python算法与数据结构-循环链表(39)
一、循环链表的介绍
上一篇我们已经讲过单链表,本篇给大家讲解循单链表的一个变形是单向循环链表,链表中最后一个节点的next域不再为None,而是指向链表的头节点,其基本操作和单链表思路一样。
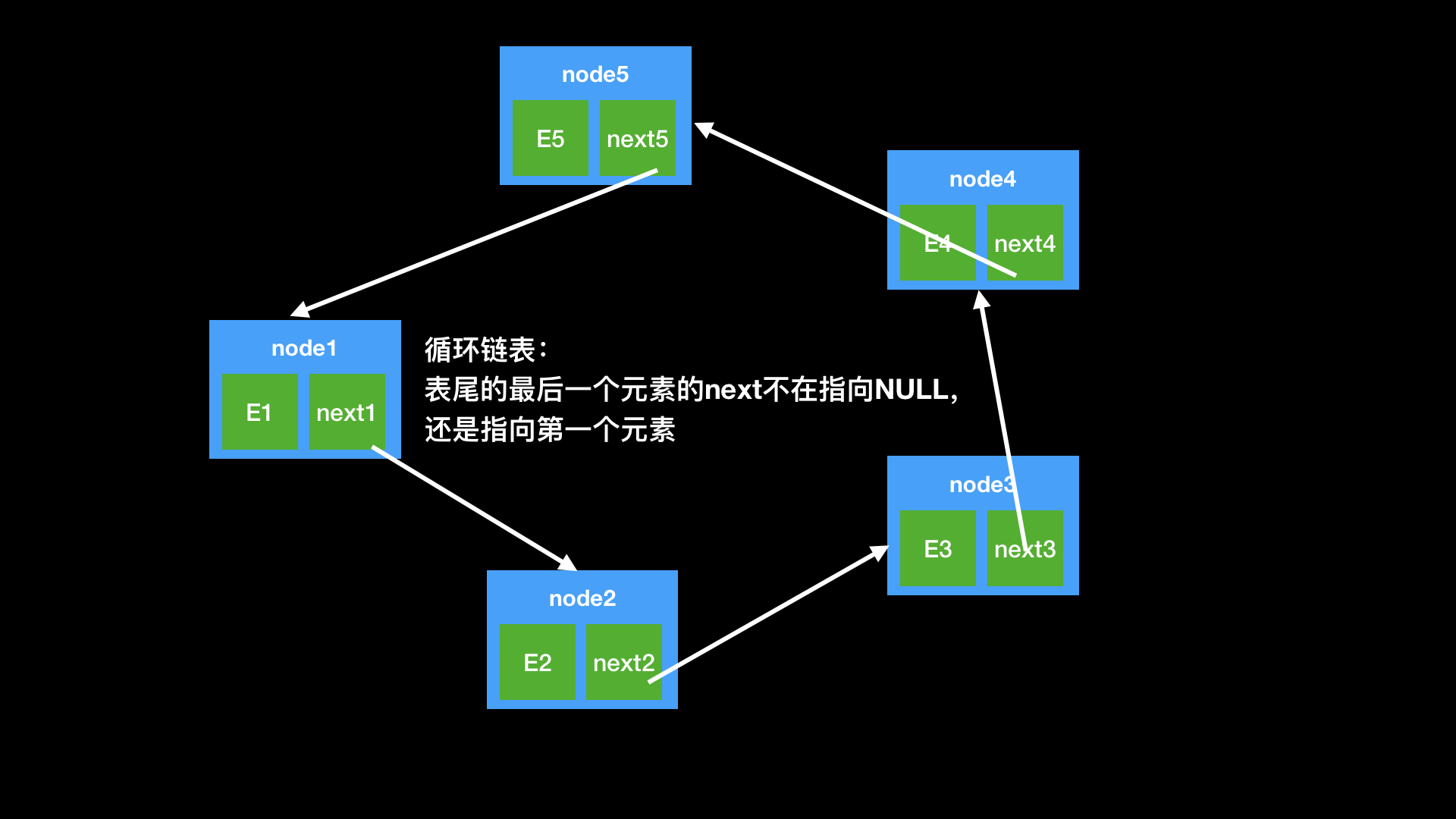
常用的操作有
- 创建节点
- 创建循环链表
- 判断是否为空
- 头部插入
- 循环链表的遍历
- 尾部插入
- 获取链表长度
- 根据下标插入一个节点
- 根据下标删除一个节点
- 查找是否包含一个节点,并返回其在链表中的位置
- 根据下标找节点
- 根据下标修改节点的值
- 对链表排序
二、循环链表基本操作的python代码实现
class Node():
def __init__(self,num):
self.element = num
self.next = None class CricleLinkList(object):
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.length = 0 # 1、判断是否为空
def is_empty(self):
if self.head == None:
return True
else:
return False # 2、头部插入
def add(self, num):
# 创建要插入的节点
node = Node(num)
if self.is_empty()==True:
# 如果为空直接插入
self.head = node
# 并且把自身的next执行头结点
node.next = self.head
else:
# 将原来的头结点作为插入节点的next
node.next = self.head
current = self.head
# 循坏找到最后一个节点
while current.next != self.head:
current = current.next
# 将最后一个节点的next执行插入节点
current.next = node
# 将插入的节点设置为头结点,完成循坏闭合
self.head = node
# 每次添加完成一次,长度加1
self.length += 1 # 3、遍历
def travel(self):
if self.is_empty() == True:
print("你要遍历的循环链表为空")
return print("你要遍历的循环链表元素有:", end=" ")
current = self.head
# 先把第一个元素打印一下
print("%d " % current.element, end=" ")
# 打印只有一个元素的时候,第一个元素打印不出来,所以先把第一个打印出来
while current.next != self.head: current = current.next
print("%d " % current.element, end=" ")
print("") # 4、尾部插入
def append(self,num):
node = Node(num)
if self.is_empty() == True:
self.add(num)
else:
current = self.head
while current.next != self.head:
current = current.next
node.next = self.head
current.next = node
# 每次添加完成一次,长度加1
self.length += 1 # 5、指定位置插入
def insertAtIndex(self,num,index):
if index<=0 or index>self.length+1:
print("你要插入的位置不对,请重新选择位置")
return
elif self.is_empty() == True:
self.add(num)
elif index==1:
self.add(num)
elif index == self.length+1:
self.append(num)
else:
current = self.head
for i in range(index-2):
current = current.next
node = Node(num)
node.next = current.next
current.next = node # 每次添加完成一次,长度加1
self.length += 1 # 6、按索引删除
def deleteByIndex(self,index): if index<=0 or index>self.length:
print("你要插入的位置不对,请重新选择位置")
return
elif self.is_empty() == True:
print("你要删除的链表为空")
return
elif index == 1:
current = self.head
for i in range(1,self.length):
current = current.next
current.next = self.head.next
self.head = self.head.next
else:
current = self.head
for i in range(index-2):
current = current.next
current.next = current.next.next
# 每次删完长度减1
self.length -= 1 # 7、查找是否包含,并返回位置
def isContain(self,num):
if self.is_empty() == True:
print("你要查询的链表为空")
return
else:
current = self.head
for i in range(self.length):
