hdu1198Farm Irrigation (DFS)
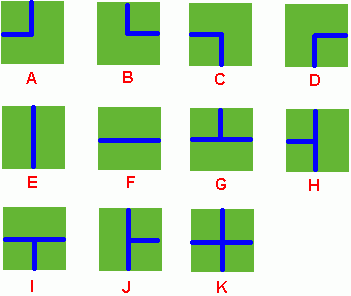
Figure 1
Benny has a map of his farm, which is an array of marks denoting the distribution of water pipes over the whole farm. For example, if he has a map
ADC
FJK
IHE
then the water pipes are distributed like
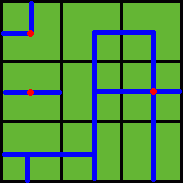
Figure 2
Several wellsprings are found in the center of some squares, so water can flow along the pipes from one square to another. If water flow crosses one square, the whole farm land in this square is irrigated and will have a good harvest in autumn.
Now Benny wants to know at least how many wellsprings should be found to have the whole farm land irrigated. Can you help him?
Note: In the above example, at least 3 wellsprings are needed, as those red points in Figure 2 show.
DK
HF
3 3
ADC
FJK
IHE
-1 -1
3
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef struct nn
{
int d[4];//按顺序左,上,右,下;0表示不路通,1表示路通
}node;
node map[55][55],N[11];
int n,m,vist[55][55],dir[4][2]={{0,-1},{-1,0},{0,1},{1,0}};
void set_N()
{
for(int i=0;i<11;i++)
{
if(i==0){N[i].d[0]=N[i].d[1]=1;N[i].d[2]=N[i].d[3]=0;}
if(i==1){N[i].d[1]=N[i].d[2]=1;N[i].d[0]=N[i].d[3]=0;}
if(i==2){N[i].d[0]=N[i].d[3]=1;N[i].d[2]=N[i].d[1]=0;}
if(i==3){N[i].d[2]=N[i].d[3]=1;N[i].d[1]=N[i].d[0]=0;}
if(i==4){N[i].d[1]=N[i].d[3]=1;N[i].d[2]=N[i].d[0]=0;}
if(i==5){N[i].d[0]=N[i].d[2]=1;N[i].d[1]=N[i].d[3]=0;}
if(i==6){N[i].d[0]=N[i].d[1]=N[i].d[2]=1;N[i].d[3]=0;}
if(i==7){N[i].d[0]=N[i].d[1]=N[i].d[3]=1;N[i].d[2]=0;}
if(i==8){N[i].d[0]=N[i].d[2]=N[i].d[3]=1;N[i].d[1]=0;}
if(i==9){N[i].d[1]=N[i].d[3]=N[i].d[2]=1;N[i].d[0]=0;}
if(i==10){N[i].d[0]=N[i].d[3]=N[i].d[2]=N[i].d[1]=1;}
}
}
void dfs(int x,int y)
{
int tx,ty;
vist[x][y]=1;
for(int e=0;e<4;e++)
if(map[x][y].d[e])
{
tx=x+dir[e][0];ty=y+dir[e][1];
if(!vist[tx][ty]&&tx>=0&&tx<n&&ty>=0&&ty<m)
{
if(e==0&&map[tx][ty].d[2]||e==1&&map[tx][ty].d[3])
dfs(tx,ty);
if(e==2&&map[tx][ty].d[0]||e==3&&map[tx][ty].d[1])
dfs(tx,ty);
}
}
}
int main()
{
char c;
int k;
set_N();
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)>0&&n+m!=-2)
{
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
getchar();
for(int j=0;j<m;j++)
{
cin>>c;
map[i][j]=N[c-'A'];
vist[i][j]=0;
}
} k=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
for(int j=0;j<m;j++)
if(!vist[i][j])
{
k++;
dfs(i,j);
}
printf("%d\n",k);
}
}
hdu1198Farm Irrigation (DFS)的更多相关文章
- hdu1198Farm Irrigation(dfs找联通)
题目链接: 啊哈哈,选我选我 思路是:首先依据图像抽象出联通关系.. 首先确定每一种图形的联通关系.用01值表示不连通与不连通... 然后从第1个图形进行dfs搜索.假设碰到两快田地能够联通的话那么标 ...
