pyecharts数据分析及展示
仅仅从网上爬下数据当然是不够用的,主要还得对数据进行分析与展示,大部分人都看重薪资,但是薪资数据有的是*k/月,有的是*万/月,还有*万/年等等,就要对数据进行清理
将所有单位统一化,全部换算成统一单位,然后分类薪资范围,在计算各个范围的数量,最后绘图展示
import pymysql
import numpy as np
from pyecharts import Bar
from pyecharts import Pie class Mysqlhelper(object):
config = {
"host": "localhost",
"user": "root",
"password": "",
"db": "test",
"charset": "utf8"
} def __init__(self):
self.connection = None
self.cursor = None # 从数据库中查询多行数据
def getlist(self, sql, *args):
try:
self.connection = pymysql.connect(**Mysqlhelper.config) # **接函数所有参数
self.cursor = self.connection.cursor()
self.cursor.execute(sql, args)
return self.cursor.fetchall()
except Exception as ex:
print(ex, ex)
finally:
self.close() def close(self):
if self.cursor:
self.cursor.close()
if self.connection:
self.connection.close() if __name__ == "__main__":
count=0
list = []
list1 = []
list2 = [5000,10000,15000,20000,25000,30000,35000,40000]
salary0 = []
salary1 = []
salary2 = []
salary3 = []
salary4 = []
salary5 = []
salary6 = []
salary7 = []
city=[]
helper = Mysqlhelper()
rows = helper.getlist("select * from t_job") #print(rows)
for n in rows:
if n[4][-1]=='月':
list.append(n[4])
elif n[4][-1]=='年':
pass
elif n[4][-1]=='天':
pass
else:
pass
for sale in list:
#print(sale)
money = sale.split('/')
#print(money[0])
money1 = money[0].split('-')
#print(money1)
if money[0][-1] == '万':
a = float(money1[0]) * 10000
b = float(money1[1][:-1]) * 10000
aveage = (a + b) / 2
count+=1
list1.append(aveage)
elif money[0][-1]=='千':
a = float(money1[0]) * 1000
b = float(money1[1][:-1]) * 1000
#print(a)
#print(b)
aveage = (a + b) / 2
#print(aveage)
count += 1
list1.append(aveage)
#print(count)
#print(list1)
for i in list1:
print(i)
if 0 < i <= 5000:
salary0.append(i)
elif 5000 < i <= 10000:
salary1.append(i)
elif 10000 < i <= 15000:
salary2.append(i)
elif 15000 < i <= 20000:
salary3.append(i)
elif 20000 < i <= 25000:
salary4.append(i)
elif 25000 < i <= 30000:
salary5.append(i)
elif 30000 < i <= 35000:
salary6.append(i)
elif 35000 < i <= 40000:
salary7.append(i)
print(min(list1))
print(max(list1))
a = len(salary0)
b = len(salary1)
c = len(salary2)
d = len(salary3)
e = len(salary4)
f = len(salary5)
g = len(salary6)
h = len(salary7)
list3=[a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h]
print(list2) #x轴
print(a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h)
print(list3) #数量 bar = Bar('Python平均工资')
bar.add("月薪", list2,list3)
# bar.show_config()
bar.render('Python工资柱状图.html') pie = Pie()
pie.add("", list2, list3, is_label_show=True)
#pie.show_config()
pie.render('Python工资饼状图.html')
''' #print(rows)
citycount=[]