if current.element == num:
print("你要找到元素在第%d个节点"%(i+1))
return i+1
current = current.next
print("没有找到你要的元素")
return -1 # 8、根据下标找节点
def searchNodeByIndex(self,index):
if index<=0 or index>self.length:
print("你要查询的位置不对,请重新选择位置")
return
elif self.is_empty() == True:
print("你要查询的链表为空")
else:
current = self.head
for i in range(1,index):
current = current.next
print("你要查找%d位置上的节点的值是%d"%(index,current.element)) # 9、根据下标修改节点的值
def modifyByIndex(self,index,num):
if index <= 0 or index > self.length:
print("你要查询的位置不对,请重新选择位置")
return
elif self.is_empty() == True:
print("你要修改的链表为空")
else:
current = self.head
for i in range(1, index):
current = current.next
current.element = num # 10、排序
def sort(self):
if self.length<=0:
return
for i in (0,self.length-1):
current = self.head
for j in range(0,self.length-i-1):
if current.element>current.next.element:
temp = current.element
current.element = current.next.element
current.next.element = temp
current = current.next if __name__ == '__main__': print("======1、创建循环链表 ======")
cricle_link_list = CricleLinkList() print("======2、验证是否为空 ======")
empty = cricle_link_list.is_empty()
if empty == True:
print("你查询的链表为空")
else:
print("你查询的链表不为空") print("\n======3、验证头插和遍历 ======")
cricle_link_list.add(1)
cricle_link_list.travel() print("\n======4、继续验证头插和遍历 ======")
cricle_link_list.add(2)
cricle_link_list.travel() print("\n======5、验证尾插 ======")
cricle_link_list.append(3)
cricle_link_list.travel() print("\n======6、验证按位置插入 ======")
cricle_link_list.insertAtIndex(0,2)
cricle_link_list.travel() print("\n======7、验证按位置删除 ======")
cricle_link_list.deleteByIndex(5)
cricle_link_list.travel() print("\n======8、验证查找是否包含元素 ======")
cricle_link_list.isContain(2) print("\n======9、验证根据下标查找元素 ======")
cricle_link_list.searchNodeByIndex(3) print("\n======10、验证修改 ======")
cricle_link_list.modifyByIndex(3,5)
cricle_link_list.travel() print("\n======11、验证排序 ======")
cricle_link_list.sort()
cricle_link_list.travel()
运行结果为:
======1、创建循环链表 ======
======2、验证是否为空 ======
你查询的链表为空 ======3、验证头插和遍历 ======
你要遍历的循环链表元素有: 1 ======4、继续验证头插和遍历 ======
你要遍历的循环链表元素有: 2 1 ======5、验证尾插 ======
你要遍历的循环链表元素有: 2 1 3 ======6、验证按位置插入 ======
你要遍历的循环链表元素有: 2 0 1 3 ======7、验证按位置删除 ======
你要插入的位置不对,请重新选择位置
你要遍历的循环链表元素有: 2 0 1 3 ======8、验证查找是否包含元素 ======
你要找到元素在第1个节点 ======9、验证根据下标查找元素 ======
你要查找3位置上的节点的值是1 ======10、验证修改 ======
你要遍历的循环链表元素有: 2 0 5 3 ======11、验证排序 ======
你要遍历的循环链表元素有: 0 2 3 5
三、循环链表基本操作的C语言实现
//
// main.m
// 循环链表
//
// Created by 侯垒 on 2019/6/27.
// Copyright © 2019 可爱的侯老师. All rights reserved.
// #include <stdio.h>
