hdu Swipe Bo(bfs+状态压缩)错了多次的题
Swipe Bo
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1549 Accepted Submission(s): 315
The main character of this game is a square blue tofu called Bo. We can swipe up / down / left / right to move Bo up / down / left / right. Bo always moves in a straight line and nothing can stop it except a wall. You need to help Bo find the way out.
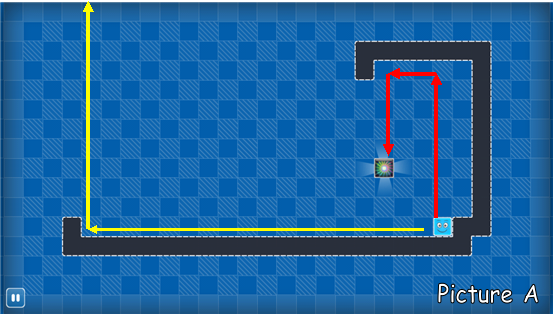
The picture A shows that we needs three steps to swipe Bo to the exit (swipe up, swipe left, swipe down). In a similar way, we need only two steps to make Bo disappear from the world (swipe left, swipe up)!
Look at the picture B. The exit is locked, so we have to swipe Bo to get all the keys to unlock the exit. When Bo get all the keys, the exit will unlock automatically .The exit is considered inexistent if locked. And you may notice that there are some turning
signs, Bo will make a turn as soon as it meets a
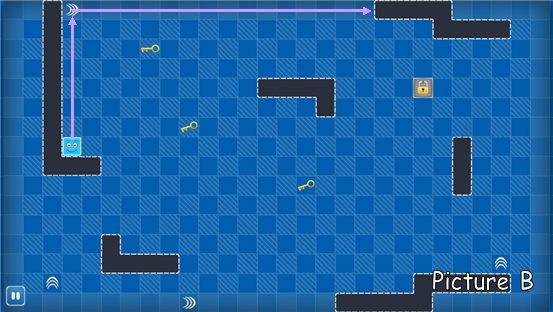
turning signs. For example, if we swipe Bo up, it will go along the purple line.
Now, your task is to write a program to calculate the minimum number of moves needed for us to swipe Bo to the exit.
The first line of each test case contains two integers N and M (1≤N, M≤200), which denote the sizes of the map. The next N lines give the map’s layout, with each line containing M characters. A character is one of the following: '#': represents the wall; 'S'
represents the start point of the Bo; 'E' represents the exit; '.' represents an empty block; ‘K’ represents the key, and there are no more than 7 keys in the map; 'L','U','D','R' represents the turning sign with the direction of left, up, down, right.
5 6
######
#....#
.E...#
..S.##
.#####
5 6
######
#....#
.....#
SEK.##
.#####
5 6
######
#....#
....K#
SEK.##
.#####
5 6
######
#....#
D...E#
S...L#
.#####
3
2
7
-1
题意:有一个迷宫,包括墙、空白格子、起点S、终点E、方向格子(LRUD)和钥匙K。要求例如以下:
(1)每次转弯仅仅能在碰到墙壁时(每次转弯的选择和初始时从S出发的方向选择均称为一次操作);
(2)对于方向格子。若到达该格子,无论周围是不是墙,必须转向该格子指示的方向(这个不算一次操作)。
(3)若迷宫中没有钥匙存在,则求出S到E的最少操作次数;若有钥匙。则必须先遍历到每一个钥匙之后才干去E(在这个过程中能够经过E也就是E不算做障碍)。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<queue>
using namespace std; const int N = 225;
const int inf = 1<<29;
struct node{
int x,y,sta,stp;
};
int n,m,k;
char mapt[N][N];
int K[N][N];
bool vist[N][N][1<<7];
int dir[4][2]={0,-1,0,1,-1,0,1,0}; int judge1(node& now,int &e){
int flag=0;
if(now.x<0||now.x>=n||now.y<0||now.y>=m)
return 0;
if(mapt[now.x][now.y]!='#'){ if(mapt[now.x][now.y]=='L')
e=0,flag=1;
else if(mapt[now.x][now.y]=='R')
e=1,flag=1;
else if(mapt[now.x][now.y]=='U')
e=2,flag=1;
else if(mapt[now.x][now.y]=='D')
e=3,flag=1;
else if(mapt[now.x][now.y]=='K')
now.sta|=(1<<K[now.x][now.y]);
if(flag&&vist[now.x][now.y][now.sta])
return 0;
else if(flag) vist[now.x][now.y][now.sta]=1; //固定方向的位置。能够直接标记
return 1;
}
else //遇到墙,退一格,在当前位置停止
{
now.x-=dir[e][0];
now.y-=dir[e][1];
return 2;
} }
int bfs(int sx,int sy){
queue<node>q;
node now,pre; for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
for(int j=0; j<m; j++)
for(int sta=0; sta<(1<<k); sta++)
vist[i][j][sta]=0; now.x=sx,now.y=sy,now.sta=0,now.stp=0;
q.push(now);
vist[now.x][now.y][now.sta]=1; while(!q.empty()){
pre=q.front(); q.pop();
pre.stp++; for(int te=0; te<4; te++){
int e=te;
now=pre;
while(1){ //找到一个停止点。或不能走。或走过了。则跳出
now.x+=dir[e][0];
now.y+=dir[e][1]; int flag=judge1(now,e); if(flag==0)break;
if(flag==1&&mapt[now.x][now.y]=='E'&&now.sta==(1<<k)-1){
return now.stp;
}
if(flag==2){
if(vist[now.x][now.y][now.sta])break;
vist[now.x][now.y][now.sta]=1;
q.push(now);
break;
}
}
}
} return -1;
}
int main()
{
int sx,sy;
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)>0){
k=0;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
scanf("%s",mapt[i]);
for(int j=0; j<m; j++)
if(mapt[i][j]=='S')
sx=i,sy=j;
else if(mapt[i][j]=='K')
K[i][j]=k++;
}
printf("%d\n",bfs(sx,sy));
}
}
hdu Swipe Bo(bfs+状态压缩)错了多次的题的更多相关文章
- hdu 4634 Swipe Bo bfs+状态压缩
题目链接 状态压缩记录当前拿到了哪些钥匙, 然后暴力搜索. 搞了好几个小时, 一开始也不知道哪里错了, 最后A了也不知道一开始哪里有问题. #include <iostream> #inc ...