cityname=['北京','异地招聘','海淀区','朝阳区','丰台区','昌平区','东城区','延庆区',
'房山区','通州区','顺义区','大兴区','怀柔区','西城区','平谷区','门头沟区']
beijing=[]
yidi=[] haidian=[]
chaoyang=[]
fengtai=[]
changping=[]
dongcheng=[]
yanqing=[]
fangshan=[]
tongzhou=[]
shunyi=[]
daxing=[]
huairou=[]
xicheng=[]
pinggu=[]
mentougou=[] for n in rows:
#print(n[3])
area=n[3].split('-')
print(area)
if len(area)==1:
print(area[0])
city.append(area[0])
else:
print(area[1])
city.append(area[1])
print(city)
print(len(city))
for i in city:
if i=='北京':
beijing.append(i)
elif i=='异地招聘':
yidi.append(i)
elif i=='海淀区':
haidian.append(i)
elif i == '朝阳区':
chaoyang.append(i)
elif i=='丰台区':
fengtai.append(i)
elif i=='昌平区':
changping.append(i)
elif i=='东城区':
dongcheng.append(i)
elif i=='延庆区':
yanqing.append(i)
elif i=='房山区':
fangshan.append(i)
elif i=='通州区':
tongzhou.append(i)
elif i=='顺义区':
shunyi.append(i)
elif i=='大兴区':
daxing.append(i)
elif i=='怀柔区':
huairou.append(i)
elif i=='西城区':
xicheng.append(i)
elif i=='平谷区':
pinggu.append(i)
elif i=='门头沟区':
mentougou.append(i) #print(beijing)
#print(len(beijing)) a = len(beijing)
b = len(yidi)
c = len(haidian)
d = len(chaoyang)
e = len(fengtai)
f = len(changping)
g = len(dongcheng)
h = len(yanqing)
j = len(fangshan)
k = len(tongzhou)
l = len(shunyi)
m = len(daxing)
n = len(huairou)
o = len(xicheng)
p = len(pinggu)
q = len(mentougou)
citycount=[a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h,j,k,l,m,n,o,p,q]
print(cityname)
print(citycount) pie = Pie()
pie.add("", cityname, citycount, is_label_show=True)
# pie.show_config()
pie.render('北京各区Python职位占比饼状图.html') bar = Bar('北京各区职位数量')
bar.add("数量", cityname, citycount)
# bar.show_config()
bar.render('北京各区Python职位占比柱状图.html') '''
前面写的是数据库的操作函数,其实可以封装成一个py文件,以后使用直接调用即可。
结果。:
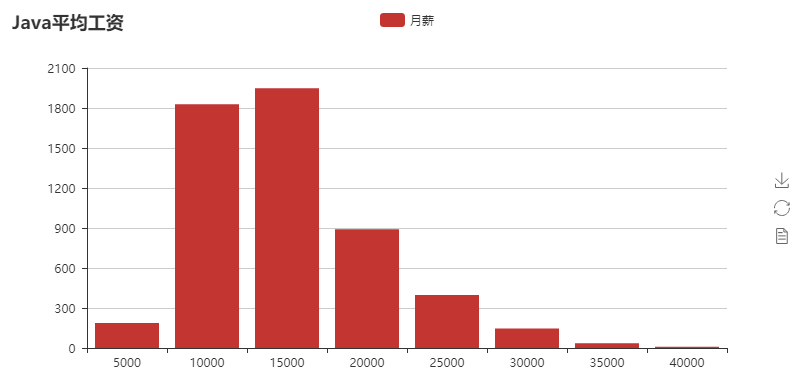
我也分析了boss直聘网站的一些数据,类似于经验要求和学历要求等等,也可以自己分析想要的数据。
import pymysql
import numpy as np
from pyecharts import Bar
from pyecharts import Pie
import jieba
from collections import Counter
from os import path class Mysqlhelper(object):
config={
"host":"localhost",
"user":"root",
"password":"",
"db":"test",
"charset":"utf8"
} def __init__(self):
self.connection=None
self.cursor=None # 从数据库中查询多行数据
def getlist(self, sql, *args):
try:
self.connection = pymysql.connect(**Mysqlhelper.config) # **接函数所有参数
self.cursor = self.connection.cursor()
self.cursor.execute(sql, args)
return self.cursor.fetchall()
except Exception as ex:
print(ex,ex)
finally:
self.close() def close(self):
if self.cursor:
self.cursor.close()
if self.connection:
self.connection.close() if __name__=="__main__":
sale=[]
exp=[]
edu=[]
one = []
three = []
five = []
onein = []
noexp = []
qita=[]
benke=[]
dazhuan=[]
