python 招聘数据分析
导入包
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
读文件
df=pd.read_csv(r'C:\Users\MSI\Desktop\1.csv')
查看数据
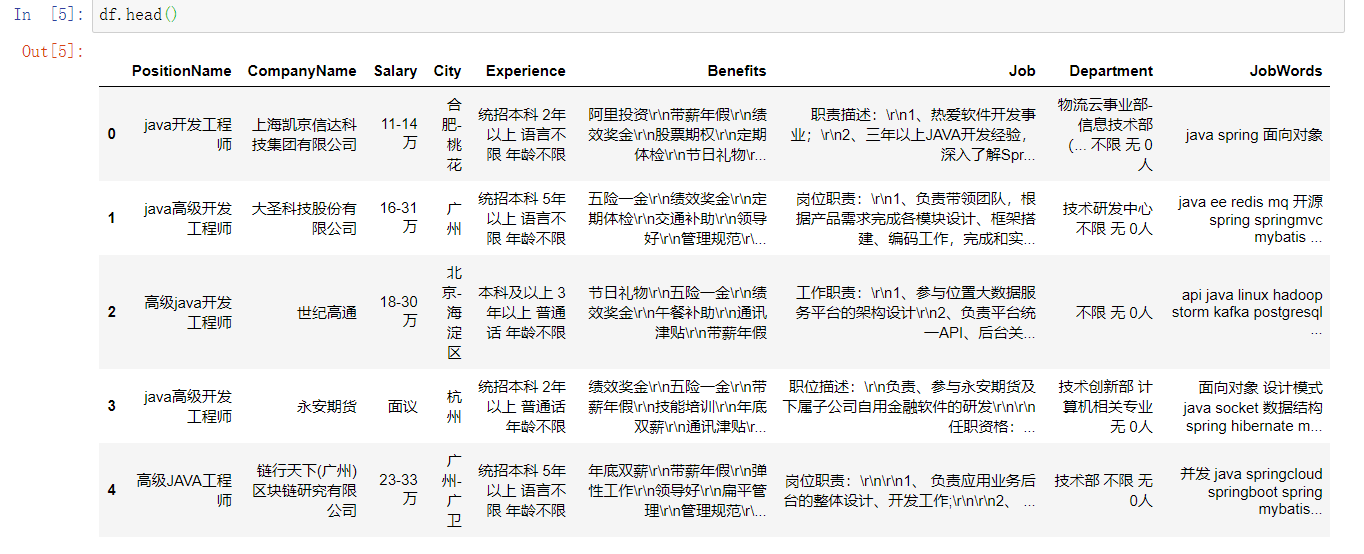
df.head()
查看基本信息
df.info()
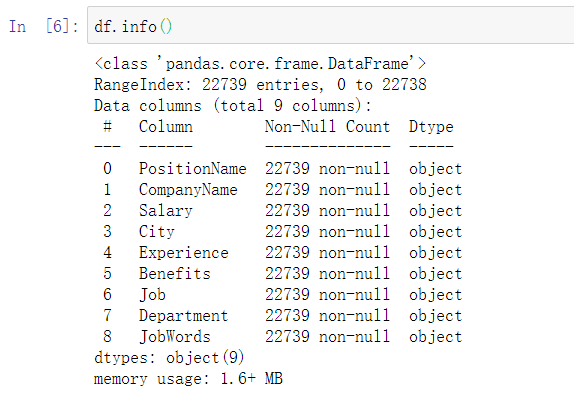
一共有九个字段,22739条数据,数据全为字符串,不存在数据为空的情况,因此不需要进行对缺少数据的处理
对重复数据进行处理,删除职位和公司重复值
df.drop_duplicates(['PositionName','CompanyName'],keep='first', inplace=True)
查看处理后的信息
df.info()
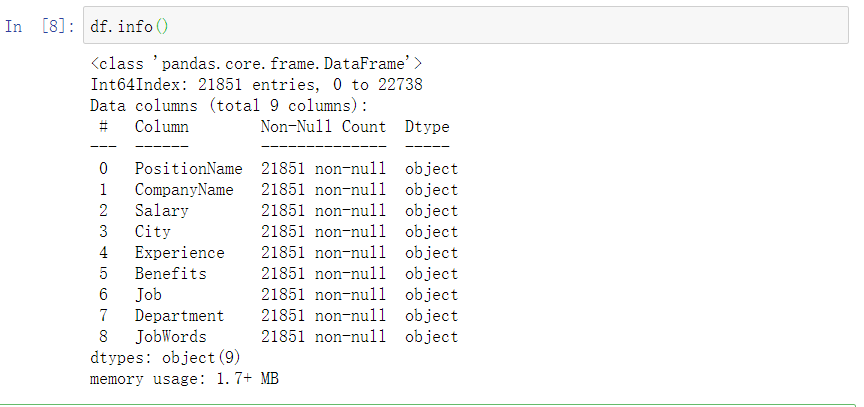
剩余21851条记录
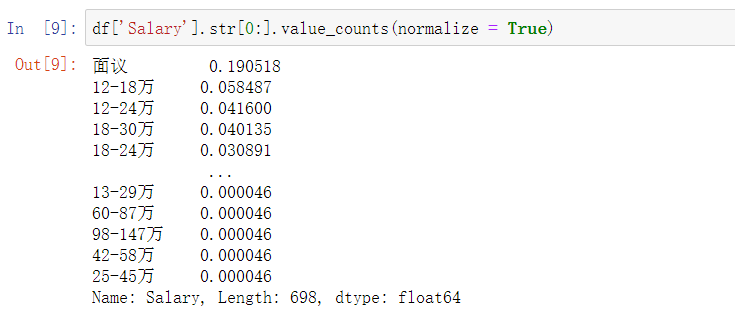
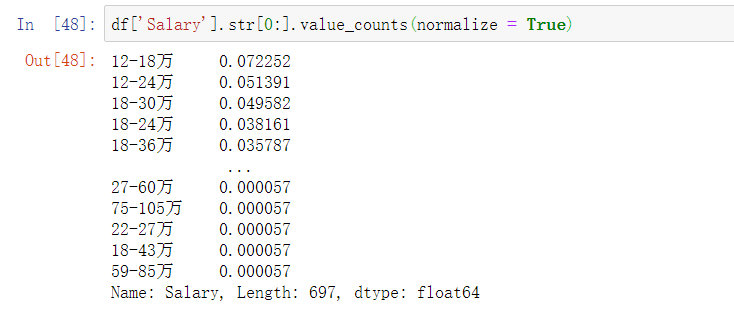
查看薪资的分布的频率,发现面议有较大的比重
df['Salary'].str[0:].value_counts(normalize = True)
自定义函数drops,删除薪资中的面议
def drops(col, tag):
df.drop(df[df[col].str.contains(tag)].index, inplace=True)
drops('Salary', '面议')
自定义函数cutWord求平均薪资
def cutWord(word,method):
position=word.find("-")
length = len(word)
if position != -1:
bottomSalary = word[:position]
topSalary = word[position + 1:length - 1]
if method == 'bottom':
return bottomSalary
else:
return topSalary
df['topSalary']=df.Salary.apply(cutWord,method='top')
df['bottomSalary']=df.Salary.apply(cutWord,method='bottom')
df.topSalary=df.topSalary.astype("int")
df.bottomSalary=df.bottomSalary.astype("int")
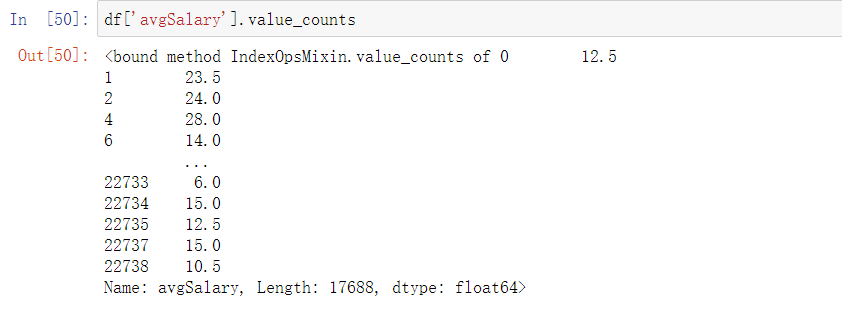
df['avgSalary']=df.apply(lambda x:(x.bottomSalary+x.topSalary)/2,axis=1)
df['avgSalary'].value_counts
由于各个仅统计各个省份,但所给数据中含有地级市及区等,因此对数据进行处理,仅保留省份/直辖市
自定义函数newCity
def newCity(city):