// 创建节点结构体
typedef struct N
{
int element;
struct N *next;
}Node; // 1、创建节点
Node *createNode(int num)
{
Node *node = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node->element = num;
node->next = NULL;
return node;
} // 2、创建循环链表
Node *createCricleLinkList(int num)
{
Node *head = createNode(num);
head->next = head;
return head;
} // 3、判断是否为空
int is_empty(Node *head)
{
if (head == NULL)
{
return ;
}
return ;
} //4、头部插入
Node *add(Node *head,int num)
{
Node* node = createNode(num);
Node *current = head;
if (is_empty(head)==)
{
head = node;
node->next = head;
}
else
{
node->next = head;
while (current->next != head)
{
current = current->next;
}
current->next = node;
head = node;
}
return head;
} // 5、遍历
void travel(Node *head)
{
if (is_empty(head) == )
{
printf("你遍历的链表为空\n");
}
else
{
printf("\n你要遍历的循环链表元素有:");
Node *current = head;
printf("%d ",current->element);
while (current->next != head)
{
current = current->next;
printf("%d ",current->element);
}
printf("\n");
}
} // 5、尾部插入
Node *append(Node *head,int num)
{
Node *node = createNode(num);
if (is_empty(head)==)
{
add(head, num);
}
else
{
Node *current = head;
while (current->next != head)
{
current = current->next;
}
node->next = head;
current->next = node;
}
return head;
} // 6、获取链表长度
int getLength(Node *head)
{
int count = ;
Node *current = head;
if (is_empty(head)==)
{
return ;
}
else
{
while (current->next !=head)
{
current = current->next;
count++;
}
return count;
}
} // 7、根据下标插入节点
Node * insertByIndex(Node *head,int num,int index)
{
int len = getLength(head);
if (index<=||index>len+)
{
printf("你要插入的位置不对,请重新选择位置");
}
else if (index == )
{
head = add(head, num);
}
else
{
Node *current = head;
for (int i=; i<index-; i++)
{
current = current->next;
}
Node *node = createNode(num);
node->next = current->next;
current->next = node;
}
return head;
} // 8、根据下标删除
Node *deleteByIndex(Node *head,int index)
{
int len = getLength(head);
if (index<=||index>len)
{
printf("\n你要删除的位置不对,请重新选择位置");
}
else if (index == )
{
Node *current = head;
for (int i=; i<len; i++)
{
current = current->next;
}
current->next = head->next;
head = head->next;
}
else
{
Node *current = head;
for (int i=; i<index-; i++)
{
current = current->next;
}
current->next = current->next->next;
}
return head;
} // 9、查找是否包含,并返回位置
int isContain(Node *head,int num)
{
int len = getLength(head);
Node *current = head;
for (int i= ; i<len; i++)
{
if (current->element == num)
{
return i+;
}
current=current->next;
}
return ;
} // 10、根据下标找节点
Node *searchNodeByIndex(Node *head,int index)
{
Node *current = head;
