ContextLoaderListener vs DispatcherServlet
In XML based Spring MVC configuration, you must have seen two declarations in web.xml file i.e. ContextLoaderListener and DispatcherServlet. Let’s try to understand their purpose in framework and their differences.
Root and child contexts
Before reading further, please understand that –
- Spring can have multiple contexts at a time. One of them will be root context, and all other contexts will be child contexts.
- All child contexts can access the beans defined in root context; but opposite is not true. Root context cannot access child contexts beans.
DispatcherServlet – Child application contexts
DispatcherServlet is essentially a Servlet (it extends HttpServlet) whose primary purpose is to handle incoming web requests matching the configured URL pattern. It take an incoming URI and find the right combination of controller and view. So it is the front controller.
When you define a DispatcherServlet in spring configuration, you provide an XML file with entries of controller classes, views mappings etc. using contextConfigLocationattribute.
<servlet> <servlet-name>employee-services</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:employee-services-servlet.xml</param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup></servlet> |
If you do not provide configuration file then it will load its own configuration file using [servlet_name]-servlet.xml. Web applications can define any number of DispatcherServlet entries. Each servlet will operate in its own namespace, loading its own application context with mappings, handlers, etc.
It means that each DispatcherServlet has access to web application context. Until specified, each DispatcherServlet creates own internal web application context.
DispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext) create a new DispatcherServlet with the given web application context. It is possible only in Servlet 3.x environment through the ServletContext.addServlet(java.lang.String, java.lang.String) API support.ContextLoaderListener – Root application context
ContextLoaderListener creates the root application context and will be shared with child contexts created by all DispatcherServlet contexts. You can have only one entry of this in web.xml.
<listener> <listener-class> org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener </listener-class></listener> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>/WEB-INF/spring/applicationContext.xml</param-value></context-param> |