if(len(str(city))>2):
newcity = city[:2]
else:
newcity=city
return newcity
df['newcity']=df.City.apply(newCity)
数据基本处理完成,保存为df_clean
df_clean = df[["PositionName", "CompanyName", "newcity", "Experience", "JobWords", "avgSalary"]]
df_clean.head()

查看数据的描述性信息
print(df_clean.describe())
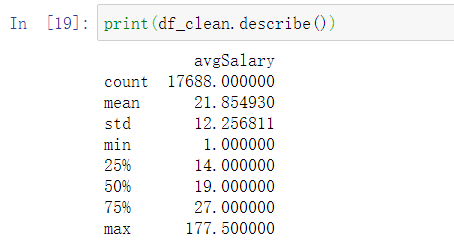
平均薪资:21.85W,中位数:19W,最高:177.5W
薪资分布情况图
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei']
df_clean.avgSalary.hist(bins=20)
plt.show()

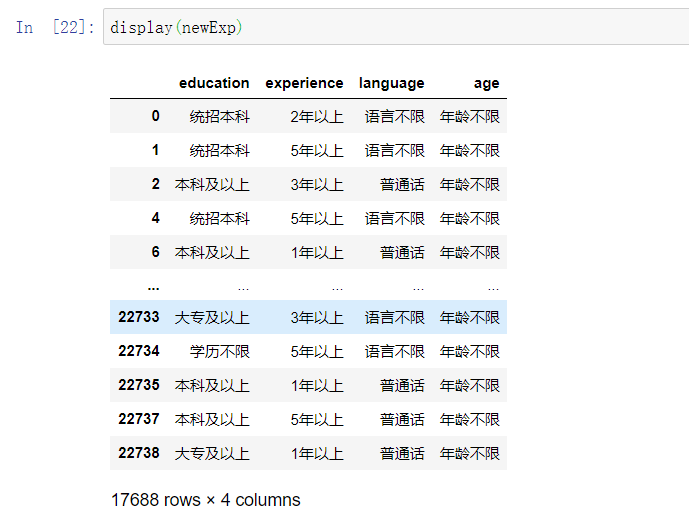
分割experience,不知道为什么这里分割了八个出来,我就定义了8列。不太懂我觉的这里应该四列才对,8列弄出来之后再把多的删了
info_split=df_clean['Experience'].str.split(' ',expand=True)
info_split.columns=['education','experience','language','age','1','2','3','4']
newExp=info_split.drop(['1','2','3','4'],axis=1)
display(newExp)
display(df_clean)

然后把两个二维表进行链接,再保存为new_df,最开始是链接之后删除experience,但是不知道为什么链接之后删除newcity就变成了city,之前的city白处理了。然后就直接保存了
newDF=pd.concat([df_clean, newExp], axis=1)
new_df = newDF[["PositionName", "CompanyName", "newcity",'education','experience','language','age' , "JobWords", "avgSalary"]]
display(new_df)

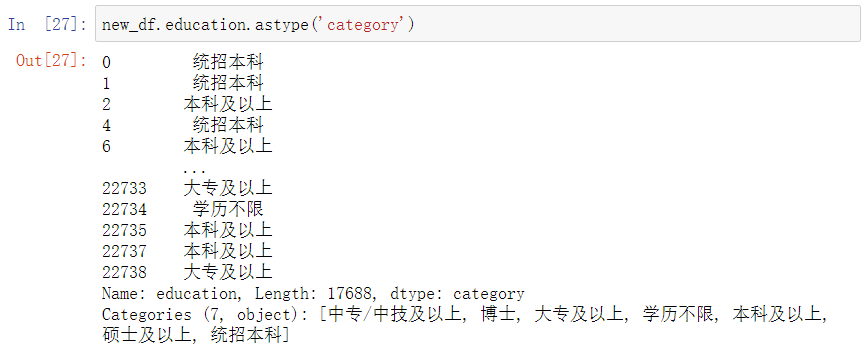
转换分类数据,这里发现本科有两个,然后其他数据不是很直观,后续有对这个数据进行了处理
new_df.education.astype('category')
自定义newEdu处理教育水平,写的有点复杂,之前的写法不知道为什么最后的结构只剩下本科和硕士。
def newEdu(education):
if education == "硕士及以上":
new_edu = "硕士"
elif education == "统招本科":
new_edu = "本科"
elif education == "本科及以上":