noedu=[]
boshi=[]
other=[]
helper = Mysqlhelper()
rows = helper.getlist("select * from boss_job")
#print(rows) for data in rows:
#print(data[2])
#print(data[5])
#print(data[6])
sale.append(data[2])
exp.append(data[5])
edu.append(data[6])
if data[5]=='1-3年':
one.append(data[5])
elif data[5]=='3-5年':
three.append(data[5])
elif data[5]=='5-10年':
five.append(data[5])
elif data[5]=='经验不限':
noexp.append(data[5])
elif data[5]=='1年以内':
onein.append(data[5])
else:
qita.append(data[5])
pass
if data[6]=='本科':
benke.append(data[6])
elif data[6]=='大专':
dazhuan.append(data[6])
elif data[6]=='博士':
boshi.append(data[6])
elif data[6]=='学历不限':
noedu.append(data[6])
else:
other.append(data[6]) # with open('./data/jingyan.txt', 'a', encoding='utf-8') as fp:
# fp.write(data[5])
# fp.write(',')
# fp.flush()
# fp.close()
print(exp)
print(edu)
print(len(exp))
print(len(edu)) '''
d = path.dirname(__file__)
jingyan_text = open(path.join(d, "data//jingyan.txt"), encoding='utf-8').read()
print(len(jingyan_text)) jieba.load_userdict("data//jingyan_dict.txt") seg_list = jieba.cut_for_search(jingyan_text)
print(u"[全模式]: ", "/ ".join(seg_list))
'''
# sanguo_words = [x for x in jieba.cut(jingyan_text)if x!=','and len(x) >=2]
# c = Counter(sanguo_words).most_common(20)
# print(c)
# print(''.join(jieba.cut(jingyan_text))) print(one)
print(three)
print(five)
print(noexp)
print(onein)
print(qita)
a=len(one)
b=len(three)
c=len(five)
d=len(noexp)
e=len(onein)
f=len(qita)
expcount=[f,e,a,b,c,d]
expfenlei=['应届生','1年以内','1-3年','3-5年','5-10年','经验不限']
print(expcount)
print(a+b+c+d+e+f) print(other)
g=len(benke)
h=len(dazhuan)
j=len(boshi)
k=len(noedu)
m=len(other)
educount=[h,g,k,j,m]
edufenlei=['大专','本科','硕士','博士','学历不限']
print(educount) '''
bar = Bar('工作年限')
bar.add("要求", expfenlei, expcount)
# bar.show_config()
bar.render('工作年限柱状图.html') pie = Pie()
pie.add("工作", expfenlei, expcount, is_label_show=True)
# pie.show_config()
pie.render('工作年限饼状图.html')
''' bar = Bar('学历要求')
bar.add("学历", edufenlei, educount)
# bar.show_config()
bar.render('学历要求柱状图.html') pie = Pie()
pie.add("学历", edufenlei, educount, is_label_show=True)
# pie.show_config()
pie.render('学历要求饼状图.html')
我使用的是最基本的数组方法,不知道有什么简单方法么,例如jieba分词模块,等等

可以看出本科生需求还是很大的。。。
pyecharts数据分析及展示的更多相关文章
- 数据分析与展示——NumPy库入门
这是我学习北京理工大学嵩天老师的<Python数据分析与展示>课程的笔记.嵩老师的课程重点突出.层次分明,在这里特别感谢嵩老师的精彩讲解. NumPy库入门 数据的维度 维度是一组数据的组 ...
- 【学习笔记】PYTHON数据分析与展示(北理工 嵩天)
0 数据分析之前奏 课程主要内容:常用IDE:本课程主要使用:Anaconda Anaconda:一个集合,包括conda.某版本Python.一批第三方库等 -支持近800个第三方库 -适合科学计算 ...
- python数据分析及展示(一)
一.IDE选择 Anaconda软件:开源免费,https://www.anaconda.com下载,根据系统进行安装.由于下载速度慢,可以去清华大学开源软件镜像站下载. Spyder软件设置:Too ...
