MyBatis从入门到放弃六:延迟加载、一级缓存、二级缓存
前言
使用ORM框架我们更多的是使用其查询功能,那么查询海量数据则又离不开性能,那么这篇中我们就看下mybatis高级应用之延迟加载、一级缓存、二级缓存。使用时需要注意延迟加载必须使用resultMap,resultType不具有延迟加载功能。
一、延迟加载
延迟加载已经是老生常谈的问题,什么最大化利用数据库性能之类之类的,也懒的列举了,总是我一提到延迟加载脑子里就会想起来了Hibernate get和load的区别。OK,废话少说,直接看代码。 先来修改配置项xml。
注意,编写mybatis.xml时需要注意配置节点的先后顺序,settings在最前面,否则会报错。
<settings>
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>
<setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/>
</settings>

前面提到延迟加载只能通过association、collection来实现,因为只有存在关联关系映射的业务场景里你才需要延迟加载,也叫懒加载,也就是常说的用的时候再去加载。OK,那么我们来配一个association来实现:
我来编写一个加载博客列表的同时加载出博客额作者, 主要功能点在id为blogAuthorResumtMap这个resultmap上,其中使用了association,关键点是它的select属性,该属性也就是你需要懒加载调用的statment id。 当然需要懒加载的statement 返回值当然是resultmap
<resultMap id="blogAuthorResumtMap" type="Blog">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="title" property="title"/>
<result column="category" property="category"/>
<result column="author_id" property="author_id"/>
<!--使用assocition支持延迟加载功能,配置延迟加载关联关系-->
<association property="author" javaType="Author" select="selectAuthorById" column="author_id"/>
</resultMap> <!--要使用延迟记载的方法-->
<select id="selectBlogAuthor" resultMap="blogAuthorResumtMap">
SELECT id,title,category,author_id FROM t_blog
</select> <!--延迟加载查询博客对应的作者方法-->
<select id="selectAuthorById" parameterType="int" resultType="Author">
SELECT id,name from t_author where id=#{value}
</select>
OK,来看测试结果:
@Test
public void getBlogAuthorByLazyloading(){
SqlSession sqlSession=null;
try{
sqlSession=sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
List<Blog> list = sqlSession.selectList("com.autohome.mapper.Author.selectBlogAuthor"); for (Blog blog:list) {
System.out.println("id:"+blog.getId()+",title:"+blog.getTitle()+",category:"+blog.getCategory());
System.out.println("author:"+blog.getAuthor().getName());
} }catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
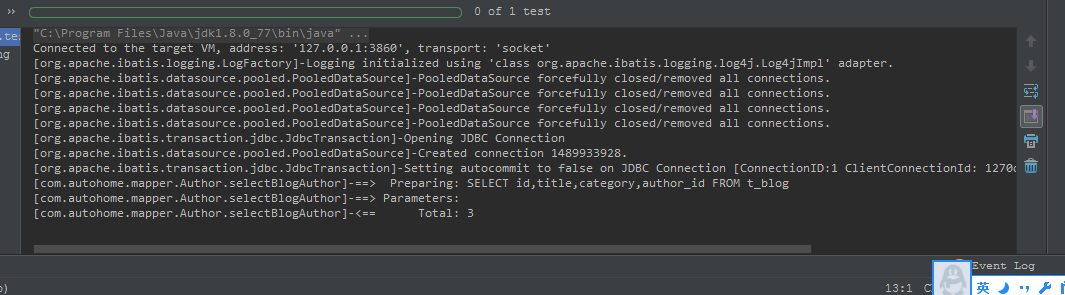
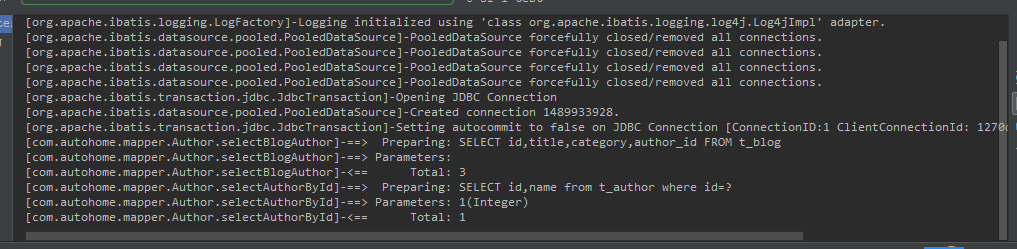
从图一中看出,执行selectBlogAuthor返回List<Blog>对象时只执行了SQL SELECT id,title,category,author_id from t_blog,循环遍历时才去执行select id,name from t_author where id=?。
二、一级缓存
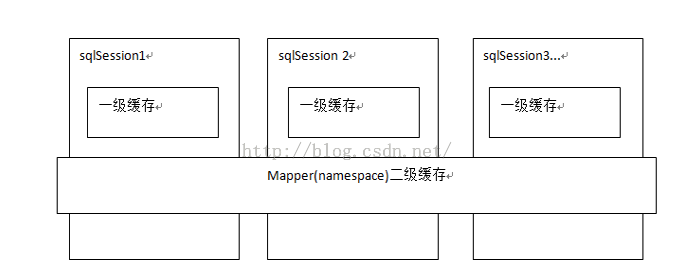