new_edu = "本科"
elif education== "学历不限":
new_edu = "不限"
elif education== "大专及以上":
new_edu = "大专"
elif education == "中专/中技及以上":
new_edu = "中专"
else:
new_edu="博士"
return new_edu
new_df['new_edu'] = new_df.education.apply(newEdu)
new_df.new_edu.astype('category')

选用线箱进行比较。其最大的优点就是不受异常值的影响,可以以一种相对稳定的方式描述数据的平均水平、波动程度和异常值分布情况。
new_df.new_edu=new_df.new_edu.astype('category')
new_df.new_edu.cat.set_categories(["中专", "博士", "大专", "不限", "本科", "硕士", ],inplace=True)
ax=new_df.boxplot(column='avgSalary',by='new_edu',figsize=(9,6))
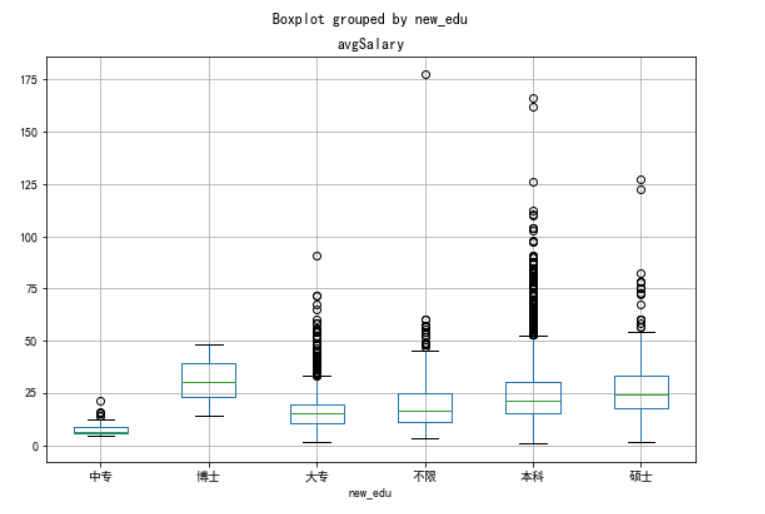
print(new_df.groupby(new_df.new_edu).avgSalary.mean().sort_values(ascending=False))
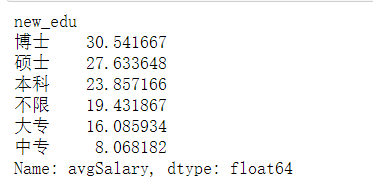
如图1,本科中位数薪资高于硕士生,容易误以为本科薪资高于硕士生,但同时结合图2,可见硕士生的平均薪资水平远高于本科生,由此可知,学历越高,薪资越高,知识改变命运。
转化数据类型(工作年限)创建线箱进行比较
new_df.experience.astype('category')
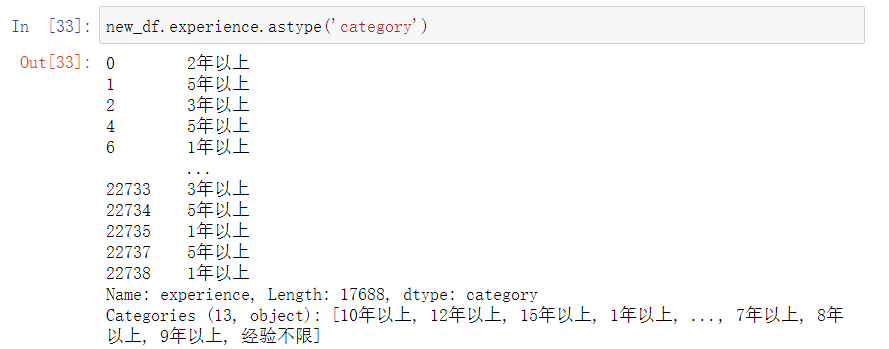
new_df.boxplot(column='avgSalary',by='experience',figsize=(9,6))
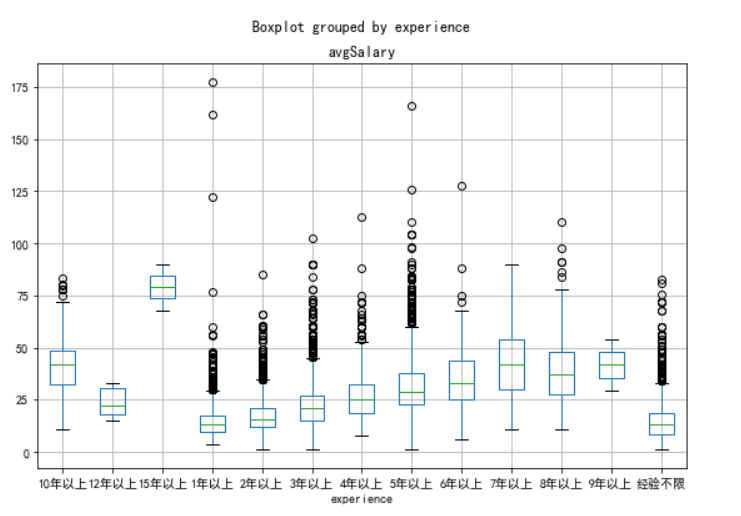
工作年限和薪资的比较
print(new_df.groupby(new_df.experience).avgSalary.mean().sort_values(ascending=False))
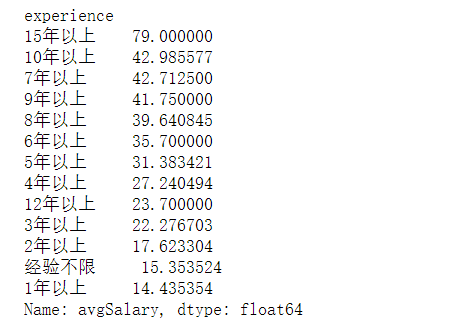
薪资与工作年限有很大关系,但优秀员工薪资明显超越年限限制。
北京和上海这两座城市,学历对薪资的影响
df_sz_bj=new_df[new_df['newcity'].isin(['上海','北京'])]
df_sz_bj.boxplot(column='avgSalary',by=['new_edu','newcity'],figsize=[14,6])
plt.show()
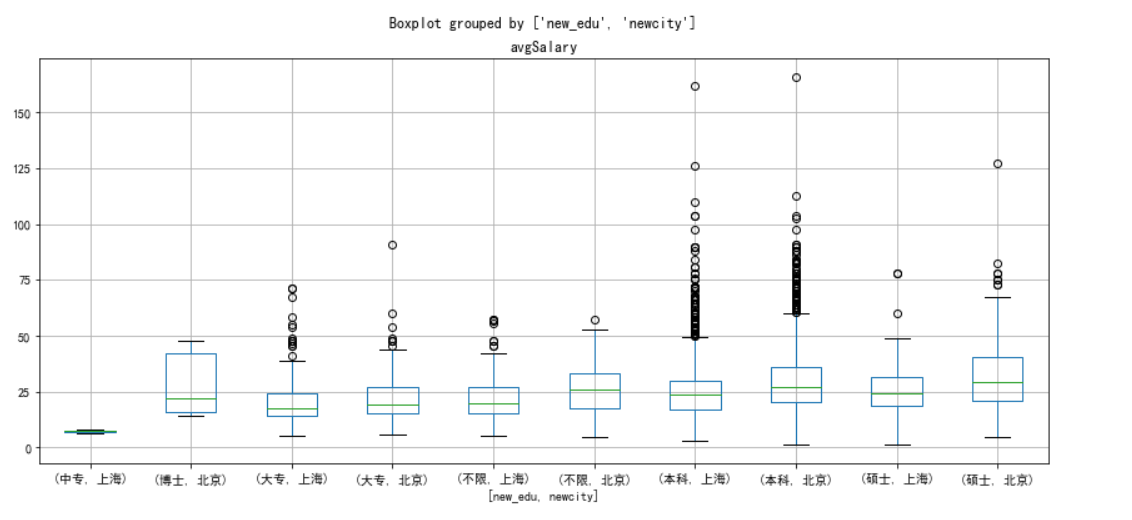
薪资与工作区域有很大关系,北京薪资不管什么学历都高于同等学历的薪资状况
不同城市,招聘数据分析需求前五的公司
