23、springboot与缓存(1)
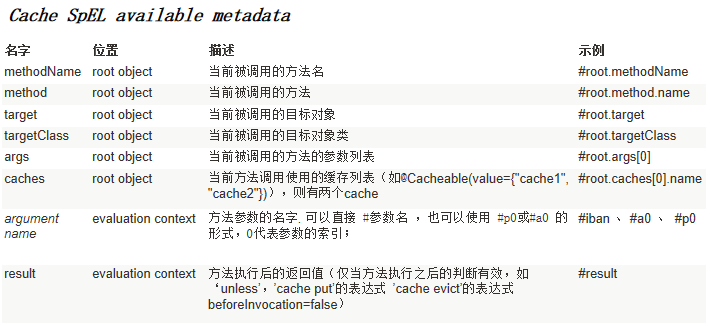
一、JSR107
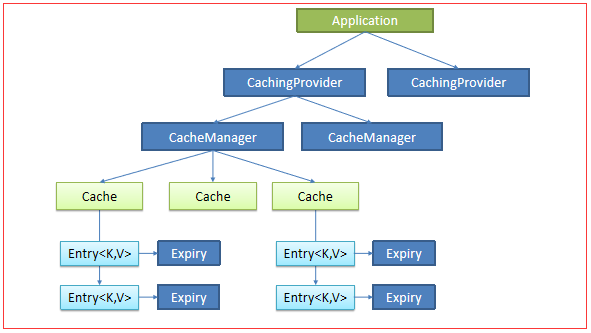
使用比较麻烦
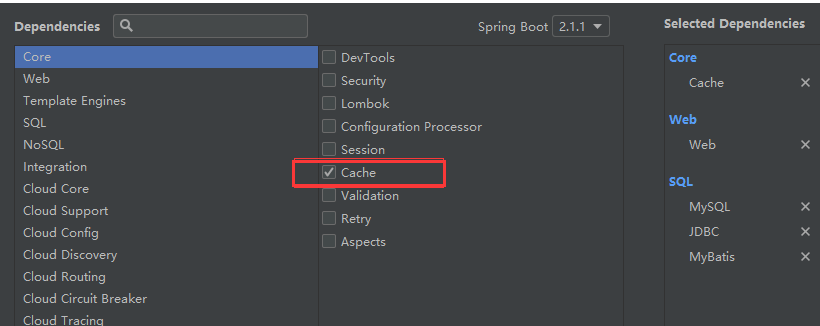
二、Spring缓存抽象
public class Department {
private Integer id;
private String departmentName;
...}
public class Employee {
private Integer id;
private String lastName;
private String email;
private Integer gender; //性别 1男 0女
private Integer dId;
...}
public interface EmployeeMapper {
@Select("SELECT * FROM employee WHERE id = #{id}")
Employee getEmpById(Integer id);
@Update("UPDATE employee SET lastName=#{lastName},email=#{email},gender=#{gender},d_id=#{dId} WHERE id=#{id}")
public void updateEmp(Employee employee);
@Delete("DELETE FROM employee WHERE id=#{id}")
public void deleteEmpById(Integer id);
@Insert("INSERT INTO employee(lastName,email,gender,d_id) VALUES(#{lastName},#{email},#{gender},#{dId})")
public void insertEmployee(Employee employee);
@Select("SELECT * FROM employee WHERE lastName = #{lastName}")
Employee getEmpByLastName(String lastName);
}
@Service
public class EmpService {
@Autowired
EmployeeMapper employeeMapper; public Employee getEmp(Integer id){
System.out.println("查询:" + id +"员工");
Employee emp = employeeMapper.getEmpById(id);
return emp;
}
}
@Controller
public class EmpController { @Autowired
EmpService empService; @ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/emp/{id}")
public Employee getEmp(@PathVariable("id")Integer id){
Employee emp = empService.getEmp(id);
return emp;
}
}
测试:
使用缓存:
在主程序中:开启缓存
@MapperScan("com.example.springbootcache.mapper")
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCaching
public class SpringbootCacheApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootCacheApplication.class, args);
}
}
此时页面连续请求两次:
@Cacheable
public Employee getEmp(Integer id){
System.out.println("查询:" + id +"员工");
Employee emp = employeeMapper.getEmpById(id);
return emp;
}

