git reset --soft --hard 区别
以下为转发的正文
The reset command. Confusing. Misunderstood. Misused. But it doesn’t need to be that way! It’s really not too confusing once you figure out what’s going on.
Definitions
首先,让我们来解释几个定义.
First, let’s define a few terms.
HEAD(头)
指向当前branch最顶端的一个commit,该分支上一次commit后的节点
This is an alias for the tip of the current branch, which is the most recent commit you have made to that branch.
Index(索引)
The index, 也可以被认为是staging area(暂存区), 是一堆将在下一次commit中提交的文件,提交之后它就是 HEAD的父节点. (译注:git add添加的文件)
The index, also known as the staging area, is the set of files that will become the next commit. It is also the commit that will become HEAD’s parent.
Working Copy(工作副本)
当前工作目录下的文件,(译注:一般指,有修改,没有git add,没有git commit的文件)
This is the term for the current set of files you’re working on in your file system.
Flow(流程如下)
当你第一次checkout一个新的分支,HEAD指向该分支上最近一次commit。它和index和working copy是一样一样的。
When you first checkout a branch, HEAD points to the most recent commit in the branch. The files in the HEAD (they aren’t technically files, they’re blobs but for the purposes of this discussion we can think of them as straight files) match that of the files in the index, and the files checked out in your working copy match HEAD and the index as well. All 3 are in an equal state, and Git is happy.
当你修改了一个文件,Git注意到了会说“哦,有些东西被改了”,你的working copy不再和index和HEAD相同了,所以当文件有改动,它会标记这些文件。
When you perform a modification to a file, Git notices and says “oh, hey, something has changed. Your working copy no longer matches the index and HEAD.” So it marks the file as changed.
然后,你执行git add命令,这条命令会将上面修改的文件缓存在index中,Git又说了“哦,你的working copy和index相同了,而他们俩和HEAD不同了”。
Then, when you do a git add, it stages the file in the index, and Git says “oh, okay, now your working copy and index match, but those are both different than HEAD.”
当你执行git commit,Git创建了一个新的commit,HEAD这时指向这个新的commit,此时,HEAD & index & working copy又相同了,Git又开心了一次。
When you then perform a git commit, Git creates a new commit that HEAD now points to and the status of the index and working copy match it so Git’s happy once more.
Reset
If you just look at the reset command by itself, all it does is reset HEAD (the tip of the current branch) to another commit. For instance, say we have a branch (the name doesn’t matter, so let’s call this one “super-duper-feature”) and it looks like so:
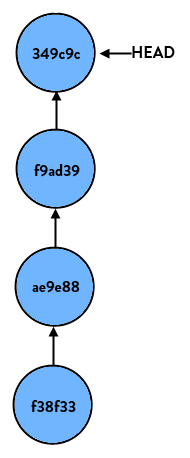
If we perform:
> git reset HEAD… nothing happens. This is because we tell git to reset this branch to HEAD, which is where it already is. But if we do:
> git reset HEAD~1(HEAD~1 is shorthand case for “the commit right before HEAD”, or put differently “HEAD’s parent”) our branch now looks like so:
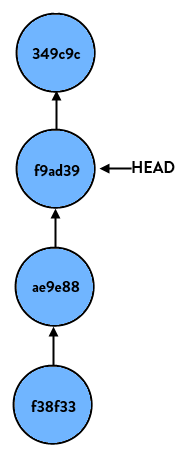
If we start at the latest commit again and do:
> git reset HEAD~2our branch would look like so:
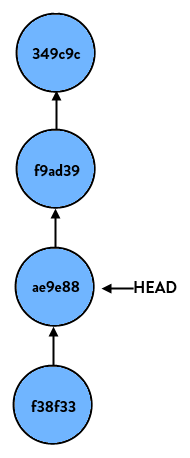
Again, all it does on a basic level is move HEAD to another commit.
Parameters
reset命令本身很简单,但是它的参数让人迷惑,主要的参数有soft, hard and mixed,它们告诉Git,当执行reset时,要对index和working copy做什么。
So the reset command itself is pretty simple, but it’s the parameters that cause confusion. The main parameters are soft, hard and mixed. These tell Git what to do with your index and working copy when performing the reset.
Soft
The --soft参数只告诉Git将其他的commit重置到HEAD,就仅此而已。index和working copy中的文件都不改变。
parameter tells Git to reset HEAD to another commit, but that’s it. If you specify --soft Git will stop there and nothing else will change. What this means is that the index and working copy don’t get touched, so all of the files that changed between the original HEAD and the commit you reset to appear to be staged.

Mixed (default)
The --mixed 改变HEAD和index,指向那个你要reset到的commit上。而working copy文件不被改变。当然会显示工作目录下有修改,但没有缓存到index中。
parameter (which is the default if you don’t specify anything) will reset HEAD to another commit, andwill reset the index to match it, but will stop there. The working copy will not be touched. So, all of the changes between the original HEAD and the commit you reset to are still in the working copy and appear as modified, but not staged.