自定义了函数topN,将传入的数据计数,并且从大到小返回前五的数据。然后以newcity聚合分组,因为求的是前5的公司,所以对CompanyName调用topN函数。
new_df.groupby('CompanyName').avgSalary.agg(lambda x:max(x)-min(x))
def topN(df,n=5):
counts=df.value_counts()
return counts.sort_values(ascending=False)[:n]
print(new_df.groupby('newcity').CompanyName.apply(topN))
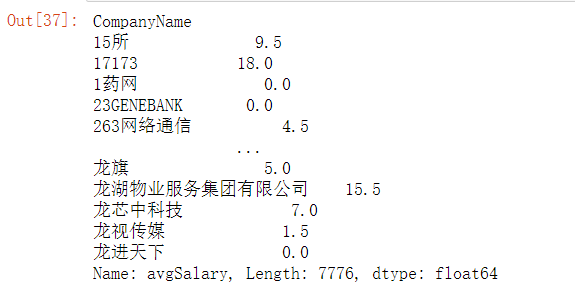
职位需求的前五,以计算机行业为主
print(new_df.groupby('newcity').PositionName.apply(topN))

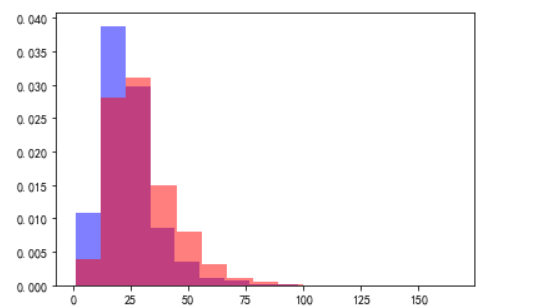
将上海和北京的薪资数据以直方图的形式进行对比
plt.hist(x=new_df[new_df.newcity=='上海'].avgSalary,
bins=15,
density=1,
facecolor='blue',
alpha=0.5)
plt.hist(x=new_df[new_df.newcity=='北京'].avgSalary,
bins=15,
density=1,
facecolor='red',
alpha=0.5)
plt.show()
做一个所需要做的工作的词云,先下载wordcloud库
在anaconda下载第三方库还挺麻烦的,镜像还不能用,只能下载之后导包
查看数据进行处理
print(new_df.JobWords)

重置索引然后作词云
df_word_counts=df_word.unstack().dropna().reset_index().groupby('level_0').count()
from wordcloud import WordCloud
df_word_counts.index=df_word_counts.index.str.replace("'","")
wc=WordCloud(font_path=r'C:\Windows\Fonts\FZSTK.TTF',width=900,height=400,background_color='white')
fig,ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(20,15))
wc.fit_words(df_word_counts.level_1)
ax=plt.imshow(wc)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()

上图可见对统计分析,数学,英语和office使用还是有一定的要求。
完整代码
#!/usr/bin/env python
# coding: utf-8
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
