AbstractList源码分析
AbstractList
1 类图
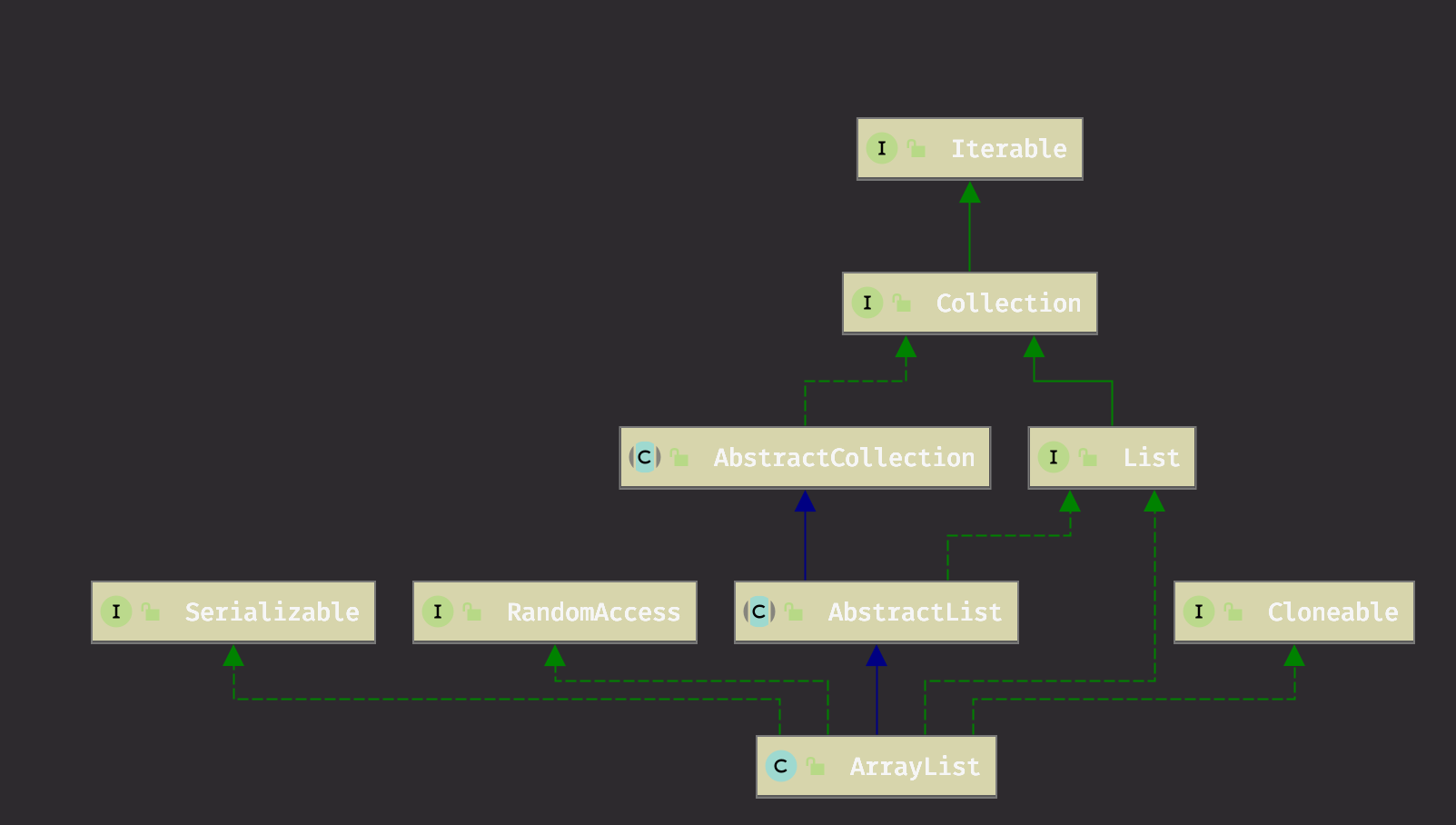
2 字段
// 默认容量
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
// 共享的空数组
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
// 共享个空数组,和EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA空数组相比是用于了解当添加第一个元素时数组应该扩容多少
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* ArrayList存储元素的buffer, ArrayList的容量就是这个数组buffer的长度
* 任何拥有DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA空数组的ArrayList在第一次
* 添加元素的时候都会扩容到DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10
*/
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
// 持有元素的个数
private int size;
3 构造器
/**
* 无参数的ArrayList的元素数组是DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
*/
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
/**
* 初始容量为0的ArrayList的元素数组是EMPTY_ELEMENTDAT
*/
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
/**
* 根据collection的迭代器返回的数据顺序构造一个ArrayList
*/
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) {
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
} else {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
}
4 增
/**
* 往列表末尾增加元素
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
- 先内部确认容量
- 数组buffer末尾添加元素
- 返回true
// 最小容量是当前size+1
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
// 如果当前的元素数组是DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
// 那么最小容量取min(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, size+1)
// 否则直接取size+1
// 可以认为如果指定了容量,那么对容量的预期越低吗?
