 所有字符都是数字或者字母s.isalpha() 所有字符都是字母s.isdigit() 所有字符都是数字s.islower() 所有字符都是小 ...
- Python格式化字符串
在编写程序的过程中,经常需要进行格式化输出,每次用每次查.干脆就在这里整理一下,以便索引. 格式化操作符(%) "%"是Python风格的字符串格式化操作符,非常类似C语言里的pr ...
- python(七)字符串格式化、生成器与迭代器
字符串格式化 Python的字符串格式化有两种方式:百分号方式.format方式 1.百分号的方式 %[(name)][flags][width].[precision]typecode (name) ...
- Python 的字符串格式化和颜色控制
(部分内容源自武神博客和网络收集.) Python的字符串格式化有两种方式: 百分号方式.format方式 百分号的方式相对来说比较老,而format方式则是比较先进的方式,企图替换古老的方式,目前两 ...
- python反转字符串(简单方法)及简单的文件操作示例
Python反转字符串的最简单方法是用切片: >>> a=' >>> print a[::-1] 654321 切片介绍:切片操作符中的第一个数(冒号之前)表示切片 ...
随机推荐
- 1_Linux
一. Linux介绍 1.1 引言 在学习Linux之前, 大家先了解开发环境,生产,测试环境 开发环境: 平时大家大多是在Windows或者Mac操作系统下去编写代码进行开发,在开发环境中安装大量的 ...
- 如何通过 Java 代码隐藏 Word 文档中的指定段落
在编辑Word文档时,我们有时需要将一些重要信息保密. 因此,可以隐藏它们以确保机密性. 在本文中,将向您介绍如何通过 Java 程序中的代码隐藏 Word 文档中的特定段落.下面是我整理的具体步骤, ...
- C#-7 结构和枚举
一 什么是结构 结构是程序员定义的数据类型,有数据成员和函数成员,和类非常类似. 类是引用类型,而结构是值类型: 结构和类一样可以实现接口: 结构是隐式密封的,不能被派生: 结构类型的变量不能为nul ...
- 洛谷P2866 [USACO06NOV]Bad Hair Day S (单调栈)
看到这道题很容易想到单调栈,但我一开始想的是从后往前扫,但发现会有问题(因为这样会对后面牛的答案造成影响),所以这时我们要及时换一个思路,从前往后扫. 维护一个单调递减的栈,插入h[i]时,小等于它的 ...
- GMOJ5673 爬山法 题解
Solution 显然先想到处理出每个点能看到的最高的顶点. 然后考虑模拟题目的过程,一段一段走时间复杂度显然不够优秀. 考虑我们要求什么,我们需要求出\(u\)到\(v\)的最近的一个点,使得这个点 ...
- RMarkdown进阶操作
技术背景 Markdown大家都比较熟悉了,特别是在写程序文档和写数学公式时,拥有着无与伦比的便利性.同时在前面的一篇博客中我们介绍了使用RMarkdown去写Latex Beamer演示文档的方法, ...
- 齐博x1标签实例:做模板组图单图无图混排的处理
代码如下, {qb:tag name="xxx" type="cms" rows="10"} {if ( count($rs['picurl ...
- CF39H
前言 谁来给我讲讲九九乘法表啊. 以上菲克向. \(\sf{Solution}\) 看题上来就是数据范围 \(2\leq k\leq 10\) ,显然打表可以轻松水过,数据这么小,手算是没问题的啦. ...
- 将vue+nodejs项目部署到服务器上(完整版)
1.后端使用express生成器 1.1.后台node项目部署 在node项目里安装cors依赖(跨域)npm install cors --save,在app.js文件中使用var cors = r ...
- 论文笔记 - MetaICL: Learning to Learn In Context
Motivation Facebook 的 MetaICL,牛逼就对了: 对 LM 针对 ICL 进行微调(而不是特定的任务): 去除了自然语言的 Template,使用更直接的方式,排除了 Temp ...