df=pd.read_csv(r'C:\Users\MSI\Desktop\1.csv')
df.head()
df.info()
df.drop_duplicates(['PositionName','CompanyName'],keep='first', inplace=True)
df.info()
df['Salary'].str[0:].value_counts(normalize = True)
def drops(col, tag):
df.drop(df[df[col].str.contains(tag)].index, inplace=True)
drops('Salary', '面议')
df['Salary'].str[0:].value_counts(normalize = True)
def cutWord(word,method):
position=word.find("-")
length = len(word)
if position != -1:
bottomSalary = word[:position]
topSalary = word[position + 1:length - 1]
if method == 'bottom':
return bottomSalary
else:
return topSalary
df['topSalary']=df.Salary.apply(cutWord,method='top')
df['bottomSalary']=df.Salary.apply(cutWord,method='bottom')
df.topSalary=df.topSalary.astype("int")
df.bottomSalary=df.bottomSalary.astype("int")
df['avgSalary']=df.apply(lambda x:(x.bottomSalary+x.topSalary)/2,axis=1)
df['avgSalary'].value_counts
def newCity(city):
if(len(str(city))>2):
newcity = city[:2]
else:
newcity=city
return newcity
df['newcity']=df.City.apply(newCity)
df_clean = df[["PositionName", "CompanyName", "newcity", "Experience", "JobWords", "avgSalary"]]
df_clean.head()
print(df_clean.describe())
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei']
df_clean.avgSalary.hist(bins=20)
plt.show()
info_split=df_clean['Experience'].str.split(' ',expand=True)
info_split.columns=['education','experience','language','age','1','2','3','4']