@Cacheable(cacheNames ="e" )
public Employee getEmp(Integer id){
System.out.println("查询:" + id +"员工");
Employee emp = employeeMapper.getEmpById(id);
return emp;
}
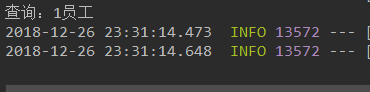
此时刷新很多遍依然只打印一次
三、缓存原理

@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({CacheManager.class})
@ConditionalOnBean({CacheAspectSupport.class})
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(
value = {CacheManager.class},
name = {"cacheResolver"}
)
@EnableConfigurationProperties({CacheProperties.class})
@AutoConfigureAfter({CouchbaseAutoConfiguration.class, HazelcastAutoConfiguration.class, HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration.class, RedisAutoConfiguration.class}) //给容器导入一些组件
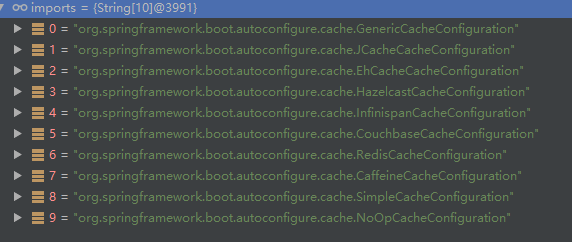
@Import({CacheAutoConfiguration.CacheConfigurationImportSelector.class})
public class CacheAutoConfiguration {
... public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {
CacheType[] types = CacheType.values();
String[] imports = new String[types.length]; for(int i = ; i < types.length; ++i) {
imports[i] = CacheConfigurations.getConfigurationClass(types[i]);
} return imports;
}
}
}
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata)中的return imports;
在配置文件中:判断那个缓存是生效的
debug=true
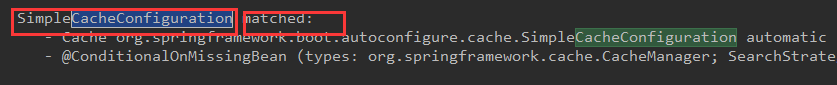
由图可知是SimpleCacheConfiguration 缓存类

@Configuration
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({CacheManager.class})
@Conditional({CacheCondition.class})
class SimpleCacheConfiguration {
private final CacheProperties cacheProperties;
private final CacheManagerCustomizers customizerInvoker; SimpleCacheConfiguration(CacheProperties cacheProperties, CacheManagerCustomizers customizerInvoker) {
this.cacheProperties = cacheProperties;
this.customizerInvoker = customizerInvoker;
} @Bean
public ConcurrentMapCacheManager cacheManager() {
ConcurrentMapCacheManager cacheManager = new ConcurrentMapCacheManager();
List<String> cacheNames = this.cacheProperties.getCacheNames();
if (!cacheNames.isEmpty()) {
cacheManager.setCacheNames(cacheNames);
} return (ConcurrentMapCacheManager)this.customizerInvoker.customize(cacheManager);
}
}

@Nullable
public Cache getCache(String name) {
Cache cache = (Cache)this.cacheMap.get(name);
if (cache == null && this.dynamic) {
ConcurrentMap var3 = this.cacheMap;
synchronized(this.cacheMap) {
cache = (Cache)this.cacheMap.get(name);
if (cache == null) {
cache = this.createConcurrentMapCache(name);
this.cacheMap.put(name, cache);
}
}
}
return cache;
}
按照名字取获取,如果为空则会创建一个缓存
运行流程:


其属性的使用:
key:数据库使用的key

此时的key就是 方法名+id; 即 getEmp[1]
@Configuration
public class MyConfig {
@Bean("MyKeyGenerator")
public KeyGenerator keyGenerator(){
return new KeyGenerator() {
@Override
public Object generate(Object o, Method method, Object... objects) {
//Objects事获得其输入的cache中的属性值
return method.getName() +"[" + Arrays.asList(objects).toString()+"]";
}
};
}
}
断点位置:
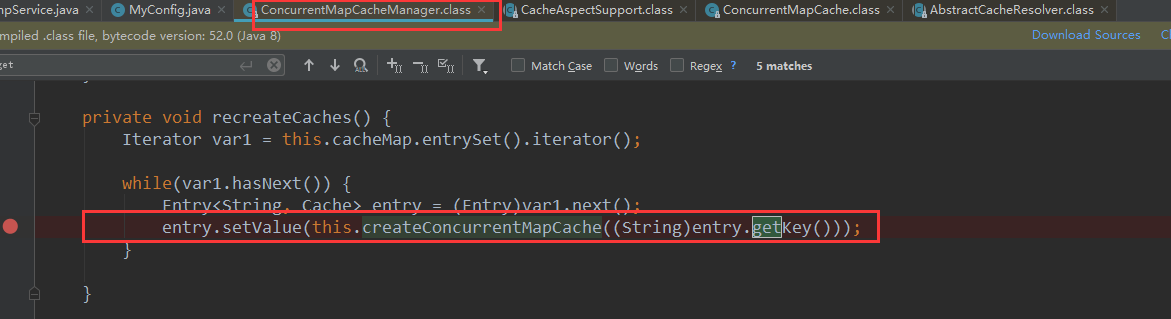
可以看到debug进入时的值: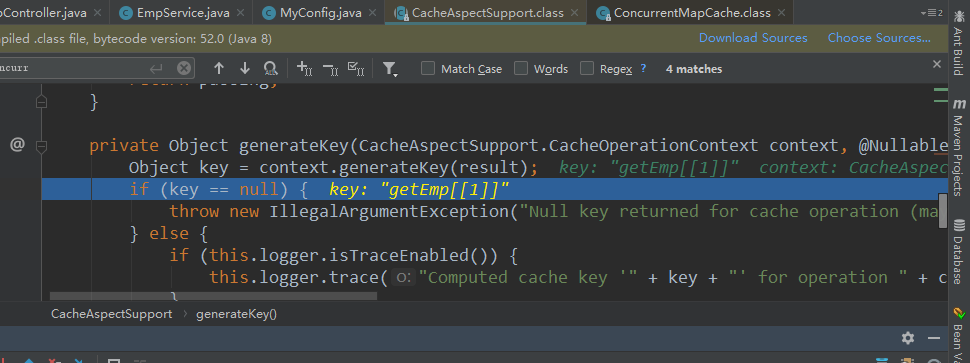
cacheManager:指定缓存管理器
condition:

@Cacheable(cacheNames ="e", keyGenerator = "MyKeyGenerator",condition = "#a0>1")
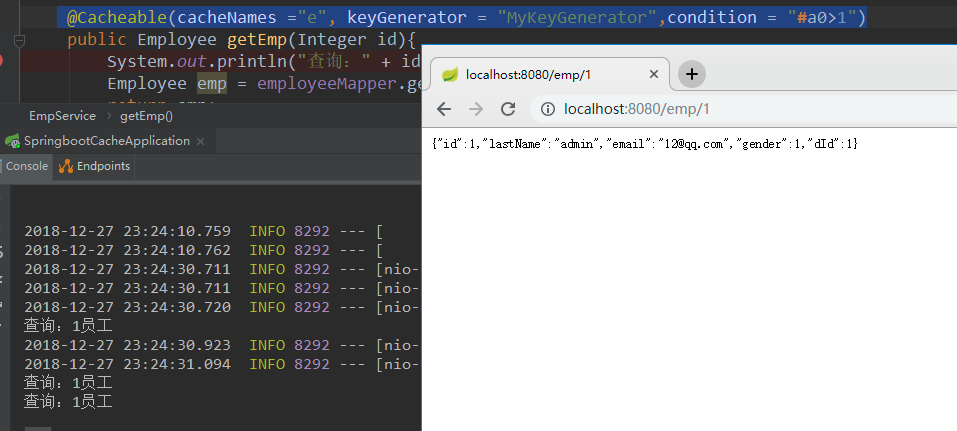
此时查询一次打印一次