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
// 确认容量的核心方法,然后扩容
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
// 修改次数++
modCount++;
// 如果最小容量大于当前数组buffer的长度,那么需要扩容的
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
/**
* 最大数组长度
*/
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
/**
* 扩容,最起码可以容纳minCapacity个元素
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
// 新容量是老容量1.5倍
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
// 取minCapacity和newCapacity的更小值
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
// 如果大于最大数组长度,再处理
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
// 溢出则抛出错误
// 如果大于MAX_ARRAY_SIZE,取Integer最大值,否则取MAX_ARRAY_SIZE
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
5 删除
/**
* 删除指定位置的元素,剩余右边元素都需要向左边移动一位
*/
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
// 修改次数+1
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null;
return oldValue;
}
/**
* 索引边界检查
*/
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
7 更新
/**
* 替换指定位置上的元素
*/
public E set(int index, E element) {
rangeCheck(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
8 查询
/**
* 返回指定位置元素
*/
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
return elementData(index);
}
/**
* 返回指定元素第一次出现的索引,如果没有返回-1
*/
public int indexOf(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
9 遍历
/**
* 返回一个迭代器
*/
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Itr();
}
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
int cursor; // 下一个返回的元素的索引
int lastRet = -1; // 上一个返回的元素的索引,如果没有则返回-1
int expectedModCount = modCount; // 期望的修改数目以及实际的修改数目
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != size;
}
// 如果实际修改次数和期望修改次数不相等则抛出ConcurrentModificationException
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
// 往后遍历,游标+1
cursor = i + 1;
// 上一个返回的元素的索引是i
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
// 调用ArrayList.remove,modCount++
ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);
// 下一个游标还是当前元素,比如说上一个索引0,数字2
// 下一个索引1,数字3,当前游标是1
// 删除2后,游标变成0,还会返回3
// 那么上一个返回的元素就没有了,索引置-1
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
// 这里把expectedModCount设置为删除后的modCount
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> consumer) {
Objects.requireNonNull(consumer);
final int size = ArrayList.this.size;
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size) {
return;
}
final Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
while (i != size && modCount == expectedModCount) {
consumer.accept((E) elementData[i++]);
}
// update once at end of iteration to reduce heap write traffic
cursor = i;
lastRet = i - 1;
checkForComodification();
}
}
/**
* An optimized version of AbstractList.ListItr
*/
private class ListItr extends Itr implements ListIterator<E> {
ListItr(int index) {
super();
cursor = index;
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return cursor != 0;
}
public int nextIndex() {
return cursor;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return cursor - 1;
}
// 可以向前遍历
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor - 1;
if (i < 0)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i;
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
ArrayList.this.set(lastRet, e);
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification();
try {
int i = cursor;
ArrayList.this.add(i, e);
cursor = i + 1;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
}
AbstractList源码分析的更多相关文章
- 集合源码分析[2]-AbstractList 源码分析
AbstractList 类型:抽象类 接口的继承以及实现关系 继承AbstractCollection 实现List接口 典型方法实现解析 public List<E> subList( ...
- 集合源码分析[3]-ArrayList 源码分析
历史文章: Collection 源码分析 AbstractList 源码分析 介绍 ArrayList是一个数组队列,相当于动态数组,与Java的数组对比,他的容量可以动态改变. 继承关系 Arra ...