newExp=info_split.drop(['1','2','3','4'],axis=1)
display(newExp)
display(df_clean)
newDF=pd.concat([df_clean, newExp], axis=1)
new_df = newDF[["PositionName", "CompanyName", "newcity",'education','experience','language','age' , "JobWords", "avgSalary"]]
display(new_df)
new_df.education.astype('category')
def newEdu(education):
if education == "硕士及以上":
new_edu = "硕士"
elif education == "统招本科":
new_edu = "本科"
elif education == "本科及以上":
new_edu = "本科"
elif education== "学历不限":
new_edu = "不限"
elif education== "大专及以上":
new_edu = "大专"
elif education == "中专/中技及以上":
new_edu = "中专"
else:
new_edu="博士"
return new_edu
new_df['new_edu'] = new_df.education.apply(newEdu)
new_df.new_edu.astype('category')
new_df.new_edu=new_df.new_edu.astype('category')
new_df.new_edu.cat.set_categories(["中专", "博士", "大专", "不限", "本科", "硕士", ],inplace=True)
ax=new_df.boxplot(column='avgSalary',by='new_edu',figsize=(9,6))
print(new_df.groupby(new_df.new_edu).avgSalary.mean().sort_values(ascending=False))
new_df.experience.astype('category')
new_df.boxplot(column='avgSalary',by='experience',figsize=(9,6))
print(new_df.groupby(new_df.experience).avgSalary.mean().sort_values(ascending=False))
df_sz_bj=new_df[new_df['newcity'].isin(['上海','北京'])]
df_sz_bj.boxplot(column='avgSalary',by=['new_edu','newcity'],figsize=[14,6])
plt.show()
new_df.groupby('CompanyName').avgSalary.agg(lambda x:max(x)-min(x))
def topN(df,n=5):