- hdu 4856 Tunnels(bfs+状态压缩)
题目链接:hdu 4856 Tunnels 题目大意:给定一张图,图上有M个管道,管道给定入口和出口,单向,如今有人想要体验下这M个管道,问最短须要移动的距离,起点未定. 解题思路:首先用bfs处理出 ...
- hdu 1429(BFS+状态压缩)
胜利大逃亡(续) Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Su ...
- HDU 3247 Resource Archiver (AC自己主动机 + BFS + 状态压缩DP)
题目链接:Resource Archiver 解析:n个正常的串.m个病毒串,问包括全部正常串(可重叠)且不包括不论什么病毒串的字符串的最小长度为多少. AC自己主动机 + bfs + 状态压缩DP ...
- BFS+状态压缩 hdu-1885-Key Task
题目链接: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1885 题目意思: 给一个矩阵,给一个起点多个终点,有些点有墙不能通过,有些点的位置有门,需要拿到相应 ...
- ACM/ICPC 之 BFS+状态压缩(POJ1324(ZOJ1361))
求一条蛇到(1,1)的最短路长,题目不简单,状态较多,需要考虑状态压缩,ZOJ的数据似乎比POj弱一些 POJ1324(ZOJ1361)-Holedox Moving 题意:一条已知初始状态的蛇,求其 ...
- HDU1429+bfs+状态压缩
bfs+状态压缩思路:用2进制表示每个钥匙是否已经被找到.. /* bfs+状态压缩 思路:用2进制表示每个钥匙是否已经被找到. */ #include<algorithm> #inclu ...
- poj 1753 Flip Game(bfs状态压缩 或 dfs枚举)
Description Flip game squares. One side of each piece is white and the other one is black and each p ...
- BFS+状态压缩 HDU1429
胜利大逃亡(续) Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others) Total S ...
随机推荐
- 数论(同余+hash)
Time Limit:3000MS Memory Limit:65536KB Description You are given a sequence a[0]a[1] ... a[N-1] of d ...
- iOS项目开发实战——制作视图的缩放动画
视图的大小应该是随时可控的.今天我们就来实现对一个View的缩放动画.该动画的实现与位移动画,透明度动画稍有不同. 详细实现例如以下: import UIKit class ScaleViewCont ...
- hdoj--1495--非常可乐(搜索+隐式图)
非常可乐 Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others) Total Submi ...
- [IOI 1998] Polygon
[题目链接] http://poj.org/problem?id=1179 [算法] 区间DP [代码] #include <algorithm> #include <bitset& ...
- 光标属性CSS cursor 属性
CSS cursor 属性 CSS cursor属性,以前不知道,如果以后用到自己看的 <html> <body> <p>请把鼠标移动到单词上,可以看到鼠标指针发生 ...
- 匹配替换指定文本为html标签
最近看了一道前端面试题,是关于正则的,用尽可能低复杂度的函数,匹配替换指定文本为html标签,题目是这样的: 特定语法匹配替换 说明:匹配字符串中形如 =g文字文字= 的语法,并将相应部分转化为对应的 ...
- Tomcat 初探(二) server.xml 配置
前言 在上一篇文章中,我们在示例中演示了网站的发布,其中涉及到了 server.xml 的修改,本文中我会给大家详细解释一下 server.xml 文件中的节点及其属性的作用,本片文章参考并摘抄了他人 ...
- Ubuntu14.04下Mongodb数据库可视化工具安装部署步骤(图文详解)(博主推荐)
不多说,直接上干货! 前期博客 Ubuntu14.04下Mongodb(离线安装方式|非apt-get)安装部署步骤(图文详解)(博主推荐) Ubuntu14.04下Mongodb官网安装部署步骤(图 ...
- 开发辅助 | 前端开发工程师必懂的 UI 知识
移动 UI 设计的世界 ... 1.屏幕尺寸 屏幕大小,指屏幕对角线的长度,而不是屏幕的宽度或高度: 单位为英寸 如 iPhone 7 屏幕尺寸为 4.7 英寸:三星 S6 屏幕尺寸为 ...
- css元素垂直居中方法
1.Line-height 适用情景:单行文字垂直居中技巧 这个方式应该是最多人知道的了,常见于单行文字的应用,像是按钮这一类对象,或者是下拉框.导航此类元素最常见到的方式了.此方式的原理是在于将单行 ...