The context of ContextLoaderListener contains beans that globally visible, like services, repositories, infrastructure beans, etc. After the root application context is created, it’s stored in ServletContext as an attribute, the name is:
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);//Where attibute is defined in /org/springframework/web/context/WebApplicationContext.java asWebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE = WebApplicationContext.class.getName() + ".ROOT"; |
To get root application context in Spring controller, you can use WebApplicationContextUtils class.
@AutowiredServletContext context; ApplicationContext ac = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(context);if(ac == null){ return "root application context is null";} |
ContextLoaderListener vs DispatcherServlet
Below image describe the whole relation in single view.
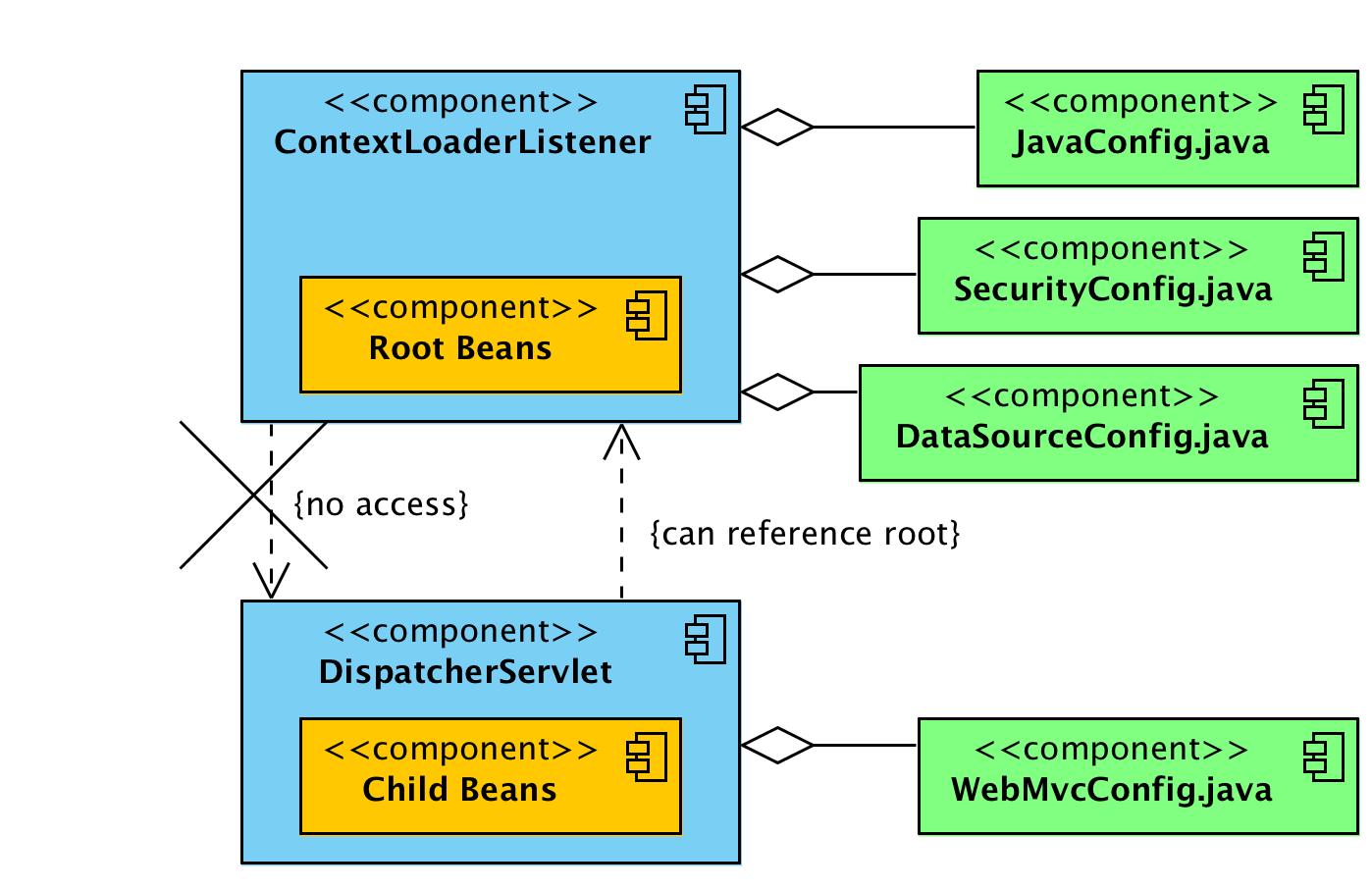 ContextLoaderListener vs DispatcherServlet
ContextLoaderListener vs DispatcherServlet
ContextLoaderListenercreates root application context.DispatcherServletentries create one child application context per servlet entry.- Child contexts can access beans defined in root context.
- Beans in root context cannot access beans in child contexts (directly).
- All contexts are added to
ServletContext. - You can access root context using
WebApplicationContextUtilsclass.
Summary
Generally, you will define all MVC related beans (controller and views etc) in DispatcherServlet context, and all cross-cutting beans such as security, transaction, services etc. at root context by ContextLoaderListener.
Generally, this setup works fine because rarely you will need to access any MVC bean (from child context) into security related class (from root context). Mostly we use security beans on MVC classes, and they can access it with above setup.
Happy Learning !!
https://howtodoinjava.com/spring-mvc/contextloaderlistener-vs-dispatcherservlet/
ContextLoaderListener vs DispatcherServlet的更多相关文章
- 【转】ContextLoaderListener和DispatcherServlet加载内容的区别
一.ContextLoaderListener加载内容 二.DispatcherServlet加载内容 ContextLoaderListener和DispatcherServlet都会在Web容器启 ...
- web.xml中的ContextLoaderListener和DispatcherServlet区别
ContextLoaderListener和DispatcherServlet都会在Web容器启动的时候加载一下bean配置. 区别在于: DispatcherServlet一般会加载MVC相关的be ...
- 使用shiro 框架 报错No WebApplicationContext found: no ContextLoaderListener or DispatcherServlet registered?
1.问题描述:ssm 框架中使用shiro 中出现问题 原来web.xml 文件如下: <!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC "-//Sun Microsystems, ...