23、springboot与缓存(1)的更多相关文章
- 带着新人学springboot的应用03(springboot+mybatis+缓存 下)
springboot+mybatis+缓存,基本的用法想必是会了,现在说一说内部大概的原理. 稍微提一下mybatis,只要导入了mybatis的依赖,那么有个自动配置类就会生效,你可以去mybati ...
- SpringBoot 与缓存
1. JSR107 Java Caching 定义了5个核心接口: CachingProvider:定义了创建,配置,获取,管理和控制多个CacheManager; CacheManager:定义了创 ...
- SpringBoot 整合缓存Cacheable实战详细使用
前言 我知道在接口api项目中,频繁的调用接口获取数据,查询数据库是非常耗费资源的,于是就有了缓存技术,可以把一些不常更新,或者经常使用的数据,缓存起来,然后下次再请求时候,就直接从缓存中获取,不需要 ...
- springboot redis 缓存对象
只要加入spring-boot-starter-data-redis , springboot 会自动识别并使用redis作为缓存容器,使用方式如下 gradle加入依赖 compile(" ...
- springboot~hazelcast缓存中间件
缓存来了 在dotnet平台有自己的缓存框架,在java springboot里当然了集成了很多,而且缓存的中间件也可以进行多种选择,向redis, hazelcast都是分布式的缓存中间件,今天主要 ...
- 带着新人学springboot的应用02(springboot+mybatis+缓存 中)
继续接着上一节,大家应该知道驼峰命名法吧!就是我们javabean中属性一般命名是lastName,userName这种类型的,而数据库中列名一般都是last_name,user_name这种的,要让 ...
- 带着新人学springboot的应用01(springboot+mybatis+缓存 上)
上一篇结束,第一次做一个这么长的系列,很多东西我也是没有说到,也许是还没有想到,哈哈哈,不过基本的东西还是说的差不多了的.假如以后碰到了不会的,随便查查资料配置一下就ok. 咳,还有大家如果把我前面的 ...
- SpringBoot Redis缓存 @Cacheable、@CacheEvict、@CachePut
文章来源 https://blog.csdn.net/u010588262/article/details/81003493 1. pom.xml <dependency> <gro ...
- springboot Redis 缓存
1,先整合 redis 和 mybatis 步骤一: springboot 整合 redis 步骤二: springboot 整合 mybatis 2,启动类添加 @EnableCaching 注解, ...
随机推荐
- protobuf简单测试应用
protobuf是google推出的一种数据交换协议,比较适合应用于底层服务交互,nodejs提供protobufjs包的实现,下面是一个简单的测试demo: 首先是.proto文件: package ...
- Linux多进程之间的文件锁
之前对于文件的操作通常在一个进程中完成,最近需要在两个进程中对同一个文件进行操作.故想到了文件锁. Linux下可以使用flock()函数对文件进行加锁解锁等操作.简单介绍下flock()函数: 表头 ...
- Vue2.0学习笔记:Vue事件修饰符的使用
事件处理 如果需要在内联语句处理器中访问原生DOM事件.可以使用特殊变量$event,把它传入到methods中的方法中. 在Vue中,事件修饰符处理了许多DOM事件的细节,让我们不再需要花大量的时间 ...
- django分页的两种方式
第一种自定义分页: def pageDemo(request): ''' 自定义分页] :param request: :return: ''' currentpage=request.GET.get ...
- [linux] shell脚本编程-ubuntu创建vsftpd服务
1. useradd -s /bin/bash -m 用户名 , 创建用户,自动创建家目录 , 设置登录shell 2. echo 用户名:密码 | chpasswd ,非交互式设置密码 3. ...
- 十二、curator recipes之双重屏障DoubleBarrier
简介 curator实现了单个屏障barrier和双重屏障DoubleBarrier,单个屏障就是在一个进程里面设置了屏障,并等待其它进程去移除这个屏障,否则一直阻塞.双重屏障就是设置了两道屏障,两个 ...
- JAVA基础之——版本控制系统之git
1 版本控制系统是什么 当多人协作开发一套产品时,需要能够保证代码都能够共用,那么版本控制系统就应运而生. 2 GIT 当前用的比较多的是svn和git,本文以git为例进行讲解. git诞生于200 ...
- hdu 3474 Necklace 单调队列
Necklace Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Su ...
- C#画个控件,指定字符特殊颜色显示
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Data; usin ...
- python中静态方法(@staticmethod)和类方法(@classmethod)的区别
一般来说,要使用某个类的方法,需要先实例化一个对象再调用方法. 而使用@staticmethod或@classmethod,就可以不需要实例化,直接类名.方法名()来调用. 这有利于组织代码,把某些应 ...