- 数据分析与展示---Pandas库数据特征分析
说明:0轴axis=0和1轴axis=1 简介 一:数据的排序 二:数据的基本统计分析 三:数据的累积统计分析 四:数据的相关分析 一:数据的排序 a b c d a b c d 二:数据的基本统计分 ...
- 数据分析与展示---Matplotlib基本绘图函数
一:基本绘图函数(这里介绍16个,还有许多其他的) 二:pyplot饼图plt.pie的绘制 三:pyplot直方图plt.hist的绘制 (一)修改第二个参数bins:代表直方图的个数,均分为多段, ...
- Python数据分析与展示(1)-数据分析之表示(1)-NumPy库入门
Numpy库入门 从一个数据到一组数据 维度:一组数据的组织形式 一维数据:由对等关系的有序或无序数据构成,采用线性方式组织. 可用类型:对应列表.数组和集合 不同点: 列表:数据类型可以不同 数组: ...
- awk - 数据分析和展示
目录 NAME 格式 常用选项 表达式 PATTERN(模式) 流程控制语句 数组 print,printf格式化输出 常用示例 NAME gawk - pattern scanning and pr ...
- 数据分析与展示——Pandas数据特征分析
Pandas数据特征分析 数据的排序 将一组数据通过摘要(有损地提取数据特征的过程)的方式,可以获得基本统计(含排序).分布/累计统计.数据特征(相关性.周期性等).数据挖掘(形成知识). .sort ...
- 数据分析与展示——Matplotlib基础绘图函数示例
Matplotlib库入门 Matplotlib基础绘图函数示例 pyplot基础图表函数概述 函数 说明 plt.plot(x,y,fmt, ...) 绘制一个坐标图 plt.boxplot(dat ...
随机推荐
- ORA-01795: 列表中的最大表达式数为1000的解决方法
IN中的数据量不能超过1000条. 解决方案:把条件分成多个少于1000的IN即: DELETEFROMT_MM_SECTION_SITE_UPDATEWHERE T.T_MM_SECTION_SL_ ...
- ZHS16GBK编码中汉字缺失
生产中使用ZHS16GBK编码的Oracle数据库,若出现字,则会出现乱码 原因是此字不存在在ZHS16GBK编码中 解决方法可以:此二字结构相同,但是后面的在ZHS16GBK编码中出现
- 12C RAC 常用检查命令,持续总结中
grid: olsnodes -s列出集群中节点crsctl check cluster -all检查几圈状态crsctl check clustercrsctl check crs 检查当前节点sr ...
- C语言socket编程----struct sockaddr 和struct sockaddr_in介绍和初始化
sockaddr结构体 struct sockaddr{ sa_family_t sa_family; //地址族,最常用的是"AF_INET"(IPV4)和"AF_ ...
- Gecko Robotics, Inc. SE II Test OA -- 菜到扣脚
There are three problems in hackrank. two sum http request to get title binary search (find first la ...
- [18/11/22] 将点分十进制的IP地址化成二进制输出
#include <stdio.h> void binary(int d){ ,j,n,b[]={}; ){ n=d%; d=d/; b[i++]=n; //不停的除2,余数保存在b[8] ...
- c#运用this.invoke() 在多线程时对UI进行修改
什么是进程呢?当一个程序开始运行时,它就是一个进程,进程所指包括运行中的程序和程序所使用到的内存和系统资源.而一个进程又是由多个线程所组成的,线程是程序中的一个执行流,每个线程都有自己的专有寄存器(栈 ...
- HDU 1160(两个值的LIS,需dfs输出路径)
传送门: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1160 FatMouse's Speed Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/ ...
- Notepad++ 插件之 TextFX (安装及作用)
<安装:打开 notepad++ 插件 -> Plugin Manager -> Show Plugin Manager -> available ->选中 TextF ...
- PL/SQL规范、块、过程、函数、包、触发器
1.pl/sql规范 标识符号的命名规范 1) 定义变量,用 v- 作为前缀 v-sal 2)定义常亮, 用 c- 作为前缀 c-rate 3) 定义游标,用 cursor作为后缀 emp_curso ...
