Codefores 507C Guess Your Way Out!(递归)
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Amr bought a new video game "Guess Your Way Out!". The goal of the game is to find an exit from the maze that looks like a perfect binary tree of height h. The player is initially standing at the root of the tree and the exit from the tree is located at some leaf node.
Let's index all the leaf nodes from the left to the right from 1 to 2h. The exit is located at some node n where 1 ≤ n ≤ 2h, the player doesn't know where the exit is so he has to guess his way out!
Amr follows simple algorithm to choose the path. Let's consider infinite command string "LRLRLRLRL..." (consisting of alternating characters 'L' and 'R'). Amr sequentially executes the characters of the string using following rules:
- Character 'L' means "go to the left child of the current node";
- Character 'R' means "go to the right child of the current node";
- If the destination node is already visited, Amr skips current command, otherwise he moves to the destination node;
- If Amr skipped two consecutive commands, he goes back to the parent of the current node before executing next command;
- If he reached a leaf node that is not the exit, he returns to the parent of the current node;
- If he reaches an exit, the game is finished.
Now Amr wonders, if he follows this algorithm, how many nodes he is going to visit before reaching the exit?
Input consists of two integers h, n (1 ≤ h ≤ 50, 1 ≤ n ≤ 2h).
Output a single integer representing the number of nodes (excluding the exit node) Amr is going to visit before reaching the exit by following this algorithm.
1 2
2
2 3
5
3 6
10
10 1024
2046
A perfect binary tree of height h is a binary tree consisting of h + 1 levels. Level 0 consists of a single node called root, level h consists of 2h nodes called leaves. Each node that is not a leaf has exactly two children, left and right one.
Following picture illustrates the sample test number 3. Nodes are labeled according to the order of visit.
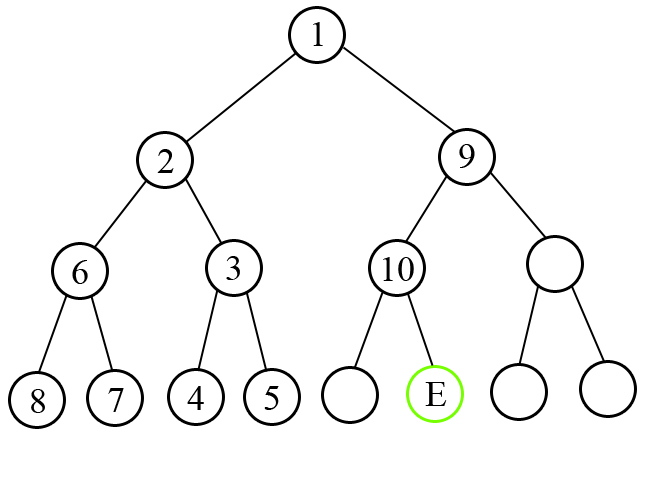
题意是按照“LRLRLRLR....”这个指令在数上走 。。
然后给了几个返回的条件, 让你算一下经过了多少个结点。
其实就是一个根据指令递归判点在左右子树还是右子树的情况。
做法就是分成4种情况
出口在左子树,指令是L
出口在左子树,指令是R
出口在右子树,指令是L
出口在右子树,指令是R
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
LL n , h , ok ;
LL cal( LL dep , LL pos , int tag ) {
if( ok ) return ;
if( dep == ) { ok = ; return ; }
LL tmp ;
if( !tag ) {
if( pos >(1LL<<(dep-))) tmp = (1LL<<dep)+cal(dep-,pos-(1LL<<(dep-)),) ;
else tmp = 1LL + cal(dep-,pos,);
}
else {
if( pos > (1LL<<(dep-)) ) tmp = 1LL+ cal( dep-,pos-(1LL<<(dep-)),) ;
else tmp = (1LL<<dep) + cal(dep-,pos,);
}
return tmp ;
}
int main()
{
while( cin >> h >> n ) {
ok = ;
cout << cal(h,n,) << endl ;
}
}
Codefores 507C Guess Your Way Out!(递归)的更多相关文章
- .NET 基础 一步步 一幕幕[面向对象之方法、方法的重载、方法的重写、方法的递归]
方法.方法的重载.方法的重写.方法的递归 方法: 将一堆代码进行重用的一种机制. 语法: [访问修饰符] 返回类型 <方法名>(参数列表){ 方法主体: } 返回值类型:如果不需要写返回值 ...