int len = getLength(head);
if (index<=||index>len)
{
printf("\n你要查询的位置不对,请重新选择位置");
}
else
{ for (int i = ; i<index; i++)
{
current = current->next;
}
printf("\n你要查找的%d位置上的值为%d",index,current->element);
}
return current;
} // 11、根据下标修改节点的值
void modefyByIndex(Node *head,int index,int num)
{
Node *current = head;
int len = getLength(head);
if (index<=||index>len)
{
printf("\n你要修改的位置不对,请重新选择位置");
}
else
{
for (int i = ; i<index; i++)
{
current = current->next;
}
current->element = num;
}
} // 12、排序
void sort(Node *head)
{
int len = getLength(head);
if (len<=)
{
return;
}
for (int i = ; i<len-; i++)
{
Node *current = head;
for (int j=; j<len-i-; j++)
{
if (current->element >current->next->element)
{
int temp = current->element;
current->element = current->next->element;
current->next->element = temp;
}
current = current->next;
}
}
} int main(int argc, const char * argv[])
{
printf("=====1、创建循环链表=====");
Node *head = createCricleLinkList(); printf("\n=====2、验证是否为空=====\n");
int empty = is_empty(head);
if (empty == )
{
printf("你创建的循环链表为空");
}
else
{
printf("你创建的循环链表不为空");
} printf("\n=====3、验证头插和遍历=====");
travel(head);
head = add(head, );
travel(head); printf("\n=====4、验证尾插=====");
head = append(head, );
travel(head); printf("\n=====5、验证根据下表插入=====");
head = insertByIndex(head, , );
travel(head); printf("\n=====6、验证根据下表删除=====");
head = deleteByIndex(head, );
travel(head); printf("\n=====7、验证是否包含=====");
int num = ;
int index = isContain(head, num);
if (index != )
{
printf("\n你查找的数据%d在第%d个位置",num,index);
}
else
{
printf("\n没有找到你要的数据\n");
} printf("\n=====8、验证根据下标找节点=====");
searchNodeByIndex(head, );
printf("\n=====9、验证根据下标修改节点值=====");
modefyByIndex(head,,);
travel(head); printf("\n=====10、验证排序=====");
sort(head);
travel(head); return ;
}
运行结果为:
=====、创建循环链表=====
=====、验证是否为空=====
你创建的循环链表不为空
=====、验证头插和遍历=====
你要遍历的循环链表元素有: 你要遍历的循环链表元素有: =====、验证尾插=====
你要遍历的循环链表元素有: =====、验证根据下表插入=====
你要遍历的循环链表元素有: =====、验证根据下表删除=====
你要遍历的循环链表元素有: =====、验证是否包含=====
你查找的数据3在第2个位置
=====、验证根据下标找节点=====
你要查找的2位置上的值为3
=====、验证根据下标修改节点值=====
你要遍历的循环链表元素有: =====、验证排序=====
你要遍历的循环链表元素有:
python算法与数据结构-循环链表(39)的更多相关文章
- Python算法与数据结构--求所有子数组的和的最大值
Python算法与数据结构--求所有子数组的和的最大值 玄魂工作室-玄魂 玄魂工作室秘书 玄魂工作室 昨天 题目:输入一个整形数组,数组里有正数也有负数.数组中连续的一个或多个整数组成一个子数组,每个 ...
- python算法与数据结构-算法介绍(31)
一.算法和数据结构 什么是算法和数据结构?如果将最终写好运行的程序比作战场,我们程序员便是指挥作战的将军,而我们所写的代码便是士兵和武器. 那么数据结构和算法是什么?答曰:兵法!故,数据结构和算法是一 ...
- python算法与数据结构-单链表(38)
一.链表 链表是一种物理存储单元上非连续.非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的.链表由一系列结点(链表中每一个元素称为结点)组成,结点可以在运行时动态生成.每个结点包括 ...