counts=df.value_counts()
return counts.sort_values(ascending=False)[:n]
print(new_df.groupby('newcity').CompanyName.apply(topN))
print(new_df.groupby('newcity').PositionName.apply(topN))
plt.hist(x=new_df[new_df.newcity=='上海'].avgSalary,
bins=15,
density=1,
facecolor='blue',
alpha=0.5)
plt.hist(x=new_df[new_df.newcity=='北京'].avgSalary,
bins=15,
density=1,
facecolor='red',
alpha=0.5)
plt.show()
print(new_df.JobWords)
df_word_counts=df_word.unstack().dropna().reset_index().groupby('level_0').count()
from wordcloud import WordCloud
df_word_counts.index=df_word_counts.index.str.replace("'","")
wc=WordCloud(font_path=r'C:\Windows\Fonts\FZSTK.TTF',width=900,height=400,background_color='white')
fig,ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(20,15))
wc.fit_words(df_word_counts.level_1)
ax=plt.imshow(wc)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
参考资料:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/1e1081ca13b5
python 招聘数据分析的更多相关文章
- 利用Python进行数据分析(12) pandas基础: 数据合并
pandas 提供了三种主要方法可以对数据进行合并: pandas.merge()方法:数据库风格的合并: pandas.concat()方法:轴向连接,即沿着一条轴将多个对象堆叠到一起: 实例方法c ...
- 利用Python进行数据分析(5) NumPy基础: ndarray索引和切片
概念理解 索引即通过一个无符号整数值获取数组里的值. 切片即对数组里某个片段的描述. 一维数组 一维数组的索引 一维数组的索引和Python列表的功能类似: 一维数组的切片 一维数组的切片语法格式为a ...
- 利用Python进行数据分析(9) pandas基础: 汇总统计和计算
pandas 对象拥有一些常用的数学和统计方法. 例如,sum() 方法,进行列小计: sum() 方法传入 axis=1 指定为横向汇总,即行小计: idxmax() 获取最大值对应的索 ...