- 算法笔记_013:汉诺塔问题(Java递归法和非递归法)
目录 1 问题描述 2 解决方案 2.1 递归法 2.2 非递归法 1 问题描述 Simulate the movement of the Towers of Hanoi Puzzle; Bonus ...
- Android 算法 关于递归和二分法的小算法
// 1. 实现一个函数,在一个有序整型数组中二分查找出指定的值,找到则返回该值的位置,找不到返回 -1. package demo; public class Mytest { public st ...
- 二叉树的递归实现(java)
这里演示的二叉树为3层. 递归实现,先构造出一个root节点,先判断左子节点是否为空,为空则构造左子节点,否则进入下一步判断右子节点是否为空,为空则构造右子节点. 利用层数控制迭代次数. 依次递归第二 ...
- 递归实现n(经典的8皇后问题)皇后的问题
问题描述:八皇后问题是一个以国际象棋为背景的问题:如何能够在8×8的国际象棋棋盘上放置八个皇后, 使得任何一个皇后都无法直接吃掉其他的皇后?为了达到此目的,任两个皇后都不能处于同一条横行.纵行或斜线上 ...
- C语言用分别用递归和循环求数字的阶乘的方法
以下代码均为 自己 实现,嘻嘻! 参考文章:http://blog.csdn.net/talk_8/article/details/46289683 循环法 int CalFactorial(int ...
- C#递归解决汉诺塔问题(Hanoi)
using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Linq;using System.Text; namespace MyExamp ...
- Java之递归求和的两张方法
方法一: package com.smbea.demo; public class Student { private int sum = 0; /** * 递归求和 * @param num */ ...
- C#语言基础——递归
递归 一.概念conception: 函数体内调用本函数自身,直到符合某一条件不再继续调用. 二.应满足条件factor: (1)有反复执行的过程(调用自身): (2)有跳出反复执行过程的条件(函数出 ...
随机推荐
- CSS样式表能否控制文字禁止选择,复制, 焦点
div中禁止文字被选择 在做div的点击计数事件时,遇到一个小问题. 因为div里面有文字,所以当点击多次时,特别是鼠标点的比较快的时候,文字会被选中. 查了下,用css和javascript可以实现 ...
- mod_jk是Apache服务器的一个可插入模块
mod_jk简称JK,是Apache服务器的一个可插入模块,用以为Apache或IIS服务器提供处理JSP/Servlet的能力. Apache作为一款强大的Web服务器,本身缺乏处理JSP/Serv ...
- 2019-8-31-C#-条件编译
title author date CreateTime categories C# 条件编译 lindexi 2019-08-31 16:55:58 +0800 2019-07-18 15:27:1 ...
- AndroidStudio之Theme、colorPrimary、colorPrimaryDark、colorAccent详解
今天就来看看在Androi5.0中常用的颜色属性. 我们可以先定义一个style,然后在这个style中设定每一个Activity或者整个App的颜色,最后在清单文件中来给某个Activity设置主题 ...
- 【LeetCode】深搜DFS(共85题)
[98]Validate Binary Search Tree [99]Recover Binary Search Tree [100]Same Tree [101]Symmetric Tree [1 ...
- https://geewu.gitbooks.io/rabbitmq-quick/content/RabbitMQ%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80%E6%93%8D%E4%BD%9C.html
https://geewu.gitbooks.io/rabbitmq-quick/content/RabbitMQ%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80%E6%93%8D%E4%BD%9C.html
- 同步mysql
ElasticSearch同步MySql 标签: elasticsearchmysql 2016-07-01 09:07 4636人阅读 评论(8) 收藏 举报 分类: Elasticsearch( ...
- python py文件转换成exe
1.首先学会了最简单的方法 1)pip install pyinstaller 安装pyinstall 2)pyinstaller aaaa.py 转换,会在当前目录下建两个文件夹,其中一个文件夹 ...
- python已处理的异常
字符串比较中,如果一个字符串有内容,另一个没有内容,python不会报错,而是认为两个字符串不相同如 a=" b="" if a[4:5]==b[4:5]: print( ...
- 人生苦短_我用Python_configparser/yaml对配置文件读取/写入操作_010
第一,我们先开始安装yaml库,configparser是自带库,yaml库是针对读取yml文件,configparser现阶段我只用于读取conf文件 首先:1)对象文件为:data.yml,下面的 ...