- python算法与数据结构-双向链表(40)
一.双向链表的介绍 一种更复杂的链表是“双向链表”或“双面链表”.每个节点有两个链接:一个指向前一个节点,当此节点为第一个节点时,指向空值:而另一个指向下一个节点,当此节点为最后一个节点时,指向空值. ...
- python算法与数据结构-栈(43)
一.栈的介绍 栈作为一种数据结构,是一种只能在一端进行插入和删除操作.它按照先进后出的原则存储数据,先进入的数据被压入栈底,最后的数据在栈顶,需要读数据的时候从栈顶开始弹出数据(最后一个数据被第一个读 ...
- python算法与数据结构-队列(44)
一.队列的介绍 队列的定义:队列是一种特殊的线性表,只允许在表的头部(front处)进行删除操作,在表的尾部(rear处)进行插入操作的线性数据结构,这种结构就叫做队列.进行插入操作的一端称为队尾,进 ...
- python算法与数据结构-数据结构中常用树的介绍(45)
一.树的定义 树是一种非线性的数据结构,是由n(n >=0)个结点组成的有限集合.如果n==0,树为空树.如果n>0,树有一个特定的结点,根结点根结点只有直接后继,没有直接前驱.除根结点以 ...
- python算法与数据结构-二叉树的代码实现(46)
一.二叉树回忆 上一篇我们对数据结构中常用的树做了介绍,本篇博客主要以二叉树为例,讲解一下树的数据结构和代码实现.回顾二叉树:二叉树是每个节点最多有两个子树的树结构.通常子树被称作“左子树”(left ...
- python算法与数据结构-冒泡排序算法(32)
一.冒泡排序介绍 冒泡排序(英语:Bubble Sort)是一种简单的排序算法.它重复地遍历要排序的数列,一次比较两个元素,如果他们的顺序错误就把他们交换过来.遍历数列的工作是重复地进行直到没有再需要 ...
随机推荐
- Material Design: NavigationView FlaotingActionBar SnackBar采用
转载 请明确说明 MingsangAndroid 本文介绍了Design Support Library的引入 拥抱Android Design Support Library新变化(导航视图.悬浮A ...
- ssh探头安全
1. ssh 合约 SSH 为建立在应用层和传输层基础上的安全协议. SSH 是眼下较可靠,专为远程登录会话和其它网络服务提供安全性的协议.利用 SSH 协议能够有效 ...
- [MVVM Light]Messenger 的使用
原文:[MVVM Light]Messenger 的使用 当我们使用MVVM开发模式进行开发时,ViewModel之间的通信常常是很头疼的事情,好在MVVM Light提供了Messenger类可以轻 ...
- Visual C++文件扩展名解读
VisualC++文件扩展名解读 [1] .APS:存储二进制资源的资源辅助中间文件(能否加快资源加载速度). [2] .BMP:位图资源文件. [3] .BSC:浏览信息文件.由浏览信息维护工具(B ...
- Leetcode 242 Valid Anagram 字符串处理
字符串s和字符串t是否异构,就是统计两个字符串的a-z的字符数量是否一值 class Solution { public: bool isAnagram(string s, string t) { ] ...
- 在Android程序中使用Modbus协议时报 java.net.SocketException: recvfrom failed: ECONNRESET解决办法
最近在开发基本Modbus协议的Android端PLC控制程序,C#版程序没有任何问题,移到JAVA下出现各种问题,其中比较苦恼的是java.net.SocketException: recvfrom ...
- EJB什么,它真的有这么神奇??
1. 我们不禁要问,什么是"服务集群"?什么是"企业发展"? 现在说EJB 至"服务集群"和"企业发展",然后,说什么是 ...
- WPF 控件的内容属性
WPF的内容属性不应定都是content, 例如TextBlock的内容属性是Text Panel的内容属性是Children ListBox的内容属性是Items
- MVC EF两种查询方法
@*@model IQueryable<EFExam.Models.Product>*@@model IQueryable<EFExam.Models.ProductViewMode ...
- ES6/ES2015核心内容(转载)
ES6其实就是ES2015,因为是2015年发布的,所以也叫ES2015.这个版本是JS的最新版本,很多浏览器还不支持,所有有了babel,专门把最新的JS转换一下,让大部分浏览器都支持的JS版本. ...