- 利用Python进行数据分析(8) pandas基础: Series和DataFrame的基本操作
一.reindex() 方法:重新索引 针对 Series 重新索引指的是根据index参数重新进行排序. 如果传入的索引值在数据里不存在,则不会报错,而是添加缺失值的新行. 不想用缺失值,可以用 ...
- 利用Python进行数据分析(7) pandas基础: Series和DataFrame的简单介绍
一.pandas 是什么 pandas 是基于 NumPy 的一个 Python 数据分析包,主要目的是为了数据分析.它提供了大量高级的数据结构和对数据处理的方法. pandas 有两个主要的数据结构 ...
- 利用Python进行数据分析(4) NumPy基础: ndarray简单介绍
一.NumPy 是什么 NumPy 是 Python 科学计算的基础包,它专为进行严格的数字处理而产生.在之前的随笔里已有更加详细的介绍,这里不再赘述. 利用 Python 进行数据分析(一)简单介绍 ...
- 《利用python进行数据分析》读书笔记 --第一、二章 准备与例子
http://www.cnblogs.com/batteryhp/p/4868348.html 第一章 准备工作 今天开始码这本书--<利用python进行数据分析>.R和python都得 ...
- 利用python进行数据分析之绘图和可视化
matplotlib API入门 使用matplotlib的办法最常用的方式是pylab的ipython,pylab模式还会向ipython引入一大堆模块和函数提供一种更接近与matlab的界面,ma ...
- 利用Python进行数据分析——Numpy基础:数组和矢量计算
利用Python进行数据分析--Numpy基础:数组和矢量计算 ndarry,一个具有矢量运算和复杂广播能力快速节省空间的多维数组 对整组数据进行快速运算的标准数学函数,无需for-loop 用于读写 ...
随机推荐
- java中给某个字段加锁
private String buildLock(String str) { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(str); String lock = sb.t ...
- 【目标检测】基于传统算法的目标检测方法总结概述 Viola-Jones | HOG+SVM | DPM | NMS
"目标检测"是当前计算机视觉和机器学习领域的研究热点.从Viola-Jones Detector.DPM等冷兵器时代的智慧到当今RCNN.YOLO等深度学习土壤孕育下的GPU暴力美 ...
- package和import机制
package是Java中的包机制,包机制的作用是方便为了程序的管理.不同功能的类机制分别存放在不同的包下面.(按照功能划分,不同的包有着不同的性质) package怎么使用:package是一个关键 ...
- 栈面板类StackPane?
创建栈面板,将在其上放置两个按钮,并用样式属性设置按钮和栈面板的外观样式. package yuan; //栈面板的应用 import javafx.application.Application; ...
- MongoDb学习(四)--Repository----语法关键字
表7.查询方法支持的关键字 关键词 样品 逻辑结果 After findByBirthdateAfter(Date date) {"birthdate" : {"$gt& ...
- .NET Core学习笔记(8)——Entity Framework Core之Database First
曾经我以为再也不会去弄啥Database First,然鹅我错了.这个世界上就是有啪啪打脸和真香的时候.当小伙伴拿着做好的DB表结构和SQL脚本递过来的时候,我知道我没法拒绝.望着他突起的肱二头肌和充 ...
- 在 CAP 中使用 AOP ( Castle.DynamicProxy )
简介 本篇文章主要介绍如何在 CAP 中集成使用 Castle.DynamicProxy,Castle DynamicProxy 是一个用于在运行时动态生成轻量级.NET代理的库.代理对象允许在不修改 ...
- Flutter 布局类组件:简介
前言 布局类组件都会包含一个或多个子组件,不同的布局类组件对子组件排版(layout)方式不同. 我们知道,Element树才是最终的绘制树,Element树是通过Widget树来创建的(通过Widg ...
- Spark学习进度11-Spark Streaming&Structured Streaming
Spark Streaming Spark Streaming 介绍 批量计算 流计算 Spark Streaming 入门 Netcat 的使用 项目实例 目标:使用 Spark Streaming ...
- Docker学习笔记之基本命令使用
测试的环境为Ubuntu1804. 1. search命令搜索镜像 sudo docker search centos 搜索centos相关的镜像,可以看到第一个最多星的的centos是官方的镜像,而 ...