- hdu.1198.Farm Irrigation(dfs +放大建图)
Farm Irrigation Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others) ...
- ZOJ 2412 Farm Irrigation(DFS 条件通讯块)
意甲冠军 两个农田管内可直接连接到壳体 他们将能够共享一个水源 有11种农田 管道的位置高于一定 一个农田矩阵 问至少须要多少水源 DFS的连通块问题 两个相邻农田的管道能够直接连接的 ...
- hdu1198 Farm Irrigation —— dfs or 并查集
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1198 dfs: #include<cstdio>//hdu1198 dfs #includ ...
- HDU 1198 Farm Irrigation (并检查集合 和 dfs两种实现)
Farm Irrigation Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others) ...
- HDU 1198 Farm Irrigation(并查集,自己构造连通条件或者dfs)
Farm Irrigation Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)T ...
- HDU 1198 Farm Irrigation(状态压缩+DFS)
题目网址:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1198 题目: Farm Irrigation Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Ja ...
- (DFS)hdoj1198-Farm Irrigation
题目链接 DFS的简单应用,比较繁琐的是处理输入的英文字母.用并查集也可以做(可是笔者现在还没有掌握并查集,之前只用过一次,以后学会回来补上) #include<cstdio> #incl ...
- hdu 1198 (并查集 or dfs) Farm Irrigation
题目:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1198 有题目图11种土地块,块中的绿色线条为土地块中修好的水渠,现在一片土地由上述的各种土地块组成,需要浇 ...
随机推荐
- ThinkPHP第七天(F函数使用,项目分组配置,项目分组模板文件放置规则配置)
1.F(文件名称,写入数据,写入地址),用于将数据写入至磁盘文件中,如F('Data',$arr,'./Data/'),作用是将$arr写入至网站根目录的Data文件夹中的Data.php中. 2.读 ...
- PHP学习笔记10-图片加水印
先找好一张图片,更名为face.jpeg,创建watermark.php: <?php /** * Created by PhpStorm. * User: Administrator * Da ...
- poj 2515 Birthday Cake
/** 大意 : 求1^m + 2^m + 3^m + 4^m +....+ n^m 解题步骤: 先构造从0到m的第1阶差分序列,然后以下所有2---->p阶的差分表. 令C[n+1][1]=n ...
- DataTable Select查询
如果是Excel中数据,空数据为DBNull.Value 查询:dt.Select("name is null") 查询长度:dt.Select("len(convert ...
- struts2的总体回想(ACTION、拦截器、值栈、OGNL表达式、ModelDriven方案等)
ValueStack:struts2的一个存放数据的数据结构(核心) ValueStack大致能够理解为:由Map和对象栈组成 ValueStack作用范围:一个请求,用它来取代request的作用域 ...
- ZOJ3640-Help Me Escape
Help Me Escape Time Limit: 2 Seconds Memory Limit: 32768 KB Background If thou doest well, ...
- Linux DM9000网卡驱动程序完全分析
Linux DM9000网卡驱动程序完全分析http://blog.csdn.net/ypoflyer/article/details/6209922
- 查锁住的表,以及kill进程,Oracle常用语句
--找出所有被锁的对象,定位出哪个回话占用 select l.session_id,o.owner,o.object_name from v$locked_object l,dba_objects o ...
- AppStore安装APP发生错误解决方法
打开网络偏好设置 高级 -> DNS -> + -> 114.114.114.114
- 原生弹窗拖拽代码demo+简单的抽奖
拖拽效果 效果: 代码: <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset=&q ...