了解缓存前我们先看一张图片(图片来源于传智播客视频图片)。从图中可以了解一级缓存是sqlsession级别、二级缓存是mapper级别。在操作数据库时我们需要先构造sqlsession【默认实现是DefaultSqlSession.java】,在对象中有一个数据结构【hashmap】来存储缓存数据。不同的sqlsession区域是互不影响的。 如果同一个sqlsession之间,如果多次查询之间执行了commit,则缓存失效,mybatis避免脏读。
OK,在看mybatis一级缓存时,我总是觉的一级缓存有点鸡肋,两个查询如果得到一样的数据,你还会执行第二次么,果断引用第一次的返回值了。 可能还没了解到一级缓存的奥妙之处。一级缓存默认是开启的,不需要额外设置,直接使用。
public void testCache(){
SqlSession sqlSession=null;
try{
sqlSession=sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
Author author = sqlSession.selectOne("com.autohome.mapper.Author.selectAuthorById",1);
System.out.println("作者信息 id:"+author.getId()+",name:"+author.getName());
author = sqlSession.selectOne("com.autohome.mapper.Author.selectAuthorById",1);
System.out.println("作者信息2 id:"+author.getId()+",name:"+author.getName());
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
sqlSession.close();
}
}

从DEBUG截图来看,当我们第一次调用方法时执行了SELECT id,name from t_author where id=? 此时缓存中还没有该数据,则执行数据库查询,当再次执行时直接从缓存中读取。
执行demo后我们来看下这个查询过程保存到缓存的源码,先看下DefaultSqlSession.java。我们调用的selectOne(),从代码中看它是直接调用selectList()然后判断返回值size大小。
@Override
public <T> T selectOne(String statement) {
return this.<T>selectOne(statement, null);
} @Override
public <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {
// Popular vote was to return null on 0 results and throw exception on too many.
List<T> list = this.<T>selectList(statement, parameter);
if (list.size() == 1) {
return list.get(0);
} else if (list.size() > 1) {
throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size());
} else {
return null;
}
}
再跟踪到selectList方法,看到先构造MappedStatement对象,然后看到真正执行query()的是一个executor对象,在DefaultSqlSession.java中executor是成员变量,再翻到org.apache.ibatis.executor包中看到executor实际是一个接口。OK,那么我们debug时发现其引用是CachingExecutor。再打开CachingExecutor.java
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
从CachingExecutor.java的两个query()可以看到先去构造CacheKey 再调用抽象类BaseExecutor.query(),这个也是最关键的一步。
//先创建CacheKey
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
} //再执行查询方法
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, parameterObject, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
list = delegate.<E> query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
return delegate.<E> query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
BaseExecutor.java
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