- 【集合框架】JDK1.8源码分析之ArrayList(六)
一.前言 分析了Map中主要的类之后,下面我们来分析Collection下面几种常见的类,如ArrayList.LinkedList.HashSet.TreeSet等.下面通过JDK源码来一起分析Ar ...
- JDK Collection 源码分析(2)—— List
JDK List源码分析 List接口定义了有序集合(序列).在Collection的基础上,增加了可以通过下标索引访问,以及线性查找等功能. 整体类结构 1.AbstractList 该类作为L ...
- Java集合源码分析(二)ArrayList
ArrayList简介 ArrayList是基于数组实现的,是一个动态数组,其容量能自动增长,类似于C语言中的动态申请内存,动态增长内存. ArrayList不是线程安全的,只能用在单线程环境下,多线 ...
- Java集合系列:-----------03ArrayList源码分析
上一章,我们学习了Collection的架构.这一章开始,我们对Collection的具体实现类进行讲解:首先,讲解List,而List中ArrayList又最为常用.因此,本章我们讲解ArrayLi ...
- Java集合类源码分析
常用类及源码分析 集合类 原理分析 Collection List Vector 扩充容量的方法 ensureCapacityHelper很多方法都加入了synchronized同步语句,来保 ...
- Java中ArrayList源码分析
一.简介 ArrayList是一个数组队列,相当于动态数组.每个ArrayList实例都有自己的容量,该容量至少和所存储数据的个数一样大小,在每次添加数据时,它会使用ensureCapacity()保 ...
- Java集合之ArrayList源码分析
1.简介 List在数据结构中表现为是线性表的方式,其元素以线性方式存储,集合中允许存放重复的对象,List接口主要的实现类有ArrayList和LinkedList.Java中分别提供了这两种结构的 ...
随机推荐
- E - Max Sum Plus Plus Plus HDU - 1244 (线性区间DP)
题目大意: 值得注意的一点是题目要求的是这些子段之间的最大整数和.注意和Max Sum Plus Plus这个题目的区别. 题解: 线性区间DP,对每一段考虑取或者不取.定义状态dp[i][j]指的 ...
- 深度学习之文本分类模型-前馈神经网络(Feed-Forward Neural Networks)
目录 DAN(Deep Average Network) Fasttext fasttext文本分类 fasttext的n-gram模型 Doc2vec DAN(Deep Average Networ ...
- Navicat自动备份数据库
@ 目录 Navicat自动备份数据库 备份与还原 修改备份位置 MySQL:5.7 Navicat:11 Windows10 重要数据库的定时备份是非常重要的,使用Navicat可以非常方便快捷地自 ...
- vue2.x学习笔记(十三)
接着前面的内容:https://www.cnblogs.com/yanggb/p/12595860.html. 组件的注册 注册组件有一些规范约定与注意事项. 组件名的命名规范 在注册一个组件的时候, ...
- gridview 合并单元格后,选中颜色重新绘制
gv_docargo.RowStyle += OnRowStyle; private void OnRowStyle(object sender, DevExpress.XtraGrid.Views. ...
- dhcp协议抓包分析
dhcp协议 DHCP,动态主机配置协议,前身是BOOTP协议,是一个局域网的网络协议,使用UDP协议工作,常用的2个端口:67(DHCP server),68(DHCP client). wires ...
- Java反射机制概念及使用
反射机制 —— 将类中的所有成员反射成对于的类. 以“com.test.Person”类为例 转换对应的类 获取方法 ...
- 学习 .net core 3----蒋金楠 笔记 构建 Asp.net core Web应用
前言:准备系统的学习一下.net core 所以购买了 蒋金楠的 ASP.NET CORE 3 书籍,为了加深印象 特此笔记,会持续更新到学习完为止 使用 命令行 dotnet new co ...
- swift 3.0字符串的简单使用
let str:String = "12314124" 获取某个指定位置的元素 print(str.characters[str.index(str.startIndex, off ...
- 详解Linux 安装 JDK、Tomcat 和 MySQL(图文并茂)
https://www.jb51.net/article/120984.htm