Hard
The --hard HEAD & index & working copy同时改变到你要reset到的那个commit上。这个参数很危险,执行了它,你的本地修改可能就丢失了。
parameter will blow out everything – it resets HEAD back to another commit, resets the index to match it, and resets the working copy to match it as well. This is the more dangerous of the commands and is where you can cause damage. Data might get lost here*!

可以用git reflog命令查看coomit ID,恢复到reset之前的状态。
* You can recover it using
git reflog but that’s out of scope here.
转自:http://davidzych.com/2014/05/24/difference-between-git-reset-soft-mixed-and-hard/
git reset --soft --hard 区别的更多相关文章
- 『现学现忘』Git后悔药 — 28、版本回退git reset --soft命令说明
git reset --soft commit-id命令:回退到指定版本.(soft:柔软的) 该命令仅仅修改分支中的HEAD指针的位置,不会改变工作区与暂存区中的文件的版本. 实现上是只做了一件事情 ...
- git reset soft,hard,mixed之区别深解
GIT reset命令,似乎让人很迷惑,以至于误解,误用.但是事实上不应该如此难以理解,只要你理解到这个命令究竟在干什么. 首先我们来看几个术语 HEAD 这是当前分支版本顶端的别名,也就是在当前分支 ...
- 撤销git reset soft head操作
一不小心在eclipse的git库中执行了Reset Soft(HEAD ONLY)操作,不料界面中竟然没有找到撤销方法(于是心中五味俱全,经过一番折腾,无果还是回归Git本身),最终通过命令行,很快 ...
- git reset 与 git revert的区别?
一,git reset的功能: 该命令修改HEAD的位置,即将HEAD指向的位置改变为之前存在的某个版本, 说明: 修改后,push到远程仓库时需要使用"git push -f"提 ...
- git reset、git checkout和git revert的区别
这三个git命令都是用来撤销代码仓库中的某些更改,而前两个命令不仅可以作用于commit层面,还可以作用于file层面Reset在commit层面,reset通过移除当前分支的一些节点来实现版本回滚; ...
- git reset与git revert的区别
http://alpha-blog.wanglianghome.org/2010/07/30/git-partial-rollback/ reset(版本撤回) 格式 git reset [-q] [ ...
- git reset revert区别
git revert HEAD~1 撤销倒数第二次提交,并将这次操作作为一个新提交添加到log里,之前的提交历史不变,是撤销某次提交 git reset,直接回退到指定版本 git reset --s ...
- git revert和git reset的区别
git revert 是撤销某次操作,此次操作之前的commit都会被保留 git reset 是撤销某次提交,但是此次之后的修改都会被退回到暂存区 具体一个例子,假设有三个commit, git s ...
- git --mixed --soft --hard之间的区别
git reset --mixed:此为默认方式,不带任何参数的git reset,即时这种方式,它回退到某个版本,只保留源码,回退commit和add信息git reset --soft:回退到某个 ...
随机推荐
- vue 跟路径加载缺少跟前缀
vue 加载资源失败:跟路径残缺,都是配置时 一个正斜杠 / 多余惹的祸
- [转]SQLite 经验集
SQLite 的默认时间 转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/pennant/archive/2011/08/11/2134897.html select strftime('%Y-% ...
- nginx上传文件大小
采用nginx作反向代理,出现了一个诡异的问题,小文件可以提交,大文件会报500内部错误.这个是什么原因导致的呢? 查wiki可知,上传文件大小相关的有三个配置 client_body_buffer_ ...
- 关于git rebase的相关讲解
http://gitbook.liuhui998.com/4_2.html 一.基本 git rebase用于把一个分支的修改合并到当前分支. 假设你现在基于远程分支"origin" ...
- Go - 基础知识
经历了五一小假期,前后差不多一周多没有坚持学习了,所以在归来的第一时间继续 Go 的学习之旅. Go 程序的基本结构 首先先贴出一段简单的代码:HelloGo.go // HelloGo packag ...
- Web页面工作流设计器
http://www.cnblogs.com/2018/archive/2011/11/22/2240259.html http://wenku.baidu.com/link?url=LSqlCiqi ...
- Centos如何设置IP地址,LINUX怎么修改IP地址
对于很多刚刚接触linux的朋友来说,如何设置linux系统的IP地址,作为第一步,下面小编以centos系统为例,给大家演示如何给centos设置IP地址,如何修改linux 系统IP地址? 步骤阅 ...
- Xming配置
提要:一般服务器是以命令模式运行,所以缺少图形化界面.当我们需要在本机进行一些测试时,这也算是一个困扰我们的问题.所以在Xming+CRT可以为我们解决此问题.请看一下介绍: 1.windows环境下 ...
- EasyUI介绍及常见问题
JQuery Easy UI介绍 1.JQuery Easy UI环境搭建和调试: https://jingyan.baidu.com/article/67508eb4342f9f9cca1ce426 ...
- ansible自动化运维工具使用详解
一. ansible 简介 1. ansible ansible是新出现的 自动化 运维工具 , 基于Python研发 . 糅合了众多老牌运维工具的优点实现了批量操作系统配置.批量程序的部署.批量运行 ...

 (2014-09-09 16:54:06)
(2014-09-09 16:54:06)