queryStack++;
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
deferredLoads.clear();
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
再看其中关键代码queryFromDatabase
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
localCache.putObject(key, list);
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}
OK,看了一长串,终于是有点眉目了,我们看到finally中先删除当前key缓存,然后再调用localCache.putObject把最新的结果集存入HashMap中。
三、二级缓存
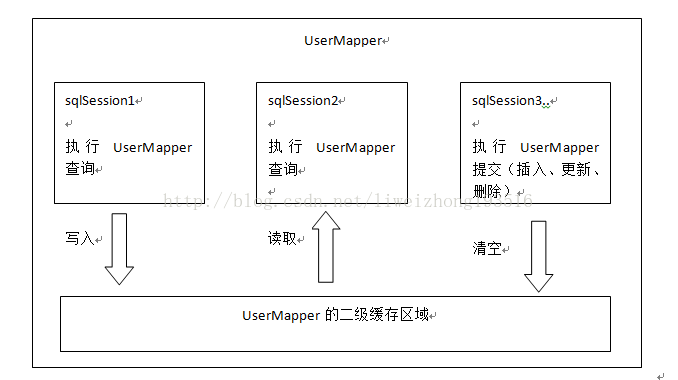
了解二级缓存之前先来看副图(图片来自传智播客视频,非本人编写),那么从图中我们可以看出,mybatis二级缓存是mapper级别,也就是说不同的sqlmapper共享不同的内存区域,不同的sqlsession共享同一个内存区域,用mapper的namespace区别内存区域。
开启mybatis二级缓存: 1、设置mybatis.xml,也就是说mybatis默认二级缓存是关闭的。
2、设置mapper。在mapper.xml内添加标签:<cache/>
3、pojo实现接口Serializable。实现该接口后也就说明二级缓存不仅可以存入内存中,还可以存入磁盘。
OK,看一个二级缓存demo:
@Test
public void testCache2(){
SqlSession sqlSession=null;
SqlSession sqlSession2=null;
try{
sqlSession=sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
sqlSession2=sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); Author author = sqlSession.selectOne("com.autohome.mapper.Author.selectAuthorById",1);
System.out.println("作者信息 id:"+author.getId()+",name:"+author.getName());
sqlSession.close(); Author author2 = sqlSession2.selectOne("com.autohome.mapper.Author.selectAuthorById",1);
System.out.println("作者信息2 id:"+author2.getId()+",name:"+author2.getName());
sqlSession2.close();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally { }
}
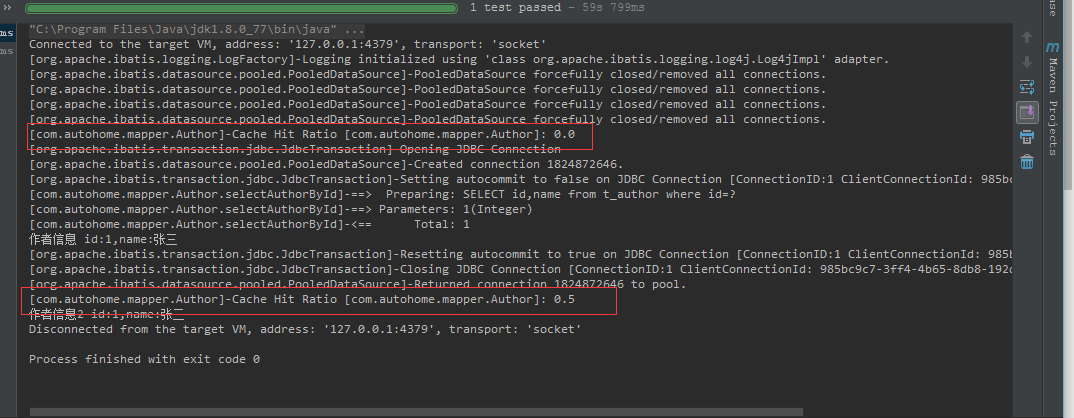
运行demo可以看出二级缓存不同的地方在于Cache Hit Ratio,发出sql查询时先看是否命中缓存,第一次则是0.0 ,再次查询时则直接读取缓存数据,命中率是0.5。当然数据结构还是HashMap。
如果数据实时性要求比较高,可以设置select 语句的
如果数据的查询实时性要求比较高,则设置select语句的useCache="false",则每次都直接执行sql。
<select id="selectBlogAuthor" resultMap="blogAuthorResumtMap" useCache="false">
SELECT id,title,category,author_id FROM t_blog
</select>
参考
http://www.cnblogs.com/DoubleEggs/p/6243223.html
http://blog.csdn.net/isea533/article/details/44566257
MyBatis从入门到放弃六:延迟加载、一级缓存、二级缓存的更多相关文章
- MyBatis基础入门《十六》缓存
MyBatis基础入门<十六>缓存 >> 一级缓存 >> 二级缓存 >> MyBatis的全局cache配置 >> 在Mapper XML文 ...
- Mybatis一级、二级缓存
Mybatis一级.二级缓存 一级缓存 首先做一个测试,创建一个mapper配置文件和mapper接口,我这里用了最简单的查询来演示. <mapper namespace="c ...
- 170214、mybatis一级和二级缓存
mybatis一级缓存是指在内存中开辟一块区域,用来保存用户对数据库的操作信息(sql)和数据库返回的数据,如果下一次用户再执行相同的请求, 那么直接从内存中读数数据而不是从数据库读取. 其中数据的生 ...