- 【转】ContextLoaderListener 和 DispatcherServlet
转载地址: http://www.guoweiwei.com/archives/797 DispatcherServlet介绍 DispatcherServlet是Spring前端控制器的实现,提供S ...
- ContextLoaderListener与DispatcherServlet所加载的applicationContext的区别
spring通过在web.xml 中配置ContextLoaderListener 来加载context配置文件,在DispatcherServlet中也可以来加载spring context配置文件 ...
- Spring ContextLoaderListener与DispatcherServlet所加载的applicationContext的区别
http://www.lai18.com/content/9755931.html Spring 容器(Spring 的上下文) https://my.oschina.net/jast90/blog/ ...
- ContextLoaderListener和Spring MVC中的DispatcherServlet加载内容的区别
一:ContextLoaderListener加载内容 二:DispatcherServlt加载内容 ContextLoaderListener和DispatcherServlet都会在Web容器启动 ...
- 【Spring】浅谈ContextLoaderListener及其上下文与DispatcherServlet的区别
一般在使用SpingMVC开发的项目中,一般都会在web.xml文件中配置ContextLoaderListener监听器,如下: <listener> <listener-clas ...
- ContextLoaderListener和Spring MVC中的DispatcherServlet加载内容的区别【转】
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/py_xin/article/details/52052627 ContextLoaderListener和DispatcherServlet都会 ...
随机推荐
- 转载:Eclipse下的java工程目录
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/milantgh/p/4029003.html 对新手来讲,一个Java工程内部的多个文件夹经常会让大家困惑.更可恶的是莫名其妙的路径问题,在 ...
- u-tools图床便捷生成markdown图片
u-tools 图床 上传图片生成markdown图片非常便捷. 支持的图片服务器有几种,其中搜狗.网易和掘金的加载速度更快些: 也可以用阿里与和腾讯云的OSS; 其中网易生成图片不是原图尺寸好像被改 ...
- Centos7安装Nginx1.14.0
一.官网下载 http://nginx.org/en/download.html 版本说明: Nginx官网提供了三个类型的版本 Mainline version:Mainline 是 Nginx 目 ...
- linux学习-linux基础和帮助
1.终端terminal (1)设备终端 键盘,鼠标,显示器 (2)物理终端(/dev/console) 控制台concole (3)串行终端(/dev/ttyS#) ttyS (4)虚拟终端(tty ...
- 如何在MaxCompute上处理存储在OSS上的开源格式数据
0. 前言 MaxCompute作为使用最广泛的大数据平台,内部存储的数据以EB量级计算.巨大的数据存储量以及大规模计算下高性能数据读写的需求,对于MaxCompute提出了各种高要求及挑战.处在大数 ...
- 如何在Ubuntu下搭建tftp服务器
远程桌面连接工具 今天开始调试arm的板子,要通过tftp下载到板子上,所以又要配置tftp服务器,真的烦死了… (本人酷爱装系统,所以经常都要搞配置) 因为之前已经在Ubuntu下搭建过很多次t ...
- jquery设置、判断、获取input单选标签选中状态
1.设置某项单选input为选中状态: $("input[type='radio']").eq(1).attr('checked',true); ②也可设其属性checked为'c ...
- IGServer for Java
Eclipse和JavaEE: DCServer是哪个? 查看服务器文件夹: Env_Var变量没有定义:JRE_HOME.JDK_HOME 这是Tomcat报错的提示,但是既然JAVA_HOME都有 ...
- ansible控制winserver笔记
原文地址: https://www.cnblogs.com/kingleft/p/6391652.html 环境描述: ansible控制远程windows .系统必须是sp1 .安装framewor ...
- [CSP-S模拟测试]:蔬菜(二维莫队)
题目描述 小$C$在家中开垦了一块菜地,可以抽象成一个$r\times c$大小的矩形区域,菜地的每个位置都种着一种蔬菜.秋天到了,小$C$家的菜地丰收了. 小$C$拟定了$q$种采摘蔬菜的计划,计划 ...