- MyBatis(七):MyBatis缓存详解(一级缓存/二级缓存)
一级缓存 MyBatis一级缓存上SqlSession缓存,即在统一SqlSession中,在不执行增删改操作提交事务的前提下,对同一条数据进行多次查询时,第一次查询从数据库中查询,完成后会存入缓 ...
- Hibernate 再接触 一级缓存 二级缓存 查询缓存
缓存 就是把本来应该放在硬盘里的东西放在内存里 将来存内存里读 一级缓存: session缓存 二级缓存: sessionFactory级别的 (适合经常访问,数据量有限,改动不大) 很多的se ...
- hibernate的获取session的两方法比较,和通过id获取对象的比较,一级缓存二级缓存
opensession与currentsession的联系与区别 在同一个线程中opensession的session是不一样的,而currentsession获取的session是一样的,这就保证了 ...
- MyBatis从入门到放弃七:二级缓存原理分析
前言 说起mybatis的一级缓存和二级缓存我特意问了几个身边的朋友他们平时会不会用,结果没有一个人平时业务场景中用. 好吧,那我暂且用来学习源码吧.一级缓存我个人认为也确实有些鸡肋,mybatis默 ...
- MyBatis从入门到精通(六):MyBatis动态Sql之if标签的用法
最近在读刘增辉老师所著的<MyBatis从入门到精通>一书,很有收获,于是将自己学习的过程以博客形式输出,如有错误,欢迎指正,如帮助到你,不胜荣幸! 本篇博客主要讲解如何使用if标签生成动 ...
- mybatis一级缓存二级缓存
一级缓存 Mybatis对缓存提供支持,但是在没有配置的默认情况下,它只开启一级缓存,一级缓存只是相对于同一个SqlSession而言.所以在参数和SQL完全一样的情况下,我们使用同一个SqlSess ...
随机推荐
- 页面异步请求会保留原有的js内容
最近在开发前端的时候发现一个问题,这个问题应该是很多前端开发人员都容易忽视的一个问题,但却是一个很重要的问题. 就是在开发一个页面的时候,在使用某个函数时,这个函数可以正常使用,便会认为这个页面中定义 ...
- App的前后台数据同步
前言 在开发一个点餐软件时,app的订单数据是使用本地Sqlite数据库,在提交订单数据后,当订单数据在后台(Mysql数据库)发生变化时(如:已买单),本地数据如何改变呢? 思路 前台在查询时,将后 ...
- Asp.Net Core 中无法使用 ConfigurationManager.AppSettings
刚刚接触.net core ,准备把之前的一些技术常用工具先移植到.net Standard上面来, 方便以后使用,结果用到ConfigurationManager 的 AppSettings 就出现 ...
- 【PHP】PHP面向对象编程--phpOOP入门
PHP从入门到精通 之PHP的面相对象编程 面向对象编程(Object Oriented Programming, OOP, 面向对象程序设计)是一种计算机编程架构,OOP的一条基本原则是计算机程序 ...
- docker学习笔记--重基础使用
最近一直在研究Elasticsearch,后来部门的同事遇到了一个docker集群的未授权访问漏洞,于是稍微看了一下docker进行了一下基本的入门,本文把自己学习docker的过程进行了一个详细的记 ...
- 浅谈web服务器的编写之http协议
本书是介绍怎么编写一个Web服务器,而Web服务器是基于HTTP(HyperText Transfer Protocol)协议实现的,所以要实现一个Web服务器就必须了解HTTP协议,本章主要介绍HT ...
- nopCommerce 3.9 大波浪系列 之 IWebHelper
接口:Nop.Core.IWebHelper 实现:Nop.Core.WebHelper 测试:Nop.Core.Tests.WebHelperTests 简介:Web辅助类 功能:获取客户端IP地址 ...
- (转)ZXing解析二维码
1 ZXing解析二维码 上一篇文件已经说过如何用ZXing进行生成二维码和带图片的二维码,下面说下如何解析二维码 二维码的解析和生成类似,也可以参考google的一个操作类 BufferedImag ...
- (转)Java线程:新特征-线程池
Java线程:新特征-线程池 Sun在Java5中,对Java线程的类库做了大量的扩展,其中线程池就是Java5的新特征之一,除了线程池之外,还有很多多线程相关的内容,为多线程的编程带来了极大便利 ...
- (转) Spring Boot MyBatis 连接数据库
最近比较忙,没来得及抽时间把MyBatis的集成发出来,其实mybatis官网在2015年11月底就已经发布了对SpringBoot集成的Release版本,Github上有代码:https://gi ...
